Intuitionistic Fuzzy Clustering Image Segmentation Based on Flower Pollination Optimization with Nearest Neighbor Searching
-
摘要:
为克服传统模糊聚类算法应用于图像分割时,易受噪声影响,对聚类中心初始值敏感,易陷入局部最优,模糊信息处理能力不足等缺陷,该文提出基于近邻搜索花授粉优化的直觉模糊聚类图像分割算法。首先设计一种新颖的图像空间信息提取策略,进而构造融合图像空间信息的直觉模糊聚类目标函数,提高对于噪声的鲁棒性,提升算法处理图像中模糊信息的能力。为了优化上述目标函数,提出一种基于近邻学习搜索机制的花授粉算法,实现对于聚类中心的寻优,解决对于聚类中心初始值敏感,易陷入局部最优的问题。实验结果表明所提算法能在多种噪声图像上取得令人满意的分割效果。
Abstract:In order to overcome shortcomings of the traditional fuzzy clustering algorithm for image segmentation, such as that are easily affected by noise, sensitive to the initial value of clustering center, easily falling into local optimum, and inadequate ability of fuzzy information processing, an intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation algorithm is proposed based on flower pollination optimization with nearest neighbor searching. Firstly, a novel extraction strategy of image spatial information is proposed, and then an intuitionistic fuzzy clustering objective function with image spatial information is constructed to improve the algorithm’s robustness against noise and enhance the ability of the algorithm to process the image fuzzy information. In order to overcome the defects of sensitivity to clustering centers and easily falling into local optimum, a flower pollination algorithm based on nearest neighbor learning search mechanism is proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed method can get satisfactory segmentation results on a variety of noisy images.
-
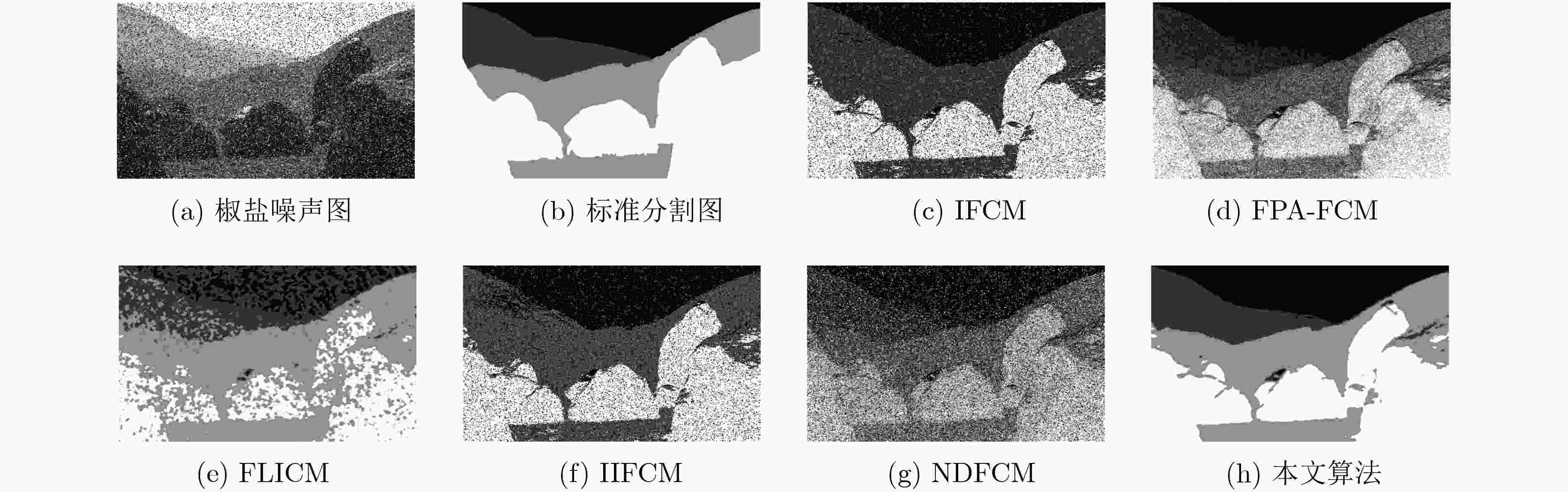
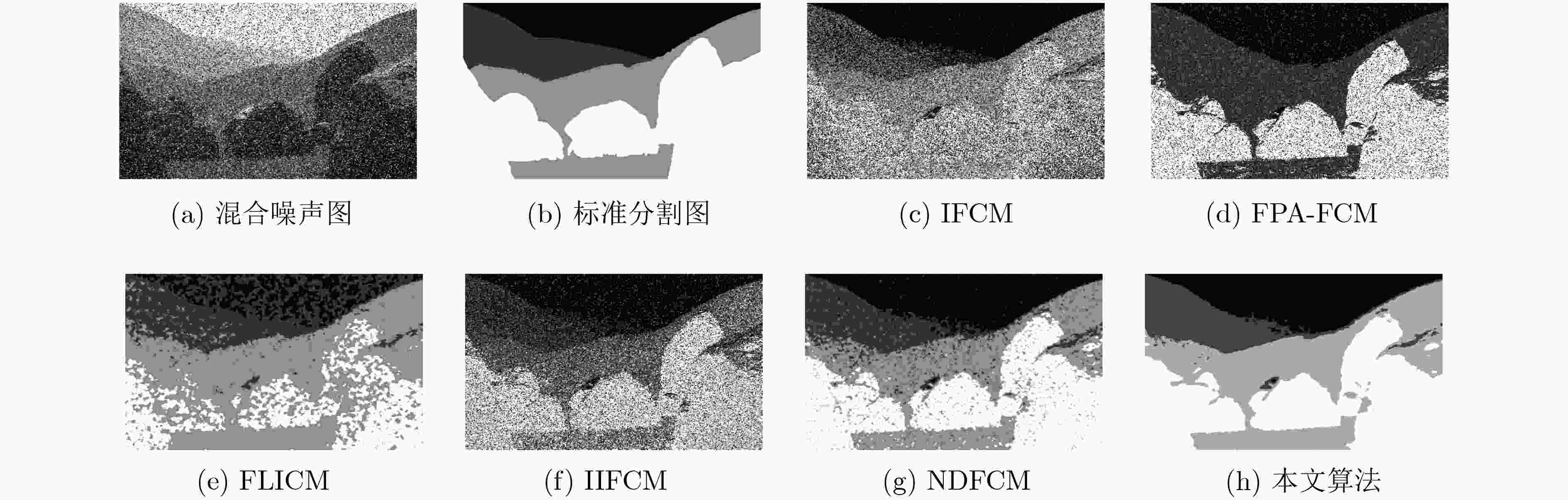
表 1 各算法聚类准确率对比
图像 噪声水平 IFCM FPA-FCM FLICM IIFCM NDFCM 本文算法 高斯 0.7536 0.7376 0.9306 0.7646 0.9279 0.9284 #113016 椒盐 0.8254 0.8320 0.9019 0.8268 0.9119 0.9290 高斯&椒盐 0.7806 0.7443 0.9163 0.7806 0.9054 0.9175 高斯 0.8373 0.8357 0.9054 0.8234 0.8945 0.8986 #101027 椒盐 0.7962 0.7939 0.8586 0.8041 0.8857 0.8913 高斯&椒盐 0.7806 0.7809 0.8834 0.7782 0.8839 0.8964 高斯 0.5640 0.5669 0.9101 0.5640 0.9112 0.8979 #241004 椒盐 0.6725 0.6725 0.6462 0.6725 0.8662 0.9116 高斯&椒盐 0.5383 0.4847 0.6487 0.5442 0.8408 0.9012 高斯 0.8346 0.7888 0.9329 0.8570 0.9323 0.9332 #15088 椒盐 0.8416 0.8395 0.9321 0.8421 0.9306 0.9331 高斯&椒盐 0.8225 0.7989 0.9326 0.8263 0.9285 0.9329 高斯 0.7719 0.8329 0.8883 0.6360 0.8806 0.8962 #296059 椒盐 0.7500 0.4822 08319 0.6671 0.8654 0.9022 高斯&椒盐 0.6975 0.2714 0.8530 0.6078 0.8582 0.8938 -
赵凤. 基于模糊聚类的图像分割[M]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2015: 1–5.ZHAO Feng. Fuzzy Clustering for Image Segmentation[M]. Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2015: 1–5. GU Jing, JIAO Licheng, YANG Shuyuan, et al. Fuzzy double c-means clustering based on sparse self-representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(2): 612–626. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2686804 BEZDEK J C, EHRLICH R, and FULL W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 1984, 10(2/3): 191–203. doi: 10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7 KRINIDIS S and CHATZIS V. A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(5): 1328–1337. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2040763 GUO Fangfang, WANG Xiuxiu, and SHEN Jie. Adaptive fuzzy c-means algorithm based on local noise detecting for image segmentation[J]. IET Image Processing, 2016, 10(4): 272–279. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2015.0236 LI M Q, XU L P, XU Na, et al. SAR image segmentation based on improved grey wolf optimization algorithm and fuzzy c-means[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018: 4576015. doi: 10.1155/2018/4576015 YANG Xinshe. Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization[C]. The 11th International Conference on Unconventional Computing and Natural Computation, Orléan, France, 2012: 240–249. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-32894-7_27. WANG Rui, ZHOU Yongquan, QIAO Shilei, et al. Flower pollination algorithm with bee pollinator for cluster analysis[J]. Information Processing Letters, 2016, 116(1): 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ipl.2015.08.007 ALYASSERI Z A A, KHADER A T, AL-BETAR M A, et al. Variants of the Flower Pollination Algorithm: A Review[M]. YANG Xinshe. Nature-Inspired Algorithms and Applied Optimization. Cham: Springer, 2018: 91–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67669-2_5. KOWALSKI P A, ŁUKASIK S, CHARYTANOWICZ M, et al. Nature Inspired Clustering-use Cases of Krill Herd Algorithm and Flower Pollination Algorithm[M]. KÓCZY L T, MEDINA-MORENO J, and RAMÍREZ-POUSSA E. Interactions between Computational Intelligence and Mathematics Part 2. Cham: Springer, 2019: 83–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01632-6_6. CUI Weijia and HE Yuzhu. Biological flower pollination algorithm with orthogonal learning strategy and catfish effect mechanism for global optimization problems[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018: 6906295. doi: 10.1155/2018/6906295 ATANASSOV K and GARGOV G. Interval valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1989, 31(3): 343–349. doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(89)90205-4 CHAIRA T. A novel intuitionistic fuzzy C means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(2): 1711–1717. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.05.005 VERMA H, AGRAWAL R K, and SHARAN A. An improved intuitionistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm incorporating local information for brain image segmentation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 46: 543–557. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.12.022 YAGER R R. On the measure of fuzziness and negation. II. Lattices[J]. Information and Control, 1980, 44(3): 236–260. doi: 10.1016/S0019-9958(80)90156-4 WOODS R E and GONZALEZ R C. Real-time digital image enhancement[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1981, 69(5): 643–654. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1981.12031 HUYNH-THU Q and GHANBARI M. The accuracy of PSNR in predicting video quality for different video scenes and frame rates[J]. Telecommunication Systems, 2012, 49(1): 35–48. doi: 10.1007/s11235-010-9351-x ALTMAN N S. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression[J]. The American Statistician, 1992, 46(3): 175–185. 吕振肃, 侯志荣. 自适应变异的粒子群优化算法[J]. 电子学报, 2004, 32(3): 416–420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.03.016LÜ Zhensu and HOU Zhirong. Particle swarm optimization with adaptive mutation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2004, 32(3): 416–420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.03.016 -





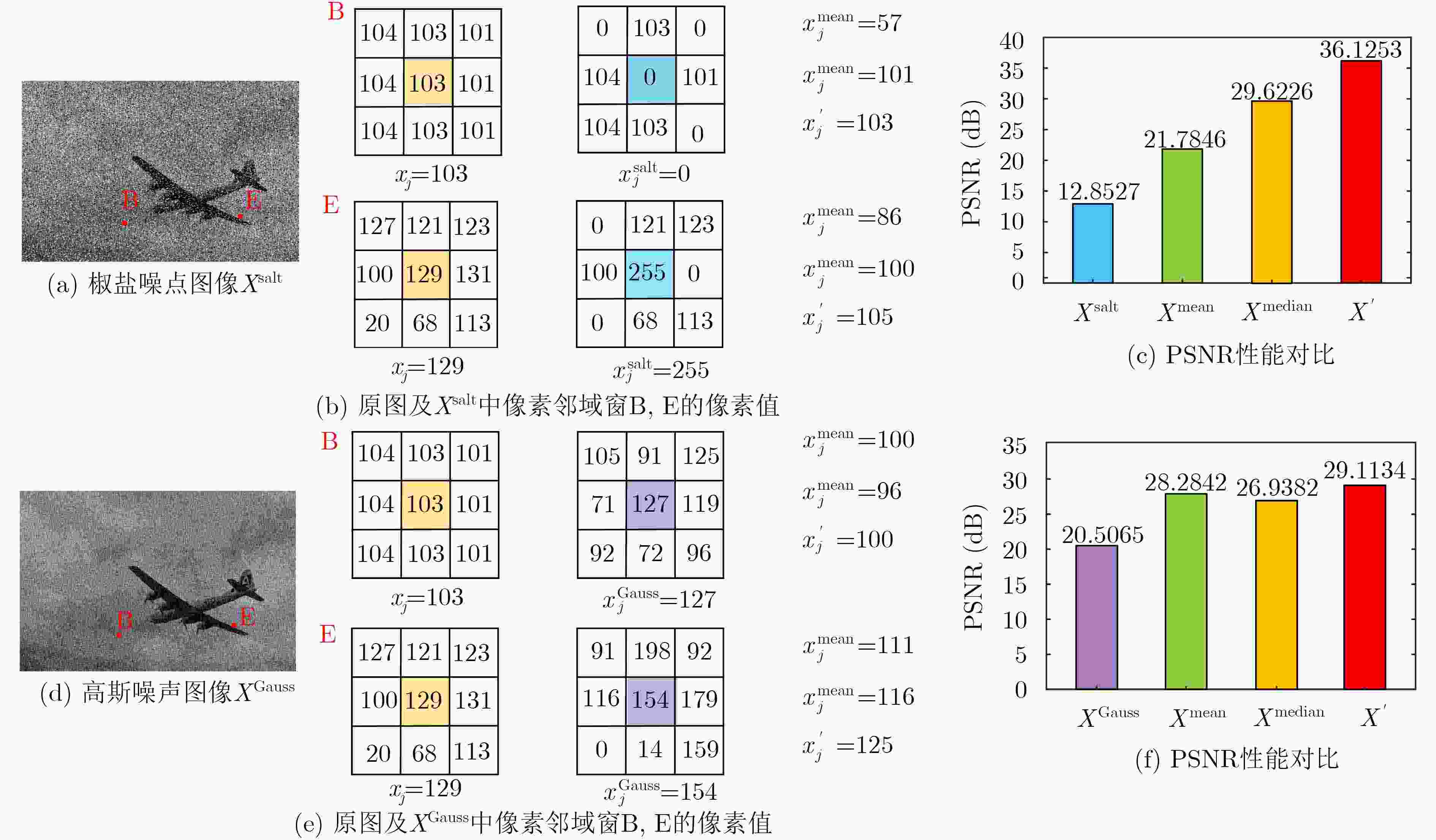
 下载:
下载:
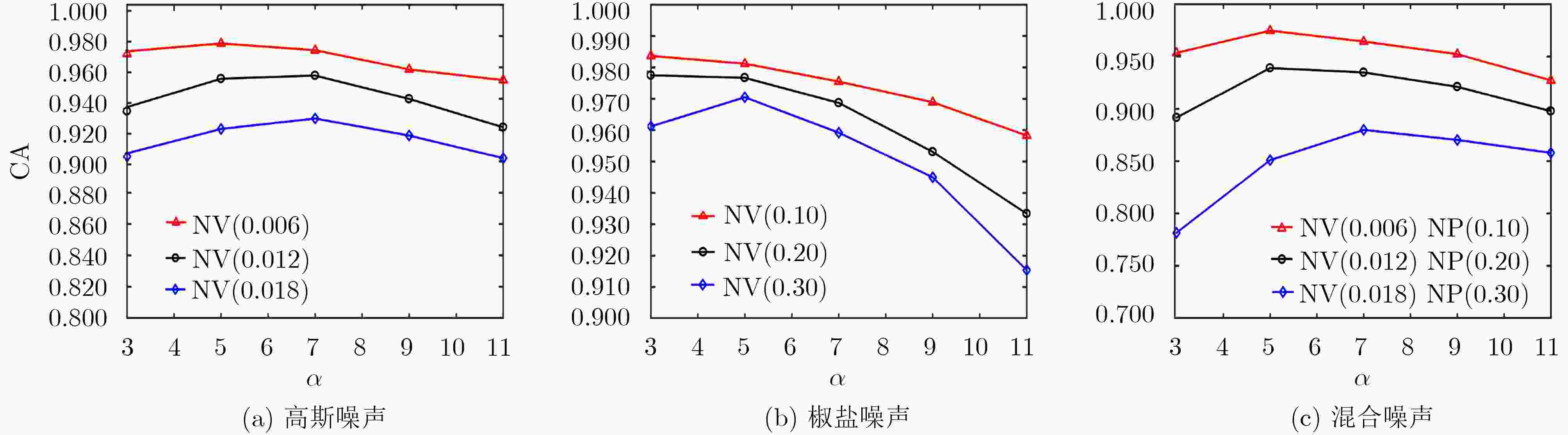
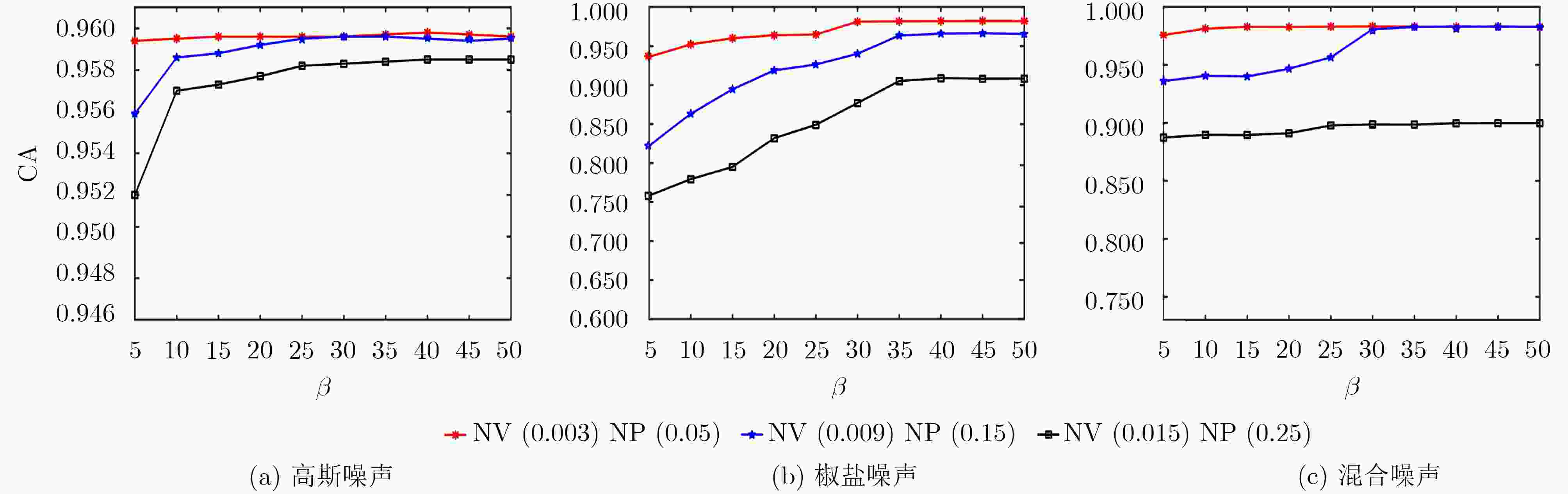
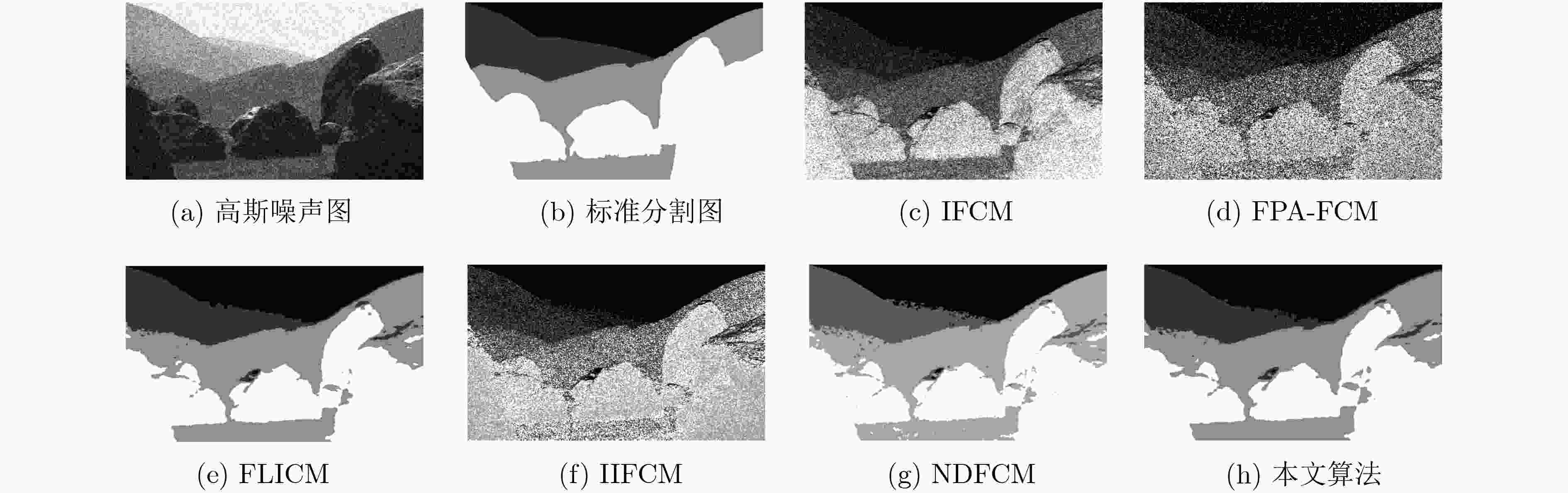


 下载:
下载:
