Joint Congestion Control and Resource Allocation Dynamic Scheduling Strategy for Network Slices in Heterogeneous Cloud Raido Access Network
-
摘要:
针对异构云无线接入网络(H-CRAN)网络下基于网络切片的在线无线资源动态优化问题,该文通过综合考虑业务接入控制、拥塞控制、资源分配和复用,建立一个以最大化网络平均和吞吐量为目标,受限于基站(BS)发射功率、系统稳定性、不同切片的服务质量(QoS)需求和资源分配等约束的随机优化模型,并进而提出了一种联合拥塞控制和资源分配的网络切片动态资源调度算法。该算法会在每个资源调度时隙内动态地为性能需求各异的网络切片中的用户分配资源。仿真结果表明,该文算法能在满足各切片用户QoS需求和维持网络稳定的基础上,提升网络整体吞吐量,并且还可通过调整控制参量的取值实现时延和吞吐量间的动态平衡。
Abstract:For online dynamic radio resources optimization for network slices in Heterogeneous Cloud Raido Access Network (H-CRAN), by comprehensively considering traffic admission control, congestion control, resource allocation and reuse, the problem is formulated as a stochastic optimization programming which maximizes network average total throughput subject to Base Station (BS) transmit power, system stability, Quality of Service (QoS) requirements of different slices and resource allocation constraints. Then, a joint congestion control and resource allocation dynamic scheduling algorithm is proposed which will dynamically allocate resources to users in network slices with distinct performance requirements within each resource scheduling time slot. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can improve the network overall throughput while satisfying the QoS requirement of each slice user and maintaining network stability. Besides, it could also flexibly strike a dynamic balance between delay and throughput by simply tuning an introduced control parameter.
-
表 1 H-CRAN网络下联合拥塞控制和资源分配的网络切片动态资源调度算法
(1) 初始化控制参量$V > 0$、各用户的初始队列长度${Q_u}(0),\forall u \in {\cal{U}}$和最大时隙数${T^{\max }}$初始化最大迭代次数$T_0^{\max }$和允许误差$\delta $ (2) for $t = 0,1, ··· ,{T^{\max } } - 1$ (3) 根据式(24)分别计算各用户当前时隙最优的流量接入控制策略 (4) Repeat: (5) 令迭代索引$n = 1$,初始化拉格朗日乘子${{\lambda}} $, ${{\eta }}$和${{\mu}} $ (6) for $s \in {\cal{S}}$ (7) 计算子载波$s$当前时隙(近似)最优的子载波复用、分配和功率分配策略${\alpha _s}^*$, ${{\beta}} _s^*$和${{{P}}_s}^*$,进而更新各用户剩余的排队队列长度 (8) 若某用户$u \in {\cal{U}}$已经获得了足够的子载波(即其队列长度为0),则将其从接下来的子载波分配过程中排除。 (9) 若所有用户均分配到足够的子载波,则break (10) end for (11) 根据得到的(近似)最优子载波复用、分配和功率分配策略${\alpha ^*}$, ${\beta ^*}$和${P^*}$计算拉格朗日函数${\cal{L}}{\left( {\alpha ,\beta ,P,\lambda ,\eta ,\mu } \right)^{(n)}}$ (12) Until$\left| { {\cal{L} }{ {\left( {\alpha ,\beta ,P,\lambda ,\eta ,\mu } \right)}^{(n)} } - {\cal{L} }{ {\left( {\alpha ,\beta ,P,\lambda ,\eta ,\mu } \right)}^{(n - 1)} } } \right| \le \delta $ or $n > T_0^{\max }$, then stop Otherwise, 利用次梯度法更新拉格朗日乘子$\lambda $,
$\eta $和$\mu $,令$n = n + 1$并返回第6步(13) 根据式(17)更新各用户在下一时隙的业务队列长度 (14) end for (15) 输出:(近似)最优流量接入控制、子载波复用和分配以及功率分配策略$r$, $\alpha $, $\beta $和$P$,${Q_u}(t),\forall u \in {\cal{U}},t$。 -
Cisco System. Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2017–2022 White Paper[R/OL]. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/white-paper-c11-738429.html, 2019. LI Xin, SAMAKA M, CHAN H A, et al. Network slicing for 5G: challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Internet Computing, 2017, 21(5): 20–27. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2017.3481355 ITU-R. IMT vision-framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond[EB/OL]. http://www.itu.int/pub/R-REC/en. 2020. LI Jian, PENG Mugen, YU Yuling, et al. Energy-efficient joint congestion control and resource optimization in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(12): 9873–9887. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2531184 ZHANG Haijun, WANG Baobao, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. Energy efficient dynamic resource optimization in NOMA system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(9): 5671–5683. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2844359 DANG Tian and PENG Mugen. Delay-aware radio resource allocation optimization for network slicing in fog radio access networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCW.2018.8403717. AMANI N, PEDRAM H, TAHERI H, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks via BBU offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(2): 1365–1377. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2882466 KIM T and CHANG J M. Profitable and energy-efficient resource optimization for heterogeneous cloud-based radio access networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 34719–34737. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904766 ZHANG Biling, MAO Xingwang, YU J L, et al. Resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous cloud radio access networks with D2D communication: a matching and coalition approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(7): 5883–5894. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2802900 唐伦, 魏延南, 马润琳, 等. 虚拟化云无线接入网络下基于在线学习的网络切片虚拟资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(7): 1533–1539. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180771TANG Lun, WEI Yannan, MA Runlin, et al. Online learning-based virtual resource allocation for network slicing in virtualized cloud radio access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(7): 1533–1539. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180771 MEI Jie, ZHENG Kan, ZHAO Long, et al. A latency and reliability guaranteed resource allocation scheme for LTE V2V communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(6): 3850–3860. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2816942 NEELY M J. Stochastic network optimization with application to communication and queueing systems[J]. Synthesis Lectures on Communication Networks, 2010, 3(1): 15–62. doi: 10.2200/S00271ED1V01Y201006CNT007 MOKDAD A, AZMI P, MOKARI N, et al. Cross-layer energy efficient resource allocation in PD-NOMA based H-CRANs: implementation via GPU[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(6): 1246–1259. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2860985 TANG Liya, ZHANG Xian, XIANG Hongyu, et al. Joint resource allocation and caching placement for network slicing in fog radio access networks[C]. The 18th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Sapporo, Japan, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC.2017.8227791. LEE Y L, LOO J, CHUAH T C, et al. Dynamic network slicing for multitenant heterogeneous cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2146–2161. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2789294 TANG Lun, YANG Xixi, WU Xiaolin, et al. Queue stability-based virtual resource allocation for virtualized wireless networks with self-backhauls[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 13604–13616. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2797088 -






 下载:
下载:
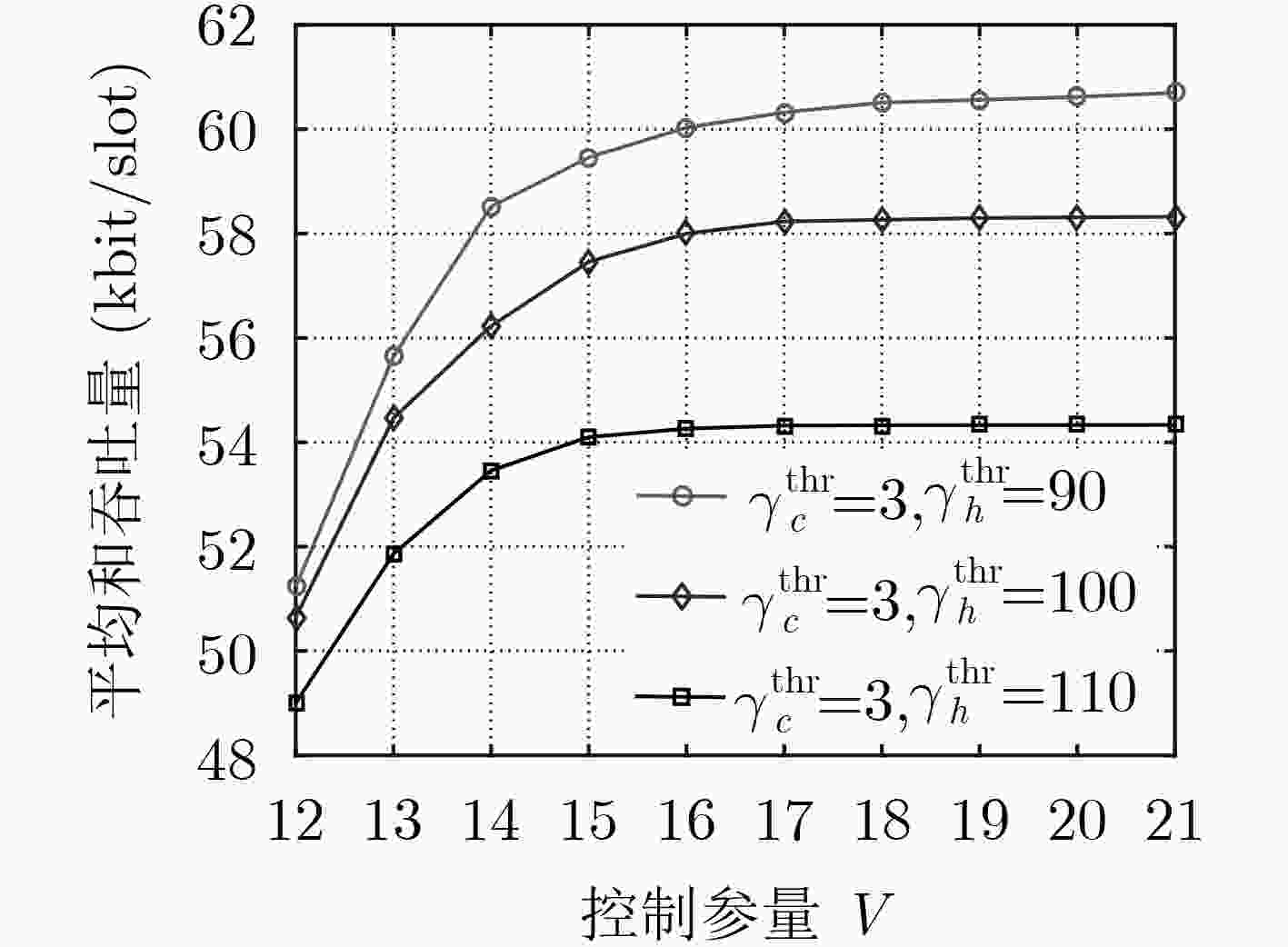
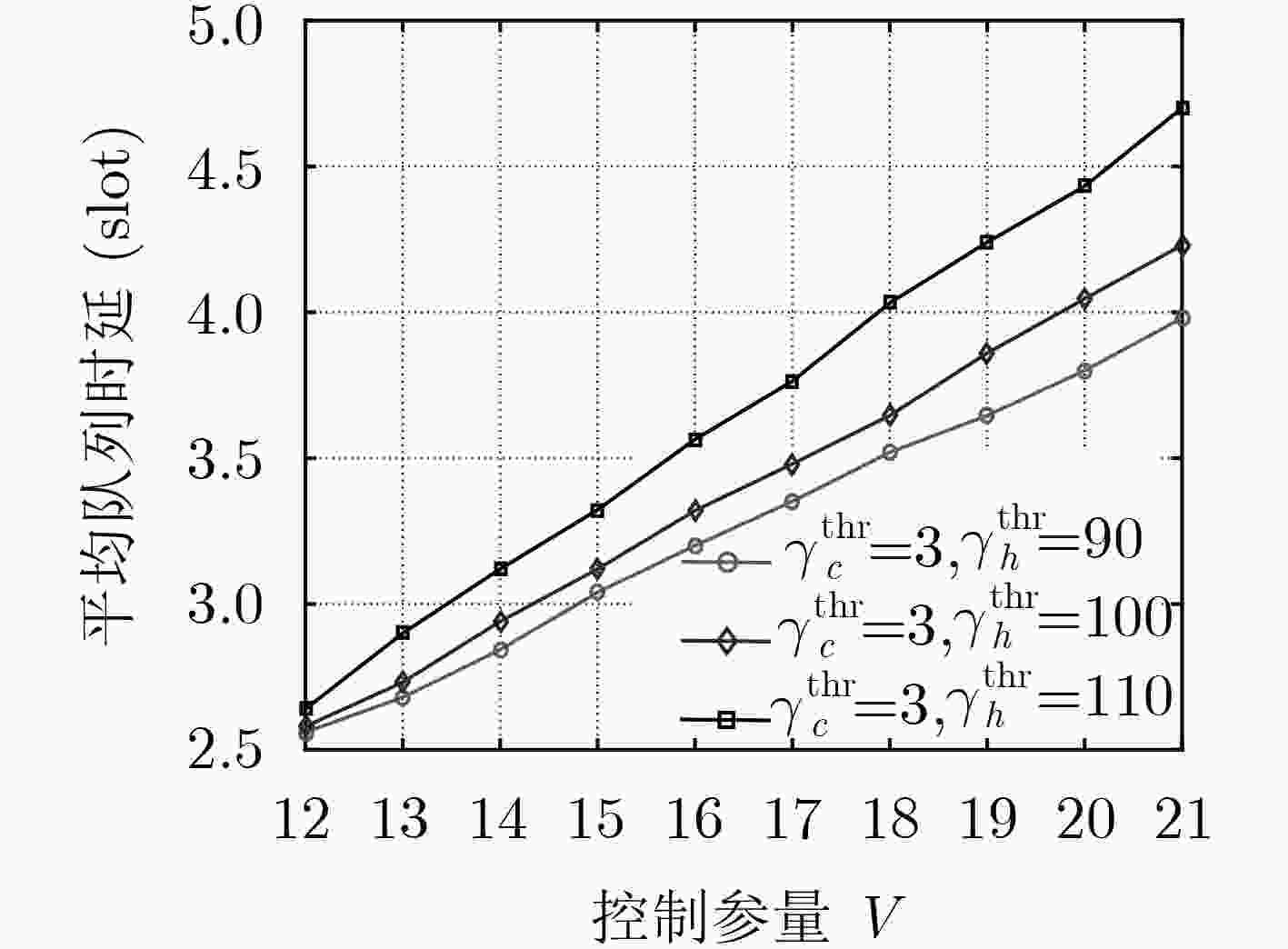
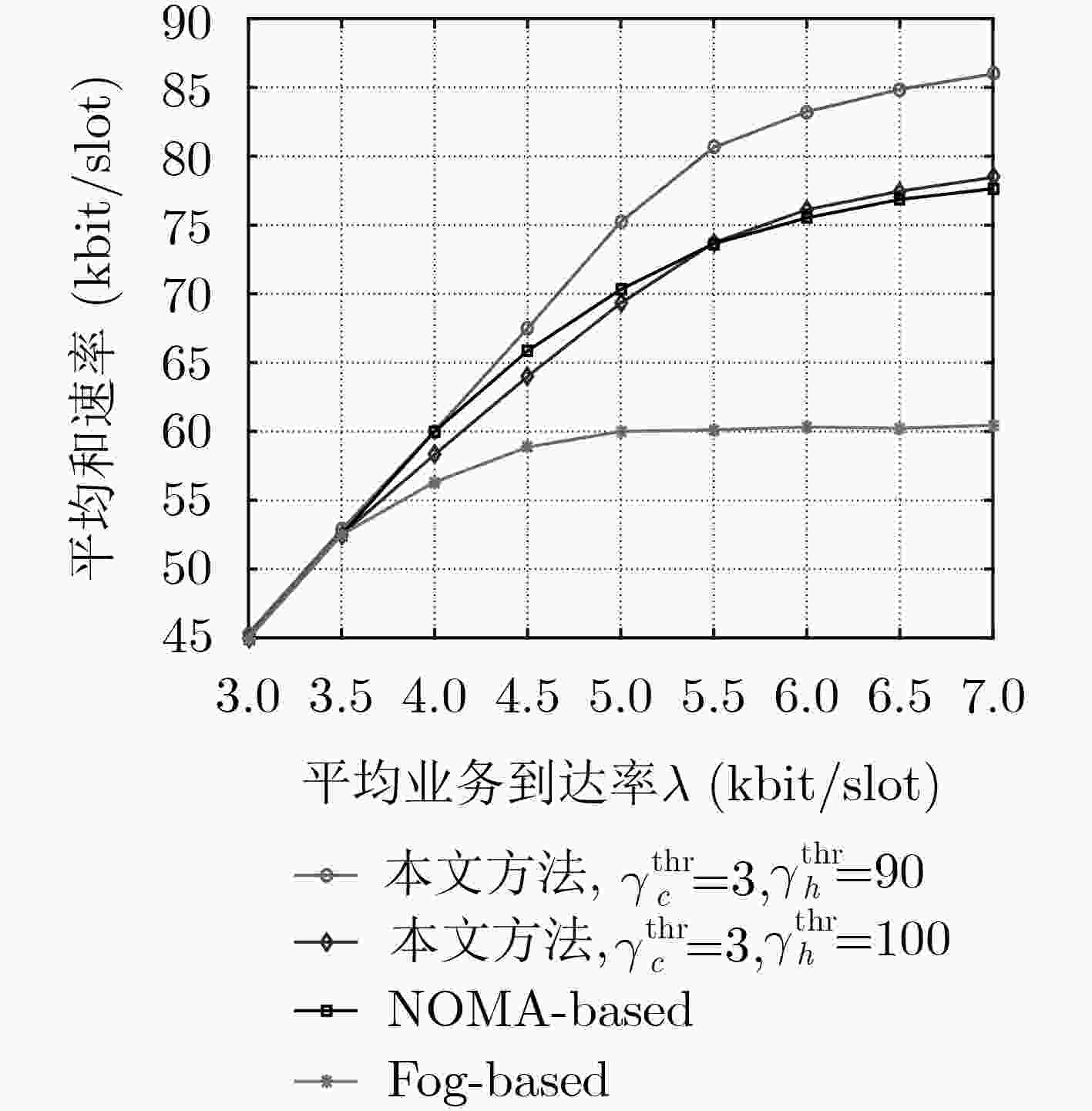

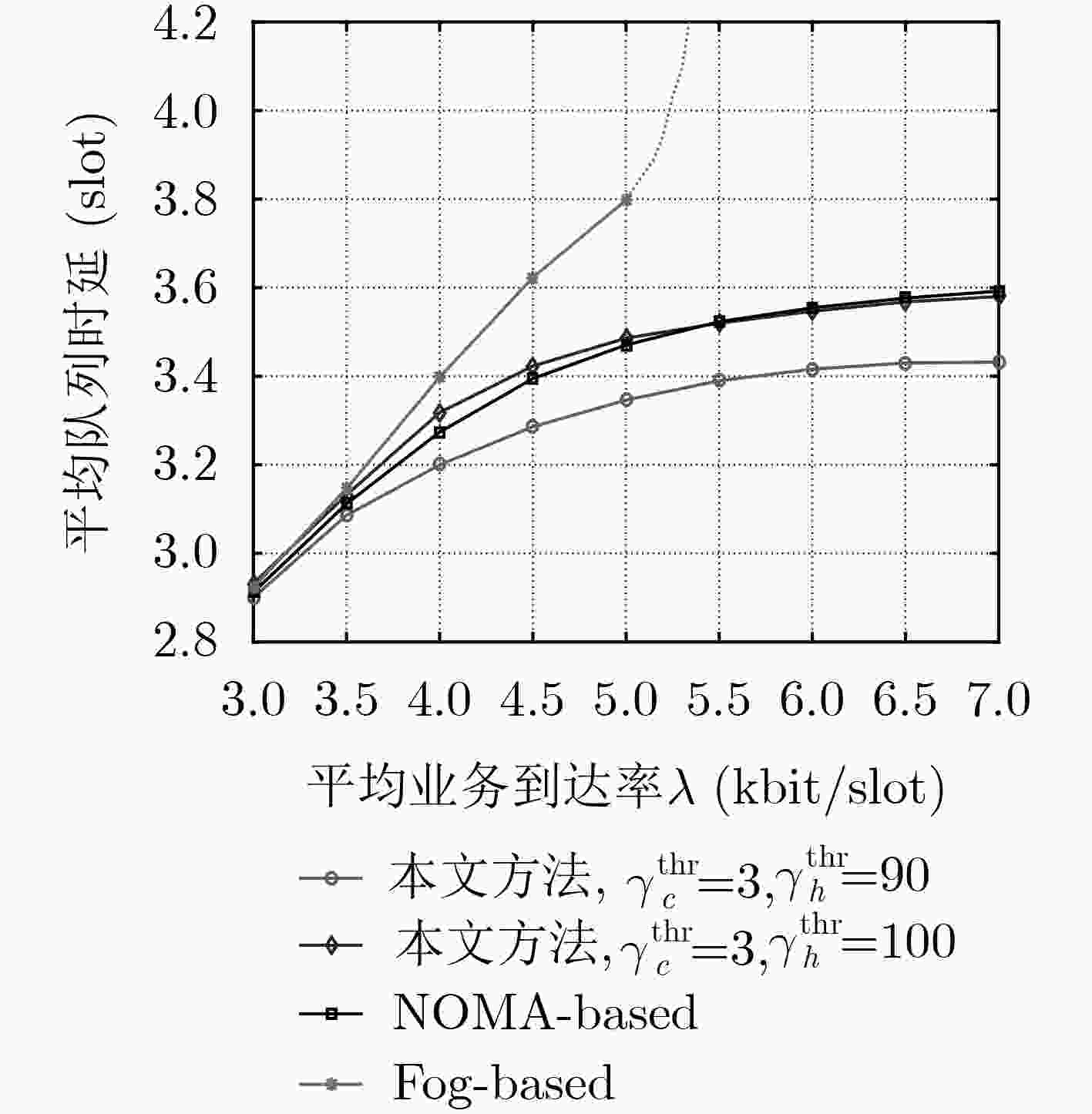



 下载:
下载:
