Tracking Method without Prior Information when Multi-group Targets Appear Successively
-
摘要:
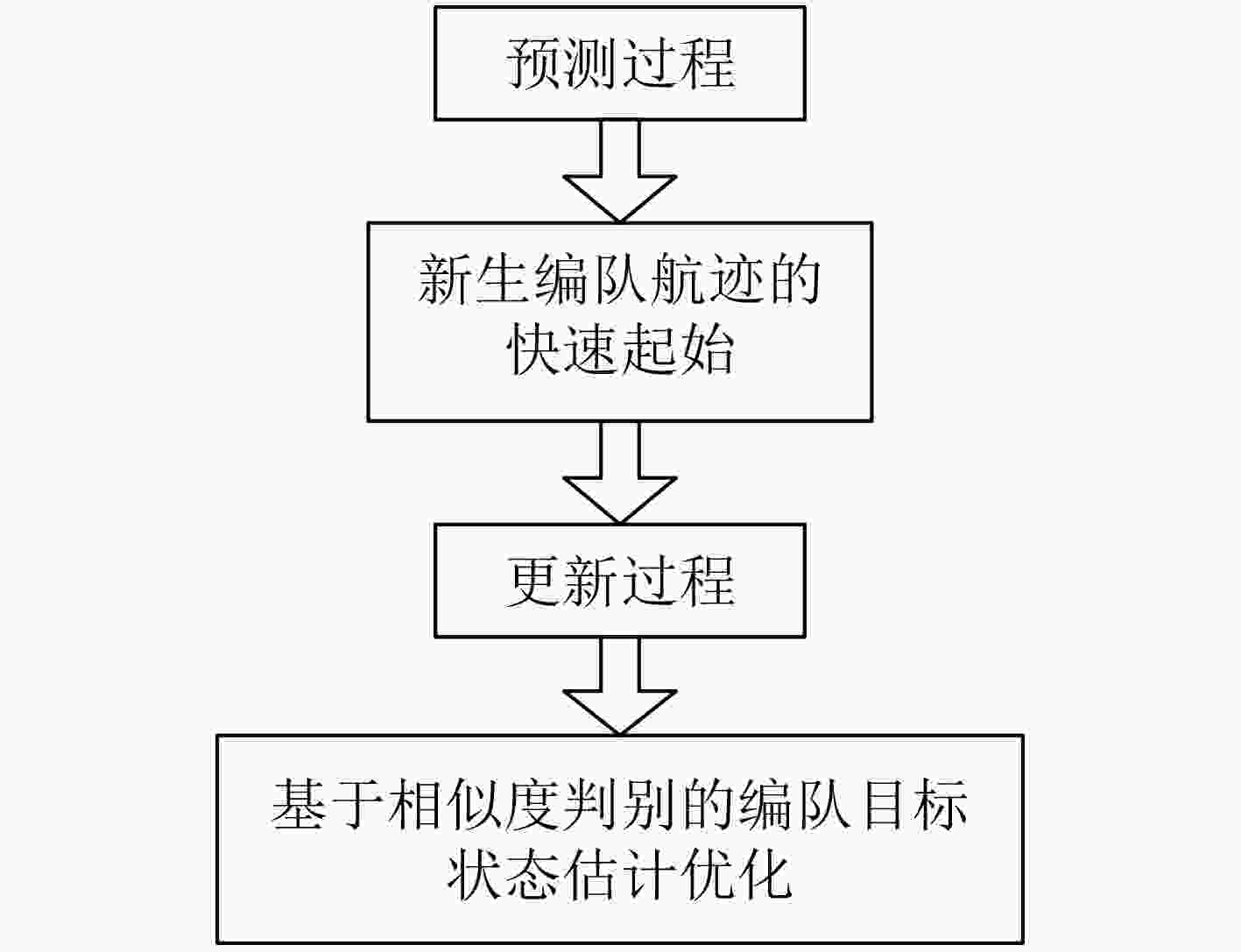
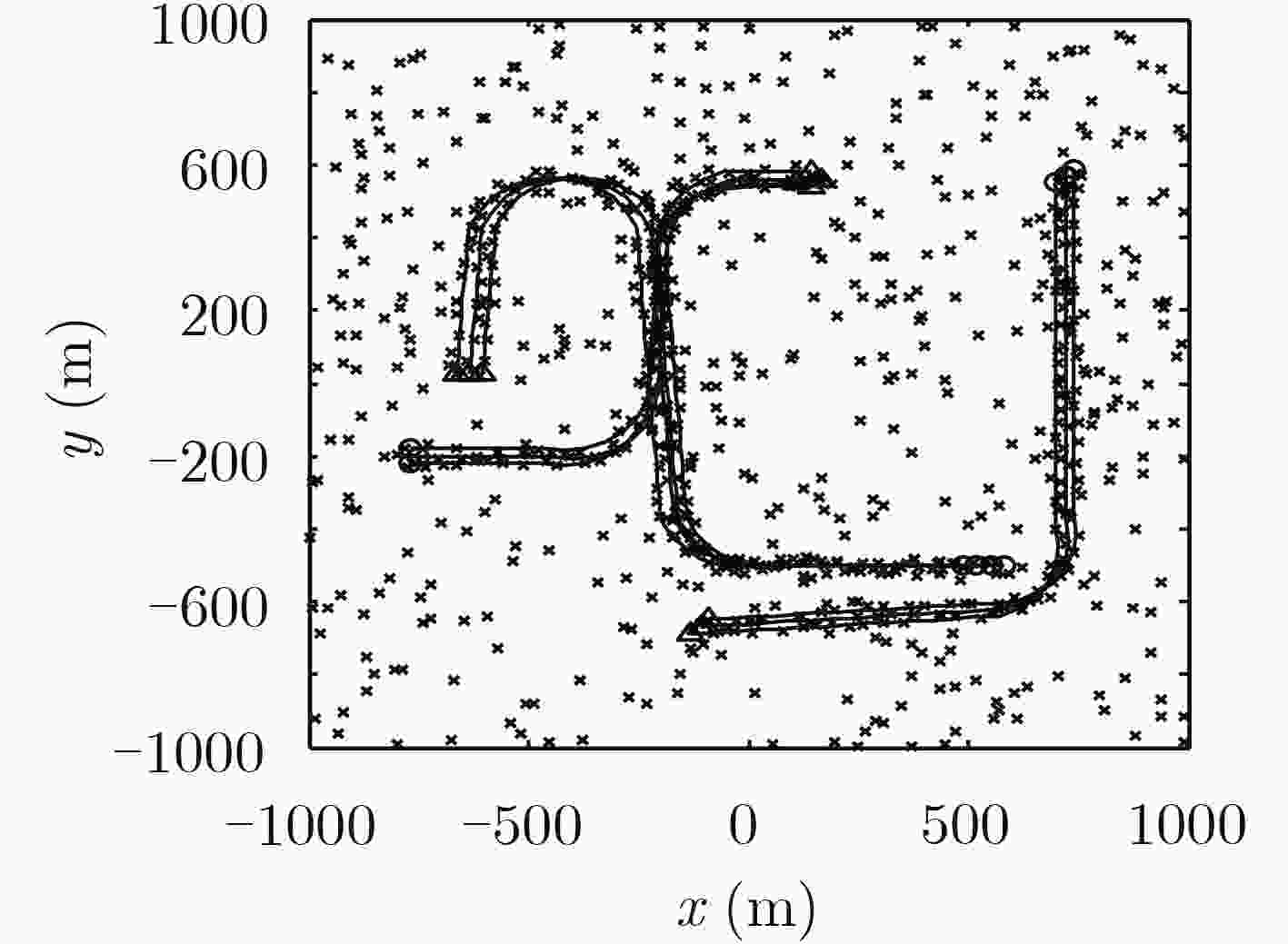
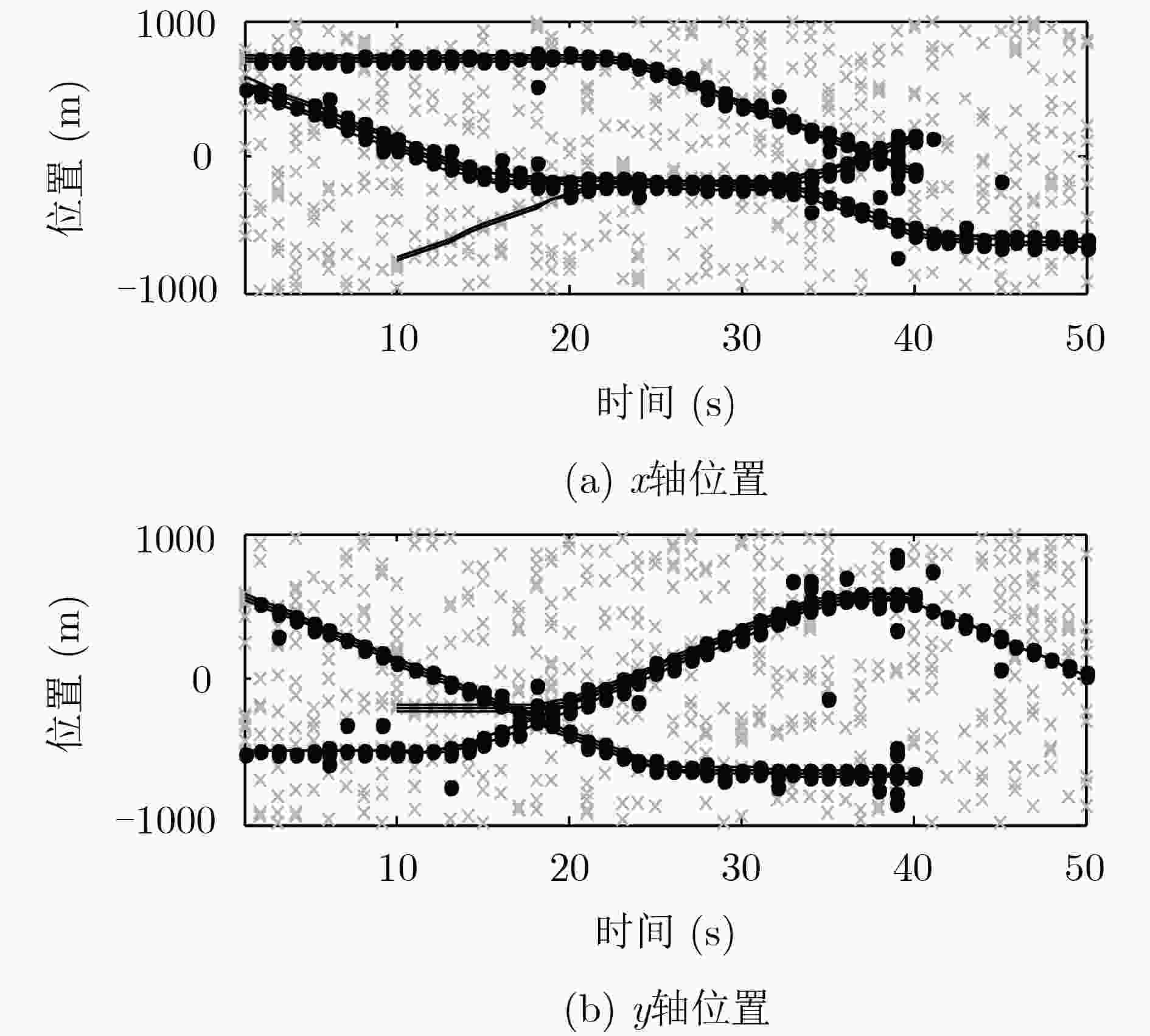
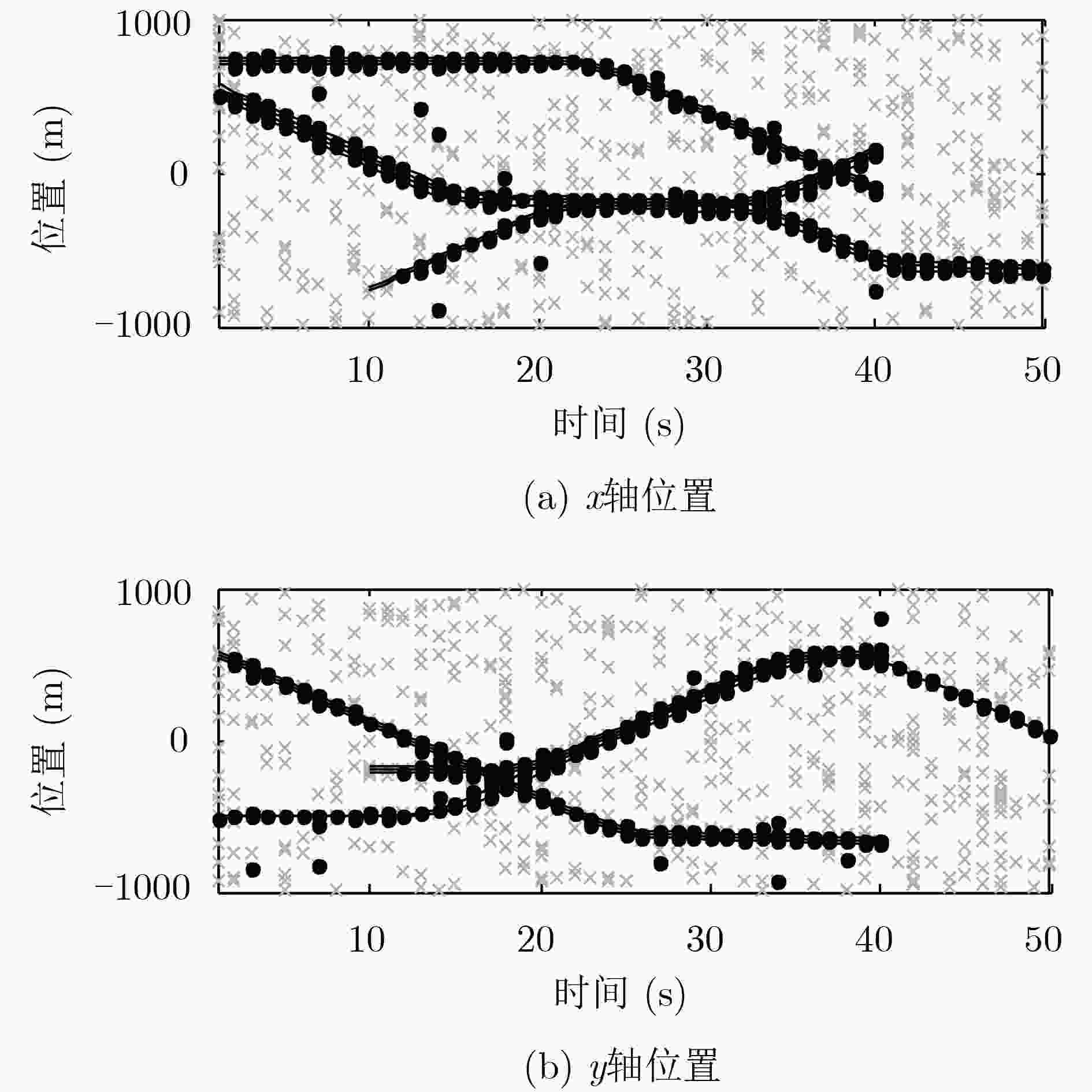
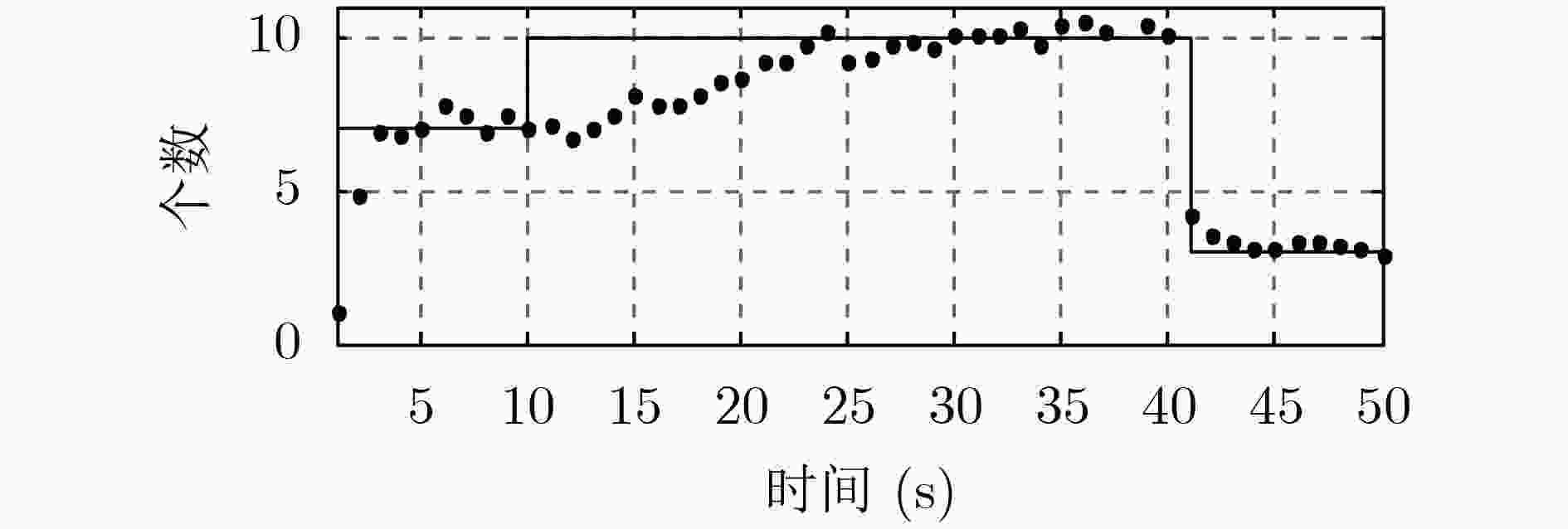
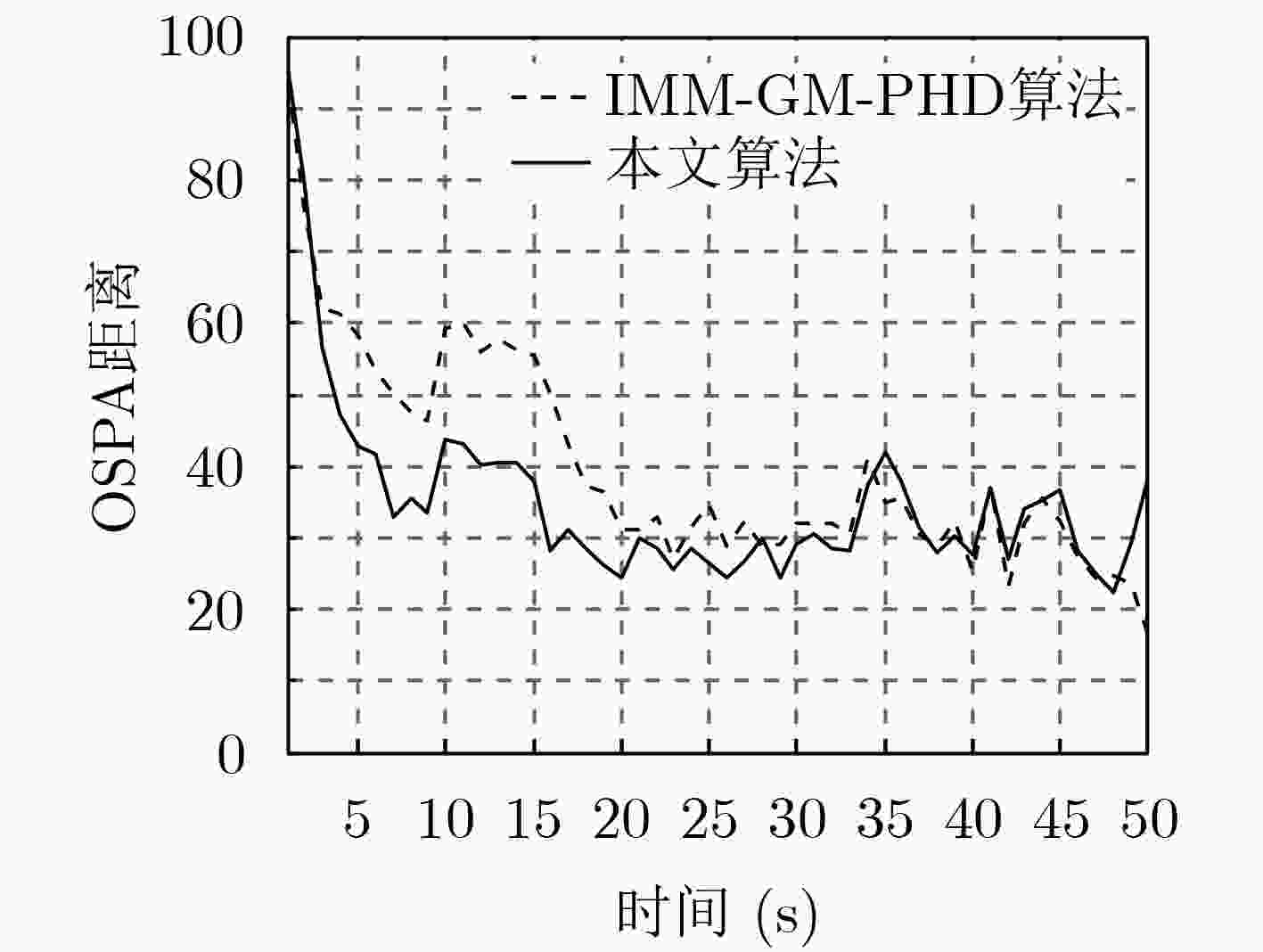
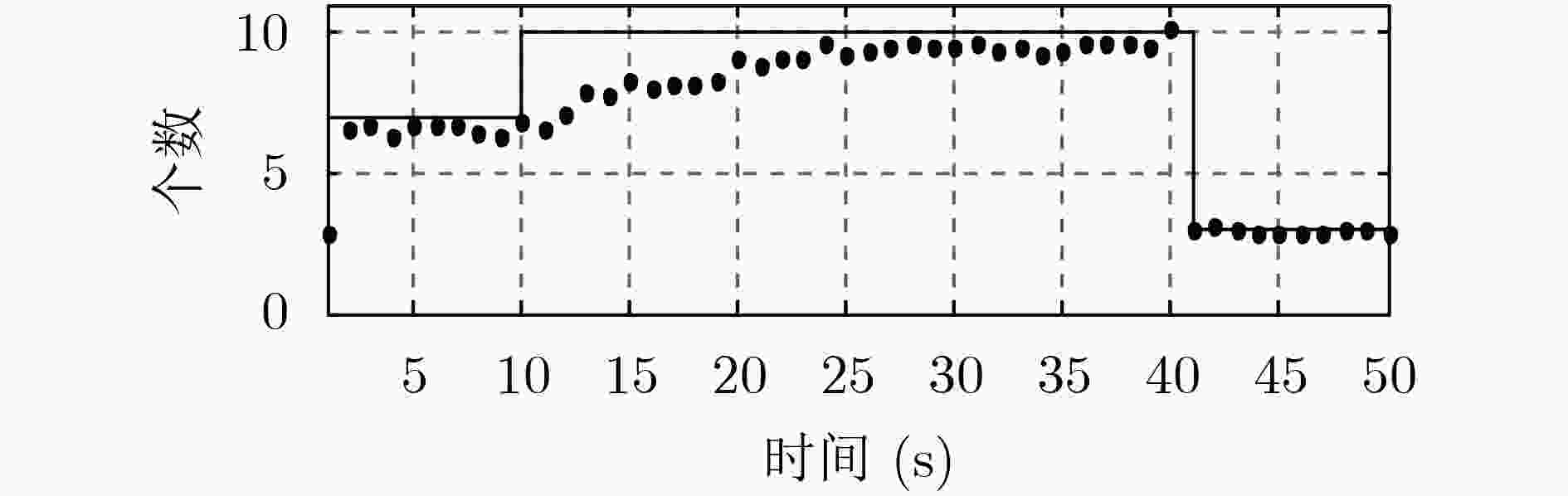
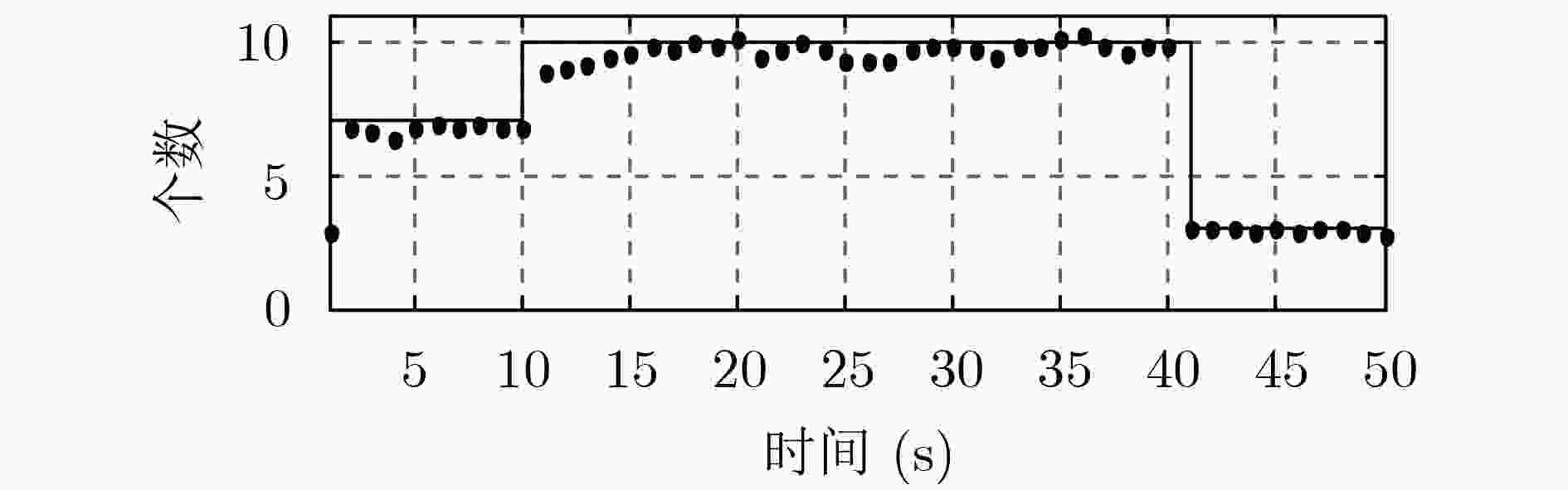
针对多编队机动目标先后出现时的跟踪问题,该文提出了一种基于交互式多模型高斯混合概率假设密度滤波(IMM-GM-PHD)算法的无先验信息跟踪方法。首先,在IMM-GM-PHD算法预测过程完成的基础上,引入密度检测机制,利用相关域为所有预测高斯分量挑选有效量测,结合密度聚类(DBSCAN)算法检测是否出现新编队目标。其次,在IMM-GM-PHD算法状态更新完成的基础上,利用更新高斯分量的组成情况完成模型概率的更新。最后,在状态估计优化过程中,结合编队目标的特点,加入相似度判别技术,利用杰森-香农(JS)散度度量高斯分量间的相似度,剔除没有相似分量的高斯分量,进一步优化估计结果。仿真结果表明,该文方法能够快速有效地跟踪非同时出现的多编队机动目标,具有较好的跟踪性能。
-
关键词:
- 多编队机动目标 /
- 交互式多模型高斯混合概率假设密度滤波算法 /
- 相关域 /
- 密度聚类算法 /
- 杰森-香农散度
Abstract:Considering the problem of multi-group maneuvering target tracking, a fast tracking method based on Interactive Multiple Maneuvering Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density (IMM-GM-PHD) algorithm is proposed. Firstly, based on the completion of the IMM-GM-PHD algorithm prediction process, the density detection mechanism is added, and the correlation domain is used to select effective measurement for all predicted Gaussian components, and the Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is combined to detect whether a new formation target appears. Secondly, based on the completion of the state update of the IMM-GM-PHD algorithm, the update of the model probability is completed by updating the composition of the Gaussian component. Finally, in the process of state estimation optimization, combined with the characteristics of formation targets, the similarity discrimination technique is added, and the Jensen-Shannon (JS) divergence is used to measure the similarity between Gaussian components, and the Gaussian components without similar components are eliminated, and the estimation results are further optimized. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can track multi-group maneuvering targets quickly and effectively, and has better tracking performance.
-
表 1 不同杂波密度下平均OSPA距离比较
算法 杂波密度 ${\rm{\lambda }} = 1$ ${\rm{\lambda }} = 10$ ${\rm{\lambda }} = 50$ IMM-GM-PHD算法 29.755 32.129 44.609 本文算法 21.821 28.617 43.996 -
YU Yihua. Consensus-based distributed linear filter for target tracking with uncertain noise statistics[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(15): 4875–4885. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2712702 但波, 姜永华, 李敬军, 等. 基于空时融合隐马尔科夫模型的舰艇编队目标识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 926–932. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140589DAN Bo, JIANG Yonghua, LI Jingju, et al. Ship formation target recognition based on spatial and temporal fusion hidden markov model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 926–932. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140589 FELDMANN M, FRÄNKEN D, and KOCH W. Tracking of extended objects and group targets using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2010.2101064 LAN Jian and LI X R. Tracking of maneuvering non-ellipsoidal extended object or target group using random matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(9): 2450–2463. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2014.2309561 王婷婷, 缪礼锋, 程然. 海上低空突防群目标跟踪的IMM-Bayesian实现[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2018, 33(1): 111–118. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.1673-1522.2018.01.003WANG Tingting, MIAO Lifeng, and CHENG Ran. IMM-bayesian tracking algorithm for the sea surface low-altitude penetration group targets[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University, 2018, 33(1): 111–118. doi: 10.7682/j.issn.1673-1522.2018.01.003 何友, 修建娟, 关欣, 等. 雷达数据处理及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013: 191–201.HE You, XIU Jianjuan, GUAN Xin, et al. Radar Data Processing with Applications[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013: 191–201. 王聪, 王海鹏, 何友, 等. 基于ICP的稳态部分可辨编队目标精细跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(6): 1123–1131. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0421WANG Cong, WANG Haipeng, HE You, et al. Refined tracking algorithm for steady partly resolvable group targets based on ICP[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(6): 1123–1131. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0421 WANG Haipeng, SUN Weiwei, JIA Shuyi, et al. A group target track correlation algorithm based on systematic error estimation[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059386. MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119 VO B N and MA W K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2006.881190 VO B N, SINGH S, and DOUCET A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multitarget filtering with random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(4): 1224–1225. doi: 10.1109/taes.2005.1561884 朱友清, 周石琳, 高贵. 结合聚类的GM-PHD滤波器辐射源群目标跟踪[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(9): 1967–1973. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.09.03ZHU Youqing, ZHOU Shilin, and GAO Gui. Emitter group targets tracking using GM-PHD filter combined with clustering[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(9): 1967–1973. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.09.03 WOOD T M. Interacting methods for manoeuvre handling in the GM-PHD filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 3021–3025. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034685 WANG Yun, HU Guoping, and LI Zhenxing. Tracking of group targets using multiple models GGIW-PHD algorithm based on best-fitting Gaussian approximation and strong tracking filter[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2018, 232(2): 331–343. doi: 10.1177/0954410016684359 GRANSTROM K and ORGUNER U. On spawning and combination of extended/group targets modeled with random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(3): 678–692. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2012.2230171 朱书军, 刘伟峰, 崔海龙. 基于广义标签多伯努利滤波的可分辨群目标跟踪算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(12): 2178–2189. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160334ZHU Shujun, LIU Weifeng, and CUI Hailong. Multiple resolvable groups tracking using the GLMB filter[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(12): 2178–2189. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160334 SAEEDI EMADI H and MAZINANI S M. A novel anomaly detection algorithm using DBSCAN and SVM in wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2018, 98(2): 2025–2035. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4961-1 LIN J. Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1991, 37(1): 145–151. doi: 10.1109/18.61115 VAN ERVEN T and HARREMOS P. Rényi divergence and Kullback-Leibler divergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(7): 3797–3820. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2014.2320500 SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2008.920469 -





 下载:
下载:

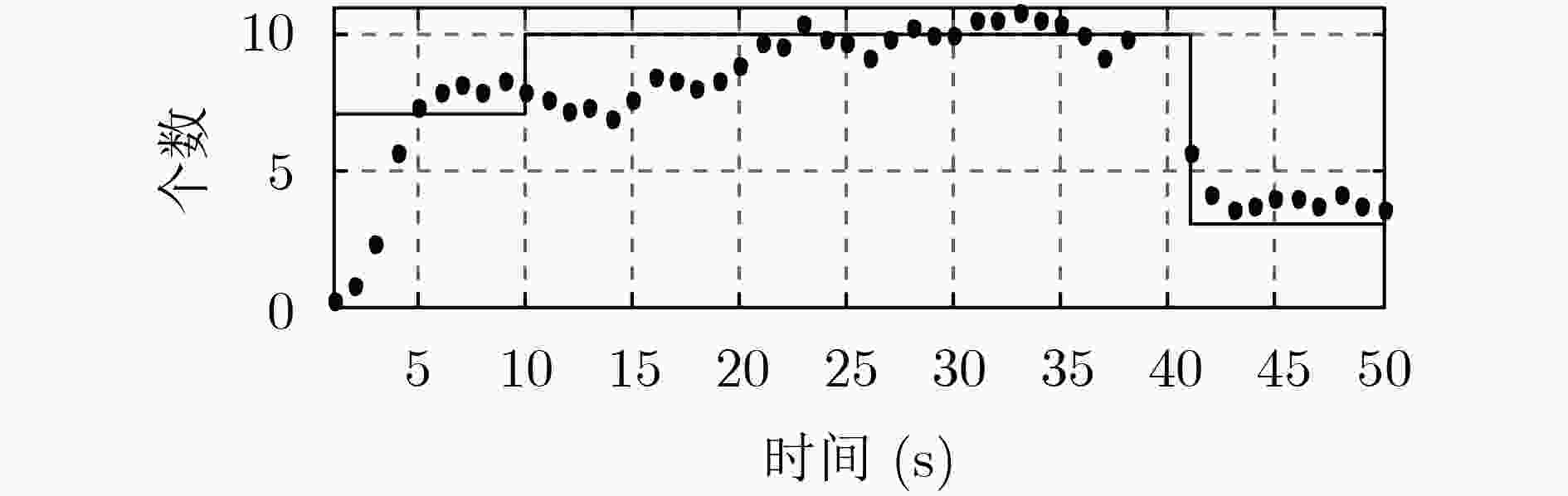
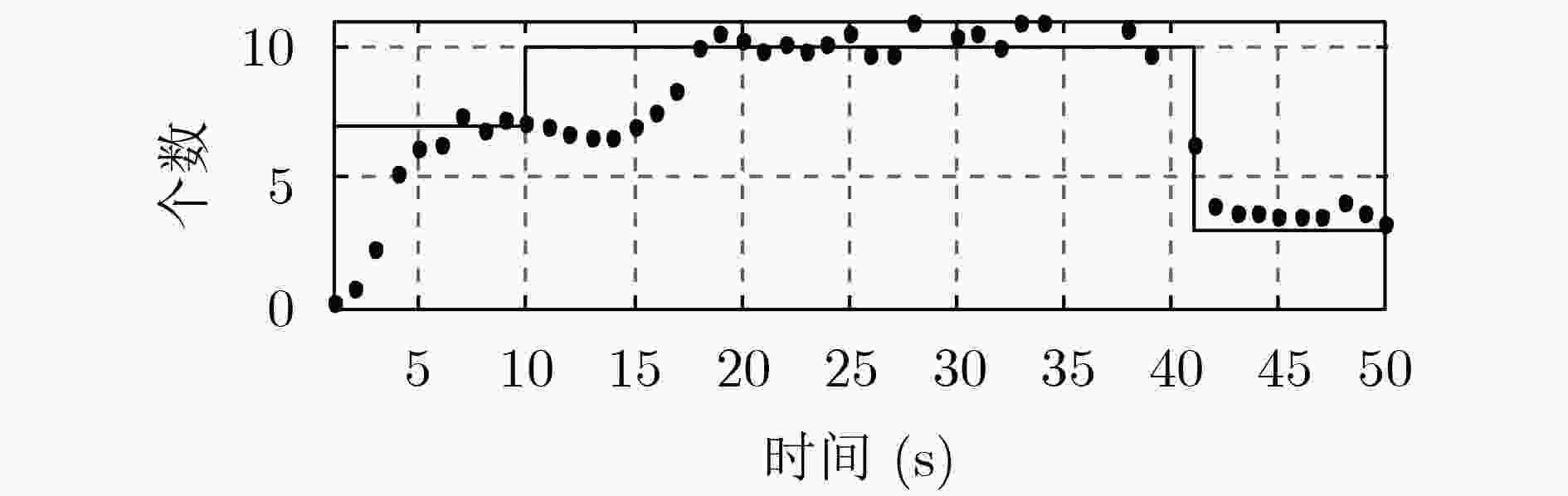

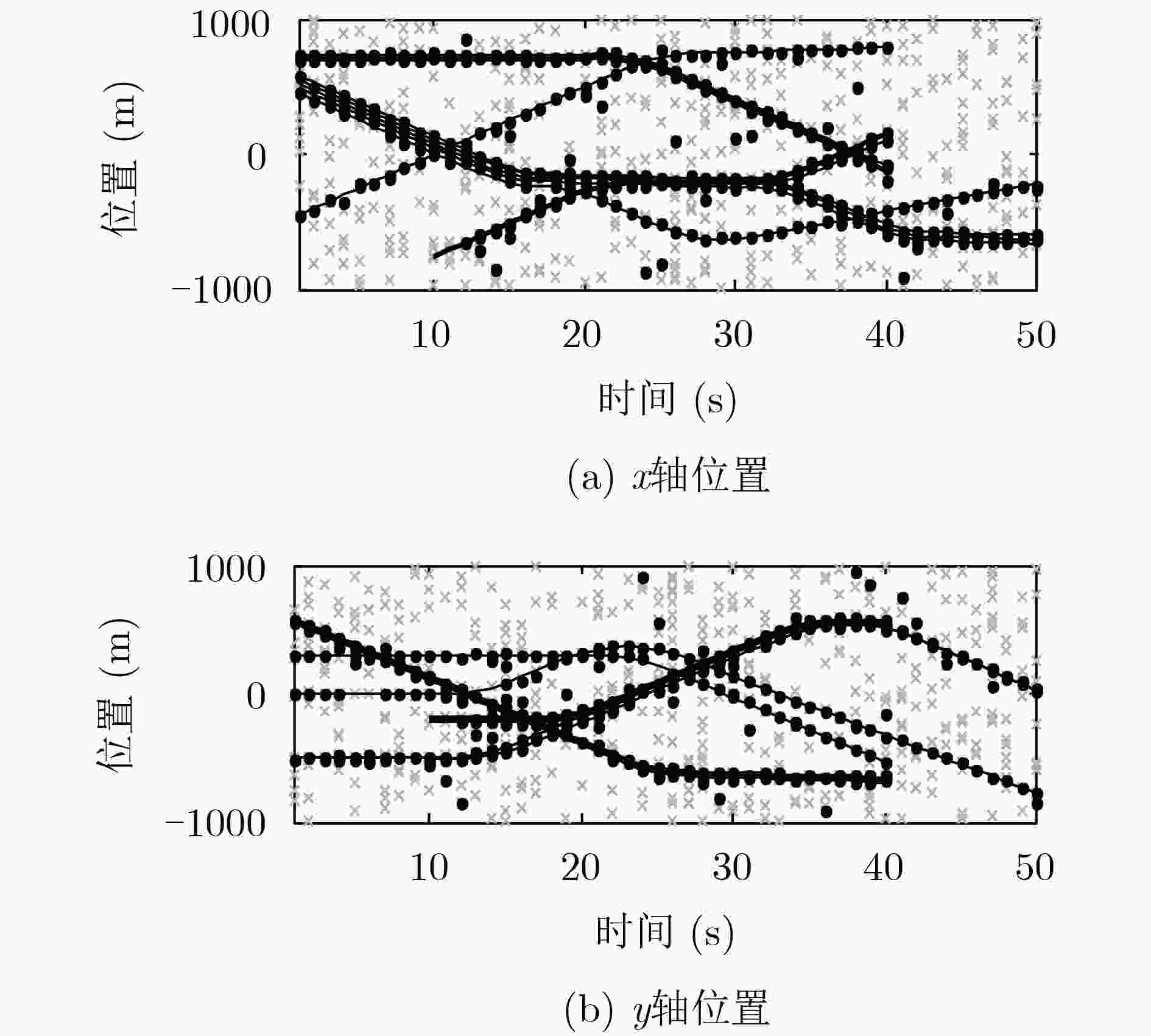
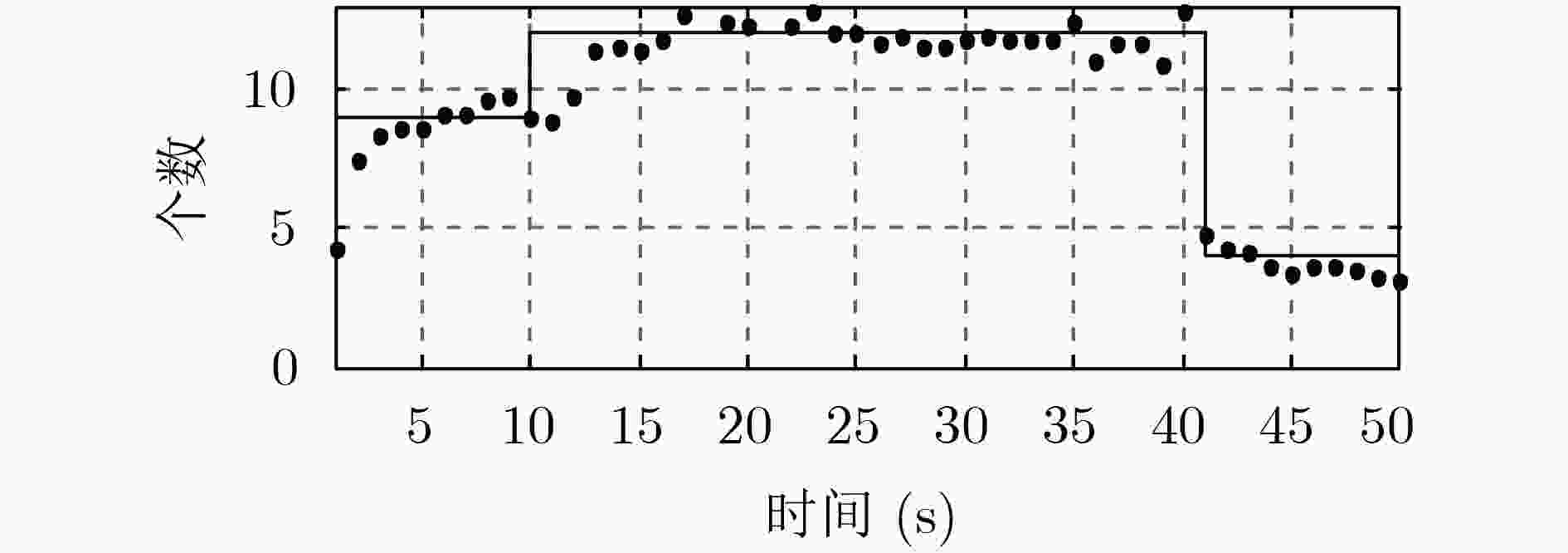


 下载:
下载:
