Measurement of Node Influence Based on Three-level Neighbor in Complex Networks
-
摘要:
已有的节点影响力度量方法均存在一定的局限性。该文基于三度影响力原则,综合考虑局部度量的适宜层次及大规模网络的可扩展性,提出一种基于3级邻居的节点影响力度量方法(TIM)。该方法将节点2, 3级具有传播衰减特性的邻居视为整体,用于度量节点的影响能力。利用传染病模型及独立级联模型,在3个真实数据集验证了该方法的有效性。实验结果表明,基于3级邻居的节点影响力度量方法在影响力一致性、区分度、排序性等指标中表现优越,且能够有效求解影响力最大化问题。
Abstract:There are some limitations in the existing metric methods for measuring node influence. A measurement method of node influence with three-level neighbors is proposed, which is based on the principle of three-degree influence, and considering the appropriate level of local measurement and the scalability of the large-scale network. Firstly, the neighbors with propagation attenuation characteristics in the second and third level of a node are regarded as a whole, which is used to measure the influence of the node. Then, an algorithm for measure called Three-level Influence Measurement (TIM) is proposed. Finally, in order to validate the effectiveness of the algorithm, the experiments on three datasets are conducted by using susceptible-infected-recovered model and independent cascade model. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is superior in consistency of influence, discrimination, sorting performance and other evaluation indexes. Furthermore, the TIM is applied to effectively solve the problem of maximizing influence.
-
Key words:
- Complex networks /
- Influence of nodes /
- Influence maximization
-
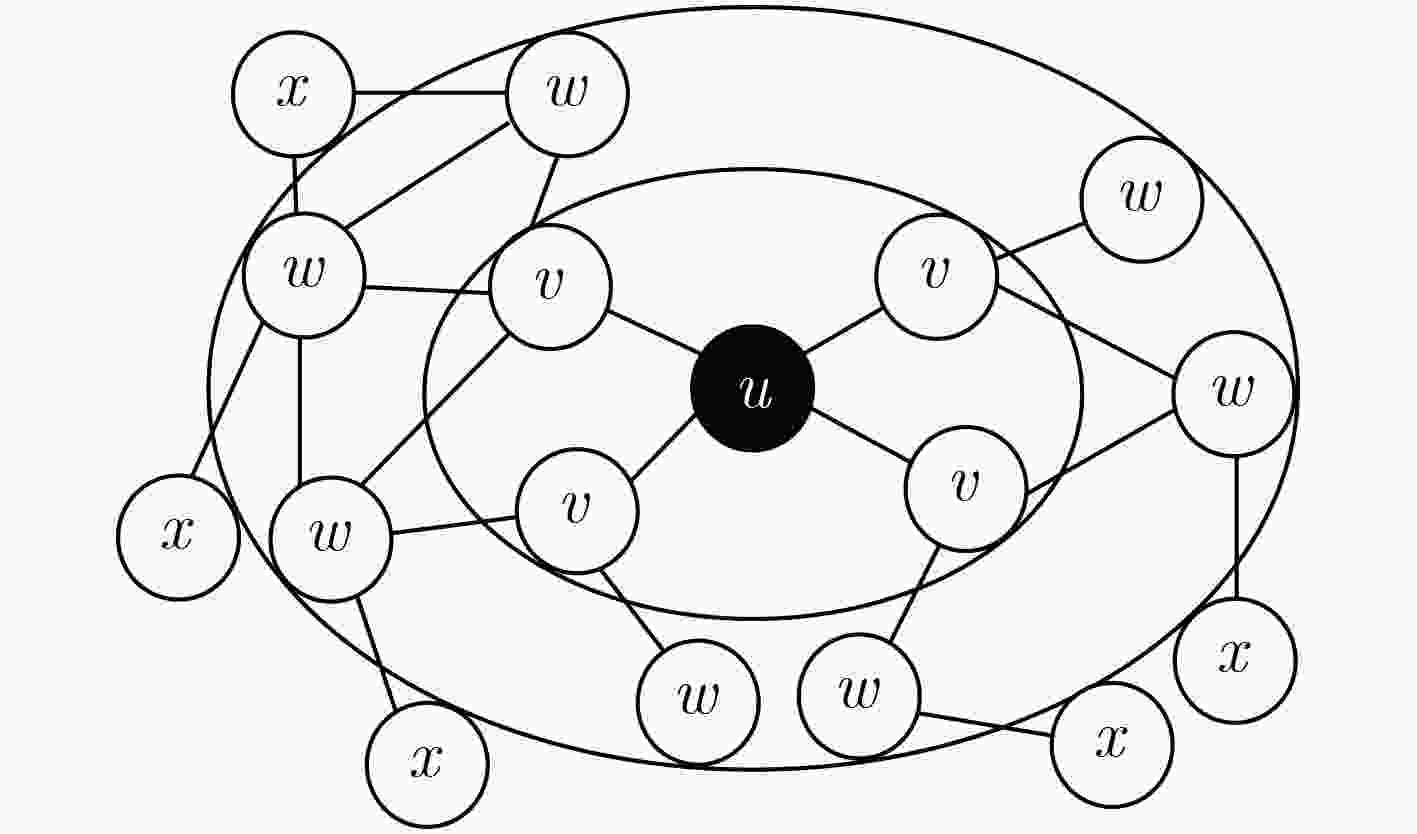
算法1 TIM度量方法 输入: G=(V, E, P) /*P 表示传播概率*/
输出: 每个节点的TIM度量值(1) function: F(·) /*1级邻居的层序遍历函数*/ (2) for each u in V do: (3) TIM(u) = 0, x=0, l=0 /*l 为集合的长度*/ (4) for each v in F(u) do: (5) x += p(u, v) (6) end for (7) TIM(u) = $\theta \cdot $ exp(x) (8) for each v in F(u) do: (9) for each w in F(v) \{u} do: (10) l=getSize ( {F(w) , w } \{ F(u)}) (11) TIM(u) += p(u, v) × p(v, w) × l (12) end for (13) end for (14) end for 表 1 网络数据集基本特征
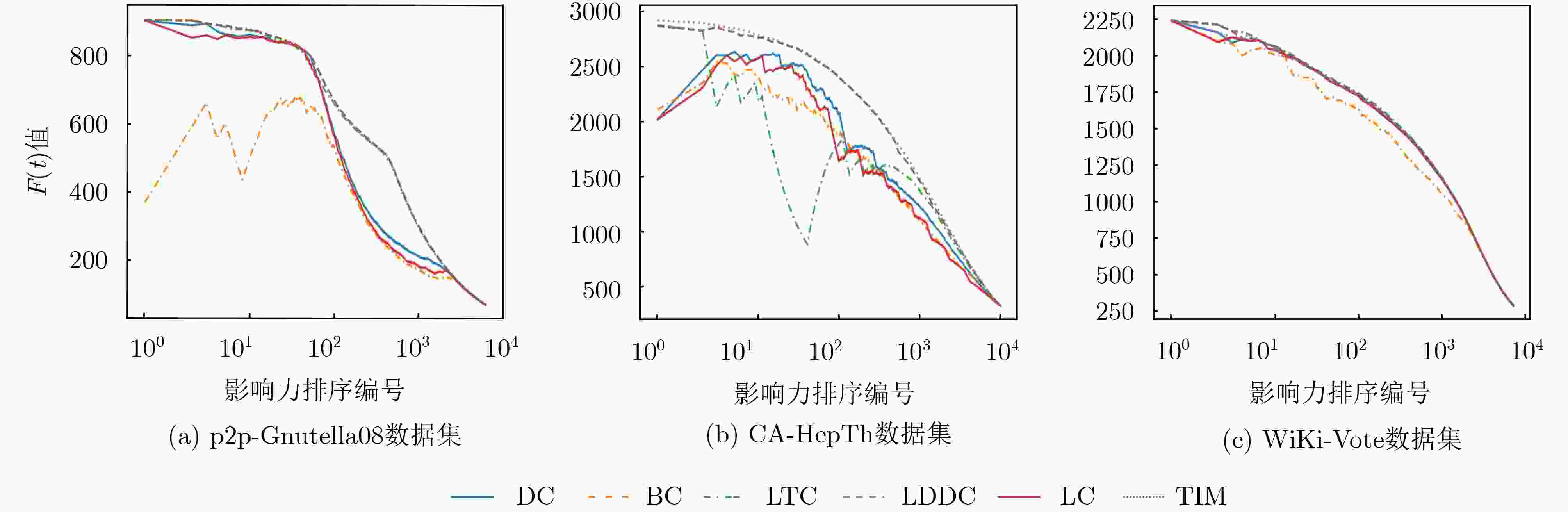
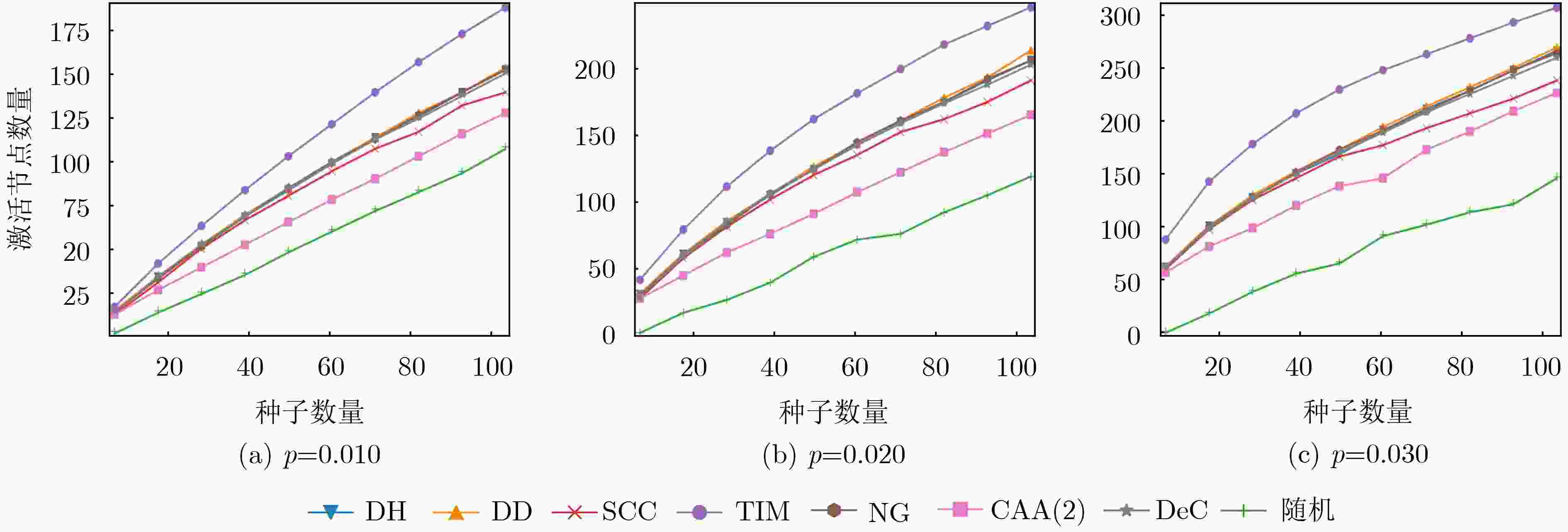
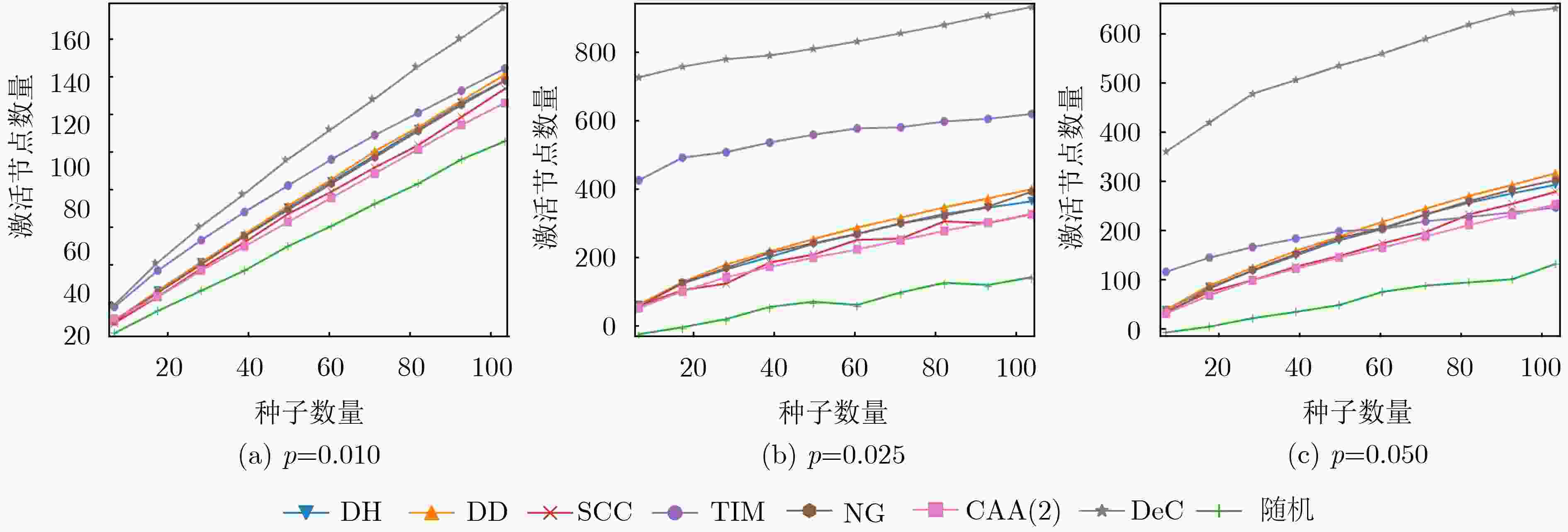
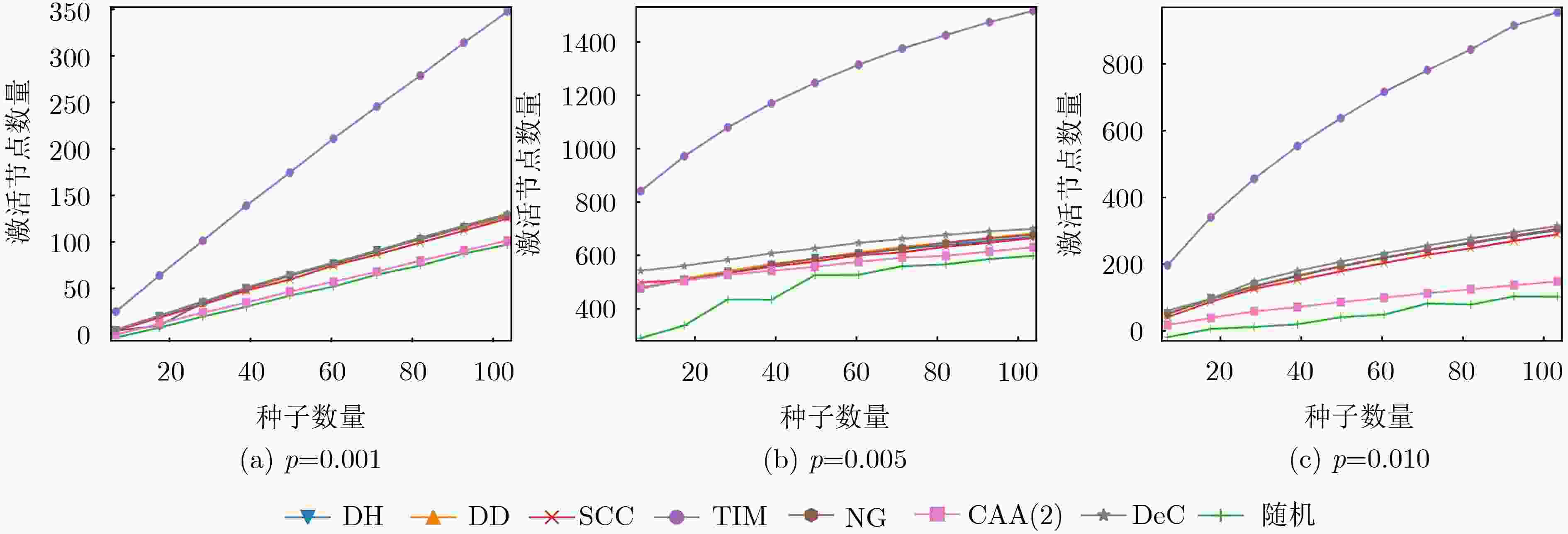
p2p-Gnutella08 CA-HepTh WiKi-Vote 节点数 6301 9877 7115 边数 20777 51971 100762 平均度 6.595 5.264 28.324 聚类系数 0.015 0.600 0.209 表 2 精度提高比(%)
p2p-Gnutella08 Wiki-Vote CA-HepTh Top-10 10.00 133.33 36.00 Top-20 22.58 280.00 16.46 Top-30 15.87 278.69 5.41 Top-40 2.20 291.60 16.09 Top50 7.56 272.59 3.32 Top-60 15.61 286.55 11.71 Top-70 13.77 263.78 10.25 Top-80 9.44 323.90 21.49 Top-90 2.71 241.53 7.13 Top-100 1.47 229.58 5.86 Avg 10.12 260.16 13.37 表 3 区分度实验结果
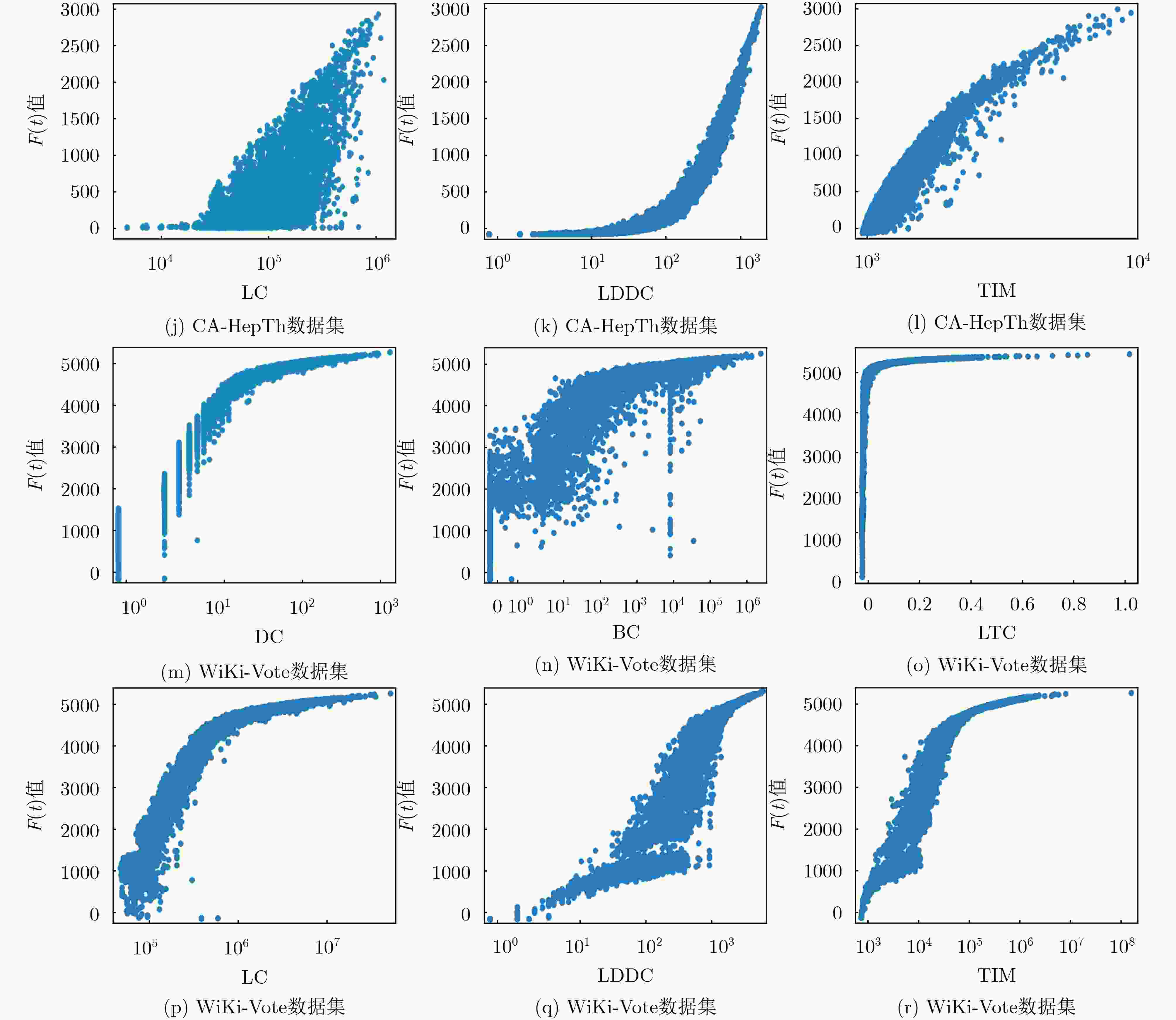
方法 p2p-Gnutella08 WiKi-Vote CA-HepTh DC 0.01206 0.04216 0.00557 LTC 0.05055 0.05205 0.04454 BC 0.71861 0.64216 0.40376 LC 0.85129 0.80689 0.72161 LDDC 0.60705 0.60899 0.32672 TIM 0.98905 0.99874 0.91789 表 4 运行时间 (s)
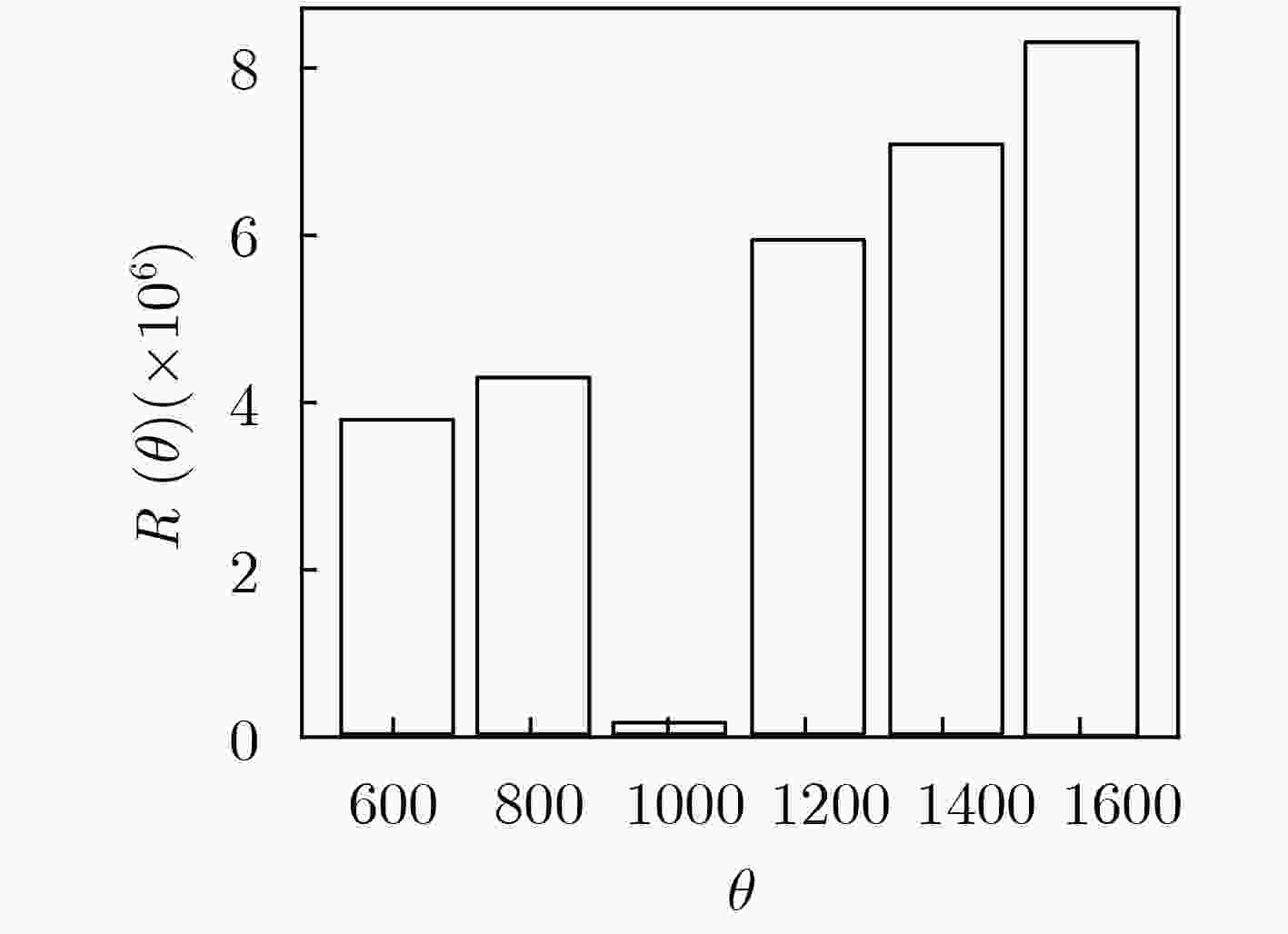
数据集 传播概率 DH DD 随机 SCC TIM NG CCA(2) DeC p2p-Gnutella08 p=0.010 0.022 0.027 0.002 0.025 0.258 0.406 0.041 0.046 p=0.020 0.028 0.029 0.003 0.036 0.278 0.415 0.043 0.058 p=0.030 0.038 0.034 0.005 0.038 0.320 0.423 0.045 0.063 CA-HepTH p=0.010 0.014 0.017 0.0016 0.019 0.194 0.573 0.054 0.030 p=0.025 0.021 0.021 0.0025 0.027 0.239 0.645 0.062 0.059 p=0.050 0.038 0.045 0.0062 0.034 0.325 0.792 0.076 0.161 WiKi-Vote p=0.001 0.141 0.136 0.011 0.157 0.517 1.921 0.434 0.412 p=0.005 0.249 0.265 0.026 0.261 0.651 1.947 0.481 0.526 p=0.010 0.793 0.776 0.480 0.772 1.153 2.434 0.975 1.001 -
刘阳, 季新生, 刘彩霞. 一种基于边界节点识别的复杂网络局部社区发现算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(12): 2809–2815. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01955LIU Yang, JI Xinsheng, and LIU Caixia. Detecting local community structure based on the identification of boundary nodes in complex networks[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2014, 36(12): 2809–2815. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01955 田晶, 方华强, 刘佳佳, 等. 运用复杂网络方法分析城市道路网的鲁棒性[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(5): 771–777. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20150334TIAN Jing, FANG Huaqiang, LIU Jiajia, et al. Robustness analysis of urban street networks using complex network method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(5): 771–777. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20150334 王凯, 刘树新, 于洪涛, 等. 基于共同邻居有效性的复杂网络链路预测算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2019, 48(3): 432–439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.03.020WANG Kai, LIU Shuxin, YU Hongtao, et al. Predicting missing links of complex network via effective common neighbors[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019, 48(3): 432–439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.03.020 韩忠明, 刘雯, 李梦琪, 等. 基于节点向量表达的复杂网络社团划分算法[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(4): 1045–1061. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005387HAN Zhongming, LIU Wen, LI Mengqi, et al. Community detection algorithm based on node embedding vector representation[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(4): 1045–1061. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005387 韩忠明, 陈炎, 李梦琪, 等. 一种有效的基于三角结构的复杂网络节点影响力度量模型[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(16): 168901. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.168901HAN Zhongming, CHEN Yan, LI Mengqi, et al. An efficient node influence metric based on triangle in complex networks[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(16): 168901. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.168901 杨青林, 王立夫, 李欢, 等. 基于相对距离的复杂网络谱粗粒化方法[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(10): 100501. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181848YANG Qinglin, WANG Lifu, LI Huan, et al. A spectral coarse graining algorithm based on relative distance[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(10): 100501. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20181848 林冠强, 莫天文, 叶晓君, 等. 基于TOPSIS和CRITIC法的电网关键节点识别[J]. 高电压技术, 2018, 44(10): 3383–3389. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180925030LIN Guanqiang, MO Tianwen, YE Xiaojun, et al. Critical node identification of power networks based on TOPSIS and CRITIC methods[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2018, 44(10): 3383–3389. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20180925030 CHRISTAKIS N A and FOWLER J H. Social contagion theory: Examining dynamic social networks and human behavior[J]. Statistics in Medicine, 2013, 32(4): 556–577. doi: 10.1002/sim.5408 CHRISTAKIS N A and FOWLER J H. Connected: The Surprising Power of Our Social Networks and How They Shape Our Lives[M]. New York: Little, Brown and Company, 2009: 30–117. 许小可, 胡海波, 张伦, 等. 社交网络上的计算传播学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015: 163–198.XU Xiaoke, HU Haibo, ZHANG Lun, et al. Computational Communication in Social Networks[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015: 163–198. 陈晓龙. 社会网络影响力最大化算法及其传播模型研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2016: 20–22.CHEN Xiaolong. Research on influence maximization and diffusion model in social networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2016: 20–22. 王俊, 余伟, 胡亚慧, 等. 基于3-layer中心度的社交网络影响力最大化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2014, 41(1): 59–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2014.01.009WANG Jun, XU Wei, HU Yahui, et al. Heuristic algorithm based on 3-layer centrality for influence maximization in social networks[J]. Computer Science, 2014, 41(1): 59–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2014.01.009 CHEN Duanbing, LÜ Linyuan, SHANG Mingsheng, et al. Identifying influential nodes in complex networks[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2012, 391(4): 1777–1787. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.09.017 FREEMAN L C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness[J]. Sociometry, 1977, 40(1): 35–41. doi: 10.2307/3033543 LI Jianxin, LIU Chengfei, XU J X, et al. Personalized influential topic search via social network summarization[C]. The 33rd IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, San Diego, USA, 2016: 1820–1834. doi: 10.1109/ICDE.2017.15. CHEN Wei, WANG Yajun, and YANG Siyu. Efficient influence maximization in social networks[C]. The 15th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Paris, France, 2009: 199–208. doi: 10.1145/1557019.1557047. KEMPE D, KLEINBERG J, and TARDOS É. Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network[C]. The 9th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, USA, 2003: 137–146. doi: 10.1145/956750.956769. 曹玖新, 董丹, 徐顺, 等. 一种基于k-核的社会网络影响最大化算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(2): 238–248. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.00238CAO Jiuxin, DONG Dan, XU Shun, et al. A k-core based algorithm for influence maximization in social networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(2): 238–248. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2015.00238 IBNOULOUAFI A and EL HAZITI M. Density centrality: Identifying influential nodes based on area density formula[J]. Chaos,Solitons&Fractals, 2018, 114: 69–80. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2018.06.022 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
