Mobility Prediction Based Computation Offloading Handoff Strategy for Vehicular Edge Computing
-
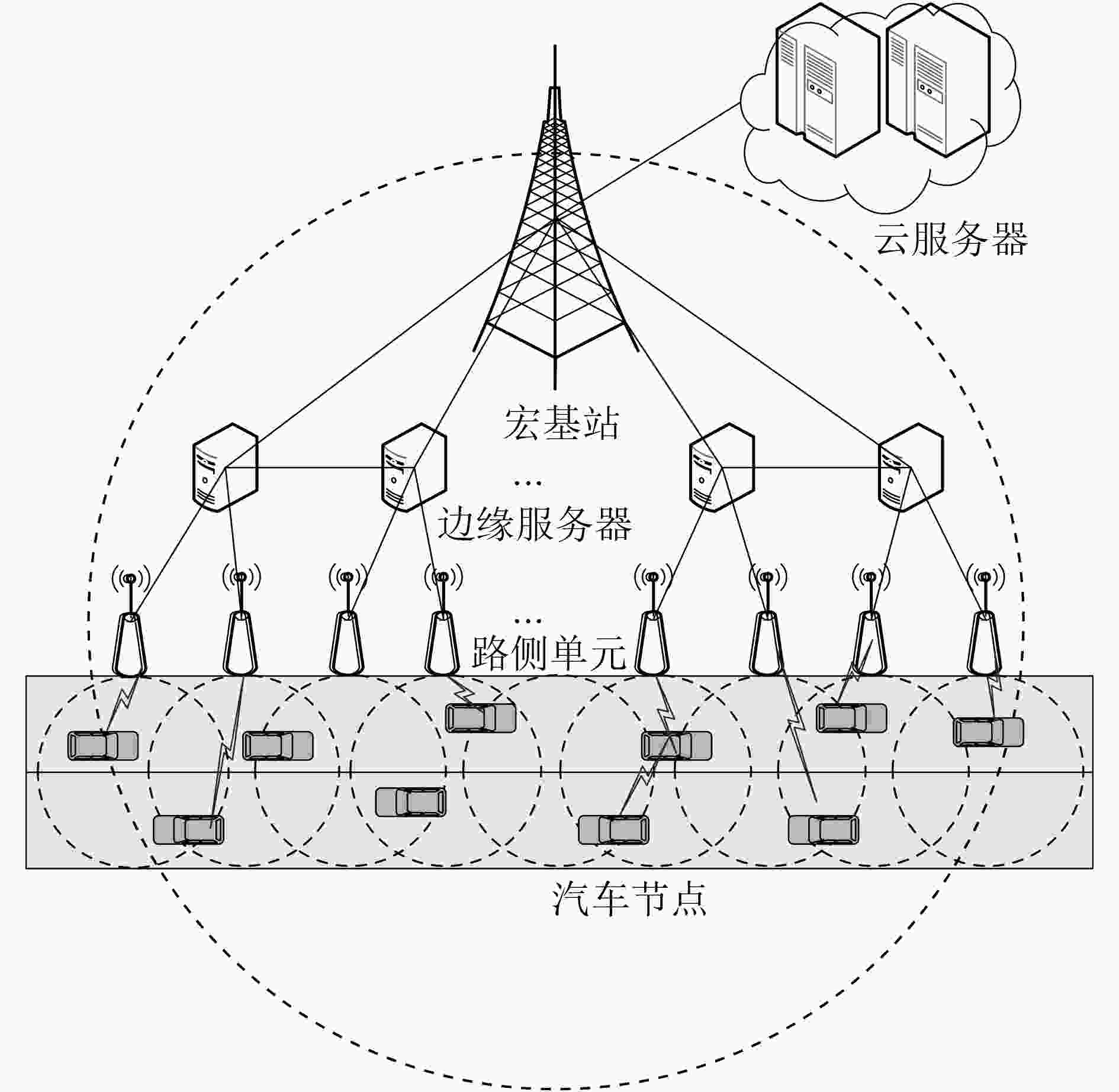
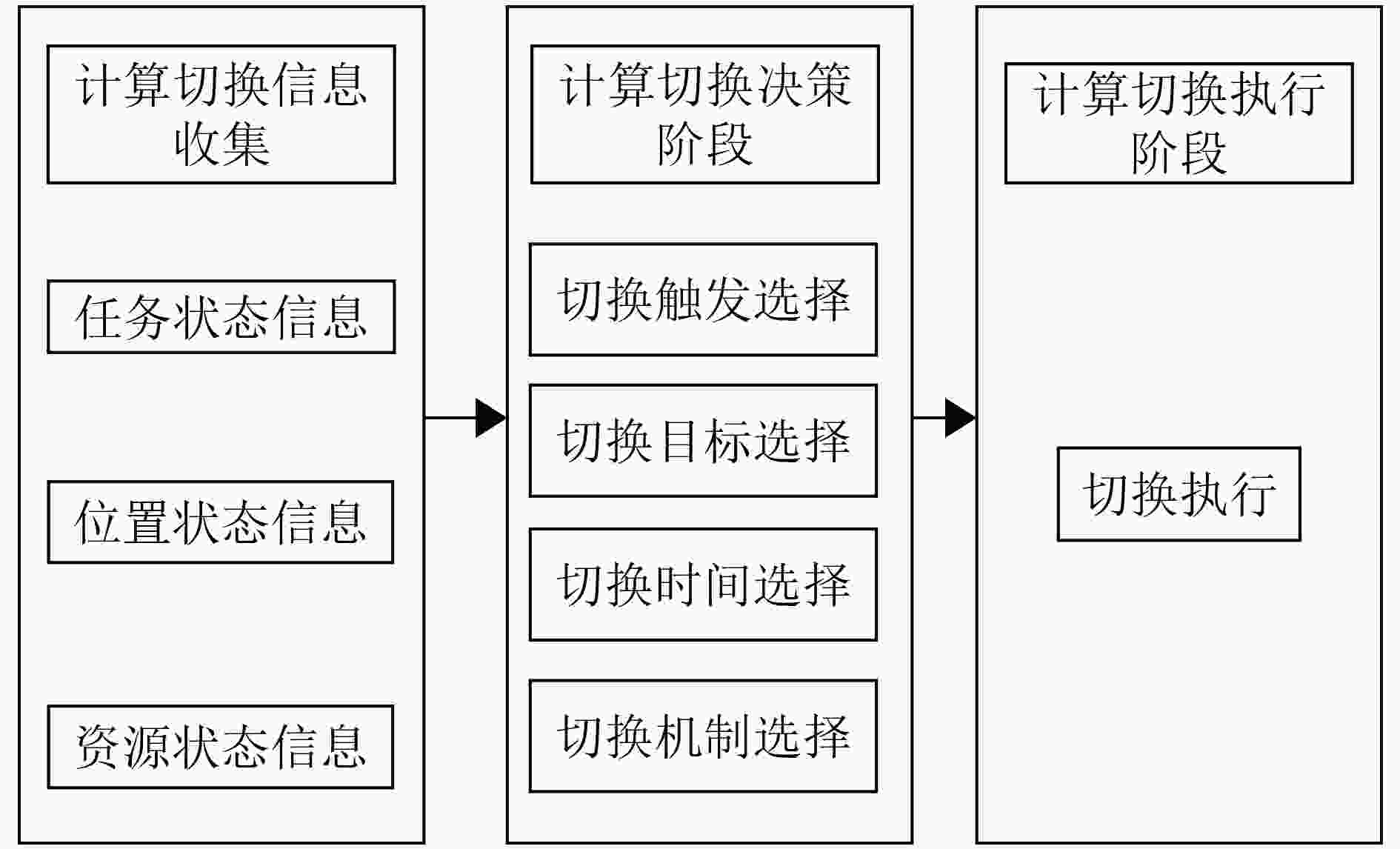
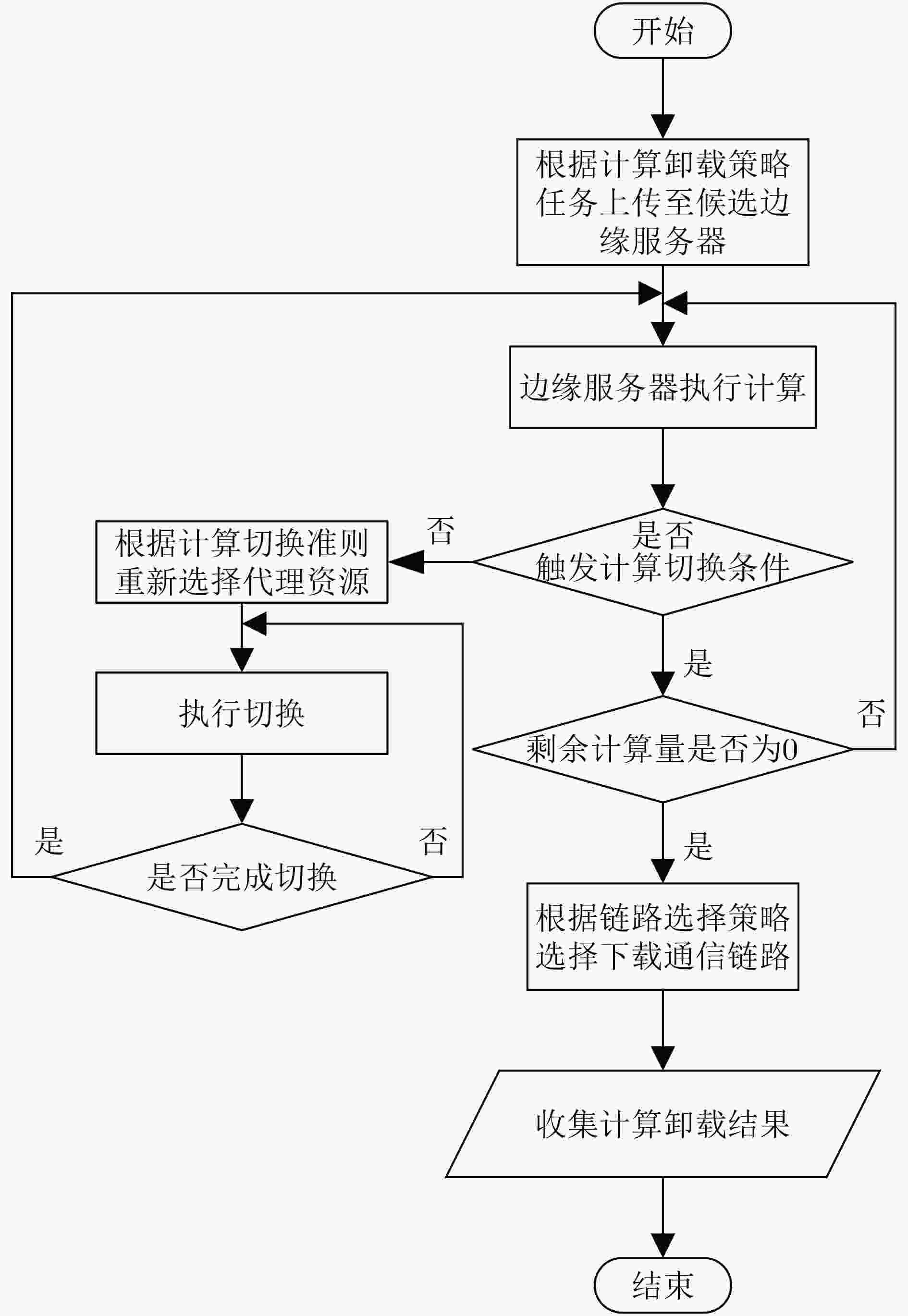
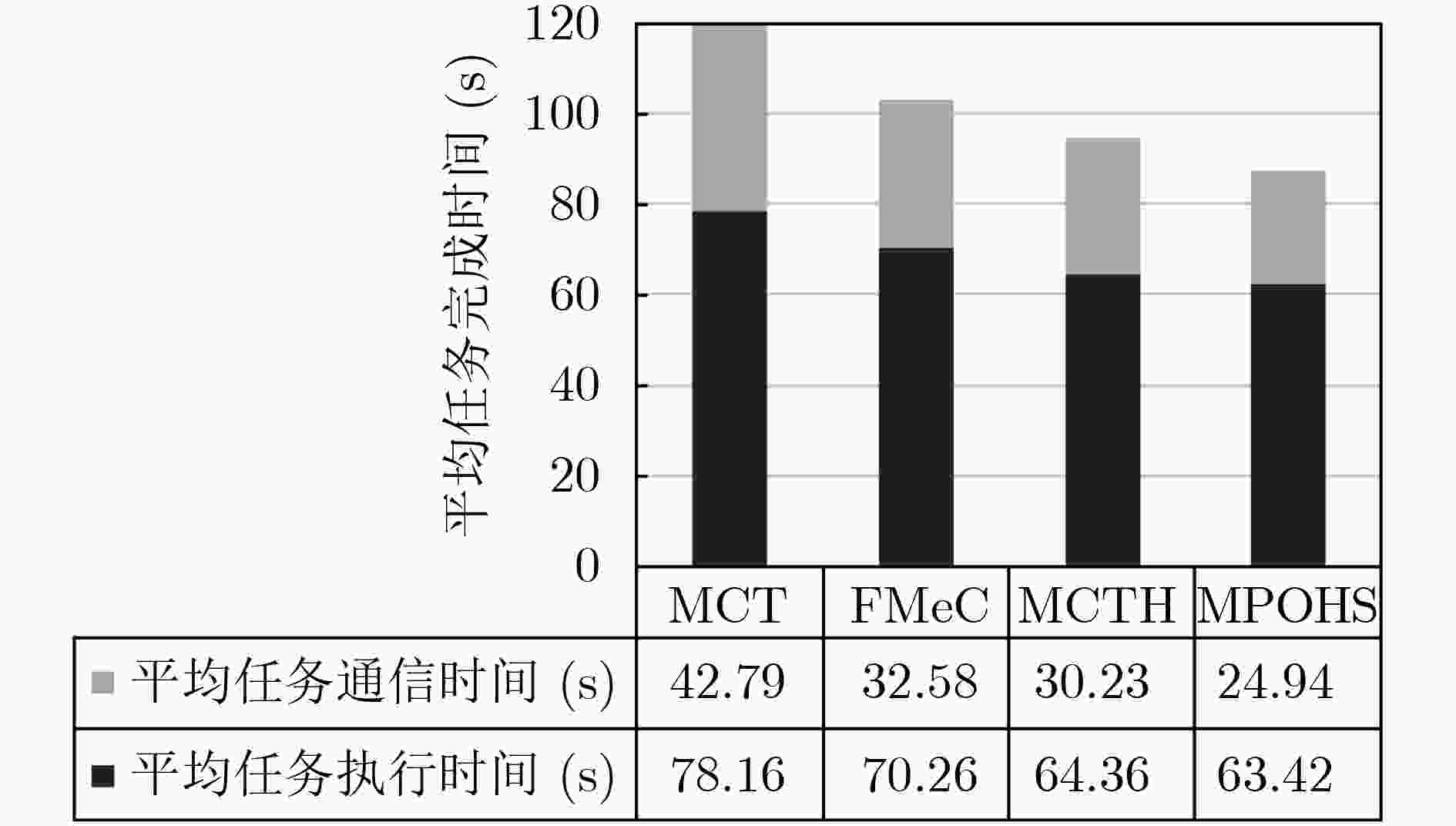
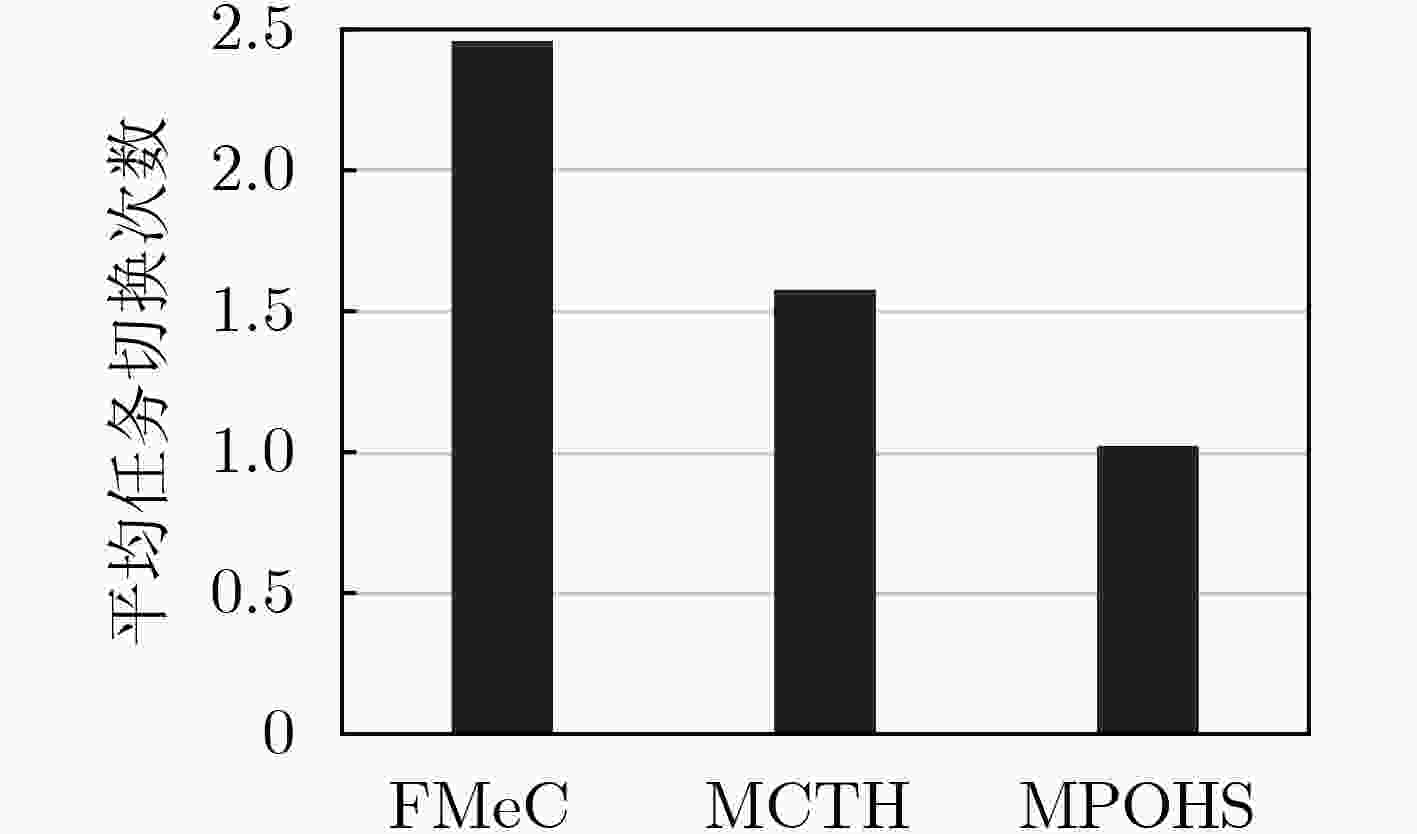
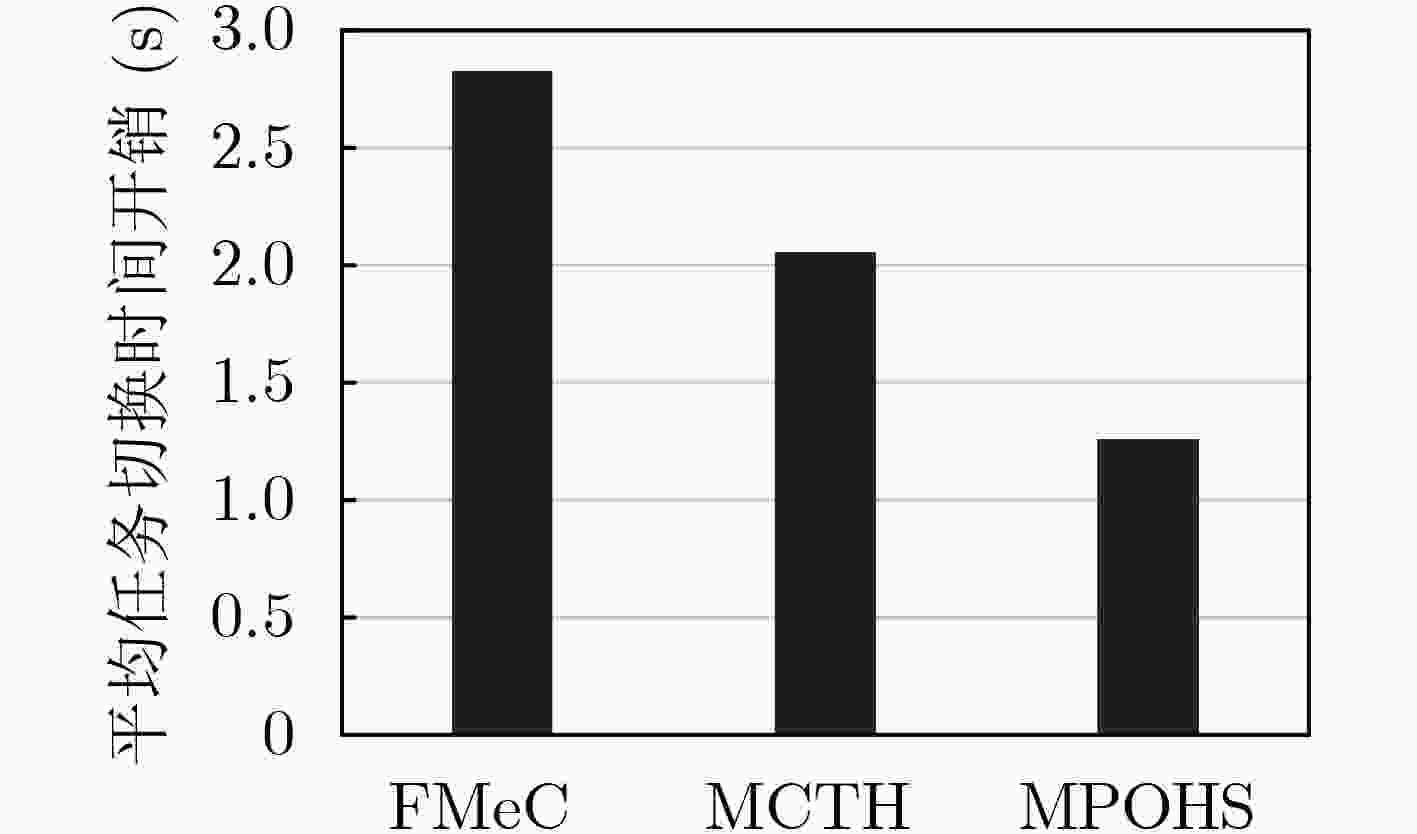
摘要: 车载云计算环境中的计算卸载存在回程网络延迟高、远程云端负载大等问题,车载边缘计算利用边缘服务器靠近车载终端,就近提供云计算服务的特点,在一定程度上解决了上述问题。但由于汽车运动造成的通信环境动态变化进而导致任务完成时间增加,为此该文提出一种基于移动路径可预测的计算卸载切换策略MPOHS,即在车辆移动路径可预测情况下,引入基于最小完成时间的计算切换策略,以降低车辆移动性对计算卸载的影响。实验结果表明,相对于现有研究,该文所提算法能够在减少平均任务完成时间的同时,减少切换次数和切换时间开销,有效降低汽车运动对计算卸载的影响。Abstract: In the vehicular cloud computing environments, computation offloading faces the problems such as high network delay and large load of the remote cloud. The vehicular edge computing takes advantage of the edge servers to be close to the vehicular terminals, and provides the cloud computing service to solve the problem mentioned above. However, due to the dynamic change of communication environment caused by vehicle movement, the task completion time will increase. For this reason, this paper proposes a Mobility Prediction-based computation Offloading Handoff Strategy (MPOHS), which tries to minimize the average completion time of offloaded tasks by migrating tasks among edge servers according to the prediction of vehicle movement. The experimental results show that, compared with the existing research, the proposed strategy can reduce the average task completion time, cut down the handoff times and handoff time overhead, and effectively reduce the impact of vehicle movement on the performance of computation offloading.
-
表 1 仿真参数表
参数名 参数值 参数名 参数值 基站覆盖范围 100% V计算能力(MIPS) 82335×0.75 RSU半径(m) U[100 150] ES计算能力(MIPS) 82335×1.5 Cloud数目(个) 1 Cloud计算能力(MIPS) 82335×2 BS数目(个) 1 V2R单跳带宽(Mbps) 15 RSU数目(个) 64 V2B单跳带宽(Mbps) 2 ES数目(个) 16 E2E单跳带宽(Mbps) U[15 20] V数目(个) 10 V2V端到端延时(ms) U[5 15] 任务计算量(MI) U[7 9]×106 V2R端到端延时(ms) U[20 30] 任务数据量(M) U[30 50] V2B端到端延时(ms) U[450 550] -
MACH P and BECVAR Z. Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1628–1656. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2682318 TRAN T X, HAJISAMI A, PANDEY P et al. Collaborative mobile edge computing in 5G networks: New paradigms, scenarios, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(4): 54–61. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600863 张海波, 李虎, 陈善学, 等. 超密集网络中基于移动边缘计算的任务卸载和资源优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592ZHANG Haibo, LI Hu, CHEN Shanxue, et al. Computing offloading and resource optimization in ultra-dense networks with mobile edge computation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(5): 1194–1201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180592 张海波, 栾秋季, 朱江, 等. 基于移动边缘计算的V2X任务卸载方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2736–2743. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180027ZHANG Haibo, LUAN Qiuji, ZHU Jiang, et al. V2X task offloading scheme based on mobile edge computing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2736–2743. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180027 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: A promising network paradigm with predictive off-loading[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(2): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2668838 AISSIOUI A, KSENTINI A, GUEROUI A M et al. On enabling 5G automotive systems using follow me edge-cloud concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(6): 5302–5316. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2805369 NING Zhaolong, WANG Xiaojie, and HUANG Jun. Mobile edge computing-enabled 5G vehicular networks: Toward the integration of communication and computing[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(1): 54–61. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2018.2882873 CHEN Hongyang, GAO Feifei, MARTINS M, et al. Accurate and efficient node localization for mobile sensor networks[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2013, 18(1): 141–147. doi: 10.1007/s11036-012-0361-7 KHAN Z, FAN Pingzhi, ABBAS F, et al. Two-level cluster based routing scheme for 5G V2X communication[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 16194–16205. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2892180 MATHEW T, SEKARAN K C, and JOSE J. Study and analysis of various task scheduling algorithms in the cloud computing environment[C]. 2014 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics, New Delhi, India, 2014: 658–664. CHEN Hongyang, WU Jianming, and SHIMOMURA T. New reference signal design for URLLC and eMBB multiplexing in new radio wireless communications[C]. The 29th IEEE Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Bologna, Italy, 2018: 1220–1225. LI Bo, PEI Yijian, WU Hao, et al. Heuristics to allocate high-performance cloudlets for computation offloading in mobile ad hoc clouds[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2015, 71(8): 3009–3036. doi: 10.1007/s11227-015-1425-9 李波, 黄鑫, 牛力, 等. 车载边缘计算环境中的任务卸载决策和优化[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2019, 36(2): 78–82.LI Bo, HUANG Xin, NIU Li, et al. Task offloading decision in vehicle edge computing environment[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2019, 36(2): 78–82. XIAO Kaiyi and LI Changgen. Vertical handoff decision algorithm for heterogeneous wireless networks based on entropy and improved TOPSIS[C]. The 18th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, Chongqing, China, 2018: 706–710. MA Lele, YI Shanhe, and LI Qun. Efficient service handoff across edge servers via docker container migration[C]. The 2nd ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing, San Jose, USA, 2017: 1–13. 郭丽芳, 李鸿燕, 李艳萍, 等. 无线Ad Hoc网络移动模型大全[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2014.GUO Lifang, LI Hongyan, LI Yanping, et al. The Encyclopedia of Wireless Ad Hoc Network Mobility Model[M]. Beijing: The People’s Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
