Task Assignment Strategy for Platoons in Cooperative Driving
-
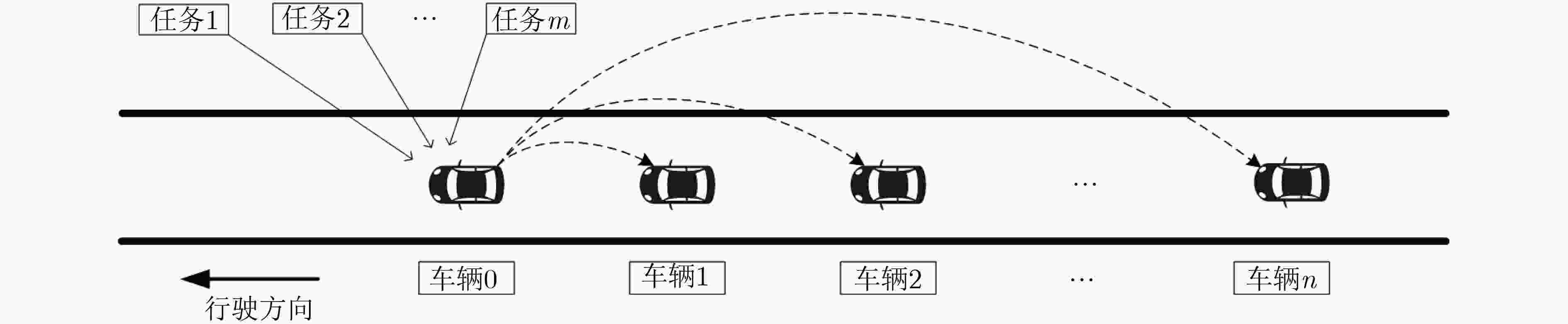
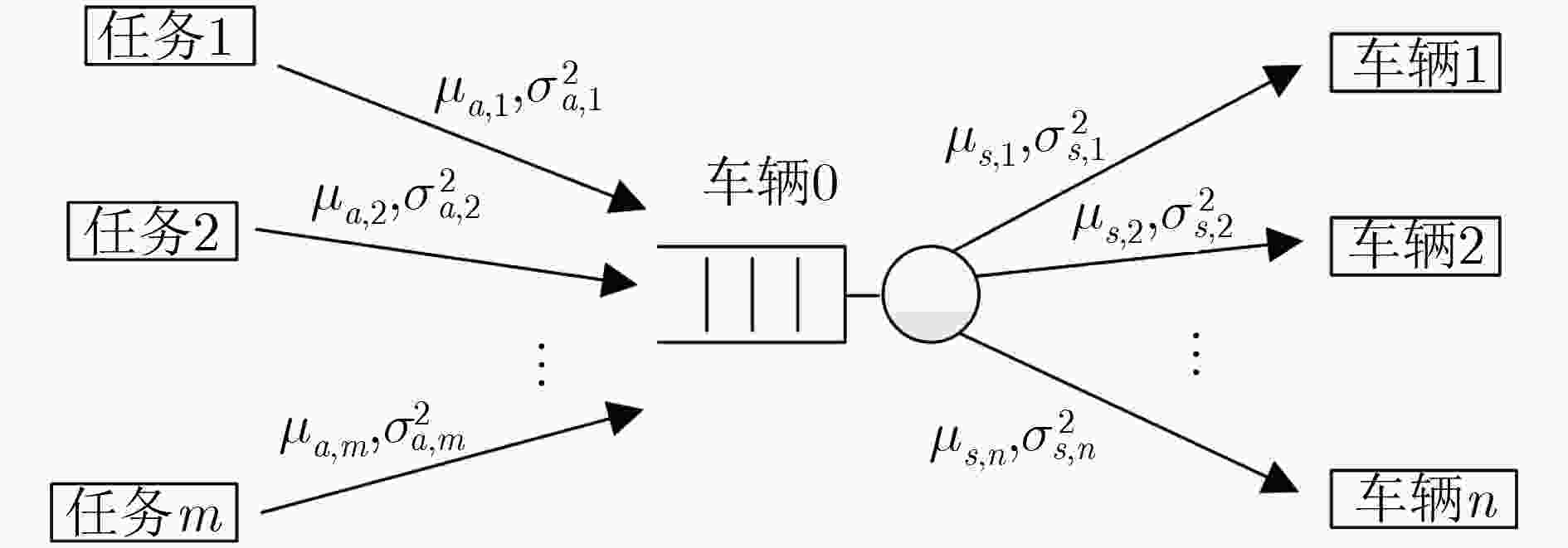
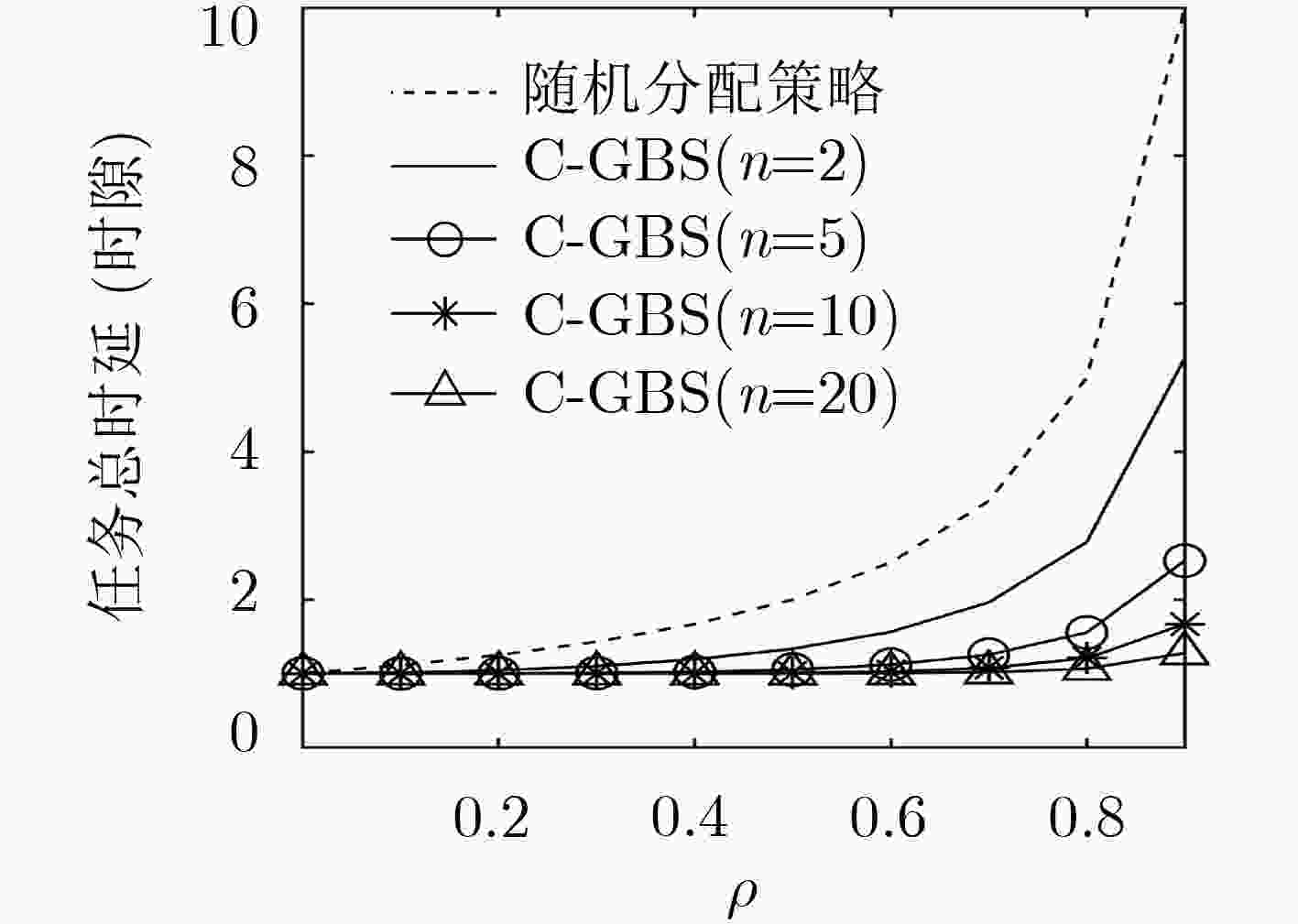
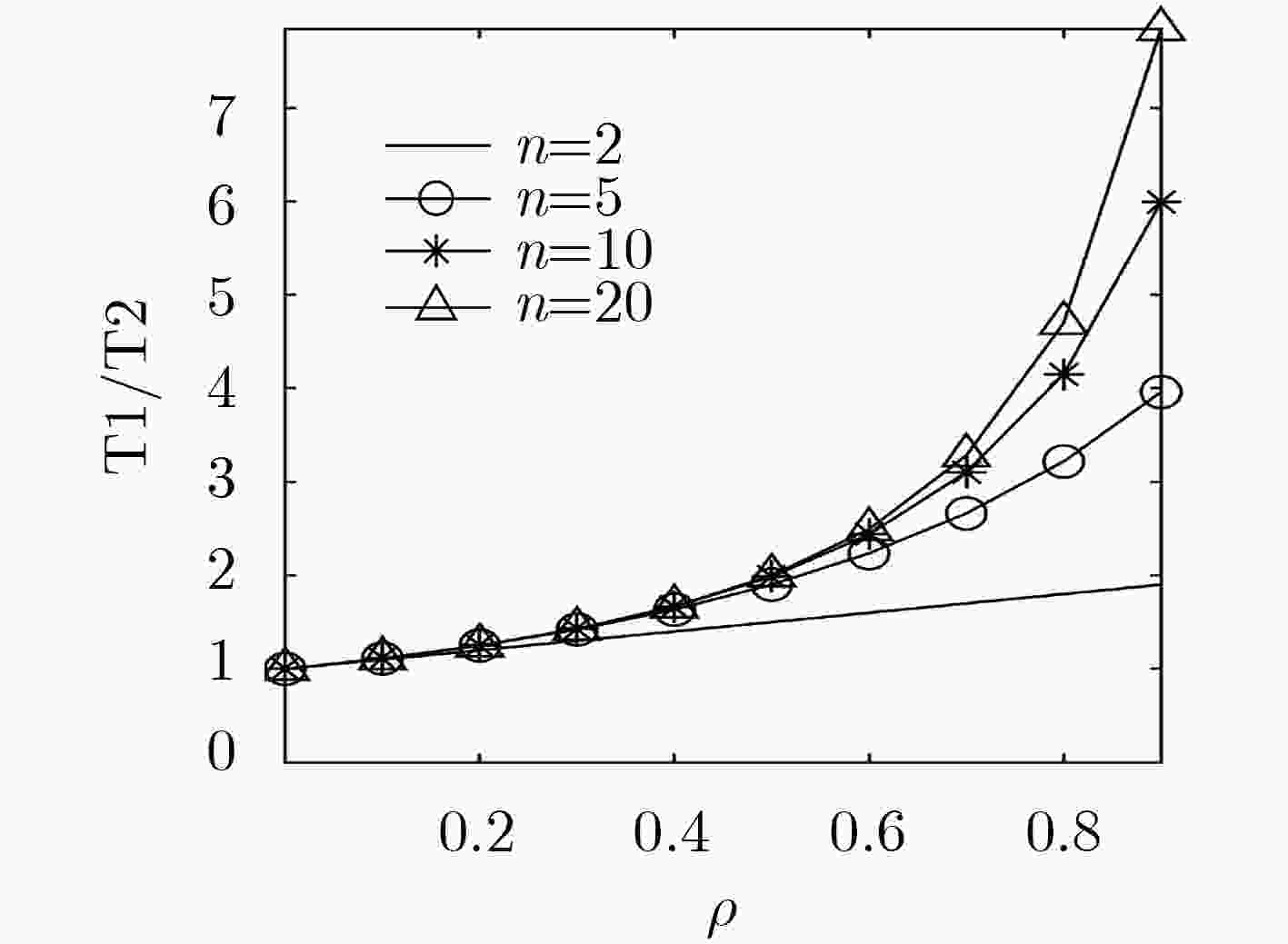
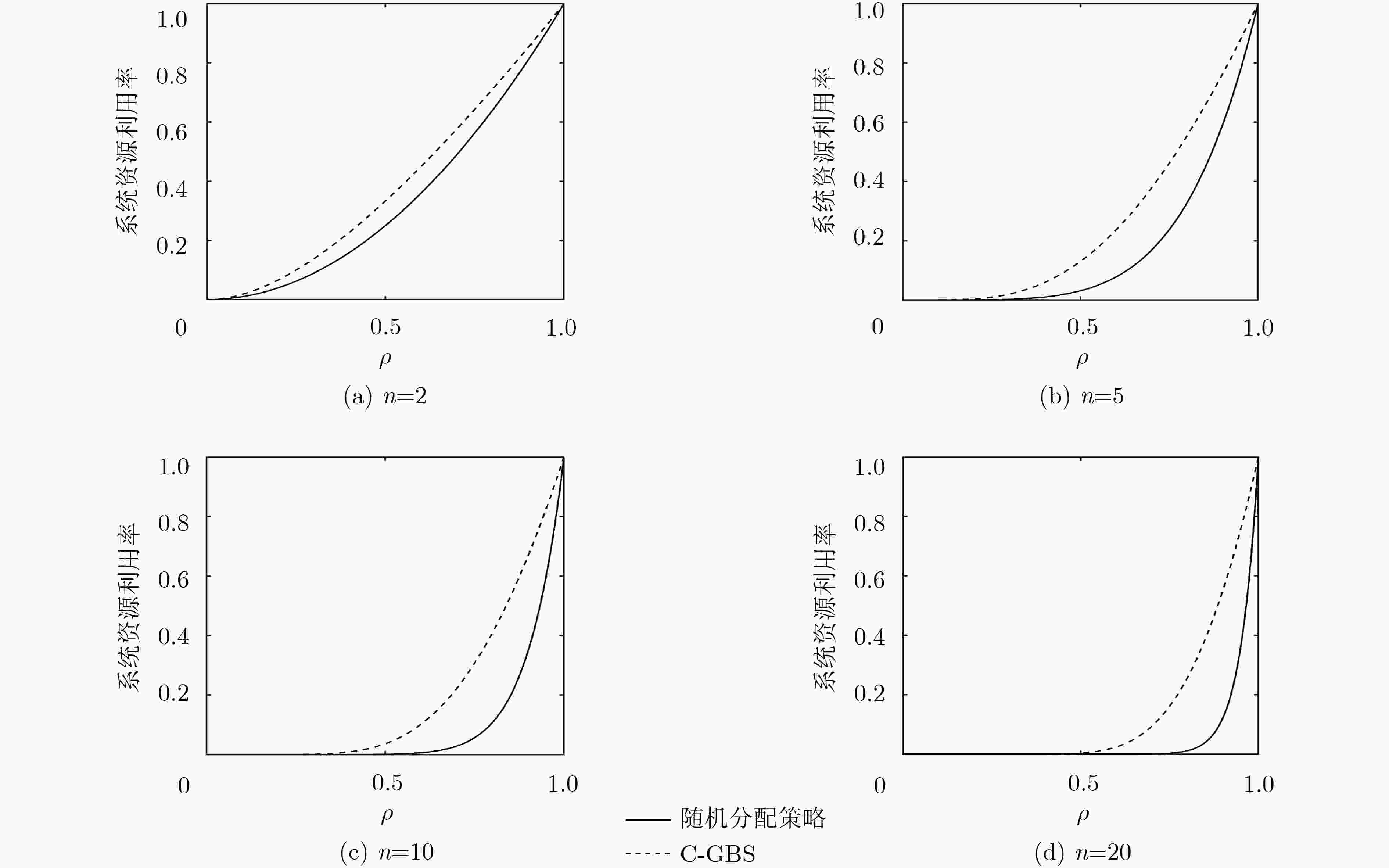
摘要: 自动驾驶的实现需要大量车载传感器的支持,然而,在有限车载计算资源条件下,由传感器所产生的庞大数据量使得自动驾驶任务的实时性难以满足,成为阻碍自动驾驶技术进一步发展的重要阻力。通过将驾驶任务进行协作处理,因而充分利用多个协作车辆的计算资源,自动协同驾驶成为解决该问题的新途径。而如何形成多车编队并实现编队中驾驶任务分配则是实现自动协同驾驶的关键。该文首先采用排队理论G/G/1模型建立一种普适性车辆编队网络拓扑分析模型,充分考虑编队内车辆间的任务协作能力和单个车辆的任务负荷,得出任务的处理时延和车辆系统中的平均任务数;其次,采用支持向量机(SVM)方法,基于车辆的负荷程度及处理能力将车辆的“空闲”、“繁忙”两状态进行分类,进而建立针对车辆协作任务分配的候选车辆集。最后,基于上述分析,该文提出面向多车编队协同驾驶的任务均衡策略——基于分类的贪婪均衡策略(C-GBS),以充分平衡编队内所有车辆的任务负荷并利用不同车辆的任务处理能力。仿真结果表明,该策略能够减小重负荷网络中的任务处理时延,有效提升自动驾驶车辆的任务处理效率。Abstract: Autonomous vehicles are equipped with multiple on-board sensors to achieve self-driving functions. However, a tremendous amount of data is generated by autonomous vehicles, which significantly challenges the real-time task processing. Through multiple-vehicle cooperation, which makes the best of vehicle onboard computing resources, autonomous and cooperative driving becomes a promising candidate to solve the aforementioned problem. In this case, it is vital for autonomous and cooperative driving to form a driving platoon and allocate driving tasks efficiently. In this paper, a more general analytical model is developed based on G/G/1 queueing theory to model the topology of platoons. Next, Support Vector Machine (SVM) method is adopted to classify the “idle” and “busy” categories of the vehicles in the platoon based on their computing load and task processing capacity. Finally, based on the analysis above, an efficient task balancing strategy of platoons in autonomous and cooperative driving called Classification based Greed Balancing Strategy (C-GBS) is proposed, in order to balance the task burden among vehicles and cooperate more efficiently. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed technique can reduce the processing delay of driving tasks in platoons with high computing load, which will improve the processing efficiency in autonomous vehicles.
-
表 1 C-GBS算法
输入:车辆集$V$,任务集T 输出:结果集S (1) 基于对车辆状态的分类,初始化候选车辆集${V_1}$和结果集S; (2) 遍历任务集T,选取T 中时延门限${T_i}$最小的任务${t_i}$,对其进行
分配;(3) 选择候选车辆集${V_1}$中的第1辆车${v_{k,1}}$,根据${v_{k,1}}$的处理速率和
任务${t_i}$的sizei估计${v_{k,1}}$处理任务${t_i}$所需的时间${\tau _{i,1}}$,并令
$ {\tau _i} = {\tau _{i,1}},\kappa = 1$;(4) 遍历候选车辆集${V_1}$,依次计算${V_1}$中每辆车vk处理任务${t_i}$所需
时间${\tau _{i,k}}$,若${\tau _{i,k}}<{\tau _{i}}$,则令$ {\tau _i} = {\tau _{i,k}},\kappa = k$;(5) 遍历${V_1}$完成后,将任务${t_i}$分配给${V_1}$中的第$ \kappa $辆车处理; (6) 更新车辆vk的状态,更新候选车辆集${V_1}$,更新任务集T并更
新结果集S记录每项任务的处理情况;(7) 返回第(2)步,继续执行,直到任务全部完成。 -
CESARI G, SCHILDBACH G, CARVALHO A, et al. Scenario model predictive control for lane change assistance and autonomous driving on highways[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2017, 9(3): 23–35. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2017.2709782 CHANG L and DORMEHL L. 6 self-driving car crashes that tapped the brakes on the autonomous revolution[EB/OL]. https://www.digitaltrends.com/cool-tech/most-significant-self-driving-car-crashes/, 2018. SU Zhou, HUI Yilong, XU Qichao, et al. An edge caching scheme to distribute content in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 5346–5356. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2824345 AISSIOUI A, KSENTINI A, GUEROUI A M, et al. On enabling 5G automotive systems using follow me edge-cloud concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 5302–5316. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2805369 TRAN T X, HAJISAMI A, PANDEY P, et al. Collaborative mobile edge computing in 5G networks: New paradigms, scenarios, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(4): 54–61. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600863 LUAN T H, CAI L X, CHEN Jiming, et al. Engineering a distributed infrastructure for large-scale cost-effective content dissemination over urban vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(3): 1419–1435. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2013.2251924 SU Zhou, HUI Yilong, and GUO Song. D2D-based content delivery with parked vehicles in vehicular social networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016, 23(4): 90–95. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2016.7553031 LI S E, GAO Feng, LI Keqiang, et al. Robust longitudinal control of multi-vehicle systems-a distributed h-infinity method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(9): 2779–2788. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2760910 JAIN A, GHOSE D, and MENON P P. Multi-vehicle formation in a controllable force field with non-identical controller gains[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 12(6): 802–811. LI Xin and ZHU Daqi. An adaptive SOM neural network method for distributed formation control of a group of AUVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(10): 8260–8270. LIU Yuanchang and BUCKNALL R. A survey of formation control and motion planning of multiple unmanned vehicles[J]. Robotica, 2018, 36(7): 1019–1047. doi: 10.1017/S0263574718000218 ZHU Daqi, CAO Xiang, SUN Bing, et al. Biologically inspired self-organizing map applied to task assignment and path planning of an AUV system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2018, 10(2): 304–313. doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2017.2727678 GODFREY G A and POWELL W B. An adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for dynamic fleet management, II: Multiperiod travel times[J]. Transportation Science, 2002, 36(1): 40–54. doi: 10.1287/trsc.36.1.40.572 VIEGAS D, BATISTA P, OLIVEIRA P, et al. Discrete-time distributed Kalman filter design for formations of autonomous vehicles[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2018, 75: 55–68. doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2018.03.014 The 5G Infrastructure Public Private Partnership (5G PPP). 5G PPP white paper on automotive vertical sectors[EB/OL]. https://5g-ppp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/5G-PPP-White-Paper-on-Automotive-Vertical-Sectors.pdf, 2015. PENG Haixia, LI Dazhou, ABBOUD K, et al. Performance analysis of IEEE 802.11p DCF for multiplatooning communications with autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(3): 2485–2498. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2571696 3GPP. Study on LTE-based V2X services[EB/OL]. https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2934. PIRO G, ORSINO A, CAMPOLO C, et al. D2D in LTE vehicular networking: System model and upper bound performance[C]. The 7th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops, Brno, Czech Republic, 2015: 281–286. WHITT W. The queueing network analyzer[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1983, 62(9): 2779–2815. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1983.tb03204.x DAVIS J L, MASSEY W A, and WHITT W. Sensitivity to the service-time distribution in the nonstationary erlang loss model[J]. Management Science, 1995, 41(6): 1107–1116. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.41.6.1107 LI Changle, ZHANG Yao, LUAN T H, et al. Building transmission backbone for highway vehicular networks: Framework and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(9): 8709–8722. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2844471 WHITT W. Approximating a point process by a renewal process, I: Two basic methods[J]. Operations Research, 1982, 30(1): 125–147. doi: 10.1287/opre.30.1.125 RAY W D. Basic queueing theory[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A, 1988, 151(3): 550–684. AVIDAN S. Support vector tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(8): 1064–1072. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.53 MOLINA-MASEGOSA R and GOZALVEZ J. LTE-V for sidelink 5G V2X vehicular communications: A new 5G technology for short-range vehicle-to-everything communications[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(4): 30–39. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2752798 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
