The Mobility Management Strategies by Integrating Mobile Edge Computing and CDN in Vehicular Networks
-
摘要:
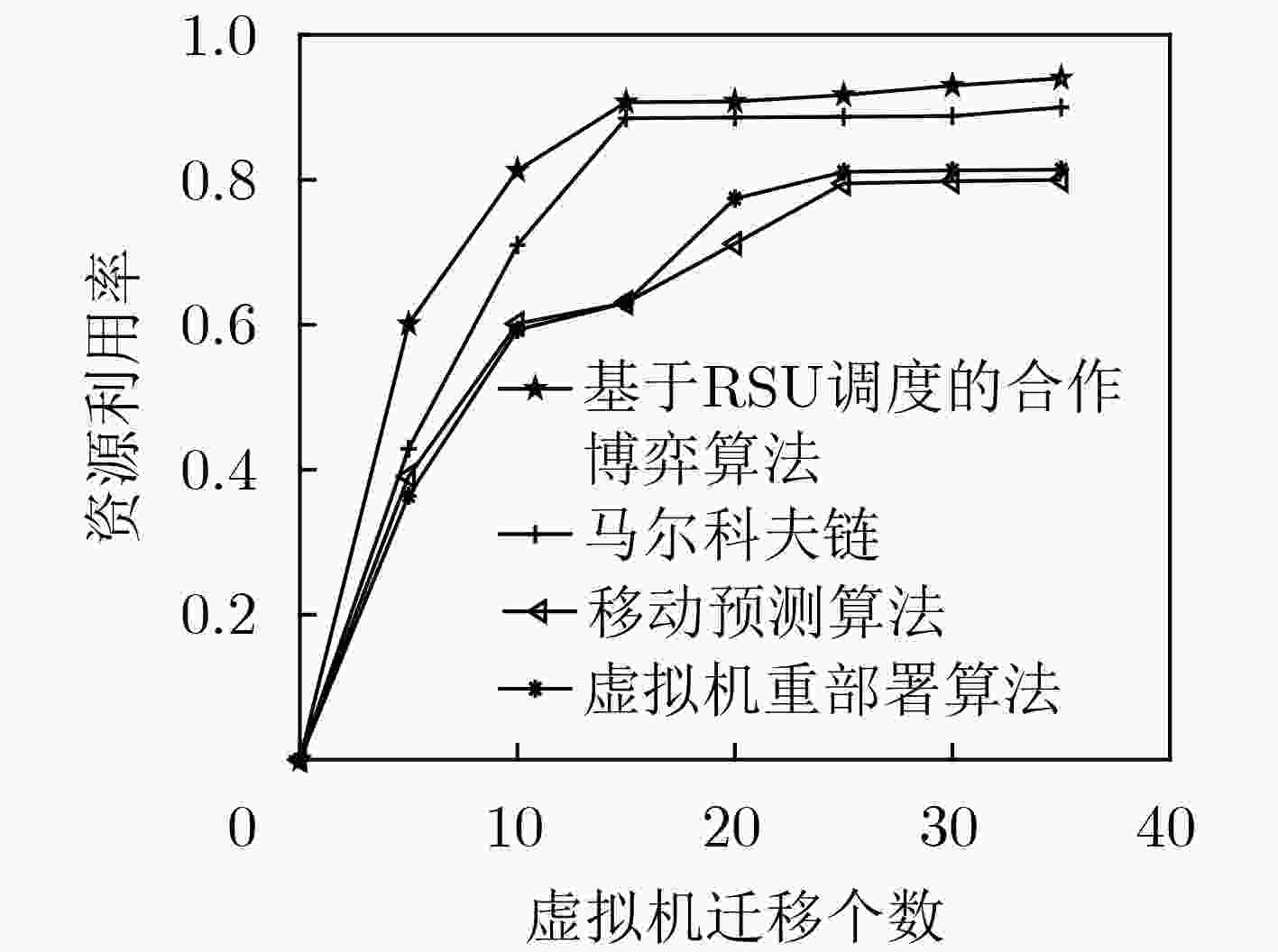
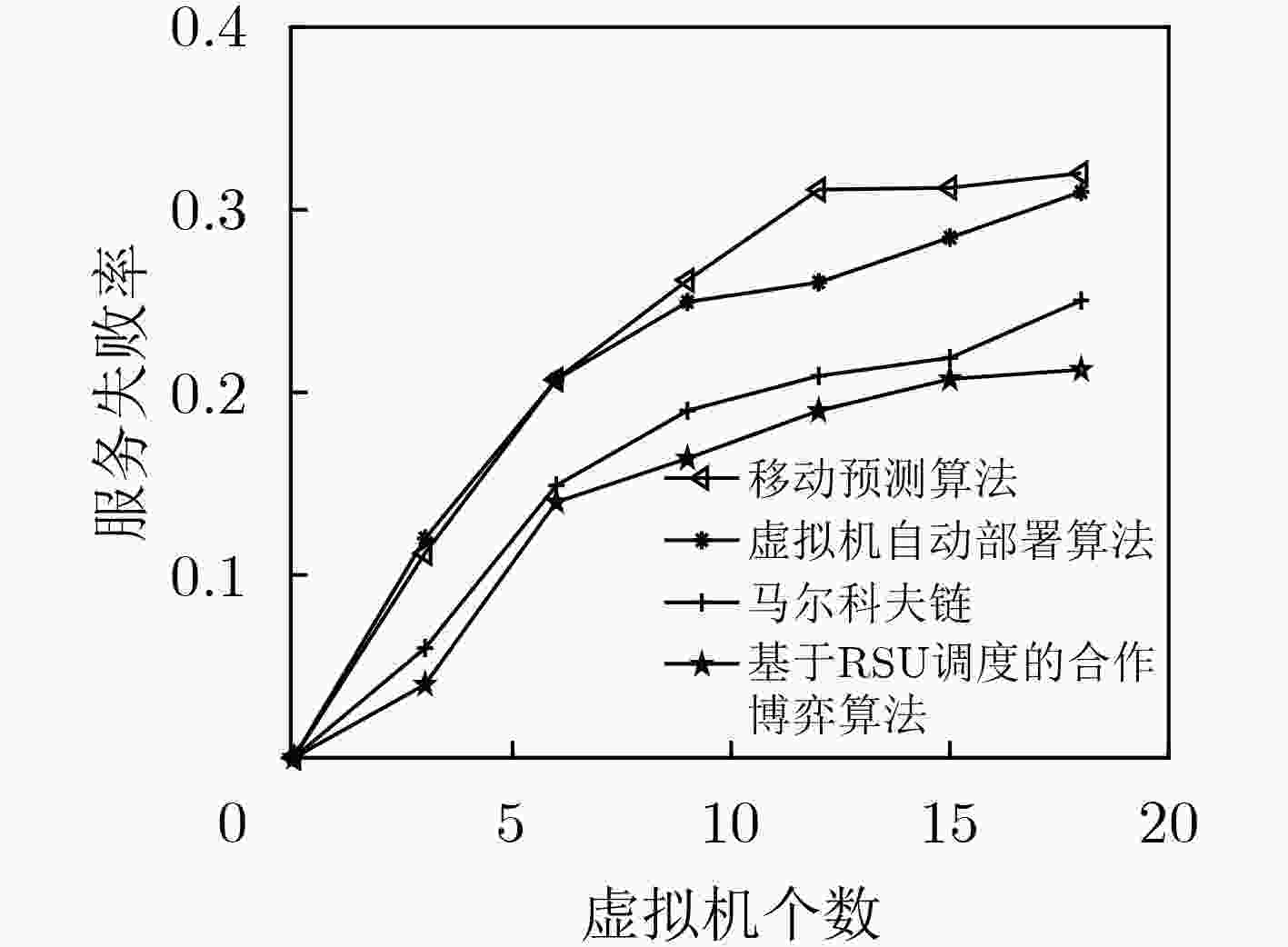
由于车载应用的普及和车辆数量的增加,路边基础设施的物理资源有限,当大量车辆接入车联网时能耗与时延同时增加,通过整合内容分发网络(CDN)和移动边缘计算(MEC)的框架可以降低时延与能耗。在车联网中,车辆移动性对云服务的连续性提出了重大挑战。因此,该文提出了移动性管理(MM)来处理该问题。采用开销选择的动态信道分配(ODCA)算法避免乒乓效应且减少车辆在小区间的切换时间。采用基于路边单元(RSU)调度的合作博弈算法进行虚拟机迁移并开发基于学习的价格控制机制,以有效地处理MEC的计算资源。仿真结果表明,所提算法相比于现有的算法能够提高资源利用率且减少开销。
Abstract:Due to the popularity of vehicle applications and the increase of the number of vehicles, the physical resources of roadside infrastructure are limited. When a large number of vehicles are connected to the vehicle networks, the energy consumption and latency are simultaneously increased. The framework for integrating the Content Delivery Network (CDN) and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) can reduce the latency and energy consumption. In vehicle network, vehicle mobility poses a major challenge to the continuity of cloud services. Therefore, Mobility Management (MM) is proposed to deal with this problem. The Dynamic Channel Allocation algorithm with Overhead selection (ODCA) is used to avoid the ping-pong effect and reduces the handover time of vehicles between cells. The cooperative game algorithm based on RoadSide Unit (RSU) is used for virtual machine migration and a learning-based price control mechanism is developed to process vehicular computation resources efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can improve resource utilization and reduce overhead compared with the existing algorithms.
-
表 1 开销选择的动态信道分配(ODCA)
(1) 输入:${I_{{\rm{dd}}}}$, ${h_i}$, ${h_j}$, $v$, $c$, $\left( {{ X},{ Y}} \right)$ (2) 输出:$\left( { {{ X}_{i,j} },{{ Y}_{i,j} } } \right)$, $t_{i,j}^{{\rm{h}} * }$, ${\rm{RS}}{{\rm{U}}^ * }$ (3) 初始化权值矩阵$\left( {{ X},{ Y}} \right)$ (4) $m \leftarrow 0$ (5) while $m \le {I_{ {\rm{dd} } } }$ (6) for $j = 1:M$ (7) L辆车同时进行分布式计算,每个连接到RSU的V-UE仅报
告未定期使用信道的开销(8) 如果许多用户同时改变其信道,可能导致乒乓效应,RSU
可通过${a_{i,j,\mathop l\limits^ {\wedge} } } = 1|\mathop l\limits^ {\wedge} = \max \dfrac{ { {p_{i,j,l} }{L_{i,j,l} } } }{ { {\sigma ^2} + {\rm{I} } } }$改变信道(9) 根据式(10)计算开销,根据开销最小来选择最优、次最优、
次优的3个RSU(10) V-UE实时上报其位置信息$\left( {{ X},{ Y}} \right)$和功率损耗门限${P^{{\rm{th}}}}$,
TCS根据式(5)计算切换位置$\left( { {{ X}_{i,j} },{{ Y}_{i,j} } } \right)$(11) 根据$\left( { {{ X}_{i,j} },{{ Y}_{i,j} } } \right)$和式(7)分别计算切换到3个RSU的时间,
如果能使$t_{i,j}^{\rm{C}}$和$t_{i,j}^{\rm{h}}$最小,此${\rm{RS}}{{\rm{U}}^ * }$性能最优,且最优切换
时间为$t_{i,j}^{{\rm{h}} * }$(12) endfor (13) endwhile 表 2 基于RSU调度的合作博弈算法
(1) 输入:${{S}}$, $\alpha $, $\beta $, ${d_{i,j}}$, ${c_{i,j}}$, ${\rm{RS}}{{\rm{U}}^ * }$, ${I_{{\rm{dd}}}}$ (2) 输出:${{A}}$ (3) 初始化权值矩阵${{A}}$,${{S}}$ (4)$m \leftarrow 0$ (5) while $m \le {I_{ {\rm{dd} } } }$ (6) for $j = 1:M$ (7) $L$辆车同时进行分布式计算,利用梯度下降算法求出最优功
率分配值$p_{i,j,l}^ * $(8) 根据式(14)判断是否迁移 (9) 根据博弈论第2阶段计算出未迁移与迁移的收益 (10) 根据行为${a_t}$观察下一时刻的状态${s_{t + 1}}$ (11) 根据式(16)—式(18)出奖励函数,通过不断地学习,找到使
奖励函数最大的策略(12) endfor (13) endwhile 表 3 模拟参数表
参数 数值 输入数据的大小${d_{i,j}}$ 300~1600 kB 噪声功率${\sigma ^2}$ 0.1~1.0 GHz MEC服务器CPU周期频率${f^{\rm{C}}}$ 6 GHz 最大延迟容限${T^{{\rm{th}}}}$ 6 s 迭代次数${I_{{\rm{dd}}}}$ 600 最大传输功${P^{{\rm{max}}}}$ 23 dBm 传输带宽$W$ 20 MHz 任务执行时所需的CPU周期数${c_{i,j}}$ 0.1~1.0 GHz -
ZHOU Siyu, NETALKAR P P, CHANG Yanan, et al. The MEC-based architecture design for low-latency and fast hand-off vehicular networking[C]. The 88th Vehicular Technology Conference, Chicago, USA, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/VTCFall.2018.8690790. BASTUG E, BENNIS M, MEDARD M, et al. Toward interconnected virtual reality: Opportunities, challenges, and enablers[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(6): 110–117. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1601089 LIN Mengdan and ZHAO Xuelin. Application research of neural network in vehicle target recognition and classification[C]. 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data & Smart City, Changsha, China, 2019: 5–8. doi: 10.1109/ICITBS.2019.00010. CICIRELLI F, GUERRIERI A, SPEZZANO G, et al. Edge computing and social internet of things for large-scale smart environments development[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(4): 2557–2571. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2775739 YALA L, FRANGOUDIS P A, and KSENTINI A. QoE-aware computing resource allocation for CDN-as-a-service provision[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842182. LIU Jiayi, YANG Qinghai, and SIMON G. Congestion avoidance and load balancing in content placement and request redirection for mobile CDN[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2018, 26(2): 851–863. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2804979 XU Jie, SUN Yuxuan, CHEN Lixing, et al. E2M2: Energy efficient mobility management in dense small cells with mobile edge computing[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2017.7996855. PENG Han, RAZI A, AFGHAH F, et al. A unified framework for joint mobility prediction and object profiling of drones in UAV networks[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2018, 20(5): 434–442. doi: 10.1109/JCN.2018.000068 LIU Fangming, SHU Peng, and LUI J C S. AppATP: An energy conserving adaptive mobile-cloud transmission protocol[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2015, 64(11): 3051–3063. doi: 10.1109/TC.2015.2401032 XU Fei, LIU Fangming, LIU Linghui, et al. iAware: Making live migration of virtual machines interference-aware in the cloud[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2014, 63(12): 3012–3025. doi: 10.1109/TC.2013.185 CHEN Hongyang, WU Jianming, and SHIMOMURA T. New reference signal design for URLLC and eMBB multiplexing in new radio wireless communications[C]. 2018 IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Bologna, Italy, 2018: 1220–1225. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2018.8580882. KHAN Z, FAN Pingzhi, ABBAS F, et al. Two-level cluster based routing scheme for 5G V2X communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 16194–16205. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2892180 WANG Chenmeng, YU F R, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Joint computation offloading and interference management in wireless cellular networks with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(8): 7432–7445. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2672701 JOSHI G, VIG R, and SINGH S. DCA-based unimodal feature-level fusion of orthogonal moments for Indian sign language dataset[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2018, 12(5): 570–577. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2017.0394 SUN Yuxuan, ZHOU Sheng, and XU Jie. EMM: Energy-aware mobility management for mobile edge computing in ultra dense networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(11): 2637–2646. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2760160 PLACHY J, BECVAR Z, and STRINATI E C. Dynamic resource allocation exploiting mobility prediction in mobile edge computing[C]. 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, Valencia, Spain, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2016.7794955. CHEN Xiaojing, NI Wei, COLLINGS I B, et al. Automated function placement and online optimization of network functions virtualization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(2): 1225–1237. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2877336 FRANGOUDIS P A and KSENTINI A. Service migration versus service replication in Multi-access Edge Computing[C]. 2018 14th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference, Limassol, Cyprus, 2018: 124–129. doi: 10.1109/IWCMC.2018.8450284. -





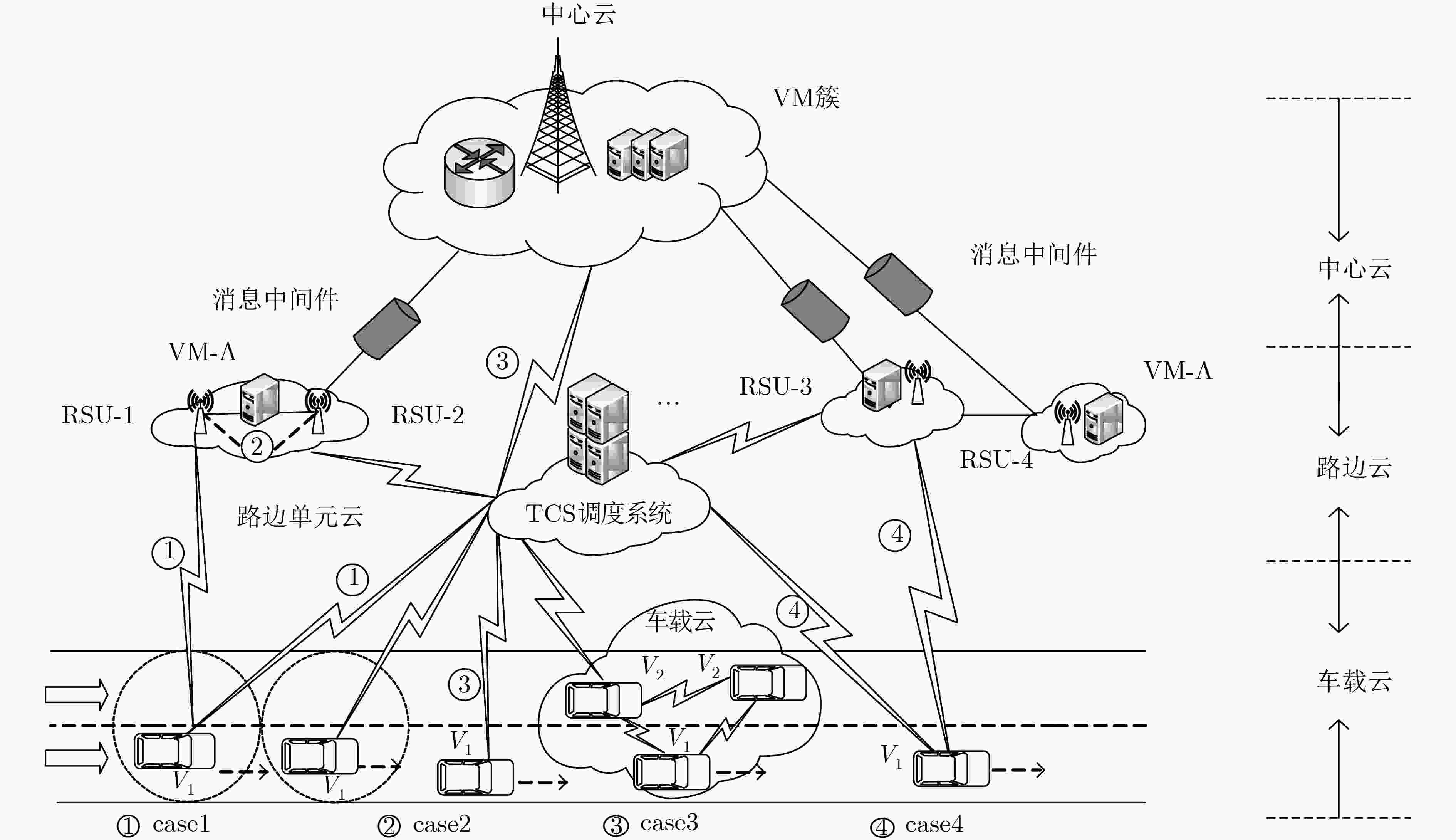
 下载:
下载:
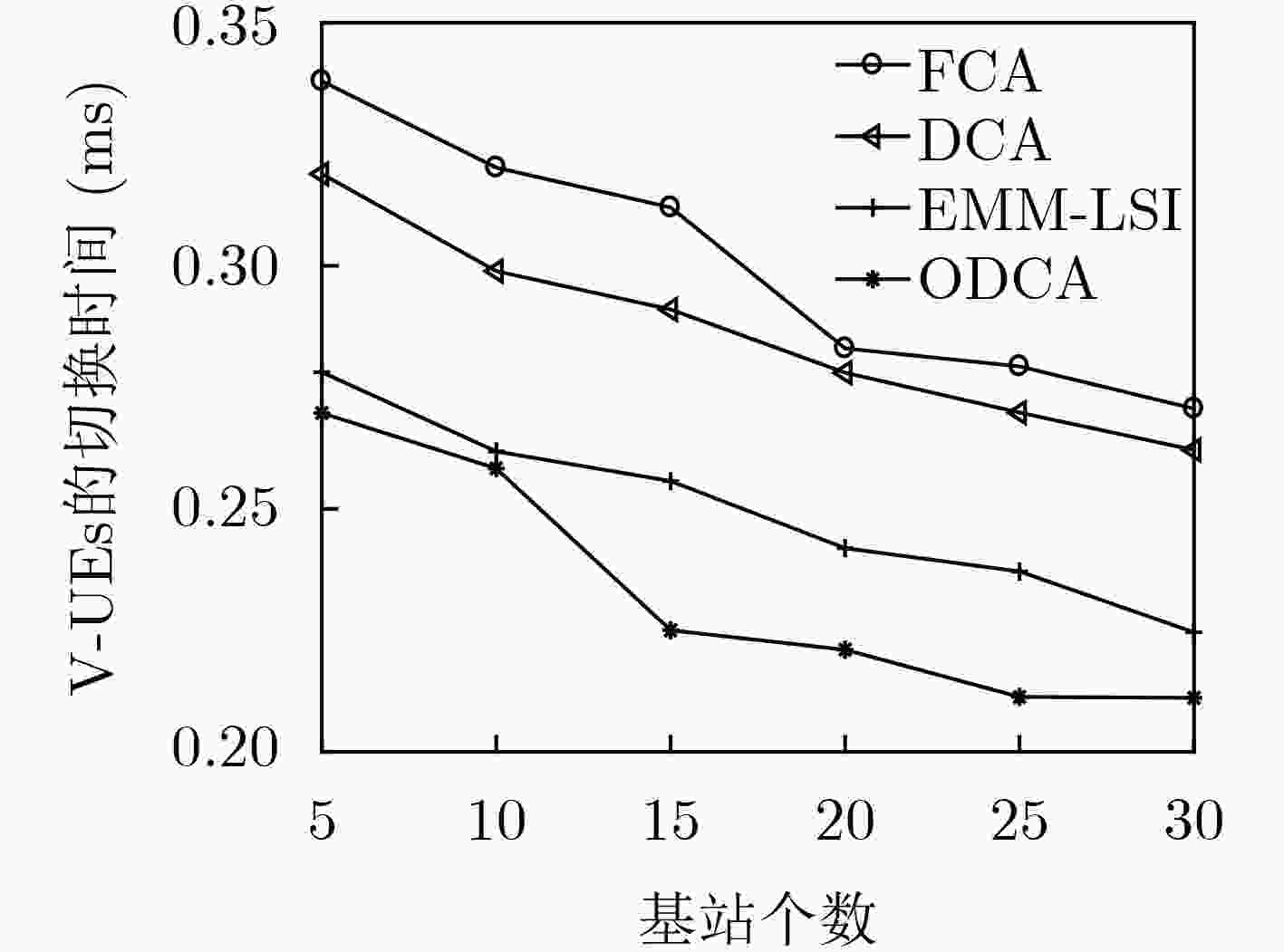
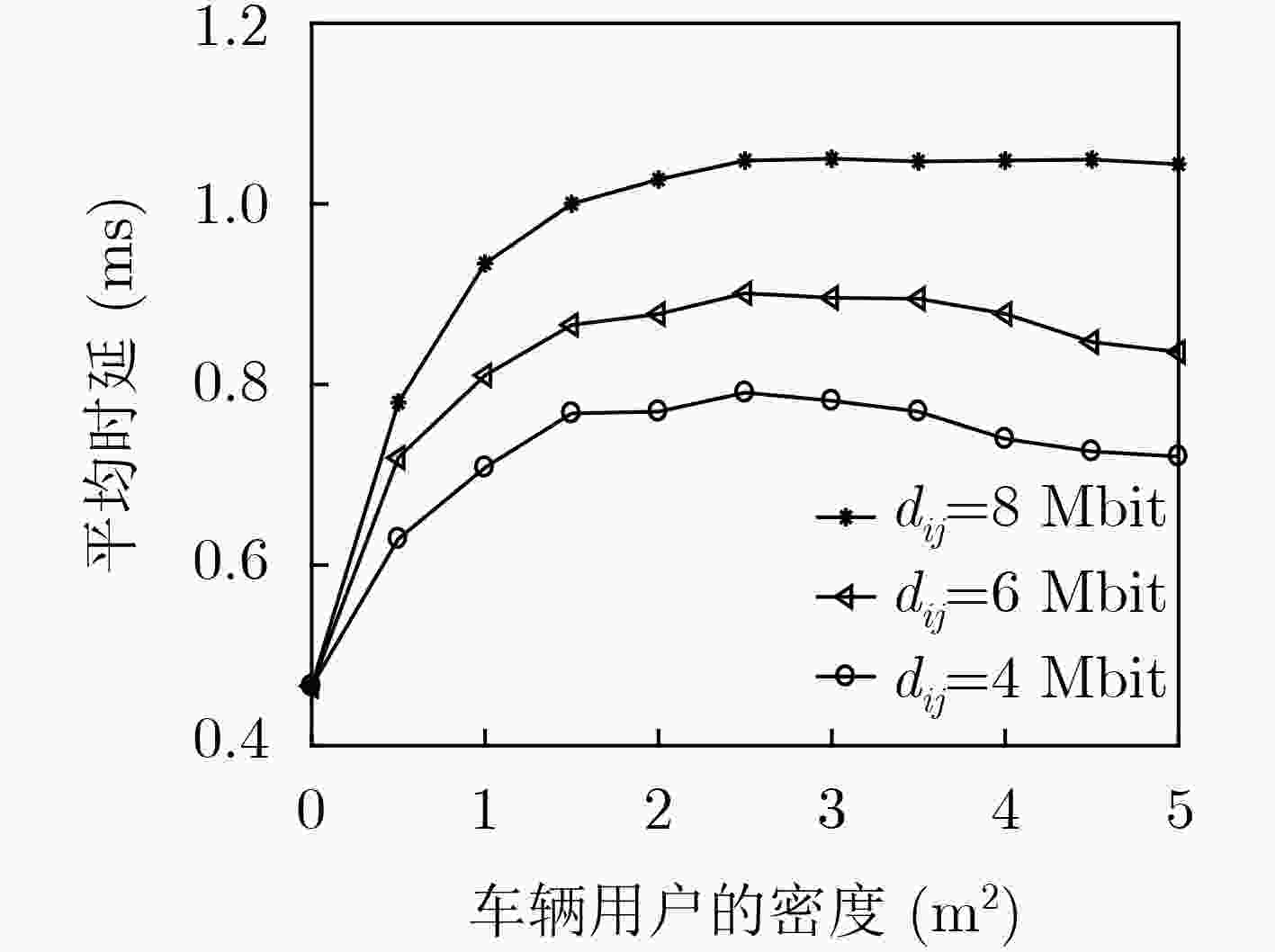
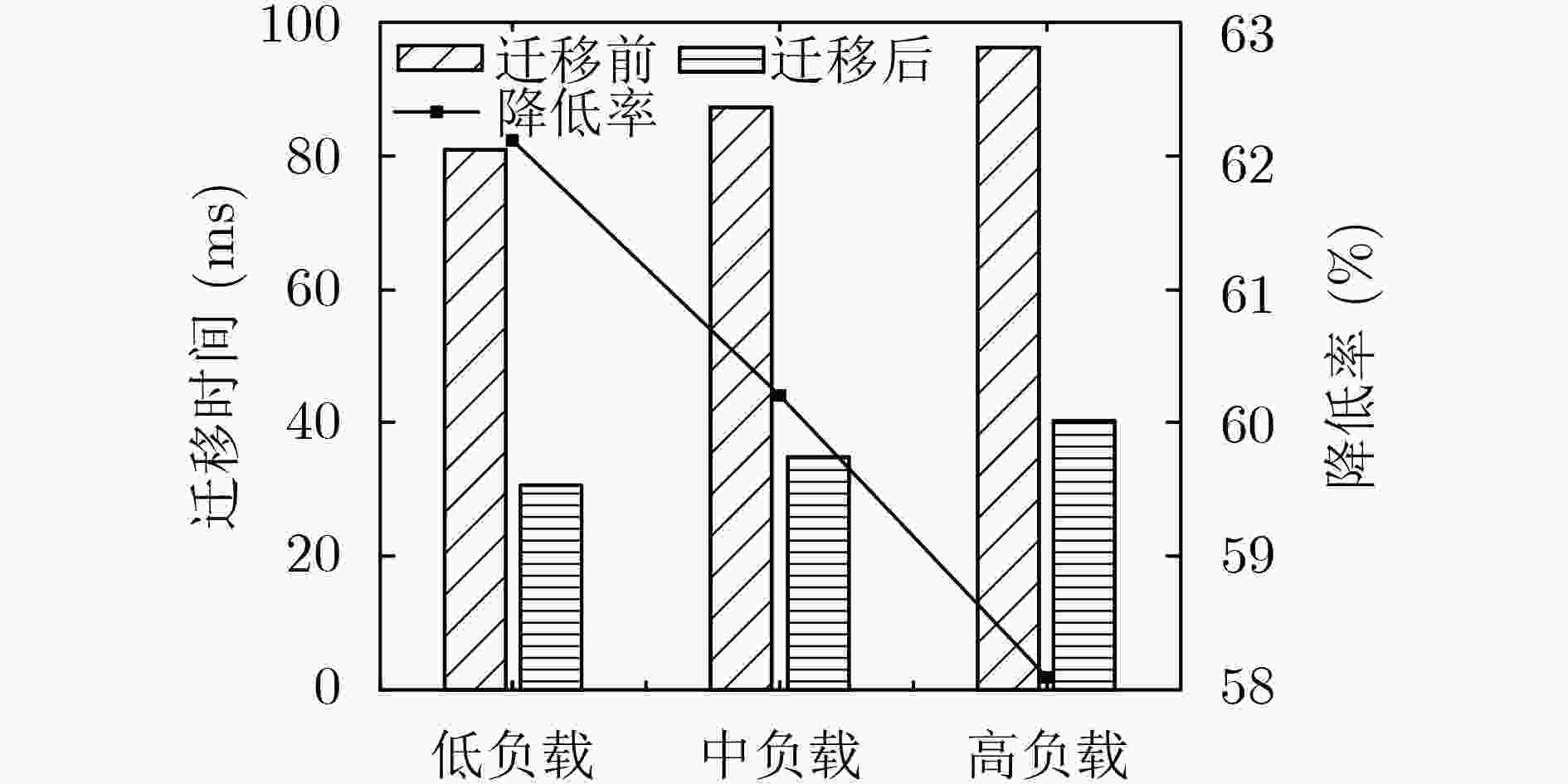


 下载:
下载:
