Controllable Magnification for Visual Saliency Object Based on Virtual Optics
-
摘要:
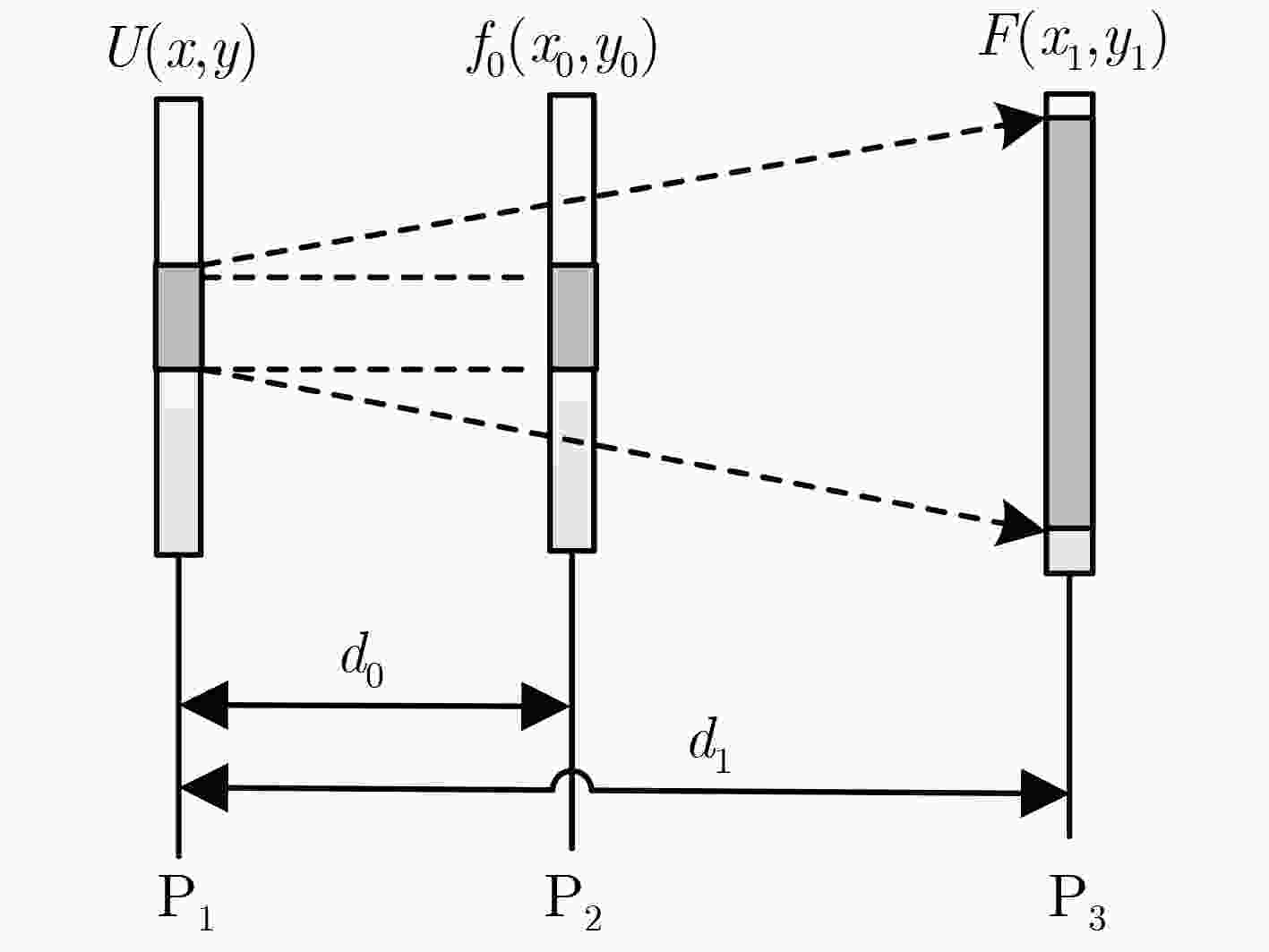
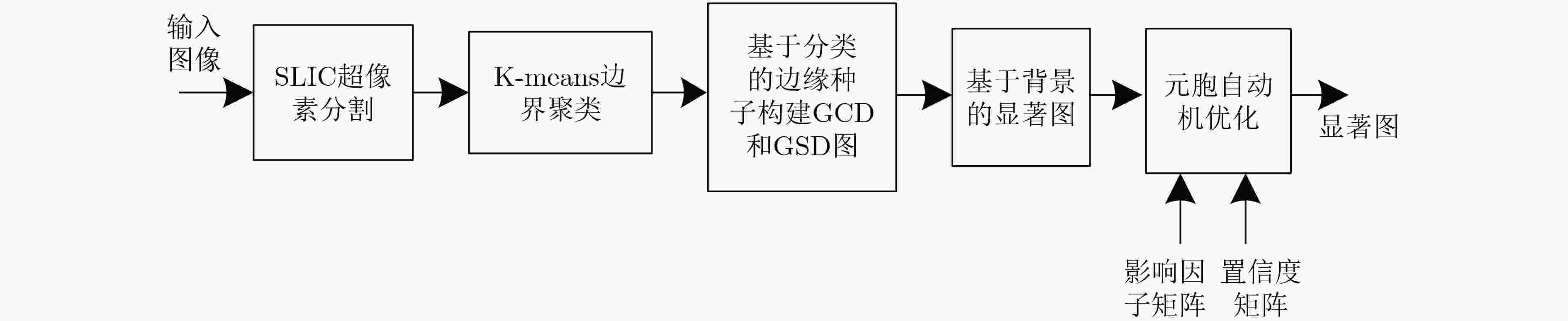
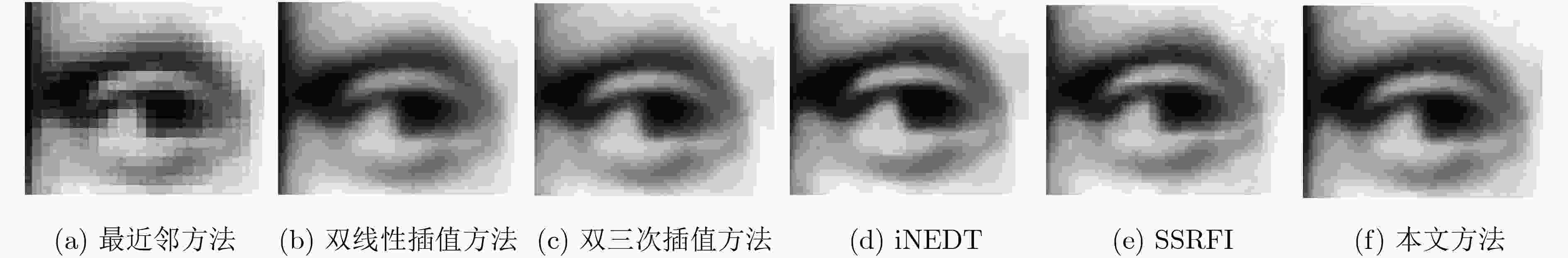
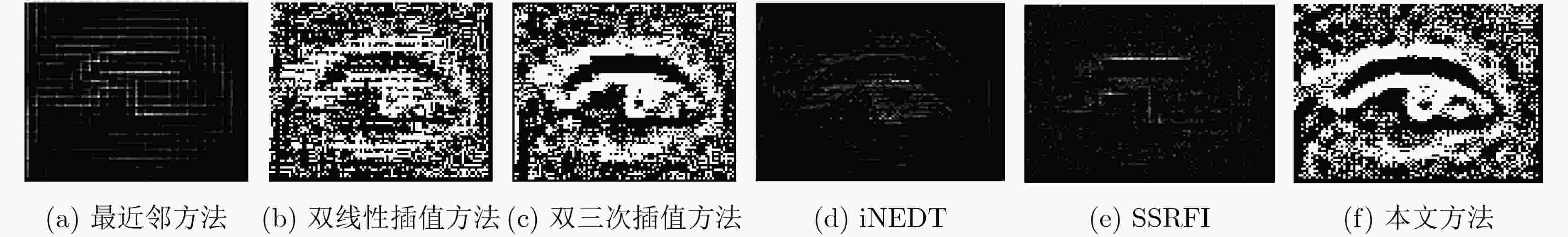
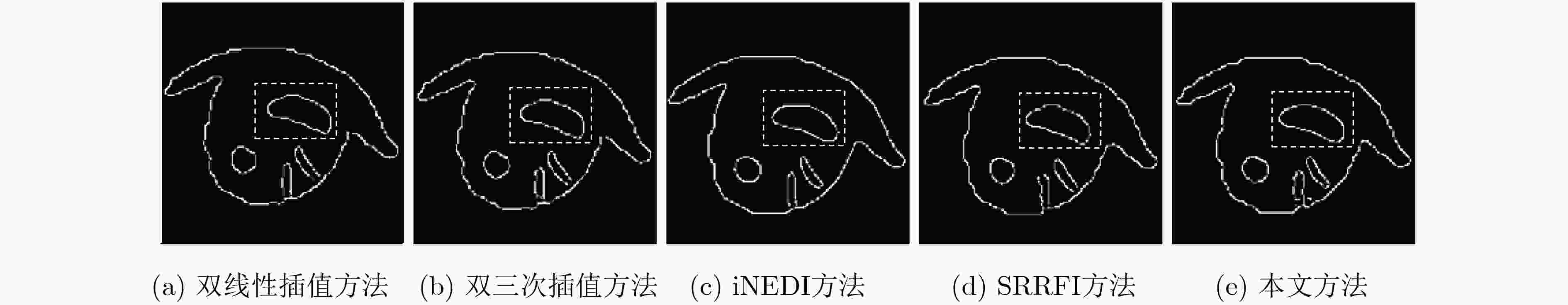
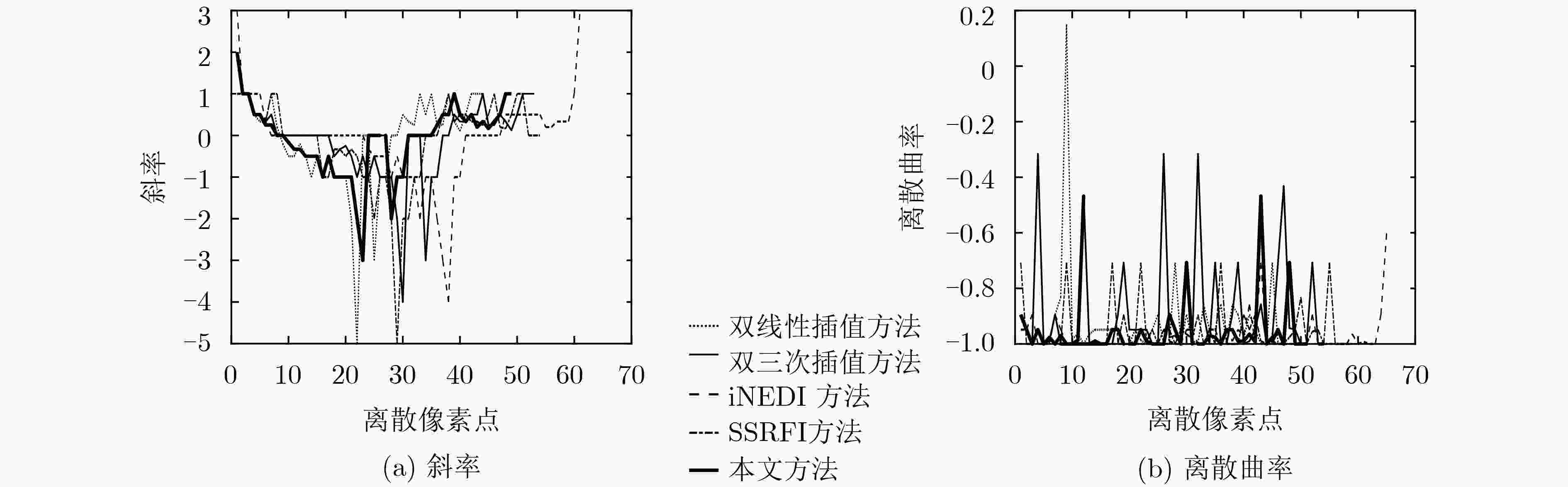
该文提出一种基于虚拟光学的视觉显著目标高分辨率可控放大重建方法。原始图像放置于虚拟光路物平面,首先通过衍射逆计算获得原始图像在虚拟衍射面的光波信号,再对虚拟衍射面光波用球面波照射后作正向衍射计算,通过改变观测平面位置可重建出不同放大率的原始图像。仿真测试结果表明,与一般的插值放大方法相比,所获得的放大后的图像特别是在显著性区域表示出良好的视觉感知效果。将包含人脸的低分辨率降质图像作为待重建信号,所重建人脸的显著性区域如眼睛、鼻子等比一般重建方法更清晰。用水平集方法结合显著图分割出原始图像中的局部显著区域并作放大重建和轮廓提取,轮廓表现出良好的光滑性。
Abstract:A high-resolution controllable magnification method for visual saliency object based on virtual optics is proposed in this paper. The original image is placed on the virtual object plane. Firstly, the diffractive wave of the original image on the virtual diffraction plane is obtained by inverse diffraction calculation, and then the forward diffraction calculation is carried out after the virtual diffraction wave is irradiated by spherical wave. The original images with different magnification can be reconstructed by changing the position of the observation plane. The simulation results show that compared with the general interpolation method, the magnified image shows a good visual perception effect, especially in the saliency region. When the degraded face image is used as the signal to be reconstructed, the significant areas such as eyes and nose are clearer than the general method. The local salient region in the original image is segmented by the level set method combined with salient map, and the magnification and contour extraction are performed. The contours show good smoothness.
-
Key words:
- Image segmentation /
- Virtual optics /
- Saliency object /
- Controllable magnification
-
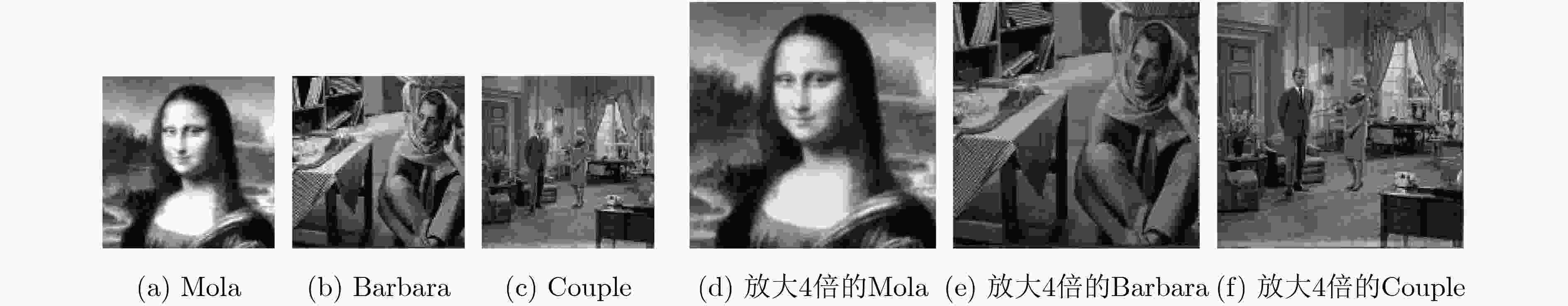
表 1 放大重建像质量指标
测试图像 NMSE NLVE SFM 归一化相关系数 Mola 0.1057 0.0157 0.0042 0.9977 Barbara 0.1106 0.0145 0.0019 0.9963 Couple 0.1045 0.0021 0.0022 0.9956 平均值 0.0769 0.0108 0.0027 0.9965 -
PARK S C, PARK M K, and KANG M G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2003, 20(3): 21–36. doi: 10.1109/msp.2003.1203207 LI Xin and ORCHARD M T. New edge-directed interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(10): 1521–1527. doi: 10.1109/83.951537 ASUNI N and GIACHETTI A. Accuracy improvements and artifacts removal in edge based image interpolation[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, Funchal, Portugal, 2008: 58–65. ZHANG Yunfeng, FAN Qinglan, BAO Fangxun, et al. Single-image super-resolution based on rational fractal interpolation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(8): 3782–3797. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2826139 YANG Wenhan, FENG Jiashi, YANG Jianchao, et al. Deep edge guided recurrent residual learning for image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(12): 5895–5907. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2750403 MORSE B S and SCHWARTZWALD D. Image magnification using level-set reconstruction[C]. 2011 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, USA, 2001: 333–340. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2001.990494. RATAKONDA K and AHUJA N. POCS based adaptive image magnification[C]. 1998 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Chicago, USA, 1998: 203–207. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.1998.727167. CAI Qing, LIU Huiying, QIAN Yiming, et al. Saliency-guided level set model for automatic object segmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 93: 147–163. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.04.019 李俊昌, 樊则宾. 彩色数字全息的非插值波面重建算法研究[J]. 物理学报, 2010, 59(4): 2457–2461. doi: 10.7498/aps.59.2457LI Junchang and FAN Zebin. Algorithm of the non-interpolation wave-front reconstruction of the color digital holography[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2010, 59(4): 2457–2461. doi: 10.7498/aps.59.2457 李俊昌, 熊秉衡. 信息光学教程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 45–57.LI Junchang and XIONG Bingheng. Information Optics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 45–57. LI Junchang, PENG Zujie, TANKAM P, et al. Digital holographic reconstruction of a local object field using an adjustable magnification[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2011, 28(6): 1291–1296. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.28.001291 RESTREPO J F and GARCIA-SUCERQUIA J. Magnified reconstruction of digitally recorded holograms by Fresnel-Bluestein transform[J]. Applied Optics, 2010, 49(33): 6430–6435. doi: 10.1364/AO.49.006430 GOODMAN J W. Introduction to Fourier Optics[M]. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Editions, 1996: 88–110. SCHNARS U and JÜPTNER W P O. Digital recording and numerical reconstruction of holograms[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2002, 13(9): R85–R101. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/13/9/201 QIN Yao, LU Huchuan, XU Yiqun, et al. Saliency detection via cellular automata[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 110–119. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298606. LI Chunming, XU Chenyang, GUI Changfeng, et al. Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(12): 3243–3254. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2069690 CANNY J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, PAMI-8(6): 679–698. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767851 吴援明, 梁恩志. 一种基于熵的放大后图像质量的评价方法[J]. 信号处理, 2004, 20(2): 201–203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2004.02.022WU Yuanming and LIANG Enzhi. A new method of zoomed images evaluation[J]. Signal Processing, 2004, 20(2): 201–203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2004.02.022 HOU Xiaodi and ZHANG Liqing. Saliency detection: A spectral residual approach[C]. 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2007.383267. QIN Yi, GONG Qiong, WANG Zhipeng, et al. Optical multiple-image encryption in diffractive-imaging-based scheme using spectral fusion and nonlinear operation[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(23): 26877–26886. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.026877 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
