Fast Training Adaboost Algorithm Based on Adaptive Weight Trimming
-
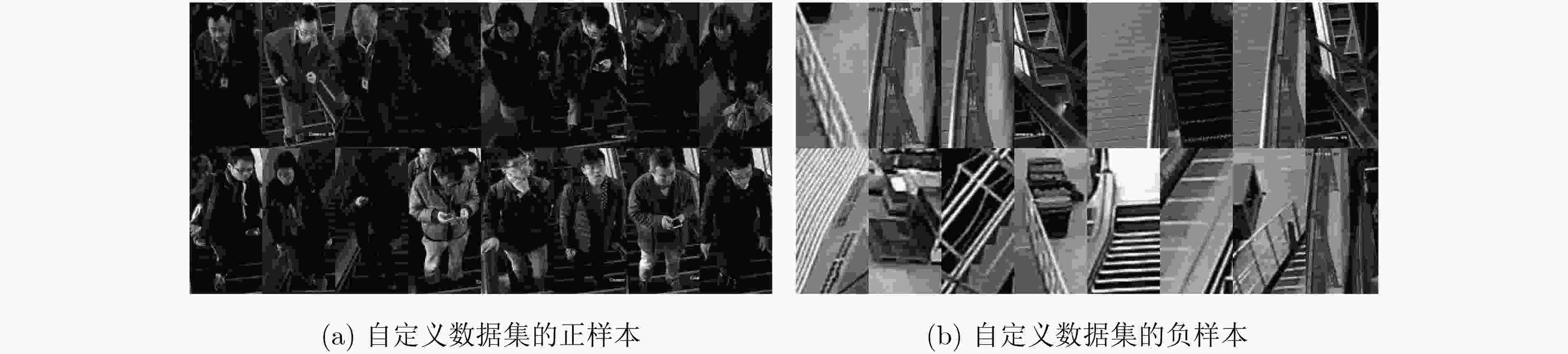
摘要: Adaboost是一种广泛使用的机器学习算法,然而Adaboost算法在训练时耗时十分严重。针对该问题,该文提出一种基于自适应权值的Adaboost快速训练算法AWTAdaboost。该算法首先统计每一轮迭代的样本权值分布,再结合当前样本权值的最大值和样本集规模计算出裁剪系数,权值小于裁剪系数的样本将不参与训练,进而加快了训练速度。在INRIA数据集和自定义数据集上的实验表明,该文算法能在保证检测效果的情况下大幅加快训练速度,相比于其他快速训练算法,在训练时间接近的情况下有更好的检测效果。
-
关键词:
- 目标检测 /
- Adaboost算法 /
- 快速训练 /
- 自适应 /
- 权值分布
Abstract: The Adaboost algorithm provides noteworthy benefits over the traditional machine algorithms for numerous applications, including face recognition, text recognition, and pedestrian detection. However, it takes a lot of time during the training process that affects the overall performance. Adaboost fast training algorithm based on adaptive weight (Adaptable Weight Trimming Adaboost, AWTAdaboost) is proposed in this work to address the aforementioned issue. First, the algorithm counts the current sample weight distribution of each iteration. Then, it combines the maximum value of current sample weights with data size to calculate the adaptable coefficients. The sample whose weight is less than the adaptable coefficients is discarded, that speeds up the training. The experimental results validate that it can significantly speed up the training speed while ensuring the detection effect. Compared with other fast training algorithms, the detection effect is better when the training time is close to each other.-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- Adaboost algorithm /
- Fast traing /
- Adaptive /
- Weight distribution
-
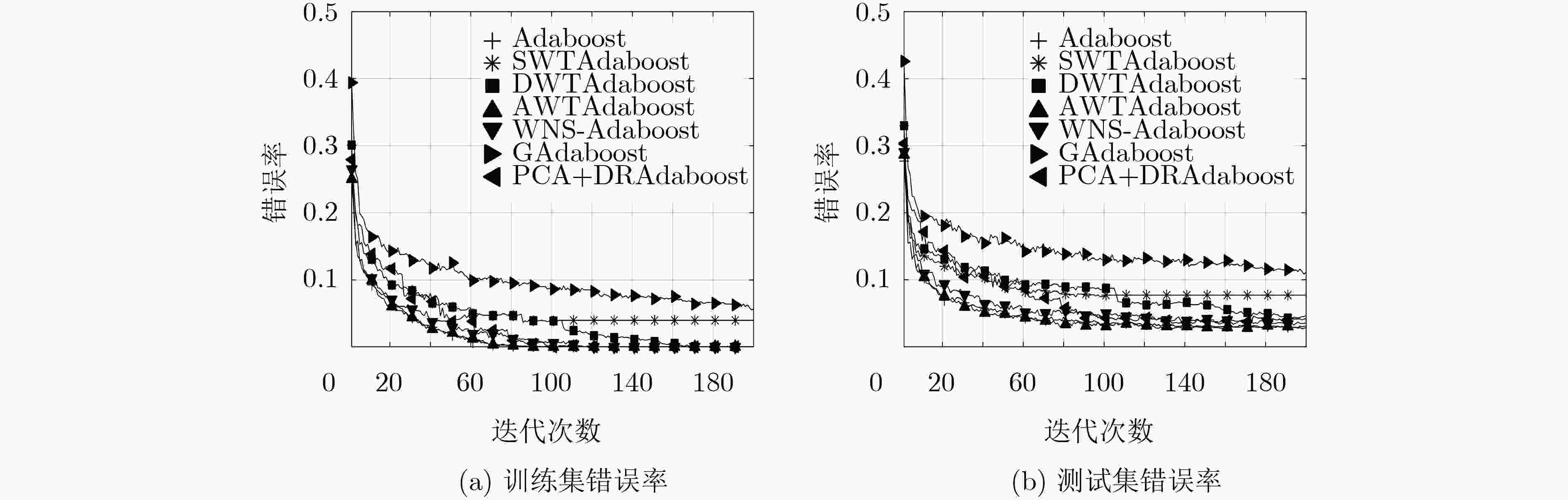
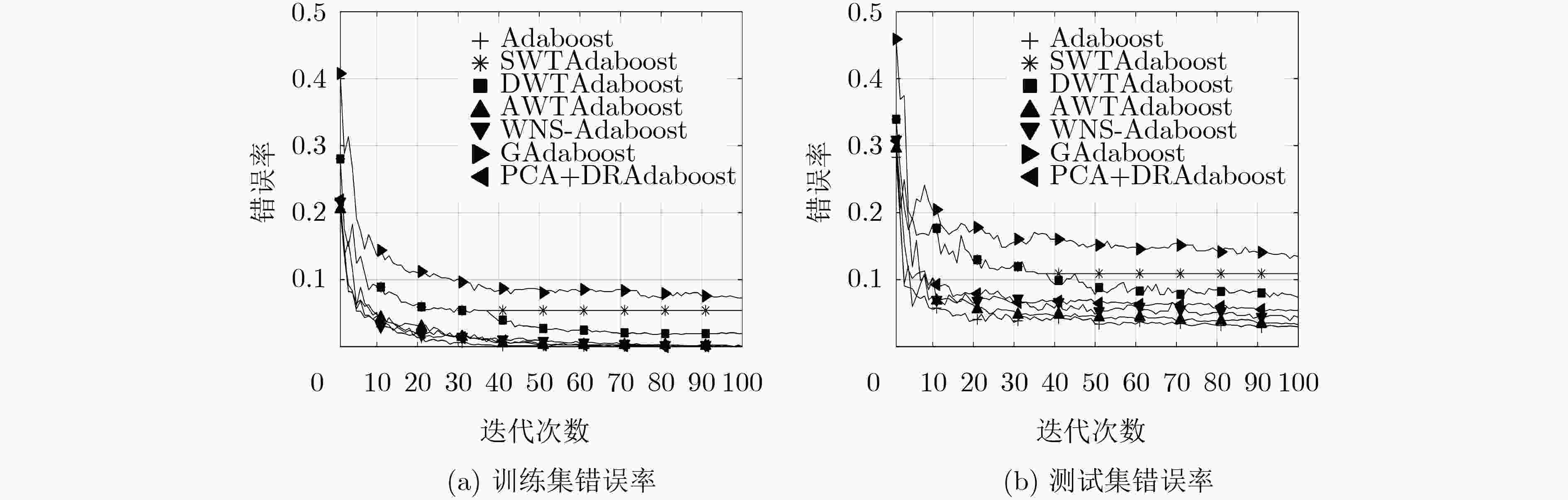
表 1 各算法在两个数据集上的错误率
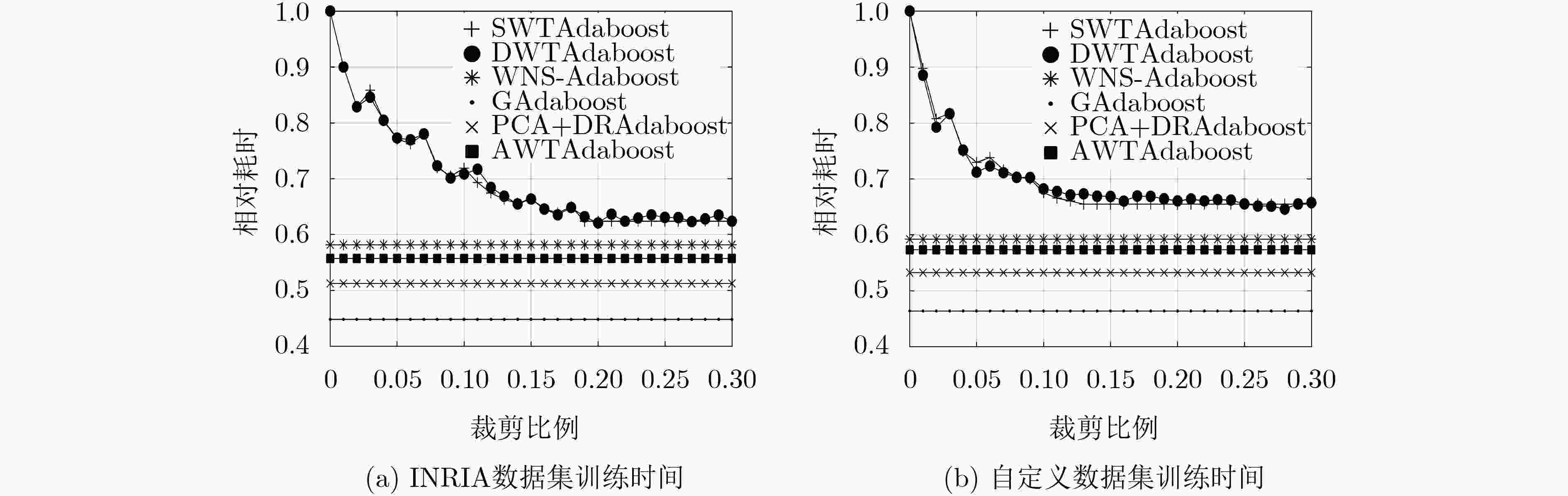
INRIA数据集 自定义数据集 训练集错误率 测试集错误率 训练集错误率 测试集错误率 Adaboost 0.0000 0.0285 0.0000 0.0296 SWTAdaboost 0.0395 0.0768 0.0538 0.1089 DWTAdaboost 0.0000 0.0466 0.0194 0.0735 WNS-Adaboost 0.0000 0.0356 0.0006 0.0439 GAdaboost 0.0563 0.1108 0.0724 0.1345 PCA+DRAdaboost 0.0000 0.0413 0.0000 0.0539 AWTAdaboost 0.0000 0.0302 0.0000 0.0324 表 2 各算法训练时间对比
算法 INRIA数据集相对
训练时间自定义数据集相对
训练时间Adaboost 1.0000 1.0000 SWTAdaboost 0.6237 0.6547 DWTAdaboost 0.6347 0.6551 WNS-Adaboost 0.5814 0.5919 GAdaboost 0.4482 0.4636 PCA+DRAdaboost 0.5124 0.5324 AWTAdaboost 0.5570 0.5732 注:表中只记录了SWTAdaboost提前停止迭代前的训练时间和相同$\beta $下DWTAdaboost的训练时间。 -
VALIANT L G. A theory of the learnable[C]. The 16th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, New York, USA, 1984: 436–445. KEARNS M and VALIANT L. Cryptographic limitations on learning Boolean formulae and finite automata[J]. Journal of the ACM, 1994, 41(1): 67–95. doi: 10.1145/174644.174647 SCHAPIRE R E. The strength of weak learnability[J]. Machine Learning, 1990, 5(2): 197–227. FREUND Y and SCHAPIRE R E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1997, 55(1): 119–139. doi: 10.1006/jcss.1997.1504 FREUND Y and SCHAPIRE R E. Experiments with a new boosting algorithm[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning, Bari, Italy, 1996: 148–156. ZHANG Xingqiang and DING Jiajun. An improved Adaboost face detection algorithm based on the different sample weights[C]. The 20th IEEE International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, Nanchang, China, 2016: 436–439. CHO H, SUNG M, and JUN B. Canny text detector: Fast and robust scene text localization algorithm[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3566–3573. GAO Chenqiang, LI Pei, ZHANG Yajun, et al. People counting based on head detection combining Adaboost and CNN in crowded surveillance environment[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 208: 108–116. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.097 FRIEDMAN J, HASTIE T, and TIBSHIRANI R. Additive logistic regression: A statistical view of boosting (With discussion and a rejoinder by the authors)[J]. Annals of Statistics, 2000, 28(2): 337–407. 贾慧星, 章毓晋. 基于动态权重裁剪的快速Adaboost训练算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2009, 32(2): 336–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2009.00336JIA Huixing and ZHANG Yujin. Fast Adaboost training algorithm by dynamic weight trimming[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2009, 32(2): 336–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2009.00336 SEYEDHOSSEINI M, PAIVA A R C, and TASDIZEN T. Fast AdaBoost training using weighted novelty selection[C]. 2011 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, San Jose, USA, 2011: 1245–1250. TOLBA M F and MOUSTAFA M. GAdaBoost: Accelerating adaboost feature selection with genetic algorithms[C]. The 8th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence, Porto, Portugal, 2016: 156-163. YUAN Shuang and LÜ Cixing. Fast adaboost algorithm based on weight constraints[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems, Shenyang, China, 2015: 825–828. 袁双, 吕赐兴. 基于PCA改进的快速Adaboost算法研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(29): 62–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.29.011YUAN Shuang and LÜ Cixing. Fast adaboost algorithm based on improved PCA[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(29): 62–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.29.011 DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. -





 下载:
下载:
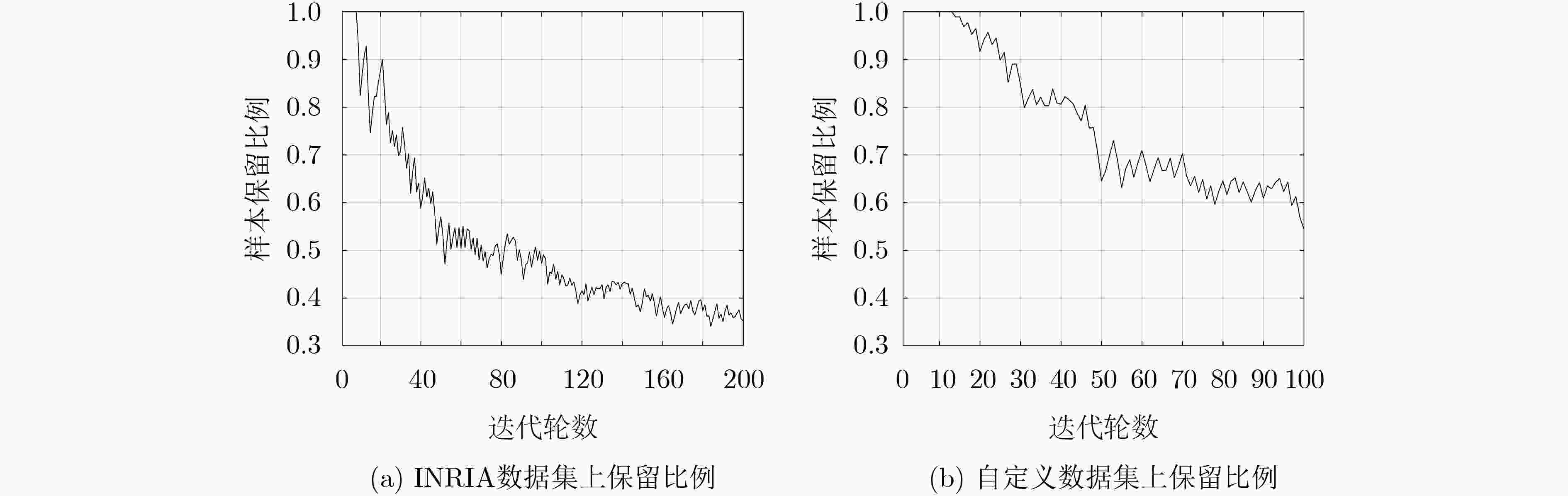


 下载:
下载:
