Moving Object Detection Method Based on Low-Rank and Sparse Decomposition in Dynamic Background
-
摘要: 针对背景运动引起动目标检测精度显著下降的问题,该文提出一种基于低秩及稀疏分解的动目标检测方法。所提方法首先引入伽马范数(
$\gamma {\rm{ - norm}}$ )近乎无偏地逼近秩函数以解决核范数过度惩罚较大奇异值从而导致所得最小化问题无法获得最优解进而降低检测性能的问题,而后利用${L_{{1 / 2}}}$ 范数抽取稀疏前景目标以增强对噪声的稳健性,同时基于虚警像素所具有稀疏且空间不连续特性提出空间连续性约束以抑制动态背景像素,进而构建目标检测模型。最后利用基于交替方向最小化(ADM)策略扩展的增广拉格朗日乘子(ALM)法对所得优化问题求解。实验结果表明,与现有主流算法对比,所提方法可显著改善动态背景情况下动目标检测精度。Abstract: Focusing on the issue that the detection accuracy of moving object is significantly reduced by background motion, a low-rank and sparse decomposition based moving object detection method is developed. Firstly, in order to solve the problem that the nuclear norm over-penalizing large singular values lead to the optimal solution of the obtained minimization problem can not be obtained and then the detection performance is decreased, the gamma norm ($\gamma {\rm{ - norm}}$ ) is introduced to acquire almost unbiased approximation of rank function. In what follows, the${L_{{1 / 2}}}$ norm is used to extract the sparse foreground object to enhance the robustness to noise, and the spatial continuity constraint is proposed to suppress dynamic background pixels such that the moving object detection model can be constructed on the basis of the sparse and spatially discontinuous nature of the false alarm pixels. After that, the Augmented Lagrange Multiplier (ALM) method, which is the extension of the Alternating Direction Minimizing (ADM) strategy, can be employed to deal with the acquired constrained minimization problem. Compared with some state-of-the-art algorithms, the experimental results show that the proposed method can significantly improve the accuracy of moving object detection in the case of dynamic background.-
Key words:
- Foreground detection /
- Dynamic background /
- Low-rank /
- Sparsity /
- L1/2 regularization
-
表 1 低秩与稀疏分解动目标检测方法
算法:使用ADM策略扩展的ALM法求解问题式(7) 输入:观测矩阵${{Z}}$,参数$\gamma $, ${\lambda _1}$, ${\lambda _2}$, ${\mu _1}$, ${\mu _2}$和$\varphi $。 输出:${{H}}$, ${{K}}$和${{G}}$。 (1):固定其他变量,计算式(12)以更新变量${{H}}$; (2):固定其他变量,由式(17)更新变量${{K}}$; (3):固定其他变量,计算式(22)以更新变量${{G}}$; (4):由式(23)和式(24)更新拉格朗日乘子${{{Y}}_1}$和${{{Y}}_2}$; (5):重复步骤(1)—(4),直至满足收敛条件。 表 2 不同场景下6种算法评价指标平均值
评价指标 PCP MoG PRMF DEC BRPCA 本文算法 Precision 0.4715 0.4896 0.5556 0.6938 0.7908 0.8967 Recall 0.7888 0.7978 0.8193 0.9199 0.8953 0.9181 F-measure 0.5440 0.5885 0.6387 0.7643 0.8333 0.9022 表 3 不同动目标检测算法平均运行时间对比(s)
算法 PCP MoG PRMF DEC BRPCA 本文算法 运行时间 541.55 177.70 105.31 288.36 6161.29 498.42 -
LUO Yuan, ZHOU Hanxing, TAN Qin, et al. Key frame extraction of surveillance video based on moving object detection and image similarity[J]. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 2018, 28(2): 225–231. doi: 10.1134/S1054661818020190 SENTHIL M A, SUGANYA D K, SIVARANJANI A, et al. A study on various methods used for video summarization and moving object detection for video surveillance applications[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(3): 23273–23290. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5671-8 CHEN Changhong, LIANG Jimin, ZHAO Heng, et al. Frame difference energy image for gait recognition with incomplete silhouettes[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2009, 30(11): 977–984. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2009.04.012 KE Ruimin, LI Zhibin, TANG Jinjun, et al. Real-time traffic flow parameter estimation from UAV video based on ensemble classifier and optical flow[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(1): 54–64. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2797697 YONG Hongwei, MENG Deyu, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Robust online matrix factorization for dynamic background subtraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(7): 1726–1740. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2732350 LIU Hongkun, DAI Jialun, WANG Ruchen, et al. Combining background subtraction and three-frame difference to detect moving object from underwater video[C]. OCEANS 2016, Shanghai, China, 2016: 1–5. SEVILLA-LARA L, SUN Deqing, JAMPANI V, et al. Optical flow with semantic segmentation and localized layers[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3889–3898. PRASAD D K, PRASATH C K, RAJAN D, et al. Object detection in a maritime environment: Performance evaluation of background subtraction methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(5): 1787–1802. doi: 10.1109/tits.2018.2836399 ZENG Zhi, JIA Jianyuan, YU Dalin, et al. Pixel modeling using histograms based on fuzzy partitions for dynamic background subtraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(3): 584–593. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2566811 STAUFFER C and GRIMSON W E L. Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking[C]. 1999 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Fort Collins, USA, 1999: 246–252. ZIVKOVIC Z. Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction[C]. The 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 2004: 28–31. CANDÈS E J, LI Xiaodong, MA Yi, et al. Robust principal component analysis?[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2011, 58(3): 11. doi: 10.1145/1970392.1970395 DING Xinghao, HE Lihan, and CARIN L. Bayesian robust principal component analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(12): 3419–3430. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2156801 GAO Junbin. Robust L1 principal component analysis and its Bayesian variational inference[J]. Neural Computation, 2008, 20(2): 555–572. doi: 10.1162/neco.2007.11-06-397 WANG Naiyan, YAO Tiansheng, WANG Jingdong, et al. A probabilistic approach to robust matrix factorization[C]. The 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 126–139. ZHOU Xiaowei, YANG Can, and YU Weichuan. Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(3): 597–610. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.132 WANG Yi, JODOIN P M, PORIKLI F, et al. CDnet 2014: An expanded change detection benchmark dataset[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, USA, 2014: 393–400. WANG Shusen, LIU Dehua, and ZHANG Zhihua. Nonconvex relaxation approaches to robust matrix recovery[C]. The 23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Beijing, China, 2013: 1764–1770. JIA Sen, ZHANG Xiujun, and LI Qingquan. Spectral–spatial hyperspectral image classification using ℓ1/2 regularized low-rank representation and sparse representation-based graph cuts[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(6): 2473–2484. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2423278 ZHANG Hengmin, YANG Jian, XIE Jianchun, et al. Weighted sparse coding regularized nonconvex matrix regression for robust face recognition[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 394–395: 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.02.020 CAO Wenfei, SUN Jian, and XU Zongben. Fast image deconvolution using closed-form thresholding formulas of regularization[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2013, 24(1): 31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2012.10.006 CAO Xiaochun, YANG Liang, and GUO Xiaojie. Total variation regularized RPCA for irregularly moving object detection under dynamic background[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(4): 1014–1027. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2419737 CHAMBOLLE A. An algorithm for total variation minimization and applications[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2004, 20(1/2): 89–97. doi: 10.1023/b:jmiv.0000011325.36760.1e XUE Yawen, GUO Xiaojie, and CAO Xiaochun. Motion saliency detection using low-rank and sparse decomposition[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 2012: 1485–1488. XU Zongben, CHANG Xiangyu, XU Fengmin, et al. L1/2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(7): 1013–1027. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2197412 BECK A and TEBOULLE M. Fast gradient-based algorithms for constrained total variation image denoising and deblurring problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(11): 2419–2434. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2028250 MAHADEVAN V and VASCONCELOS N. Spatiotemporal saliency in dynamic scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(1): 171–177. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.112 GOLUB G H and REINSCH C. Singular value decomposition and least squares solutions[J]. Numerische Mathematik, 1970, 14(5): 403–420. doi: 10.1007/BF02163027 -









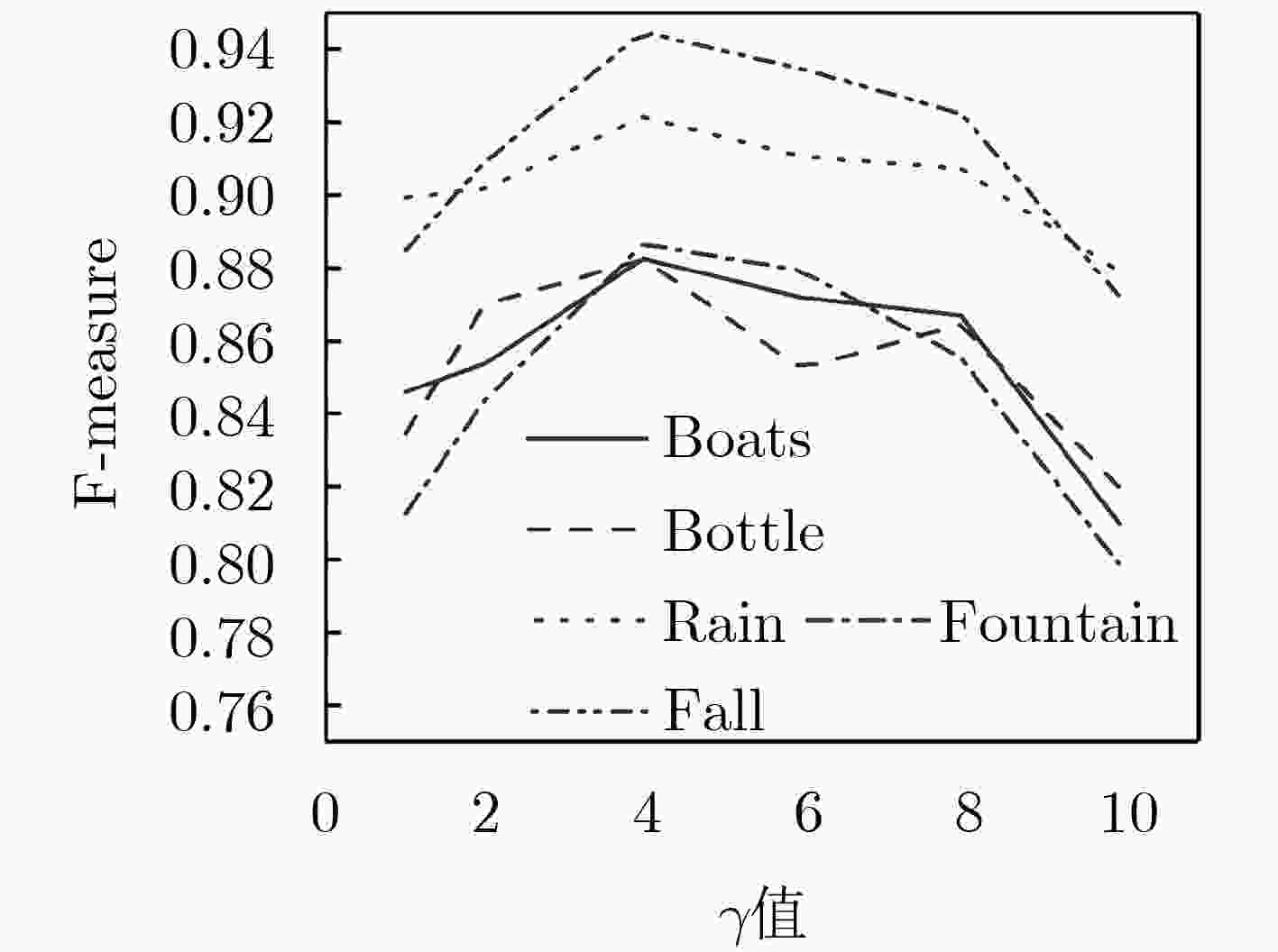

 下载:
下载:
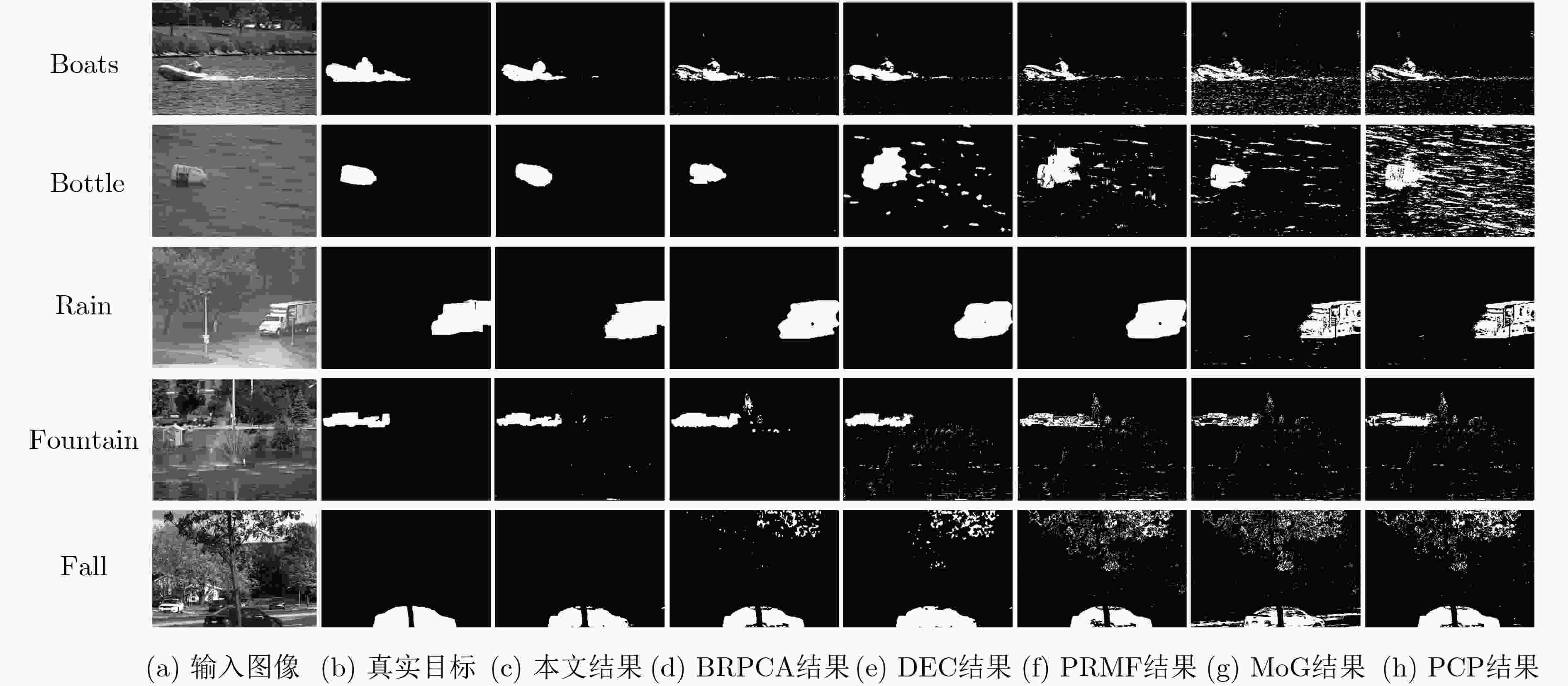
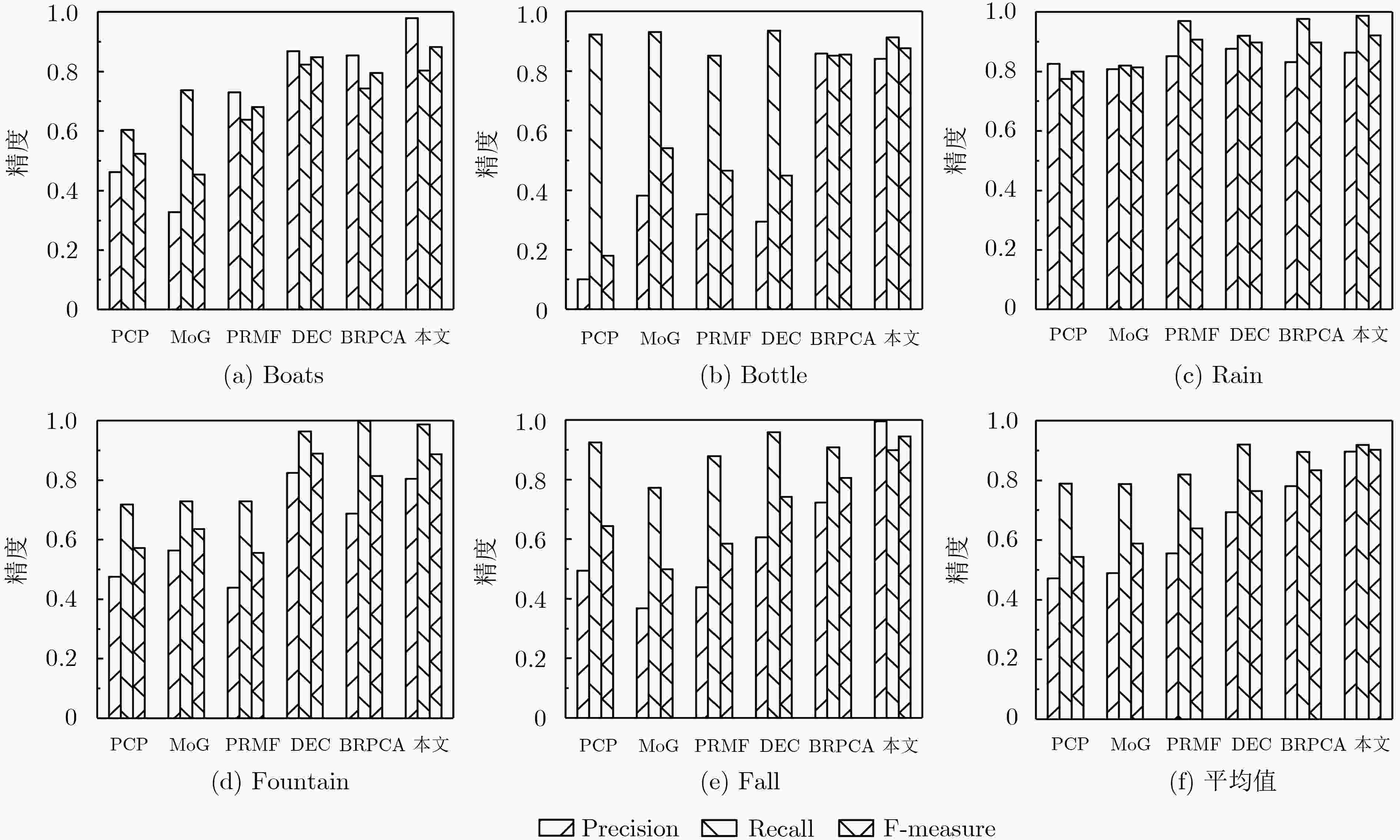
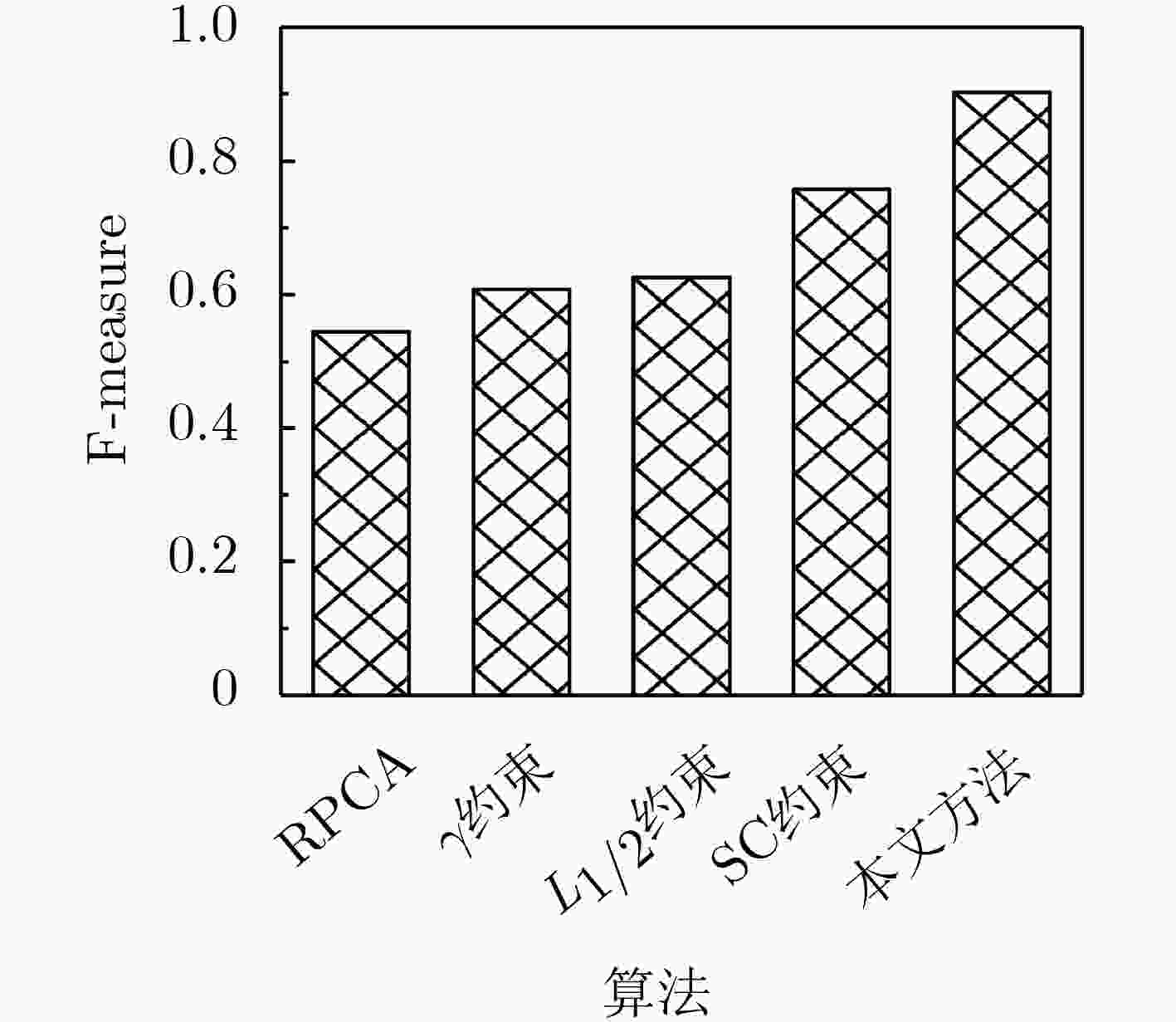


 下载:
下载:
