The Effects of Complex Weather and Sea Wind on the Performance of Space-borne Passive Interferometric Microwave Detection System
-
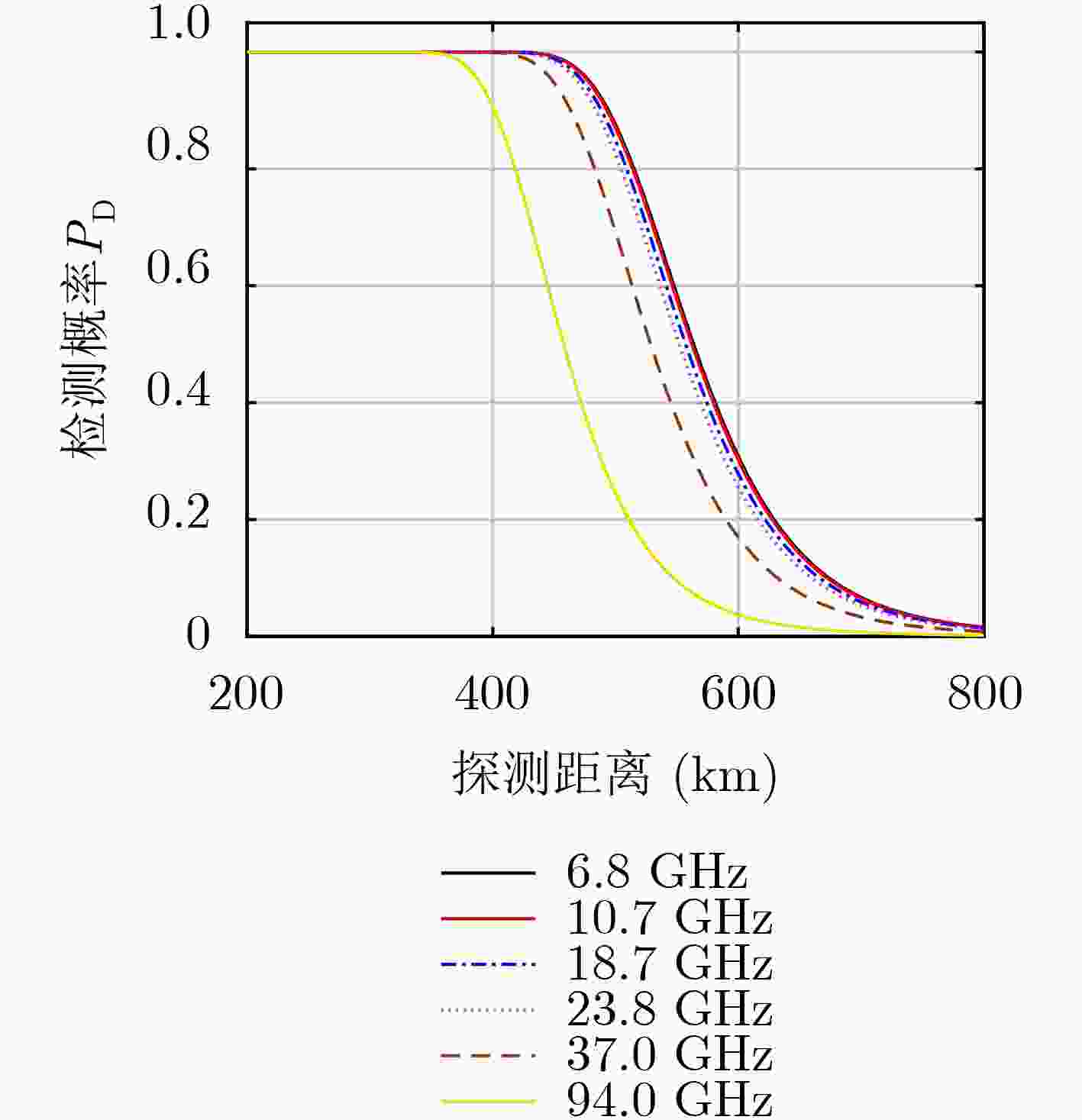
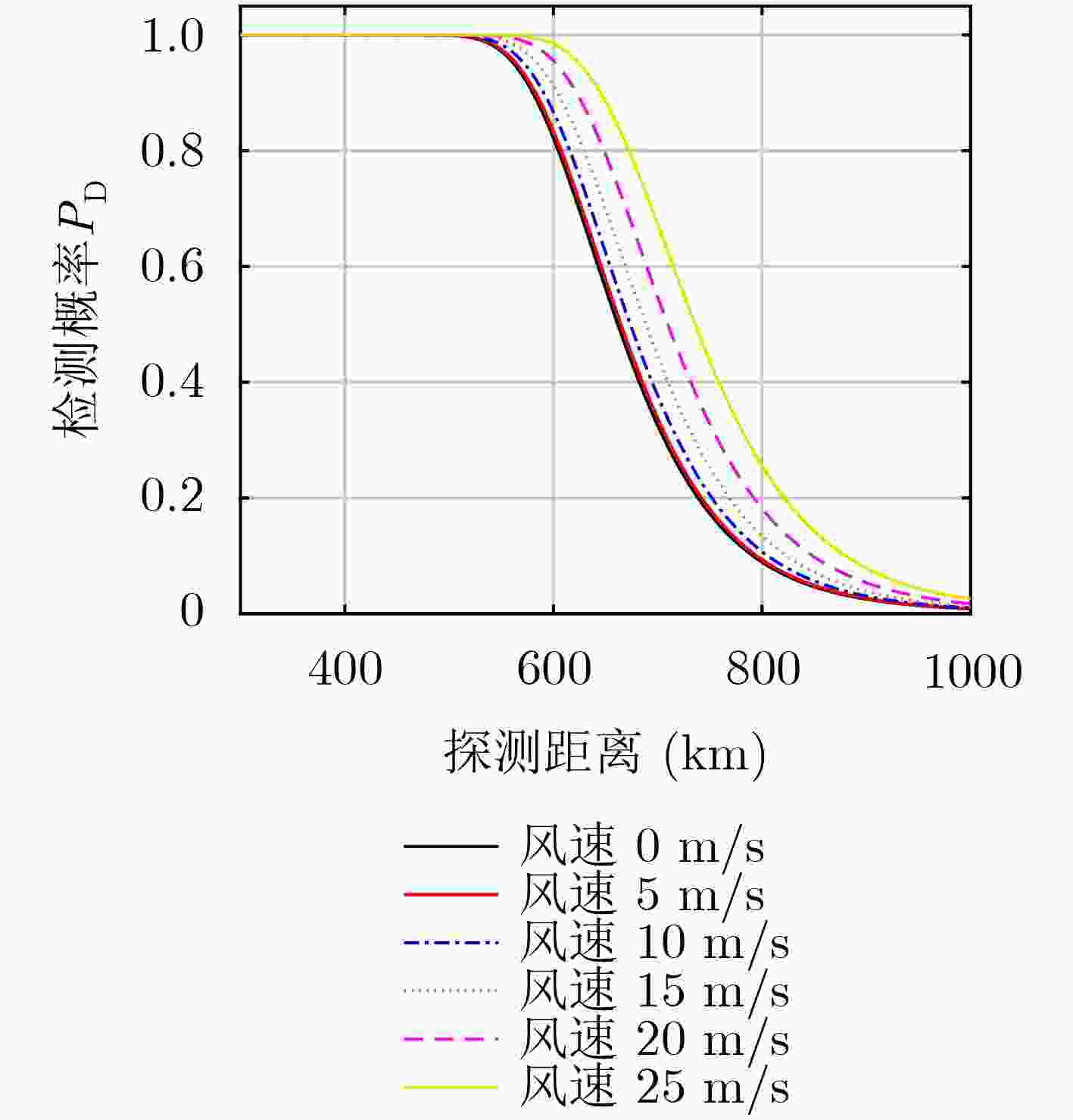
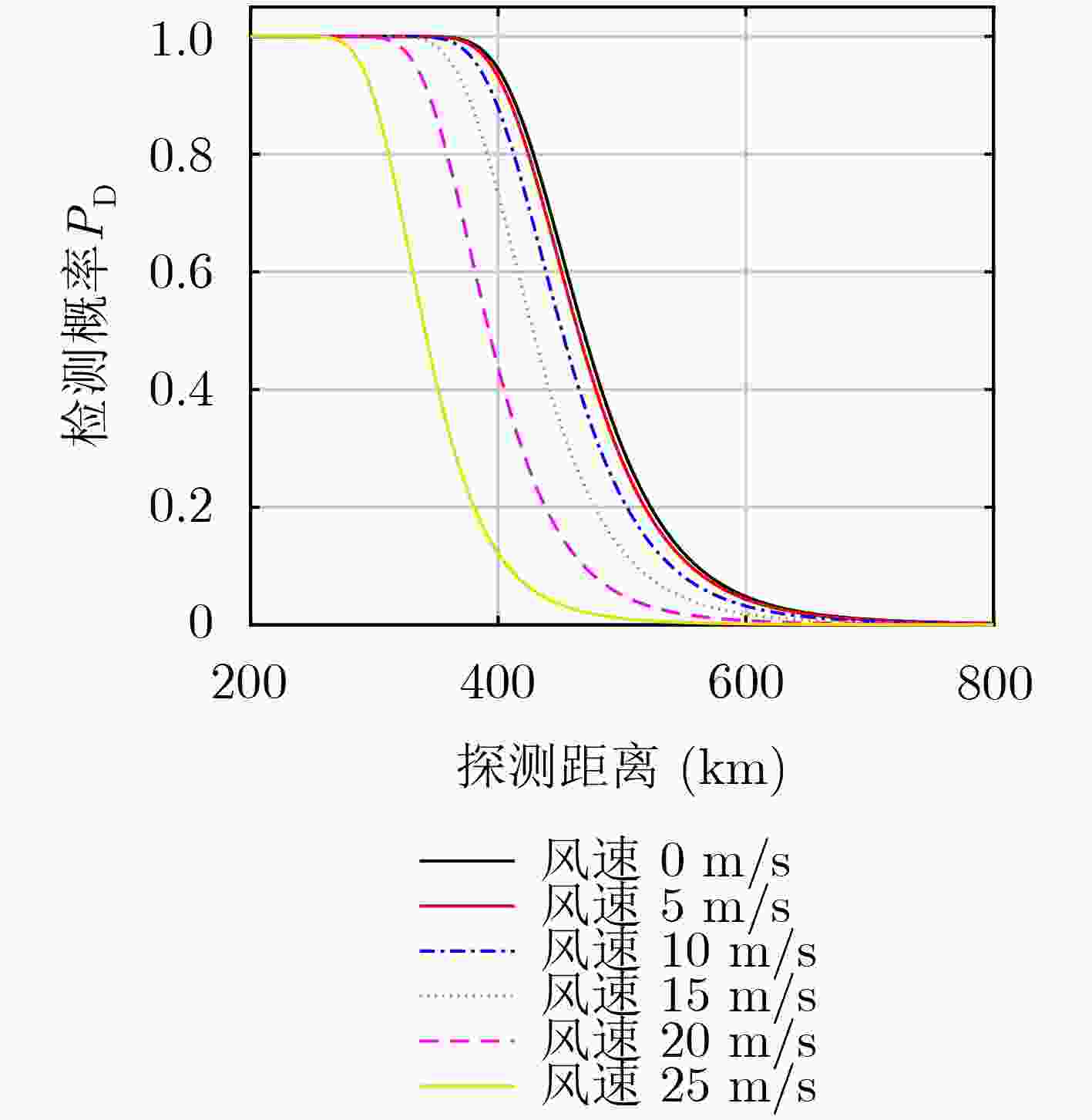
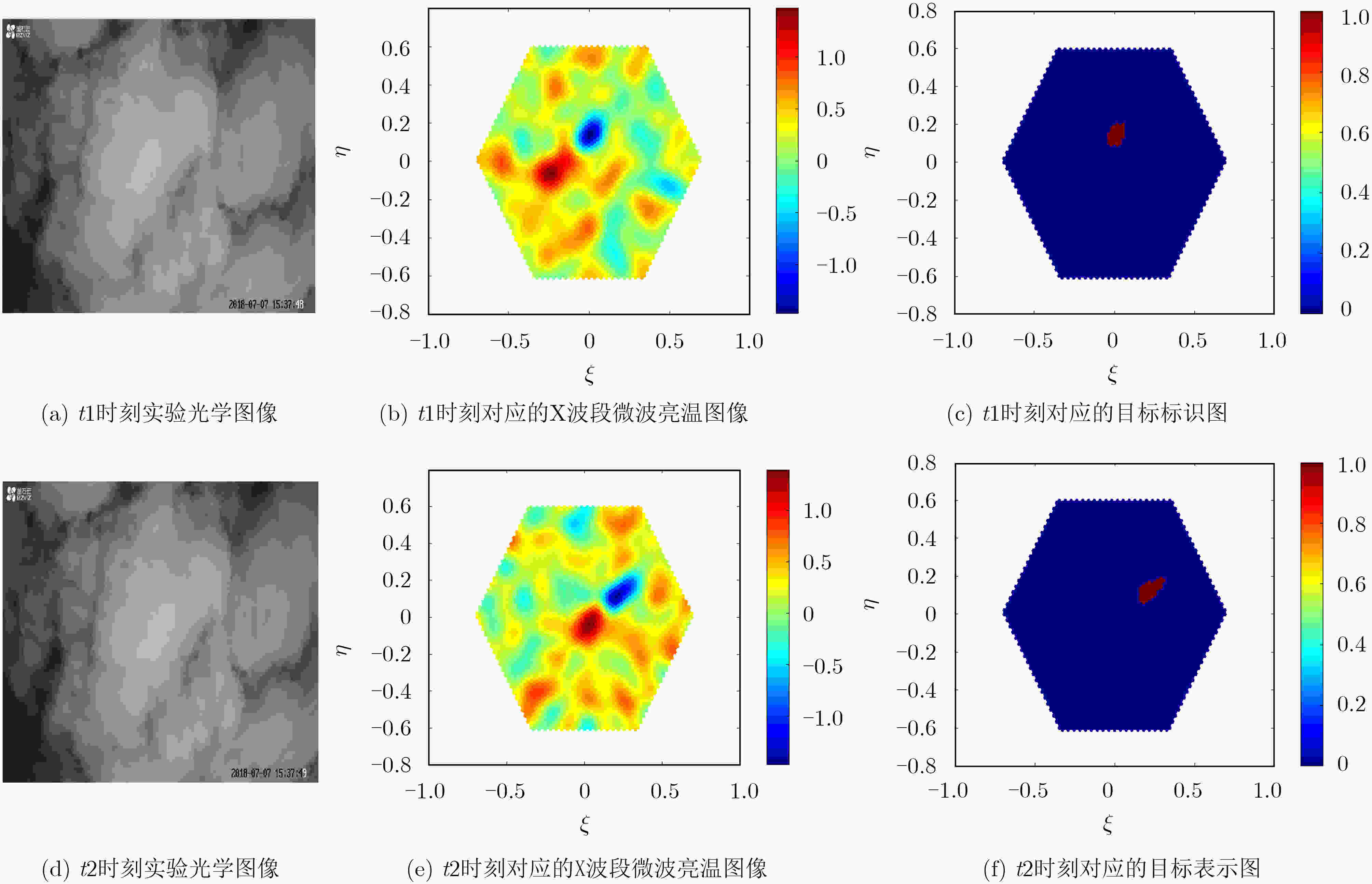
摘要: 基于微波辐射无源探测系统的目标探测方程,该文探讨了云、雾和雨等复杂天气以及海风对天基被动干涉微波辐射无源探测系统的影响,定量化仿真分析了这些因素对系统探测能力的影响,实验验证了被动干涉微波辐射无源探测系统对云层的穿透能力。研究结果表明:云、雾和雨等复杂天气对被动干涉微波辐射无源探测系统对海面目标的探测有一定的影响,但在低频段云雾影响较小,可忽略不计;而降雨会对系统的目标探测能力影响较大;海风对海面金属目标的探测是有利的,而海风对隐身目标探测是不利的,会降低系统的探测能力。Abstract: Based on the target detection equation of the passive interferometric microwave system, the effects of complex weather on the detection ability of the passive interferometric microwave system are discussed for the sea surface target, such as clouds, fog and rain, and sea winds. Quantitative simulations are also performed to assess the effects of these previous mentioned factors. The experiments are also performed to demonstrate the passive interferometric microwave system penetrating the clouds. Both theoretical and simulation results show that complex weather has a negative impact on the passive interferometric microwave systems in the sea target detection, such as clouds, fog and rain. However, the impacts can be neglected in low frequency, since the impacts of clouds in low frequency is very small. On the other hand, rainfall will seriously degrade the system’s target detection capability. Sea winds have a positive impact in the metallic target detection. However, sea winds have a negative impact and reduce the system’s detection capability for the stealthy target detection.
-
Key words:
- Passive detection /
- Complex weather /
- Sea wind
-
表 1 温度10°、星下点,雾高100 m的衰减(dB)
雾型 能见度(km) 雾含水量$({\rm{g}}/{{\rm{m}}}^{3})$ 94 GHz 37 GHz 23.8 GHz 18.7 GHz 10.7 GHz 平流雾 重雾0.05 11.3135 4.8569 1.0016 0.4305 0.2686 0.0890 浓雾0.20 1.5583 0.6690 0.1380 0.0593 0.0370 0.0123 中雾0.50 0.4203 0.1805 0.0372 0.0160 0.0100 0.0033 轻雾1.00 0.1560 0.0670 0.0138 0.0059 0.0037 0.0012 表 2 温度10°、星下点、不同云型的衰减(dB)
云型 云底层(km) 云底层(km) 含水量$({\rm{g}}/{{\rm{m}}}^{3})$ 94 GHz 37 GHz 23.8 GHz 18.7 GHz 10.7 GHz 晴空积云 0.5 1 0.50 1.0732 0.2213 0.0951 0.0594 0.0197 卷积云 5.0 7 0.10 0.8586 0.1771 0.0761 0.0475 0.0157 低层云 0.5 1 0.25 0.5366 0.1107 0.0476 0.0297 0.0098 浓积云 1.6 2 0.80 1.3738 0.2833 0.1238 0.0760 0.0252 表 3 温度10°、星下点、不同雨型衰减(dB)
雨型 降雨率(mm/h) 94 GHz 37 GHz 23.8 GHz 18.7 GHz 10.7 GHz 微雨 0.25 12.9574 1.5068 0.4642 0.2235 0.0281 小雨 1.00 36.7631 5.1375 1.8805 1.0317 0.1604 中雨 4.00 96.5170 17.5168 7.6177 4.6378 0.9154 大雨 16.00 219.3243 59.7251 30.8595 20.5155 5.2244 表 4 X波段综合孔径微波辐射计系统相关参量
指标 参量 中心频率 10.65 GHz 带宽 100 MHz 积分时间 100 ms 天线类型 Y型 天线个数 19 单元间距 0.95倍波长 -
HUANG Jian and GAN Tiguo. A novel millimeter wave synthetic aperture radiometer passive imaging system[C]. The 4th International Conference on, Proceedings Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Beijing, China, 2004: 414–417. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2004.1411554. LI Qingxia, CHEN Ke, GUO Wei, et al. An aperture synthesis radiometer at millimeter wave band[C]. 2008 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Nanjing, China, 2008: 1699–1701. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2008.4540797. 倪炜, 胡飞, 陈柯. 综合孔径辐射计空中隐身目标探测性能分析[J]. 微波学报, 2012, 28(2): 28–31, 41. doi: 10.14183/j.cnki.1005-6122.2012.02.015NI Wei, HU Fei, and CHEN Ke. Performance analysis of synthetic aperture radiometer in aerial stealthy targets detection[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2012, 28(2): 28–31, 41. doi: 10.14183/j.cnki.1005-6122.2012.02.015 吴露露, 胡飞, 朱耀庭, 等. 毫米波热辐射阵列的空间谱估计误差模型研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2010, 29(2): 123–127. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2010.00123WU Lulu, HU Fei, ZHU Yaoting, et al. Error model for spatial spectrum estimation of millimeter-wave thermal radiation array[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2010, 29(2): 123–127. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2010.00123 CHENG Yayun, HU Fei, WU Hongfei, et al. Multi-polarization passive millimeter-wave imager and outdoor scene imaging analysis for remote sensing applications[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(16): 20145–20159. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.020145 苏兴华, 贺平. THz隐身目标无源遥感建模及仿真分析[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2017, 15(6): 898–902. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201706.0898SU Xinghua and HE Ping. Modeling and simulation of stealth target with THz passive sensing[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2017, 15(6): 898–902. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201706.0898 高远, 张光锋, 于畅畅, 等. 典型金属立体目标的毫米波辐射特性研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2019, 27(1): 233–236. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2019.01.048GAO Yuan, ZHANG Guangfeng, YU Changchang, et al. Research on MMW radiation characteristic of typical mental targets[J]. Computer Measurement &Control, 2019, 27(1): 233–236. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2019.01.048 李曙光, 于守江, 姜伟, 等. 综合孔径辐射计空中隐身目标探测技术[J]. 无线电工程, 2015, 45(3): 50–53, 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2015.03.14LI Shuguang, YU Shoujiang, JIANG Wei, et al. Detection of aerial stealthy targets by synthetic aperture microwave radiometer[J]. Radio Engineering, 2015, 45(3): 50–53, 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2015.03.14 卢海梁, 李一楠, 宋广南, 等. 海面目标星载微波辐射无源探测技术研究[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2019, 38(5): 674–681. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2019.05.020LU Hailiang, LI Yinan, SONG Guangnan, et al. Research on the passive detection technology using space-borne synthesis aperture microwave radiometers for the sea surface target[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2019, 38(5): 674–681. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2019.05.020 卢海梁, 王志强, 高超, 等. 基于被动干涉微波亮温图像的海面目标探测算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 563–572. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190256LU Hailiang, WANG Zhiqiang, GAO Chao, et al. Research on the detection algorithm for sea surface targets based on passive interferometric microwave images[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 563–572. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190256 LU Hailiang, LI Yinan, LI Hao, et al. Ship detection by an airborne Passive Interferometric Microwave Sensor (PIMS)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2682–2694. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2953355 WENTZ F J and MEISSNER T. Atmospheric absorption model for dry air and water vapor at microwave frequencies below 100 GHz derived from spaceborne radiometer observations[J]. Radio Science, 2016, 51(5): 381–391. doi: 10.1002/2015RS005858 MEISSNER T and WENTZ F J. The emissivity of the ocean surface between 6 and 90 GHz over a large range of wind speeds and earth incidence angles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3004–3026. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2179662 刘西川, 宋堃, 高太长, 等. 复杂大气条件对微波传播衰减的影响研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 181–188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170253LIU Xichuan, SONG Kun, GAO Taichang, et al. Research on the effect of complex atmospheric condition on microwave propagation attenuation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 181–188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170253 倪炜. 空中目标微波辐射特性及检测方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 华中科技大学, 2012.NI Wei. Microwave radiation characteristics and detection method research in aerial target detection[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012. -





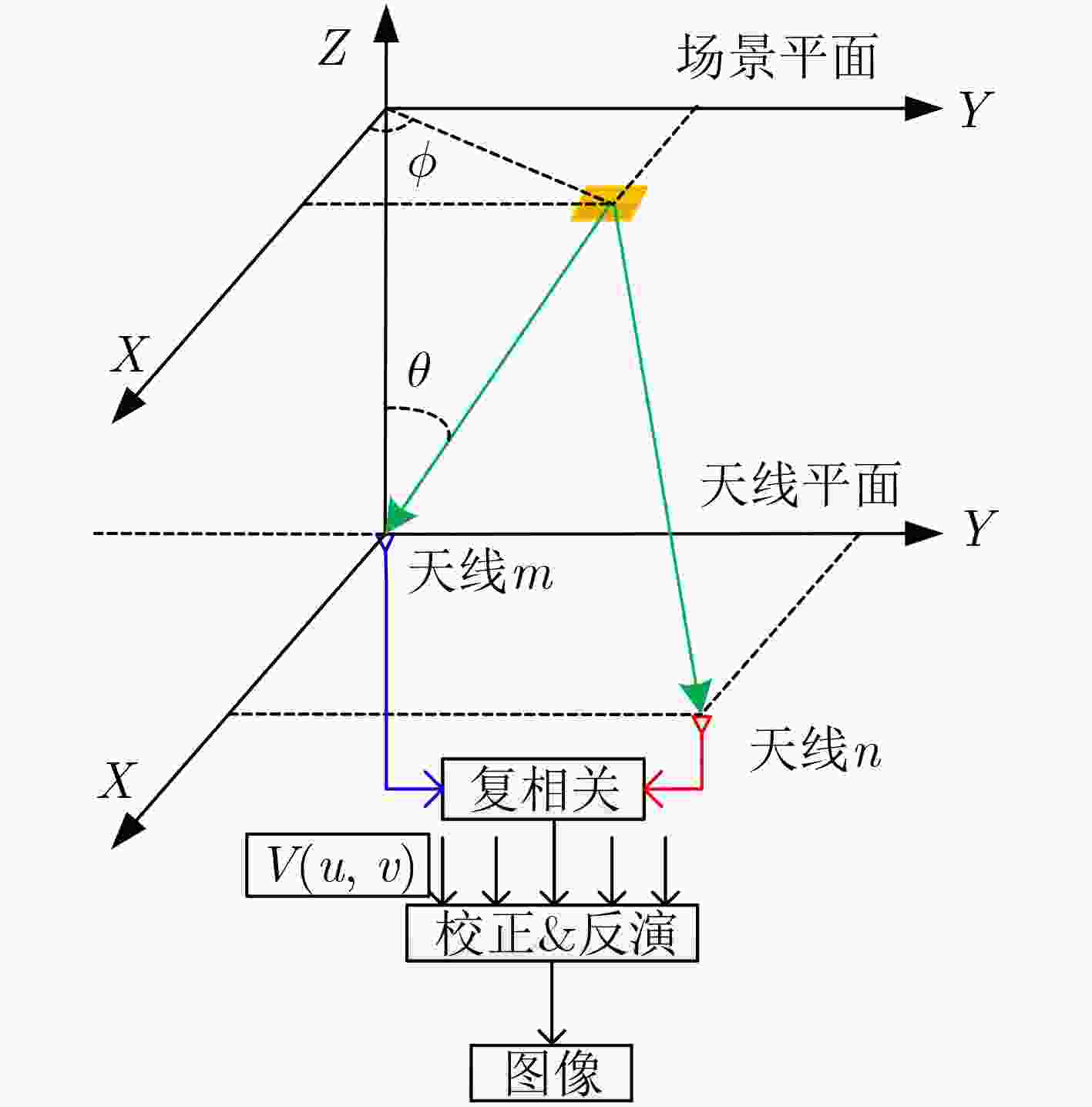
 下载:
下载:
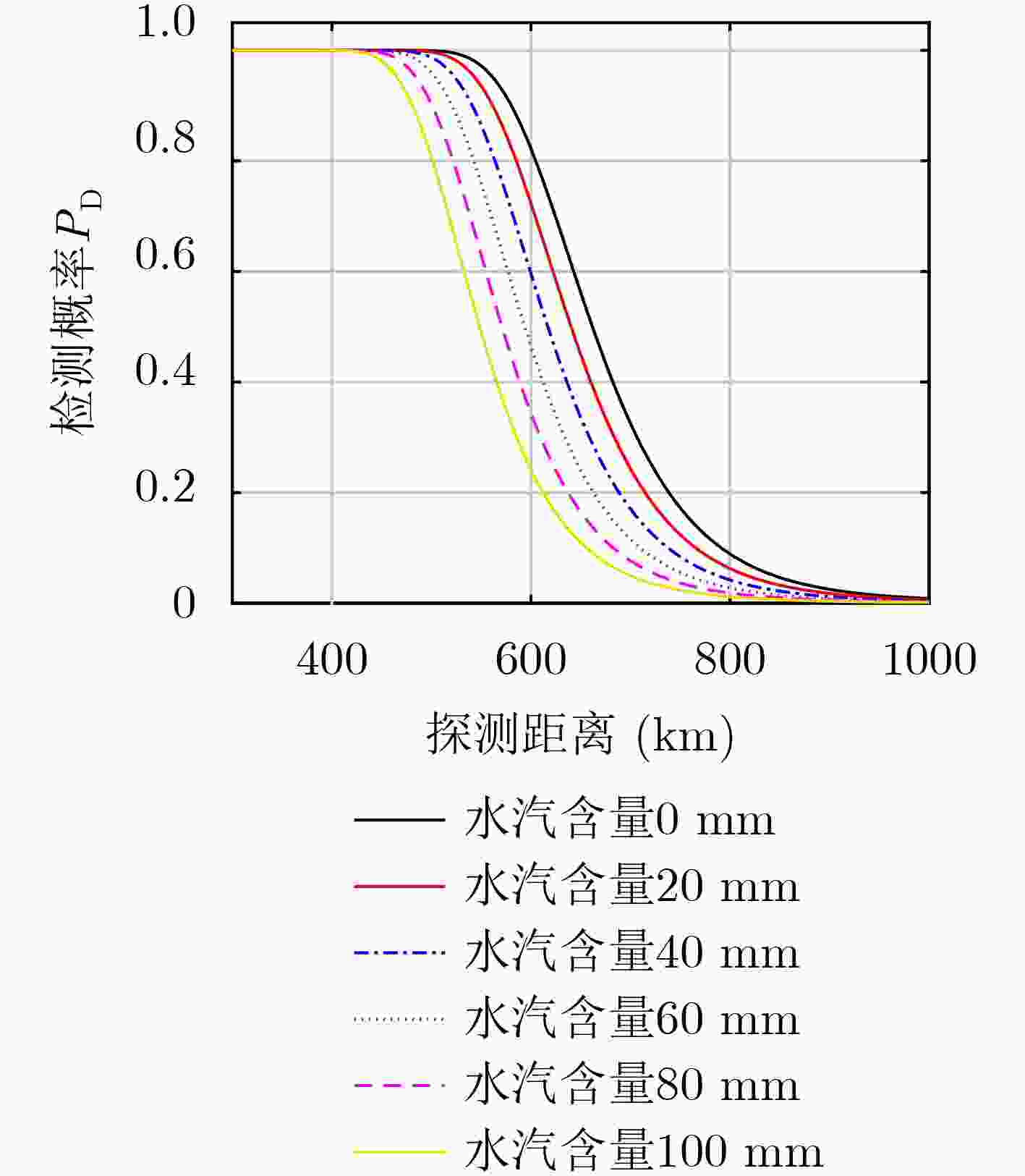
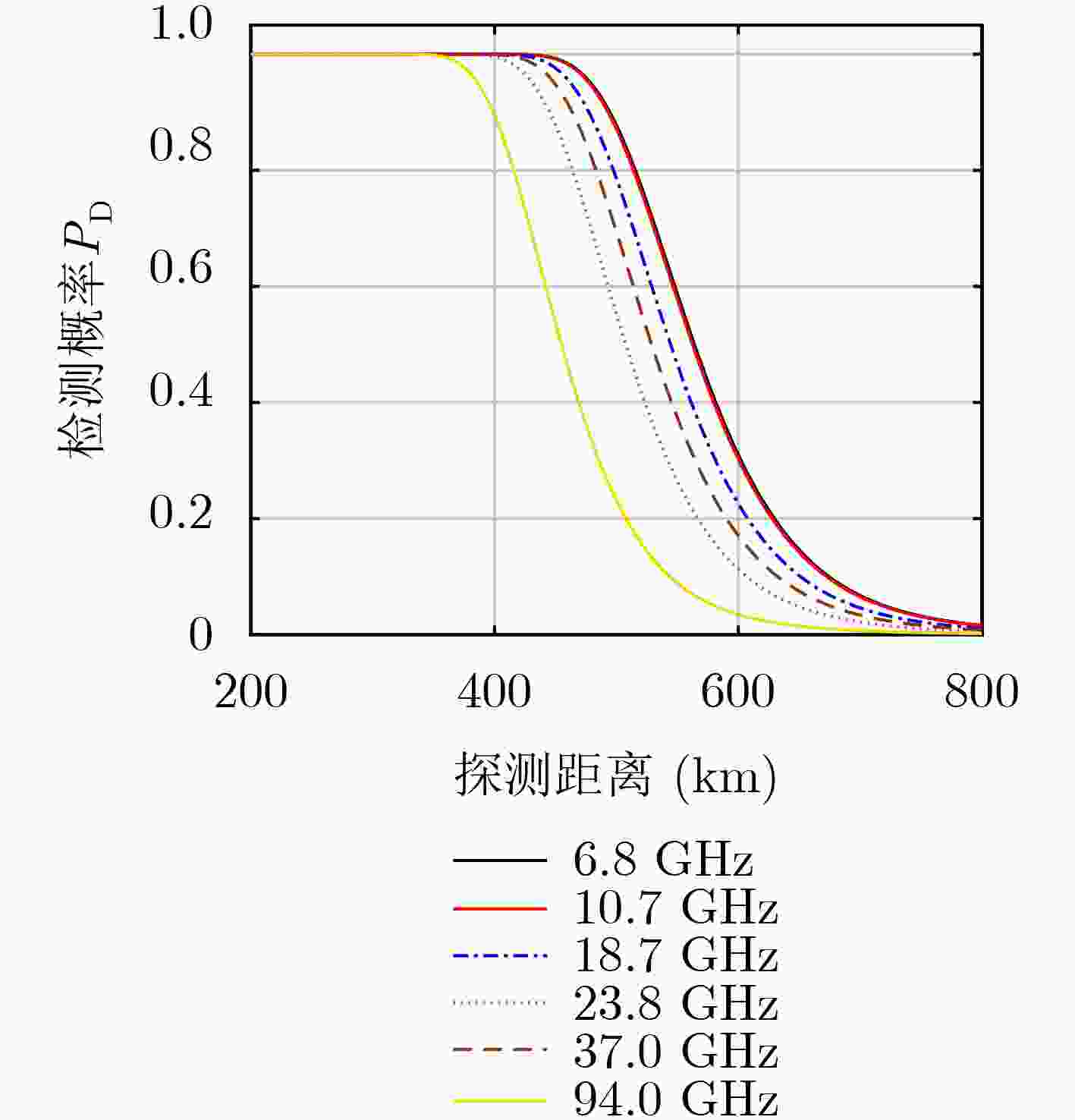
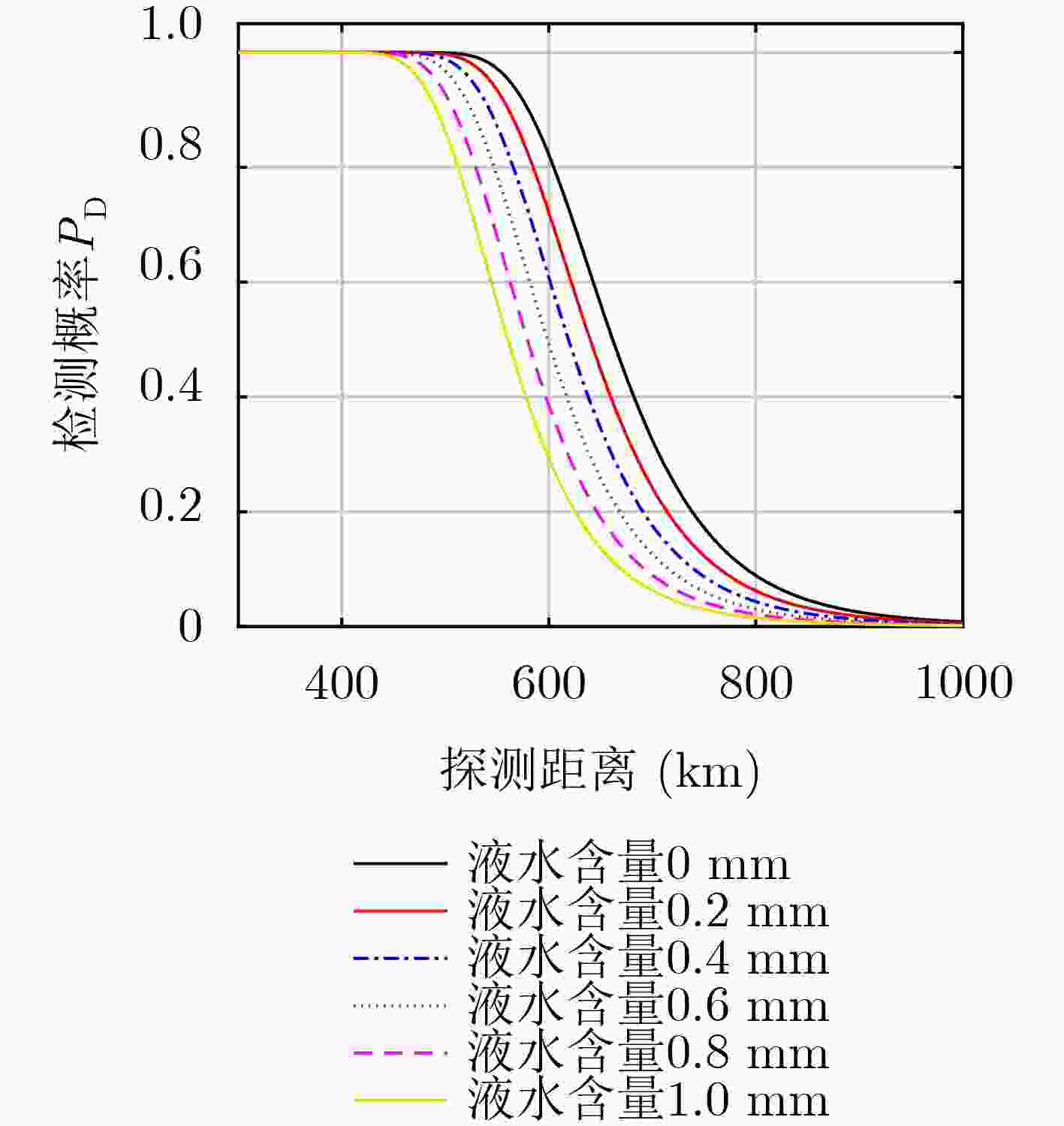


 下载:
下载:
