Deployment Algorithm of Service Function Chain Based on Transfer Actor-Critic Learning
-
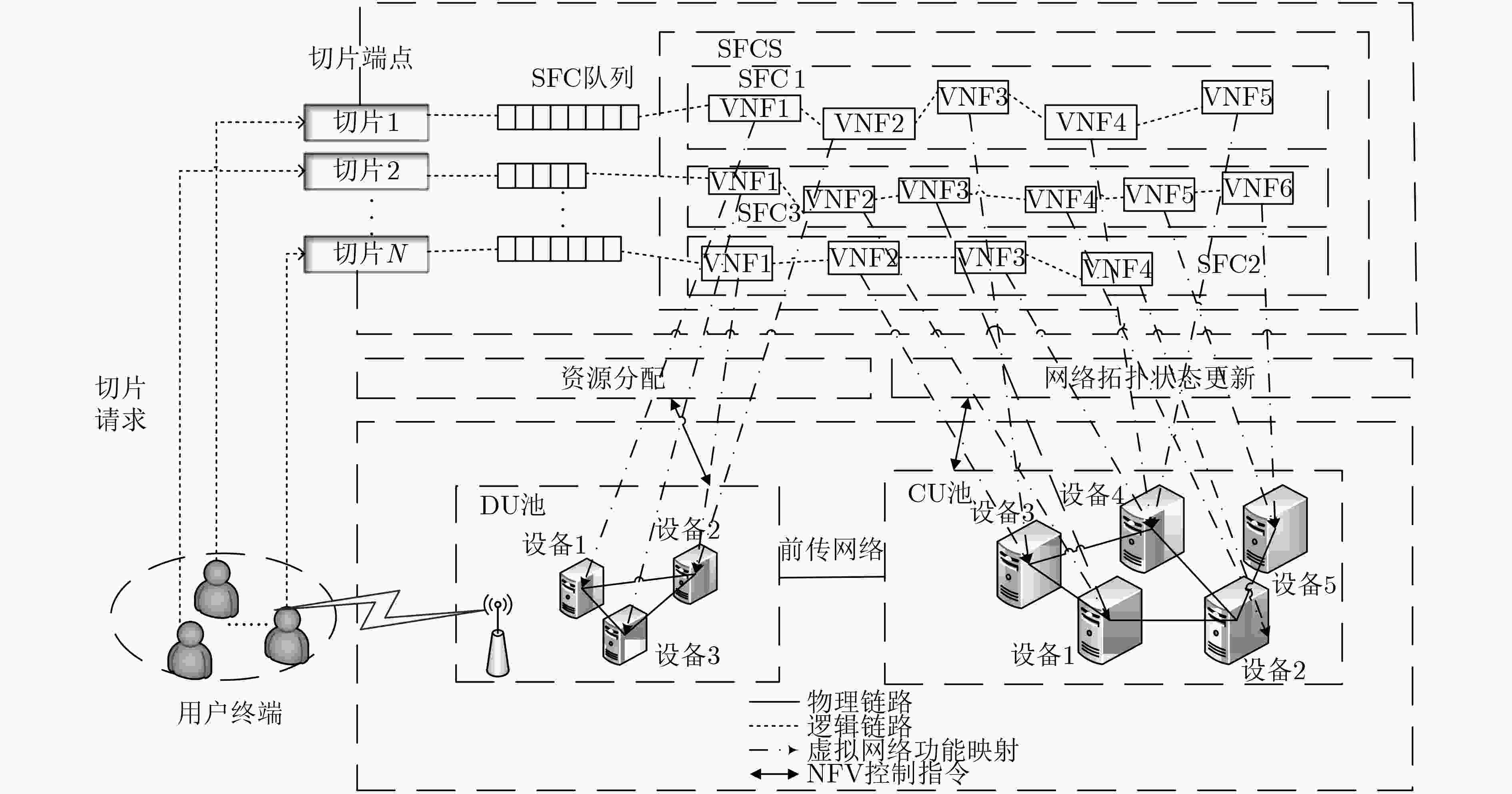
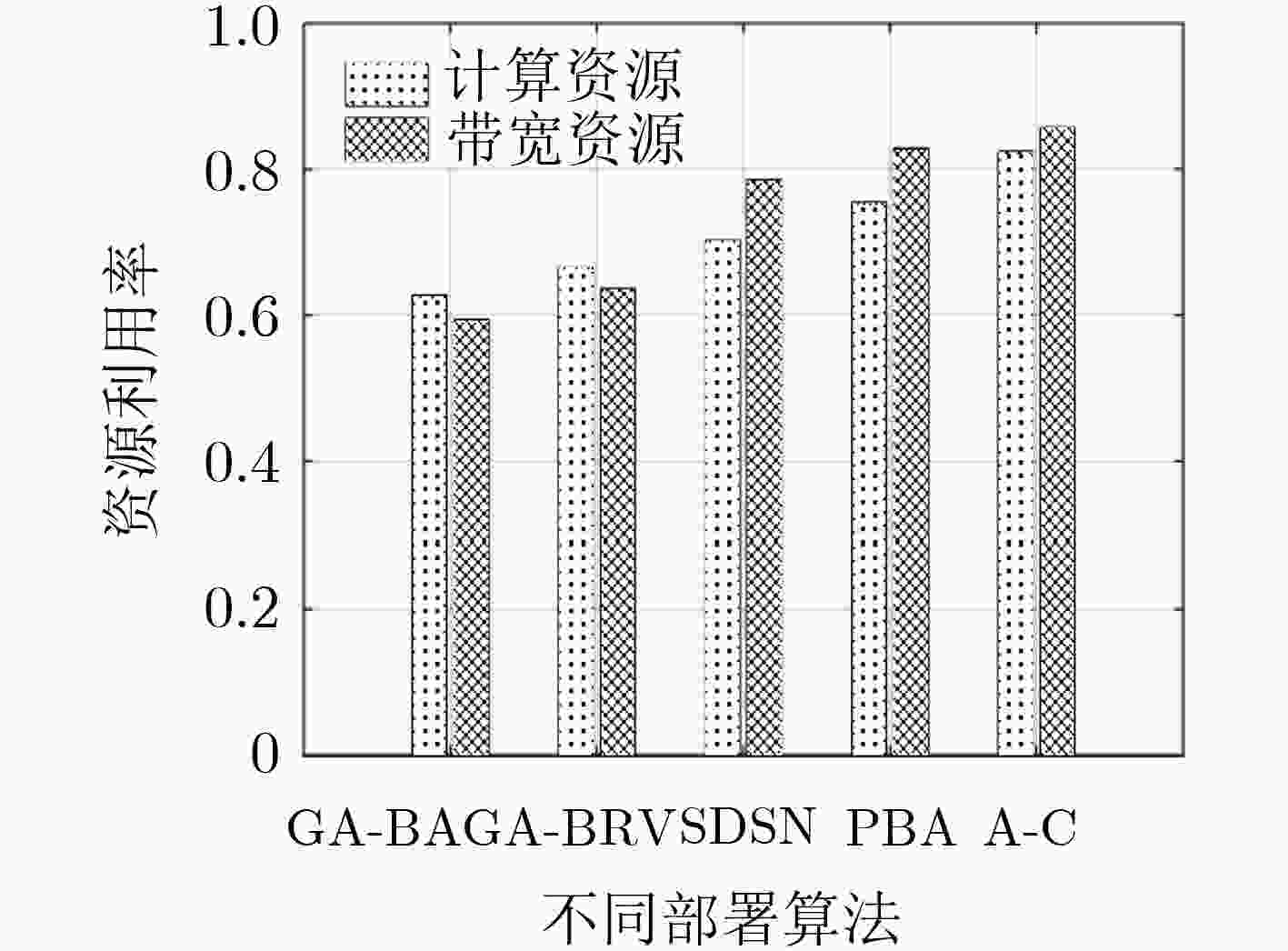
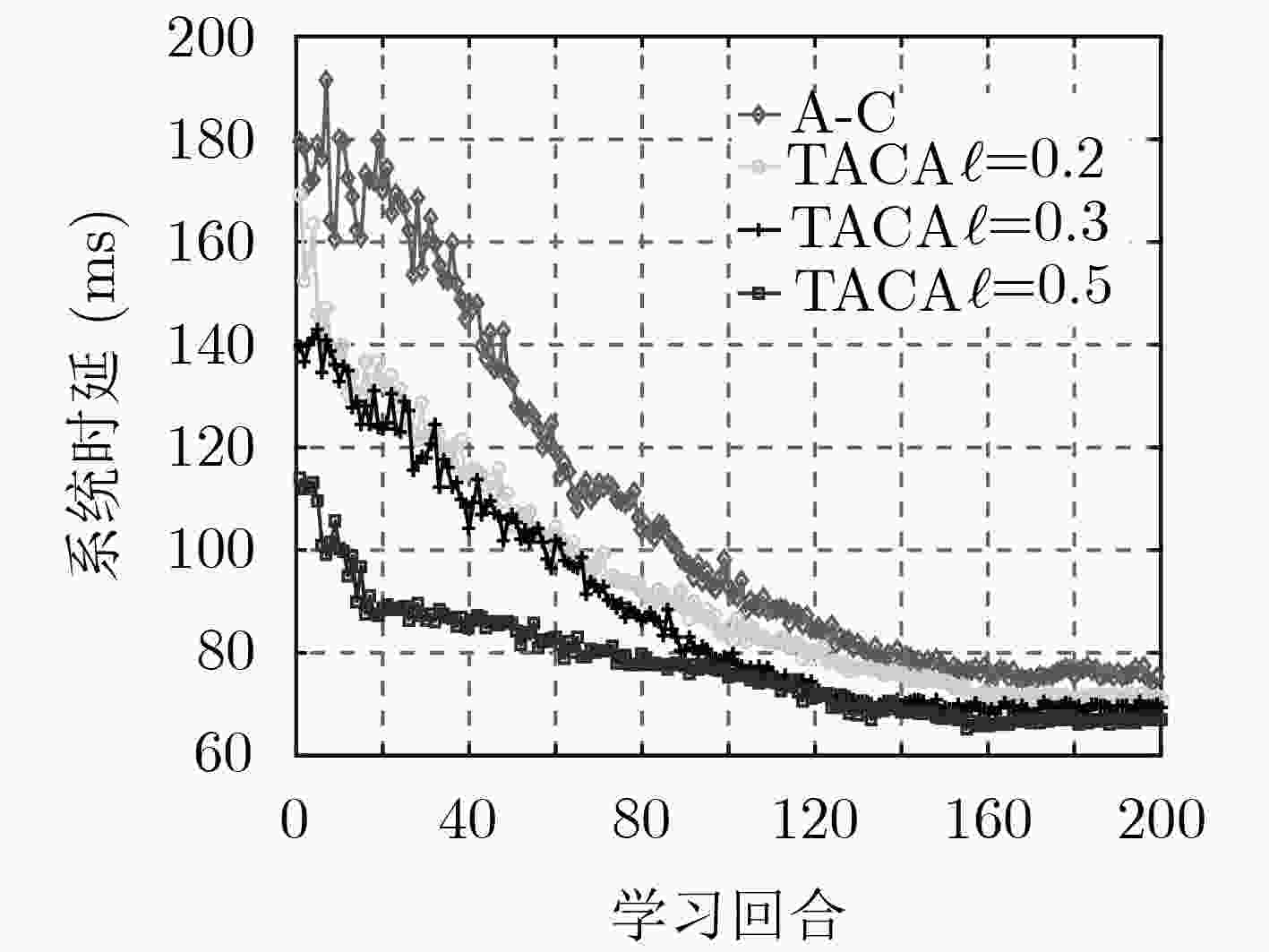
摘要: 针对5G网络切片环境下由于业务请求的随机性和未知性导致的资源分配不合理从而引起的系统高时延问题,该文提出了一种基于迁移演员-评论家(A-C)学习的服务功能链(SFC)部署算法(TACA)。首先,该算法建立基于虚拟网络功能放置、计算资源、链路带宽资源和前传网络资源联合分配的端到端时延最小化模型,并将其转化为离散时间马尔可夫决策过程(MDP)。而后,在该MDP中采用A-C学习算法与环境进行不断交互动态调整SFC部署策略,优化端到端时延。进一步,为了实现并加速该A-C算法在其他相似目标任务中(如业务请求到达率普遍更高)的收敛过程,采用迁移A-C学习算法实现利用源任务学习的SFC部署知识快速寻找目标任务中的部署策略。仿真结果表明,该文所提算法能够减小且稳定SFC业务数据包的队列积压,优化系统端到端时延,并提高资源利用率。Abstract: To solve the problem of high system delay caused by unreasonable resource allocation because of randomness and unpredictability of service requests in 5G network slicing, this paper proposes a deployment scheme of Service Function Chain (SFC) based on Transfer Actor-Critic (A-C) Algorithm (TACA). Firstly, an end-to-end delay minimization model is built based on Virtual Network Function (VNF) placement, and joint allocation of computing resources, link resources and fronthaul bandwidth resources, then the model is transformed into a discrete-time Markov Decision Process (MDP). Next, A-C learning algorithm is adopted in the MDP to adjust dynamically SFC deployment scheme by interacting with environment, so as to optimize the end-to-end delay. Furthermore, in order to realize and accelerate the convergence of the A-C algorithm in similar target tasks (such as the arrival rate of service requests is generally higher), the transfer A-C algorithm is adopted to utilize the SFC deployment knowledge learned from source tasks to find quickly the deployment strategy in target tasks. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can reduce and stabilize the queuing length of SFC packets, optimize the system end-to-end delay, and improve resource utilization.
-
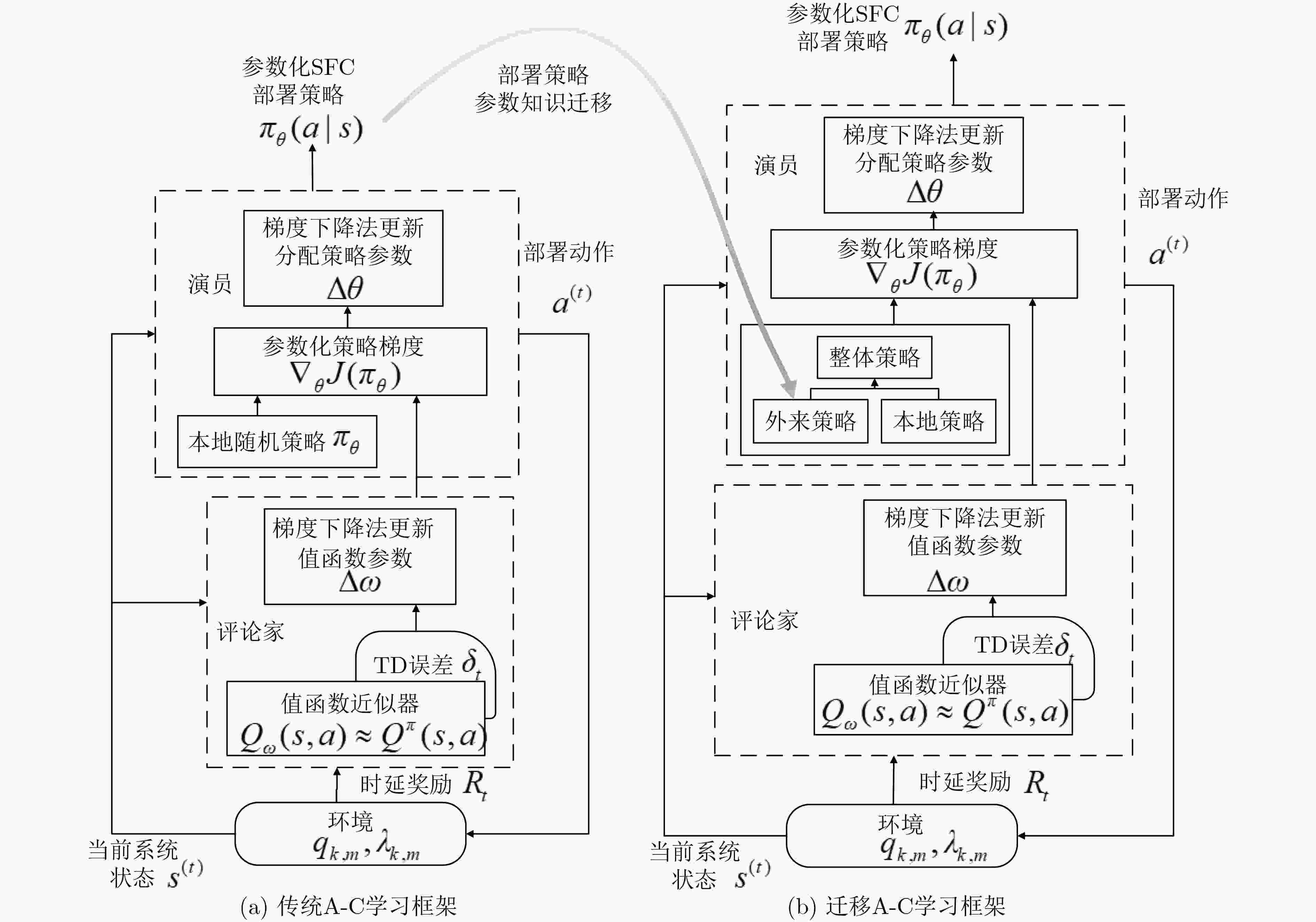
表 1 基于迁移A-C学习的SFC部署算法
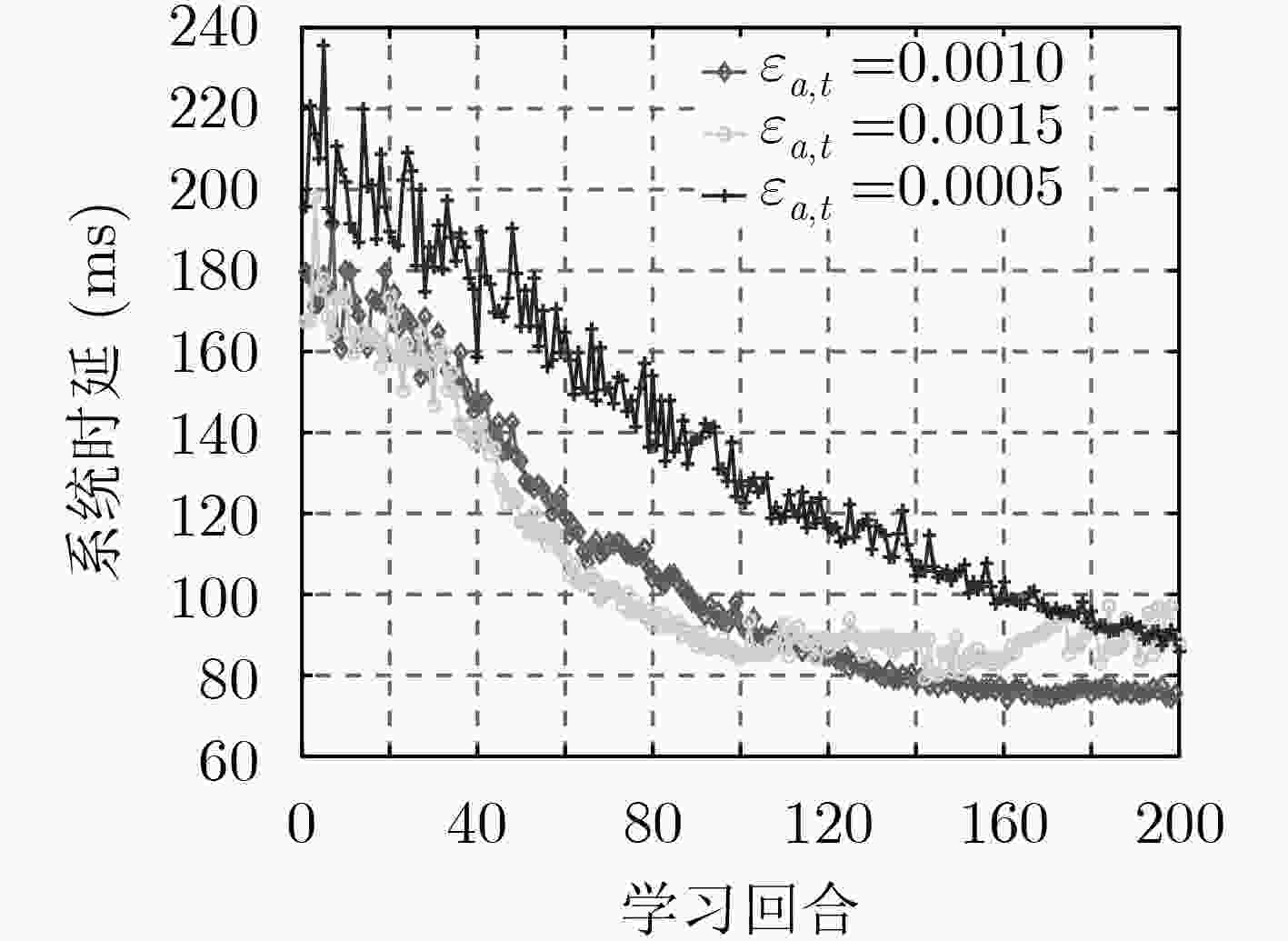
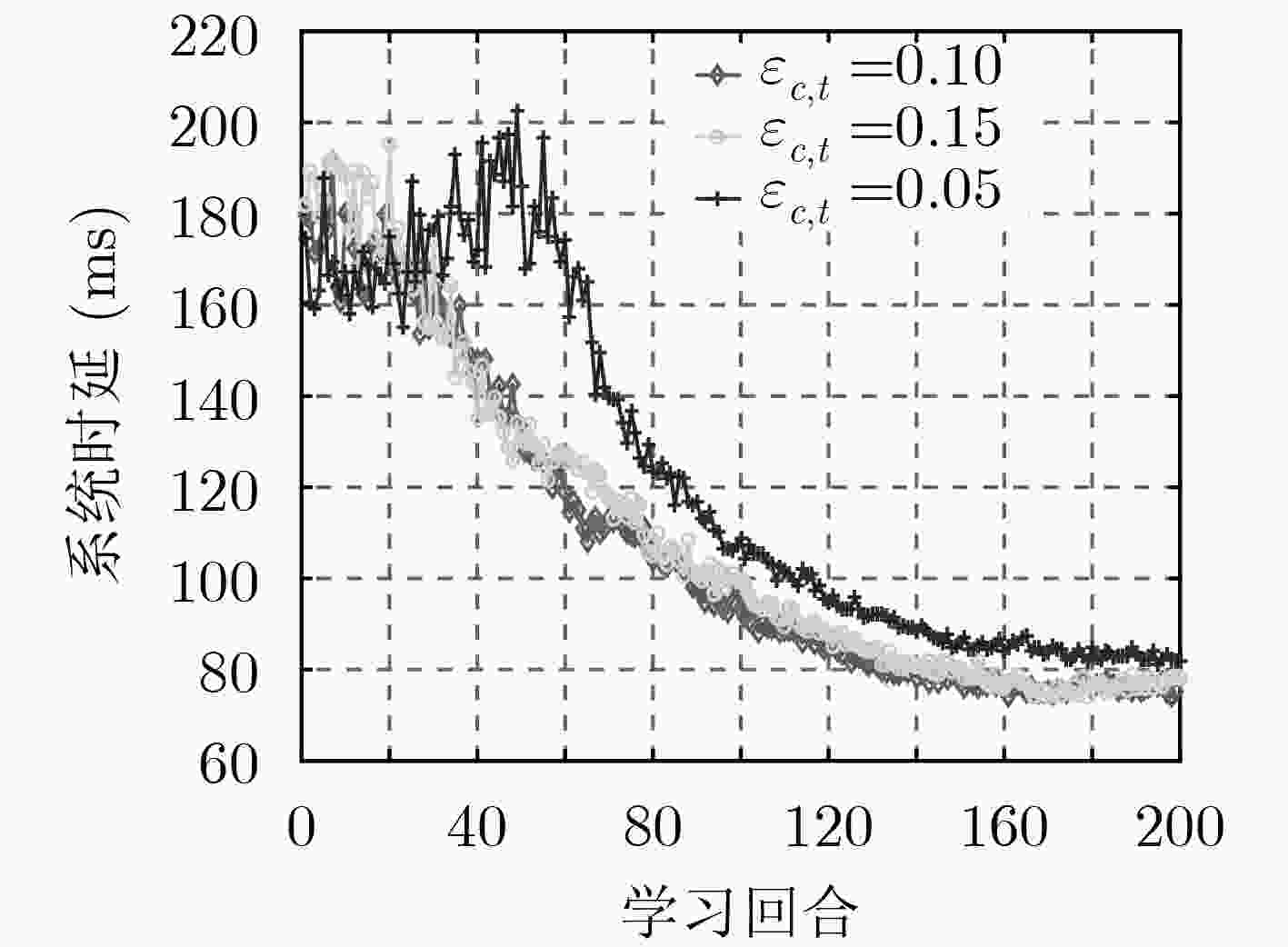
输入:高斯策略${ {\pi} _\theta }(s,a)\sim N(\mu (s),{\sigma ^2})$,以及其梯度${{\text{∇}} _\theta }\ln { {\pi} _\theta }(s,a)$,状态分布${d^{\pi} }(s)$,学习率${\varepsilon _{a,t}}$和${\varepsilon _{c,t}}$,折扣因子$\beta $ (1) for ${\rm{epsoide } }= 0,1,2, ··· ,E{p_{\max} }$ do (2) 初始化:策略参数向量${{{\theta }}_t}$,状态-动作值函数参数向量${\omega _t}$,状态值函数参数向量${{{\upsilon}} _t}$,初始状态${s_0}\sim{d_{\pi} }(s)$,本地部署策略${\pi} _\theta ^n(s,a)$,外
来迁移部署策略${\pi} _\theta ^e(s,a)$(3) for 回合每一步$t = 0,1, ··· ,T$do (4) 由式(20)得到整体部署策略,遵循整体策略${ {\pi} _\theta }(s,a)$选择动作${a^{(t)}}$,进行VNF放置和资源分配,而后更新环境状态${s^{(t + 1)}}$,并得到立即
奖励${R_t} = - \tau (t)$(5) end for (6) 评论家过程: (a) 计算相容特征:由式(10)得处于状态$s$的基函数向量,结合式(14),式(15)得相容特征 (b) 相容近似:由式(11)得状态-动作值函数近似,由式(16)得状态值函数近似 (c) TD误差计算:由式(12),式(17)分别得状态-动作值函数、状态值函数的TD误差 (d) 更新评论家参数:由式(13)得状态-动作值函数参数向量更新,由式(18)得状态值函数参数向量更新 (7) 演员过程: (a) 计算优势函数 (b) 重写策略梯度:代入优势函数由式(19)得策略梯度 (c) 更新演员参数:由式(8)得策略参数向量更新 (8) end for -
AGARWAL S, MALANDRINO F, CHIASSERINI C F, et al. VNF placement and resource allocation for the support of vertical services in 5G networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, 27(1): 433–446. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2890631 史久根, 张径, 徐皓, 等. 一种面向运营成本优化的虚拟网络功能部署和路由分配策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 973–979. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180522SHI Jiugen, ZHANG Jing, XU Hao, et al. Joint optimization of virtualized network function placement and routing allocation for operational expenditure[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 973–979. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180522 LI Defang, HONG Peilin, XUE Kaiping, et al. Virtual network function placement considering resource optimization and SFC requests in cloud datacenter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2018, 29(7): 1664–1677. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2018.2802518 PEI Jianing, HONG Peilin, and LI Defang. Virtual network function selection and chaining based on deep learning in SDN and NFV-Enabled networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCW.2018.8403657. CAI Yibin, WANG Ying, ZHONG Xuxia, et al. An approach to deploy service function chains in satellite networks[C]. NOMS 2018–2018 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Taipei, China, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/NOMS.2018.8406159. QU Long, ASSI C, and SHABAN K. Delay-aware scheduling and resource optimization with network function virtualization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(9): 3746–3758. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2580150 陈前斌, 杨友超, 周钰, 等. 基于随机学习的接入网服务功能链部署算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 417–423. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180310CHEN Qianbin, YANG Youchao, ZHOU Yu, et al. Deployment algorithm of service function chain of access network based on stochastic learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 417–423. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180310 PHAN T V, BAO N K, KIM Y, et al. Optimizing resource allocation for elastic security VNFs in the SDNFV-enabled cloud computing[C]. 2017 International Conference on Information Networking, Da Nang, Vietnam, 2017: 163–166. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN.2017.7899497. XIA Weiwei and SHEN Lianfeng. Joint resource allocation using evolutionary algorithms in heterogeneous mobile cloud computing networks[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(8): 189–204. doi: 10.1109/CC.2018.8438283 ZHU Zhengfa, PENG Jun, GU Xin, et al. Fair resource allocation for system throughput maximization in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 5332–5340. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2790963 MAO Yuyi, ZHANG Jun, and LETAIEF K B. Dynamic computation offloading for mobile-edge computing with energy harvesting devices[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3590–3605. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2611964 MEHRAGHDAM S, KELLER M, and KARL H. Specifying and placing chains of virtual network functions[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Cloud Networking, Luxembourg, Luxembourg, 2014: 7–13. doi: 10.1109/CloudNet.2014.6968961. HAGHIGHI A A, HEYDARI S S, and SHAHBAZPANAHI S. MDP modeling of resource provisioning in virtualized content-delivery networks[C]. The 25th IEEE International Conference on Network Protocols, Toronto, Canada, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICNP.2017.8117600. GRONDMAN I, BUSONIU L, LOPES G A D, et al. A survey of actor-critic reinforcement learning: Standard and natural policy gradients[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) , 2012, 42(6): 1291–1307. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2218595 LEE D H and LEE J J. Incremental receptive field weighted actor-critic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(1): 62–71. doi: 10.1109/TII.2012.2209660 LI Rongpeng, ZHAO Zhifeng, CHEN Xianfu, et al. TACT: A transfer actor-critic learning framework for energy saving in cellular radio access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(4): 2000–2011. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.022014.130840 KOUSHI A M, HU Fei, and KUMAR S. Intelligent spectrum management based on transfer actor-critic learning for rateless transmissions in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(5): 1204–1215. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2744620 -





 下载:
下载:
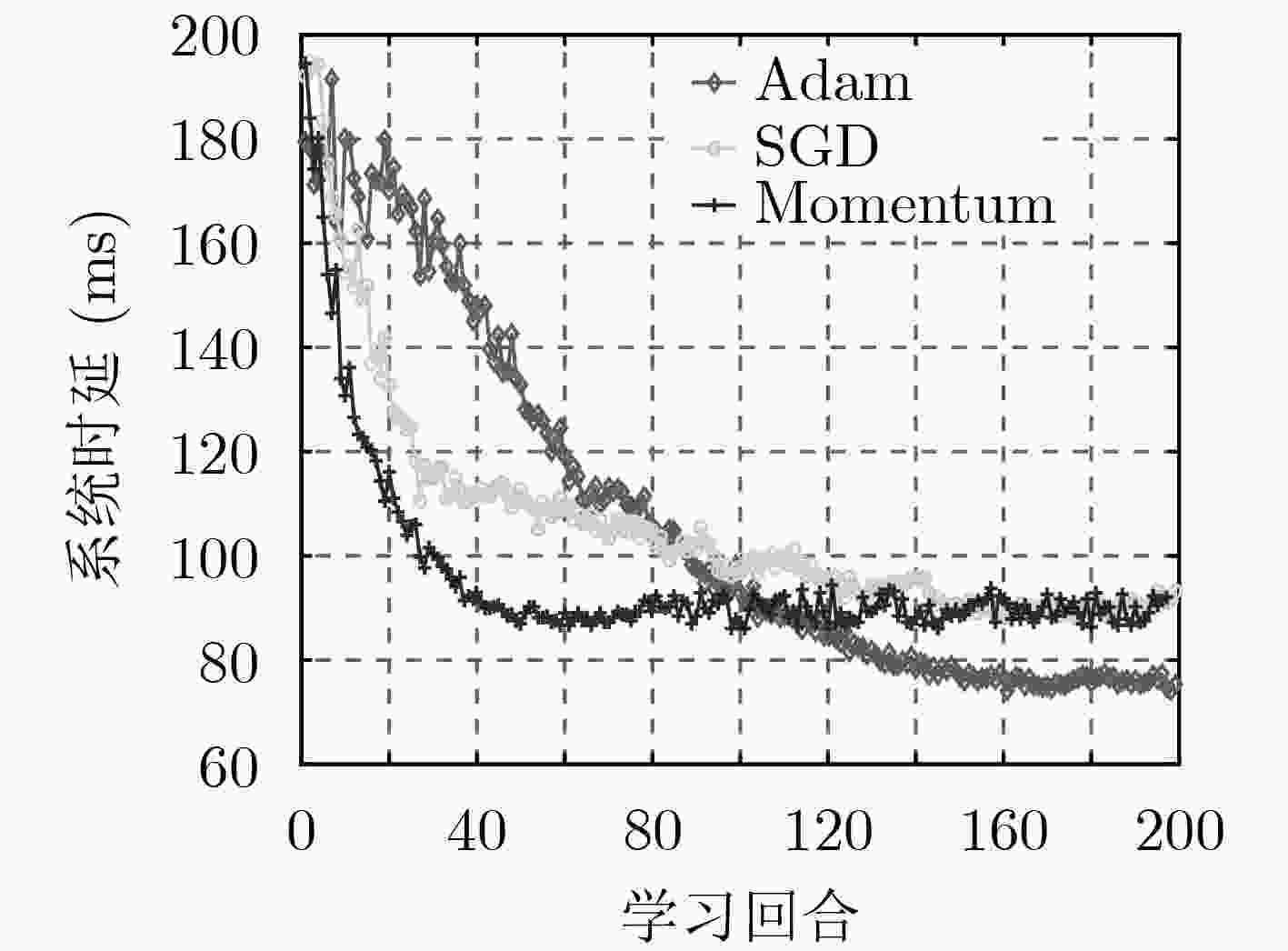
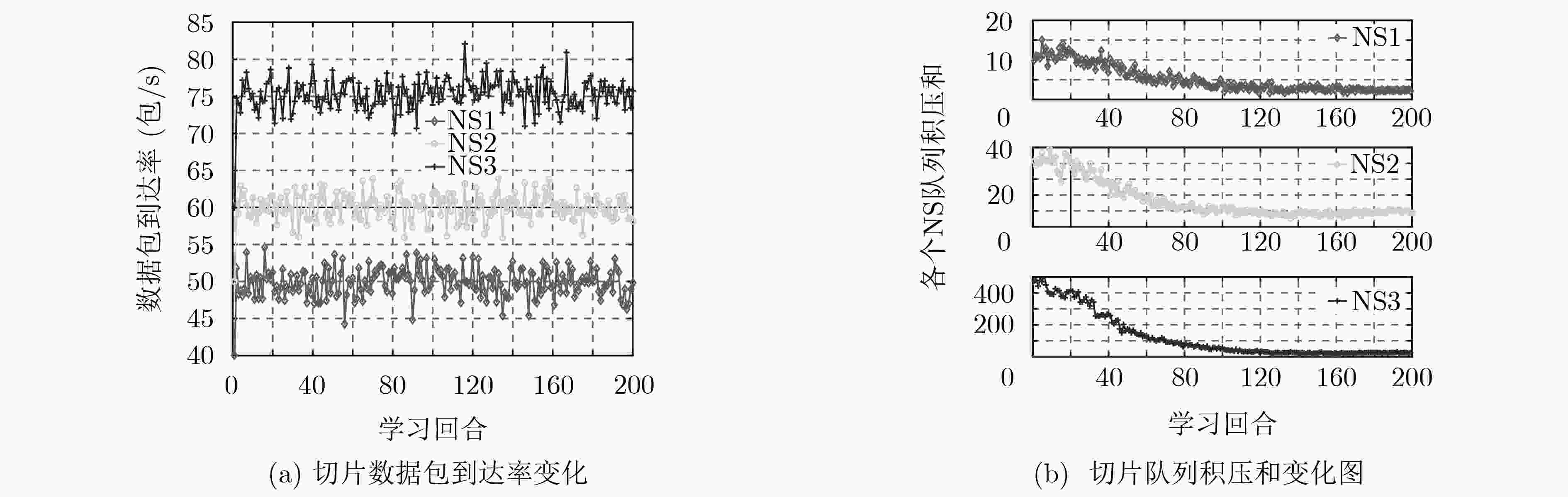
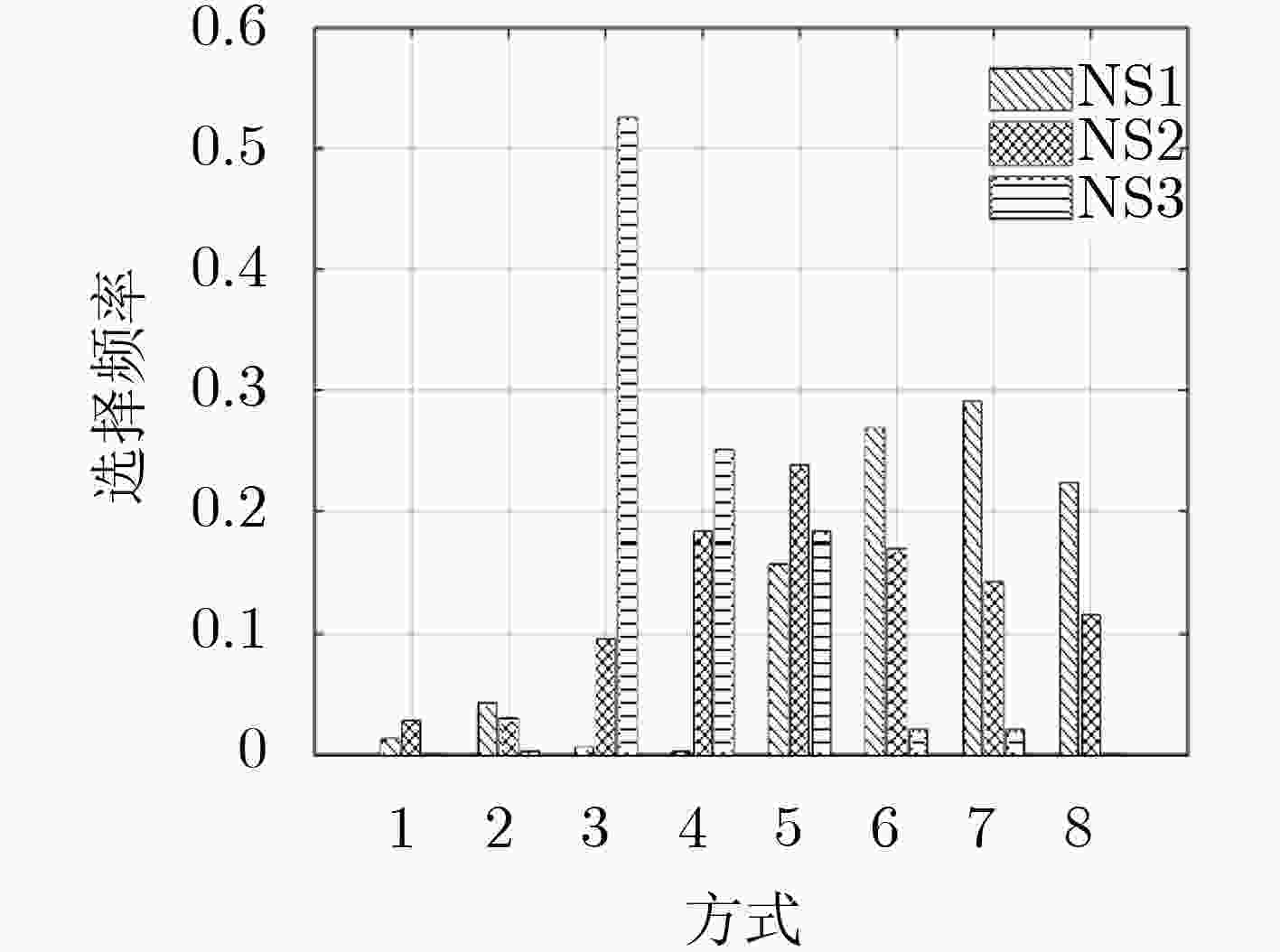
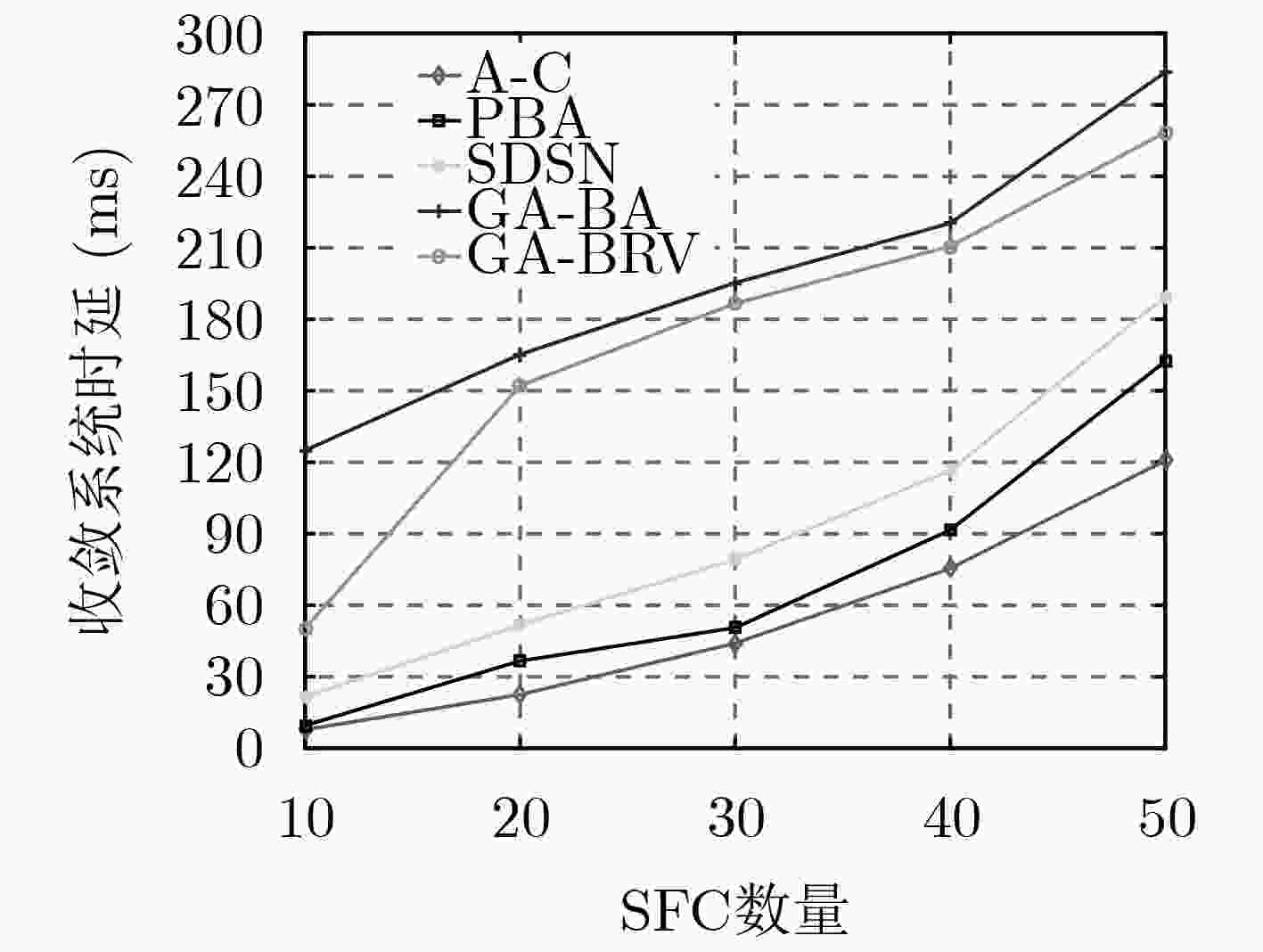


 下载:
下载:
