Research on High Reflective Imaging Technology Based on Compressed Sensing
-
摘要:
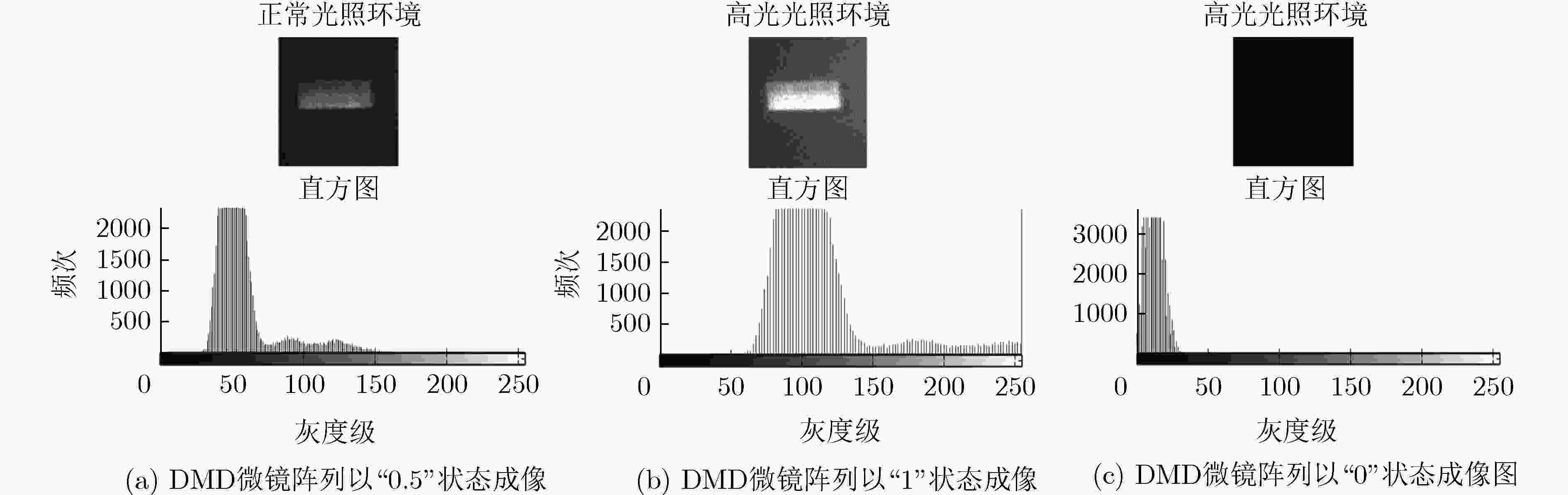
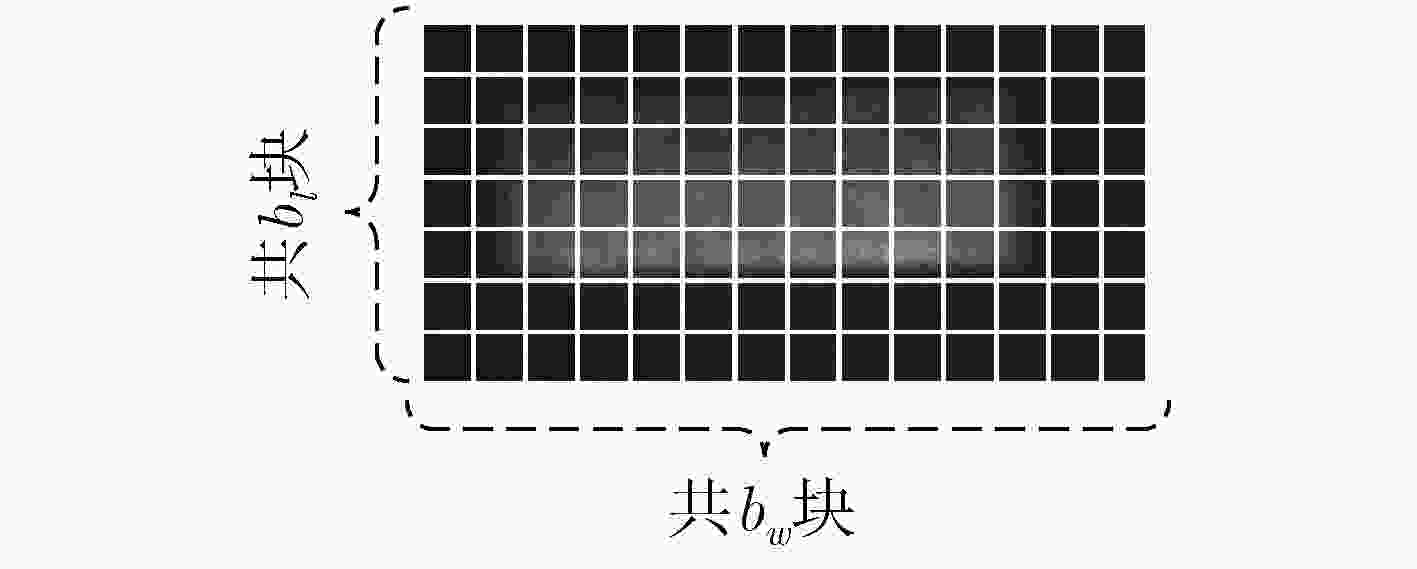
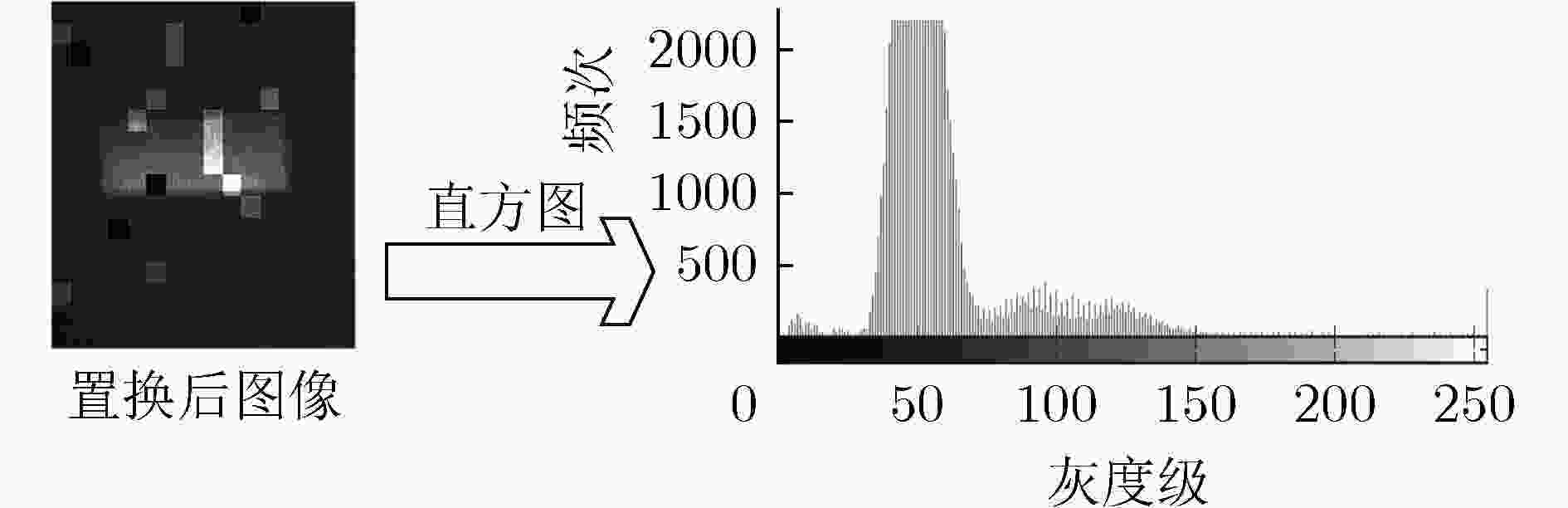
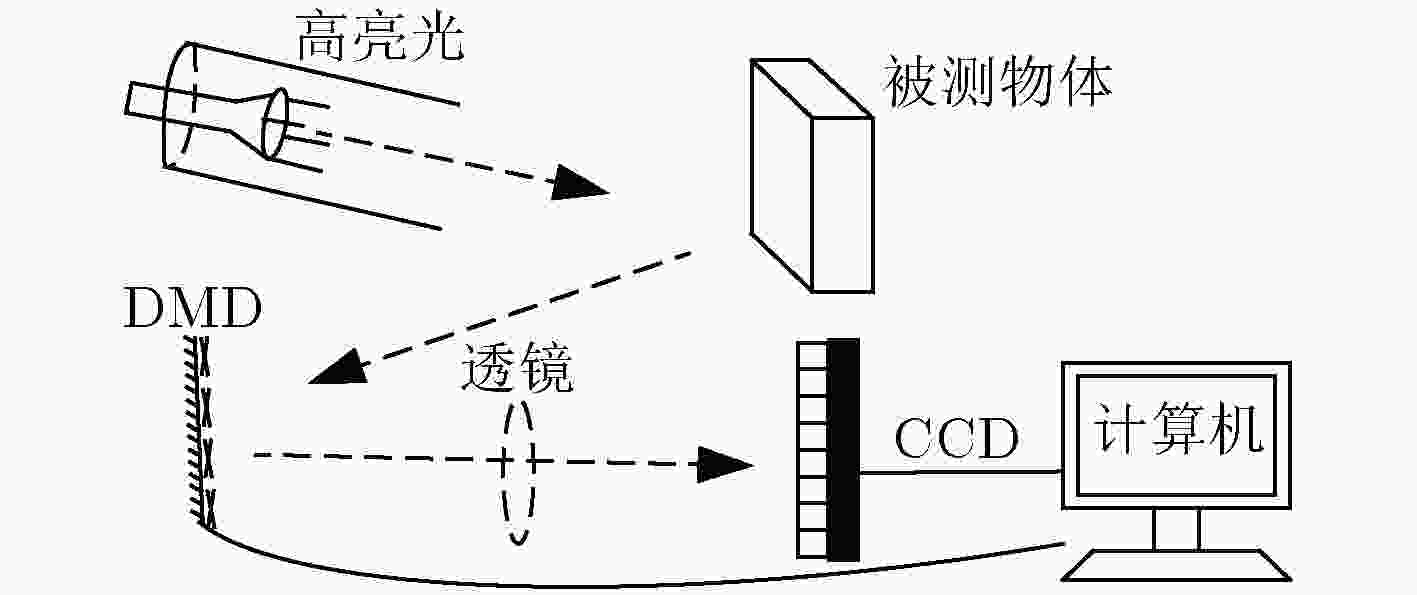
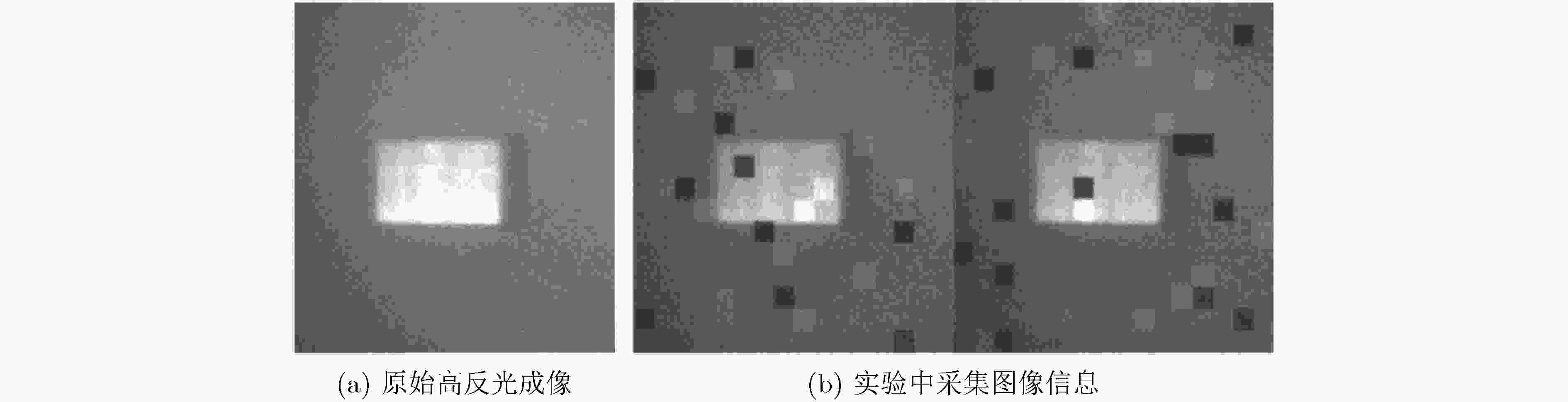
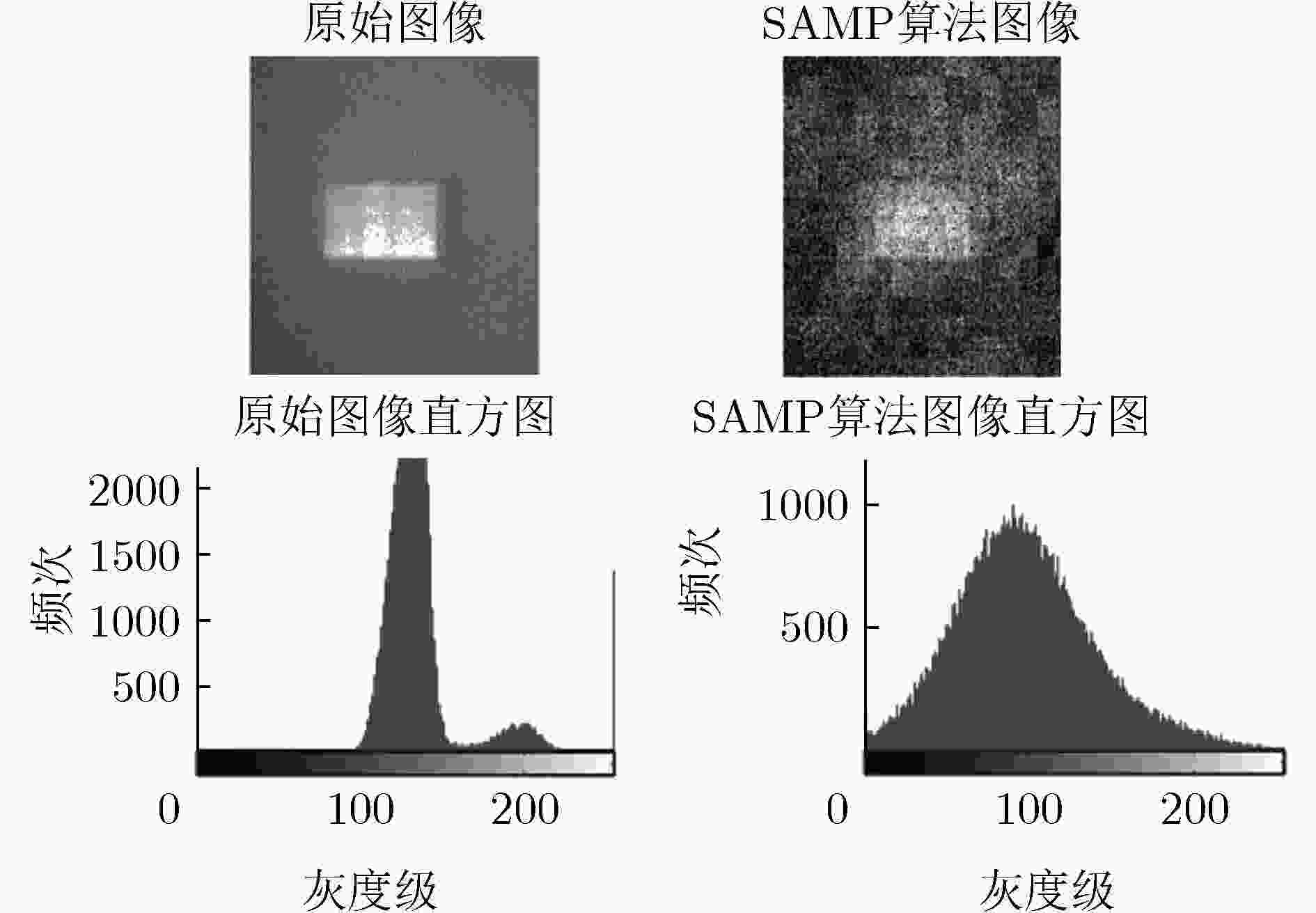
高反光物体成像时反射的光强容易超出传感器接收光强的最大量化值,使得采集图像部分区域图像失真,严重影响信息传递。为了改善高反光成像饱和区域中数据丢失的状况,该文结合压缩感知这一新的采样理论提出基于压缩感知高反光成像方法,利用特定测量矩阵对目标图像进行线性采样,将CCD图像传感器的单个光强采样值与测量矩阵中的分布数据对应结合,对整合后的数据用算法进行恢复重建实现被测目标在高光环境中成像。以峰值信噪比和灰度直方图作为客观评定标准。实验表明,该成像方法鲁棒性较强、可行性较高,直方图检测饱和像素占比为0%,峰值信噪比为58.37 dB实现了在高光环境下不含饱和光成像,为压缩感知在成像应用中提供了新的方向。
Abstract:When imaging a highly reflective object, the light intensity reflected easily exceeds the maximum quantized value of the light intensity received by the sensor, which causes image distortion of the captured image in the saturated region of light intensity and seriously affects the quality of information transmission. In order to improve the data loss in the high-reflection imaging saturation region, a compression-sensing of high-reflection imaging method based on the new sampling theory of compressed sensing is proposed. A specific measurement matrix is used to conduct linear sampling of the target image, and the single light intensity sampling value of the CCD image sensor is combined with the distribution data in the measurement matrix, and the integrated data is restored and reconstructed with the algorithm to achieve the imaging of the measured target in the high-light environment. The peak signal to noise ratio and gray histogram are used as objective evaluation criteria. Experiments show that this imaging method is robust and feasible, with the proportion of saturated pixels in histogram detection 0% and the peak signal to noise ratio 58.37 dB, realizing the imaging without saturated light in the high-light environment, providing a new direction for the application of compressed sensing in imaging.
-
Key words:
- High reflected light imaging /
- Compressed sensing /
- Data integration /
- Histogram
-
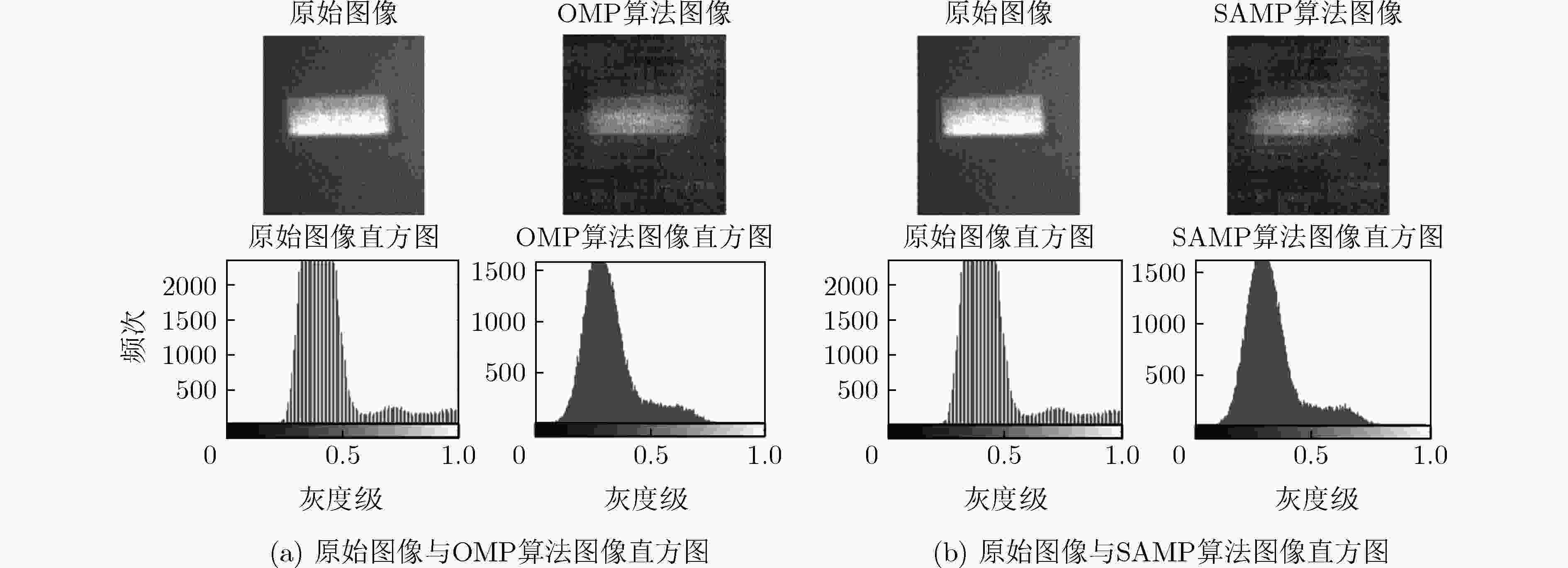
表 1 不同采样率下两种恢复算法的MSE值与PSNR值
CS采样率 OMP算法 SAMP算法 MSE PSNR MSE PSNR 0.30 0.0158 66.1481 0.0166 65.9403 0.35 0.0150 66.3739 0.0154 66.2512 0.40 0.0143 66.5625 0.0142 66.6061 0.45 0.0139 66.7149 0.0135 66.8149 0.50 0.0136 66.7928 0.0133 66.9078 -
赵首博, 曲兴华, 冯维, 等. 成像前光学调制系统的眩光测量[J]. 光电工程, 2016, 43(1): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.01.003ZHAO Shoubo, QU Xinghua, FENG Wei, et al. A measurement method for glare based on the Optical modulation system before image formation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(1): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.01.003 范剑英, 刘力源, 赵首博. 电机铜排表面毛刺缺陷检测技术研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(3): 14–22. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804559FAN Jianying, LIU Liyuan, and ZHAO Shoubo. Research on detection technology of burr defects in motor copper[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(3): 14–22. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1804559 ZHAO Shoubo, MA Mingyang, and GUO Cong. Accurate Pixel-to-Pixel alignment method with Six-Axis adjustment for computational photography[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2018, 10(3): 6802416. doi: 10.1109/jphot.2018.2839093 JIANG Hongzhi, ZHAO Huijie, and LI Xudong. High dynamic range fringe acquisition: A novel 3-D scanning technique for high-reflective surfaces[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2012, 50(10): 1484–1493. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.11.021 ZHAO Shoubo, ZHANG Fumin, QU Xinghua, et al. Removal of parasitic image due to metal specularity based on digital micromirror device camera[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(6): 063105. doi: 10.1117/1.oe.53.6.063105 YAN Qingsen, ZHU Yu, and ZHANG Yanning. Robust artifact-free high dynamic range imaging of dynamic scenes[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(9): 11487–11505. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6625-x KALANTARI N K, SHECHTMAN E, BARNES C, et al. Patch-based high dynamic range video[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2013, 32(6): No. 202. doi: 10.1145/2508363.2508402 ZHAO Shoubo, LIU Liyuan, and MA Mingyang. Adaptive high-dynamic range three-dimensional shape measurement using DMD camera[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 67934–67943. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2918843 DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 ELDAR Y C, KUTYNIOK G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 1289–1306. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511794308. CANDES E J, ROMBERG J, and TAO T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(2): 489–509. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.862083 RISTOBAL-HUERTA A, POOT D H J, VOGEL M W, et al. Compressed sensing 3D-GRASE for faster high-resolution MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2019, 82(3): 984–999. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27789 ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Superresolving SAR tomography for multidimensional imaging of urban areas: Compressive sensing-based tomoSAR inversion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 51–58. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2312098 王伟, 胡子英, 龚琳舒. MIMO雷达三维成像自适应Off-grid校正方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1294–1301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180145WANG Wei, HU Ziying, and GONG Linshu. Adaptive off-grid calibration method for MIMO radar 3D imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1294–1301. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180145 金艳, 周磊, 姬红兵. 基于稀疏时频分布的跳频信号参数估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 663–669. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170525JIN Yan, ZHOU Lei, and JI Hongbing. Parameter estimation of frequency-hopping signals based on sparse time-frequency distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 663–669. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170525 FAZEL F, FAZEL M, and STOJANOVIC M. Random access compressed sensing for energy-efficient underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(8): 1660–1670. doi: 10.1109/jsac.2011.110915 孙玉宝, 李欢, 吴敏, 等. 基于图稀疏正则化多测量向量模型的高光谱压缩感知重建[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(12): 2942–2948. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00566SUN Yubao, LI Huan, WU Min, et al. Compressed sensing reconstruction of hyperspectral image using the graph sparsity regularized multiple measurement vector model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(12): 2942–2948. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00566 LIAO Wenchao, HSIEH J, WANG Chengming, et al. Compressed sensing spectral domain optical coherence tomography with a hardware sparse-sampled camera[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(12): 2955–2958. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002955 DUARTE M F, DAVENPORT M A, TAKHAR D, et al. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 83–91. doi: 10.1109/msp.2007.914730 余慧敏, 方广有. 压缩感知理论在探地雷达三维成像中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(1): 12–16. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00040YU Huimin and FANG Guangyou. Research on compressive sensing based 3D imaging method applied to ground penetrating radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(1): 12–16. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00040 庄佳衍, 陈钱, 何伟基, 等. 基于压缩感知的动态散射成像[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(4): 040501. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.040501ZHUANG Jiayan, CHEN Qian, HE Weiji, et al. Imaging through dynamic scattering media with compressed sensing[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(4): 040501. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.040501 LI Bo, LIU Falin, ZHOU Chongbin, et al. Mixed sparse representation for approximated observation-based compressed sensing radar imaging[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(3): 035015. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.12.035015 LI Yunhui, WANG Xiaodong, WANG Zhi, et al. Modeling and image motion analysis of parallel complementary compressive sensing imaging system[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 423: 100–110. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.04.018 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
