Multi-User Detection Based on Sparsity Adaptive Matching Pursuit Compressive Sensing for Uplink Grant-free Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access
-
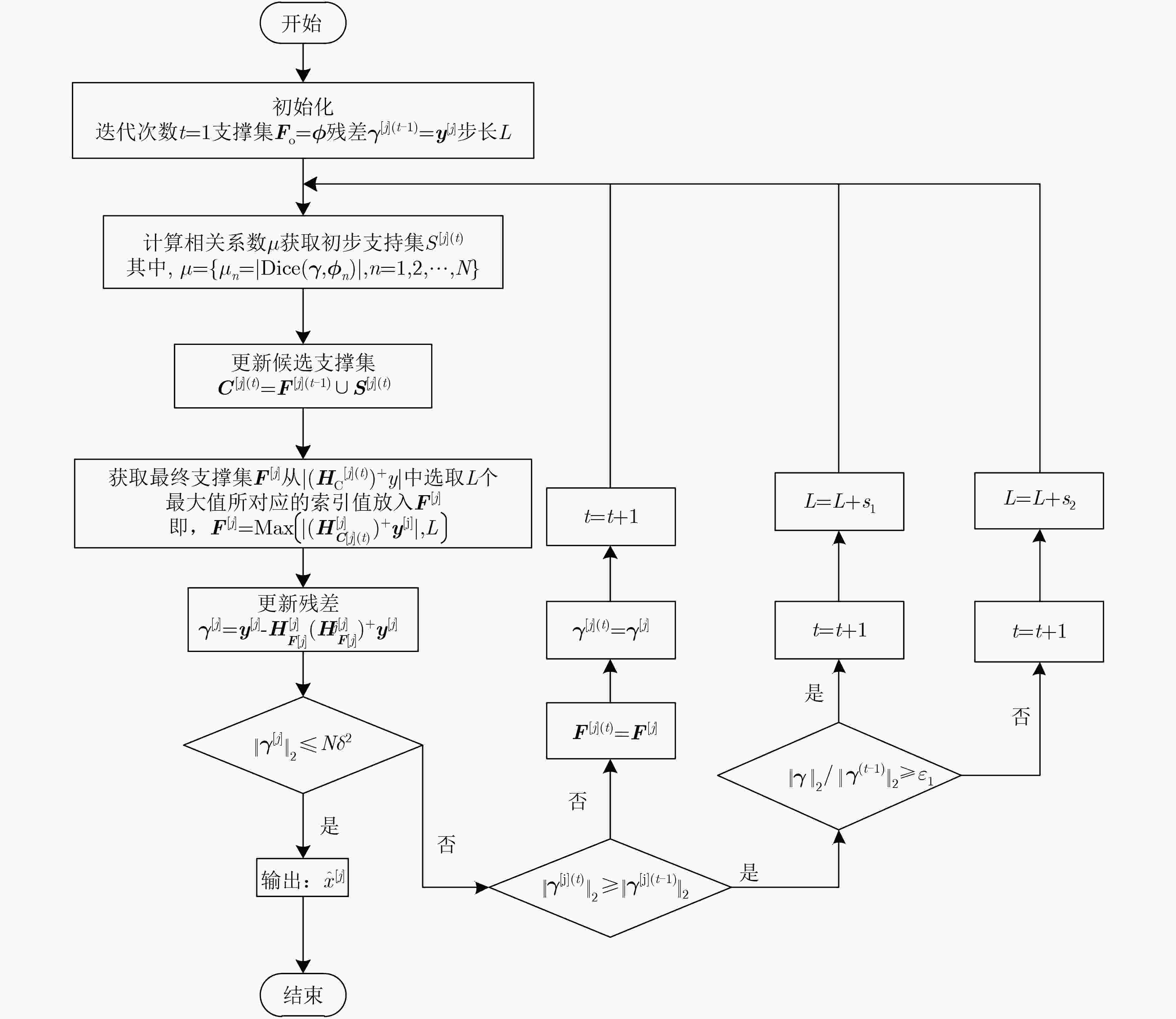
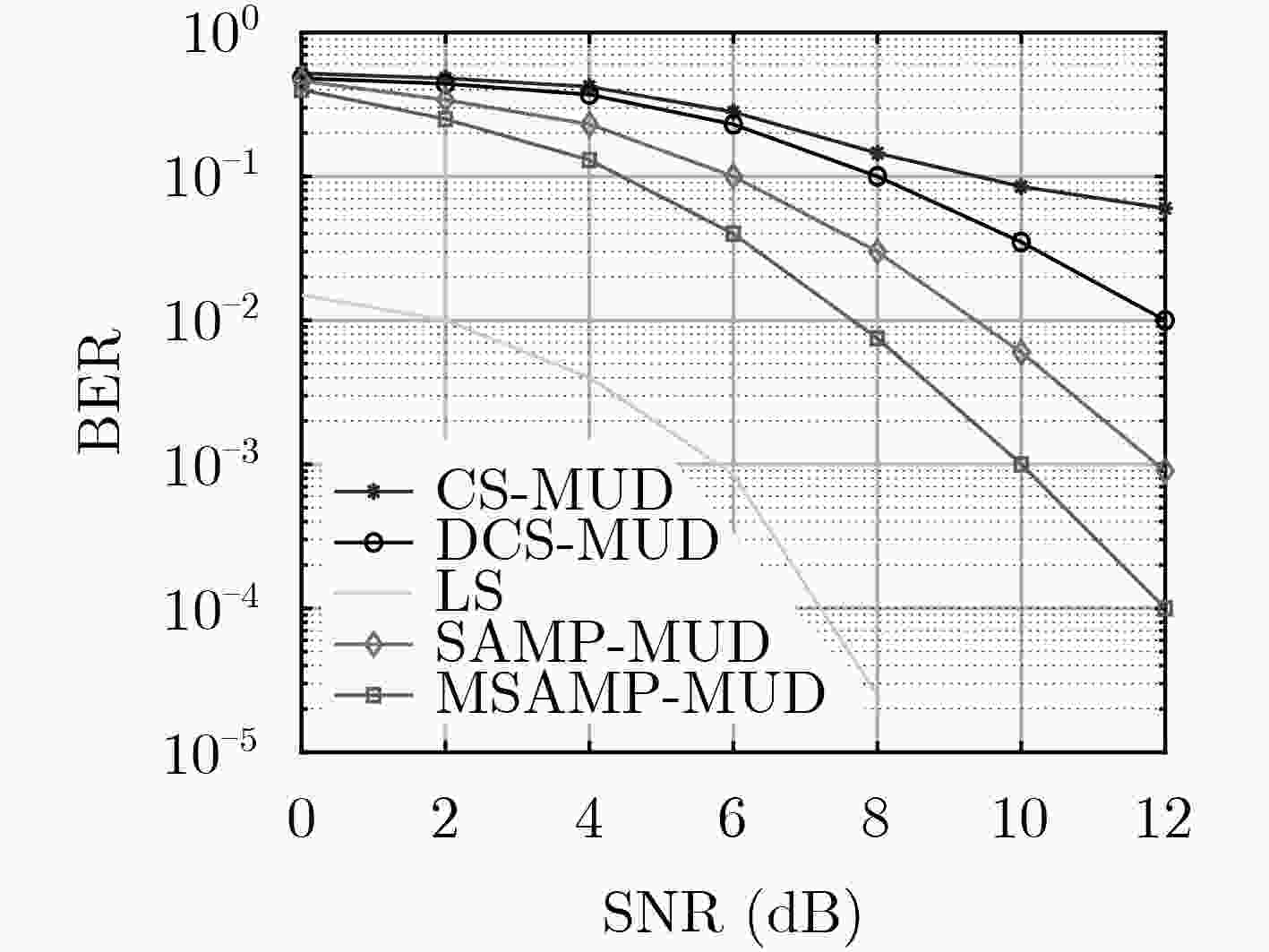
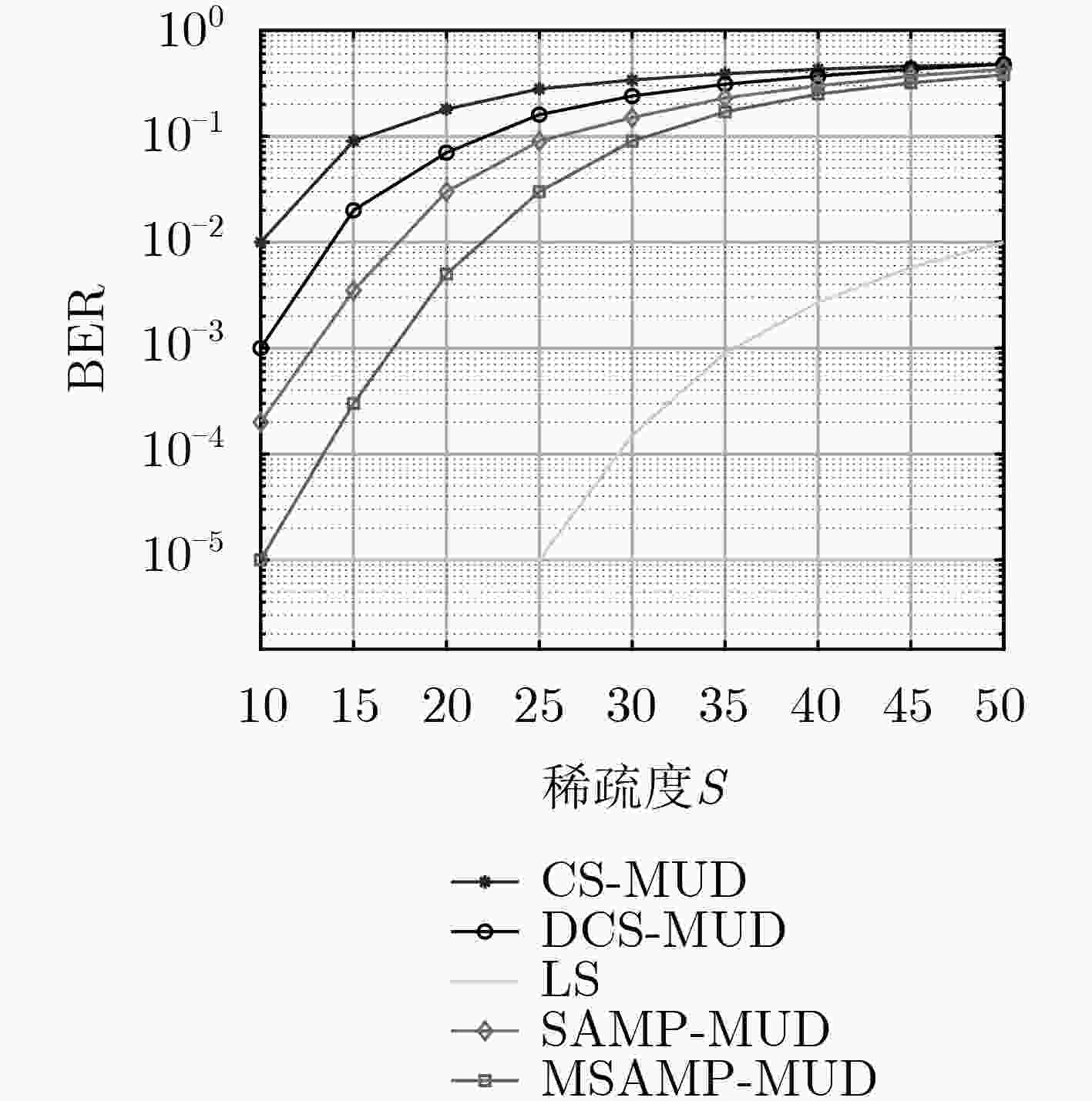
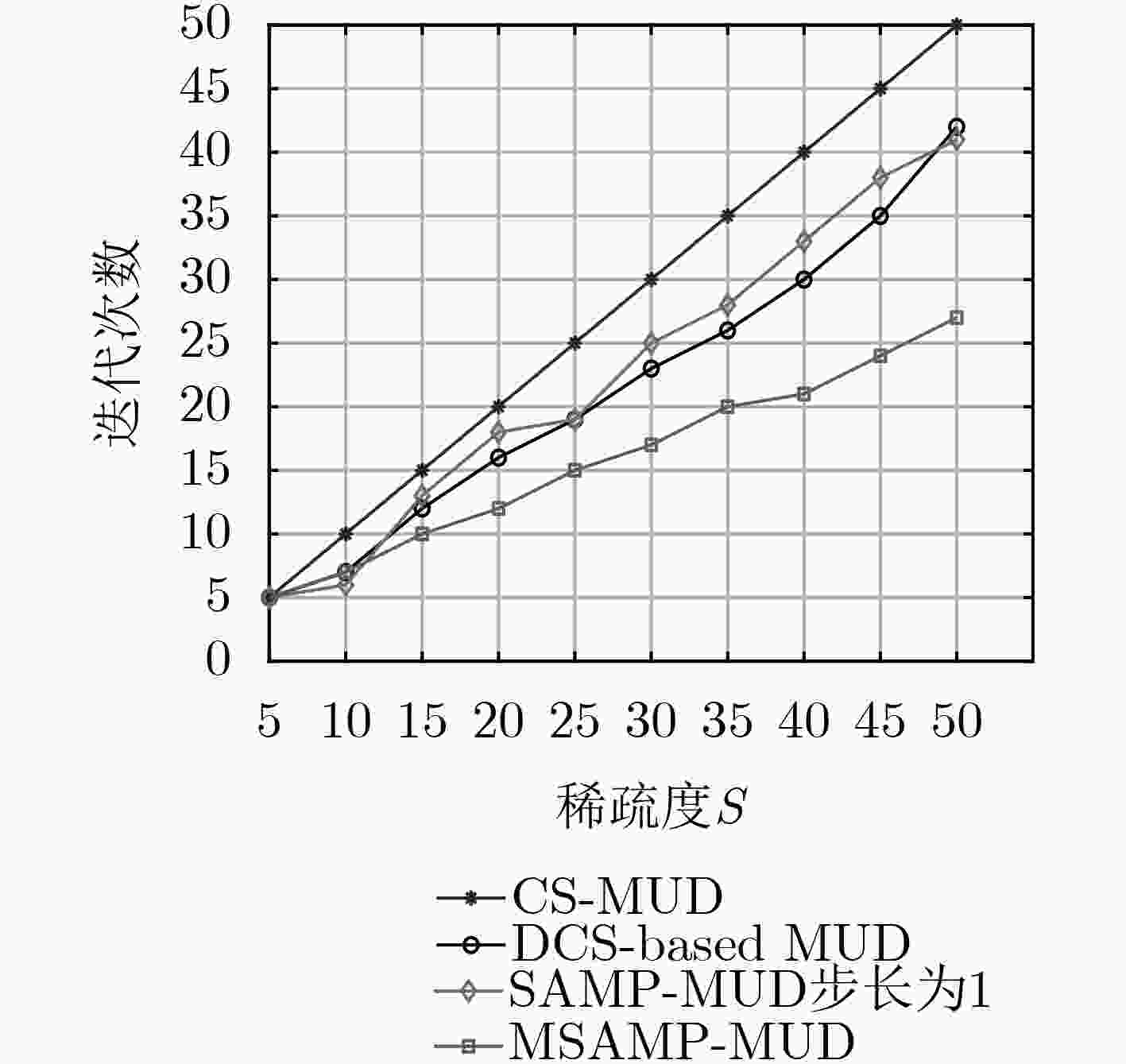
摘要: 免授权非正交多址接入技术(NOMA)结合多用户检测技术(MUD),能够满足大规模机器通信(mMTC)场景中的大连接量、低信令开销和低时延传输等需求。在基于压缩感知(CS)的MUD算法中,活跃用户数往往作为已知信息,而实际通信系统中很难准确估计。基于此,该文提出一种改进稀疏度自适应匹配的多用户算法(MSAMP-MUD)。该算法首先利用广义Dice系数匹配准则选择与残差最匹配的原子,更新用户支撑集;当残差能量接近噪声能量时,终止迭代,从而获得最终支持集;否则,采取上述准则更新用户支撑集,提高支撑集中活跃用户数估计精度。在迭代过程中,根据最近两次残差能量之比,选取不同的迭代步长,以降低检测迭代次数。仿真结果表明,所提算法与传统基于CS的MUD算法相比,误码率降低约9%,迭代次数减少约10%。Abstract: Grant-free Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) combined with Multi-User Detection (MUD) technology can meet the requirements of large connection volume, low signaling overhead and low latency transmission in massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC) scenarios. In the MUD algorithm based on Compressed Sensing (CS), the number of active users is often used as known information, but it is difficult to accurately estimate in the actual communication system. Based on this, this paper proposes a multi-user algorithm (Modified Sparsity Adaptive Matching Pursuit MUD, MSAMP-MUP) to improve the adaptive matching of sparsity. Firstly, the algorithm uses the generalized Dice coefficient matching criterion to select the atom that best matches the residual, and updates the user support set. When the residual energy is close to the noise energy, the iteration is terminated to obtain the final support set; Otherwise, the above criteria are used to update the user support set, and the estimation accuracy of the active users in the support set is improved. In the iteration process, different iteration steps are selected according to the ratio of the last two residual energies, so as to reduce the number of detection iterations. The simulation results show that, compared with the traditional CS-based MUD algorithm, the proposed algorithm reduces the bit error rate by about 9% and the number of iterations by about 10%.
-
表 1 系统仿真主要参数
参数 参数值 系统用户数$K$ 200 子载波数$N$ 100 时隙数$J$ 7 阈值${\varepsilon _1}$ 1.2 调制方式 QPSK 过载率$\lambda $ 200% 扩频矩阵 Toeplitz矩阵 -
杨维, 赵懿伟, 侯健琦. 一种改进基于门限的稀疏码多址接入低复杂度多用户检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1044–1049. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170647YANG Wei, ZHAO Yiwei, and HOU Jianqi. An improved threshold-based low complexity multiuser detection scheme for sparse code multiple access system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1044–1049. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170647 FAN Bin, SU Xin, JIE Zeng, et al. Method of CS-IC detection in the grant-free NOMA system[C]. The 12th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT), Sydney, Australia, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISMICT.2018.8573723. XU Xiao, RAO Xiongbin, and LAU V K N. Active user detection and channel estimation in uplink CRAN systems[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 2015: 2727–2732. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2015.7248738. 李燕龙, 陈晓, 詹德满, 等. 非正交多址接入中稀疏多用户检测方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 44(3): 151–156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.03.026LI Yanlong, CHEN Xiao, ZHAN Deman, et al. Method of sparse multi-user detection in non-orthogonal multiple access[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2017, 44(3): 151–156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.03.026 HAN Zhu, LI Husheng, and YIN Wotao. Compressive Sensing for Wireless Networks[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. doi: 10.1017/CBO9781139088497. SHIM B and SONG B. Multiuser detection via compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2012, 16(7): 972–974. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2012.050112.111980 WANG Bichai, DAI Linglong, MIR T, et al. Joint user activity and data detection based on structured compressive sensing for NOMA[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(7): 1473–1476. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2560180 WANG Bichai, DAI Linglong, ZHANG Yuan, et al. Dynamic compressive sensing-based multi-user detection for uplink grant-free NOMA[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(11): 2320–2323. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2602264 OYERINDE O O. Multiuser detector for uplink grant free NOMA systems based on modified subspace pursuit algorithm[C]. The 12th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Cairns, Australia, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCS.2018.8631787. ABEBE A T and KANG C G. Iterative order recursive least square estimation for exploiting frame-wise sparsity in compressive sensing-based MTC[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(5): 1018–1021. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2539255 HONG J P, CHOI W, and RAO B D. Sparsity controlled random multiple access with compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(2): 998–1010. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2363165 WANG Chao, CHEN Yang, WU Yiqun, et al. Performance evaluation of grant-free transmission for Uplink URLLC services[C]. The 85th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2017.8108593. MASOUDI M, AZARI A, YAVUZ E A, et al. Grant-free radio access IoT networks: Scalability analysis in coexistence scenarios[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2018.8422890. 赵晓娟, 张爱华, 杨守义, 等. 基于结构化压缩感知的NOMA系统多用户检测[J]. 现代电子技术, 2018, 41(5): 1–4. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2018.05.001ZHAO Xiaojuan, ZHANG Aihua, YANG Shouyi, et al. NOMA system′s multi-user detection based on structurization compressed sensing[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2018, 41(5): 1–4. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2018.05.001 3GPP. 3GPP TR-36.211 V13.2. 0 3rd Generation partnership project; technical specification group radio access network; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); physical channels and modulation[S]. France: 3GPP, 2016. DO T T, GAN L, NGUYEN N, et al. Sparsity adaptive matching pursuit algorithm for practical compressed sensing[C]. The 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2008: 581–587. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2008.5074472. 张宇, 刘雨东, 计钊. 向量相似度测度方法[J]. 声学技术, 2009, 28(4): 532–536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.04.021ZHANG Yu, LIU Yudong, and JI Zhao. Vector similarity measurement method[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2009, 28(4): 532–536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.04.021 MALEKI S, CHEPURI S P, and LEUS G. Optimal hard fusion strategies for cognitive radio networks[C]. 2011 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Cancun, Quintana Roo, Mexico, 2011: 1926–1931. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2011.5779453. DU Yang, DONG Binhong, CHEN Zhi, et al. Efficient multi-user detection for uplink grant-free NOMA: Prior-information aided adaptive compressive sensing perspective[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(12): 2812–2828. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2726279 ZHAO Xiaojuan, YANG Shouyi, ZHANG Aihua, et al. A compressive sensing based multi-user detection algorithm for SIMa-NOMA systems[C]. The 15th International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), Lisbon, Portugal, 2018: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISWCS.2018.8491213. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
