Energy Saving Mechanism with Incentive of Offloading Compression in Cloudlet Enhanced Fiber-Wireless Network
-
摘要:
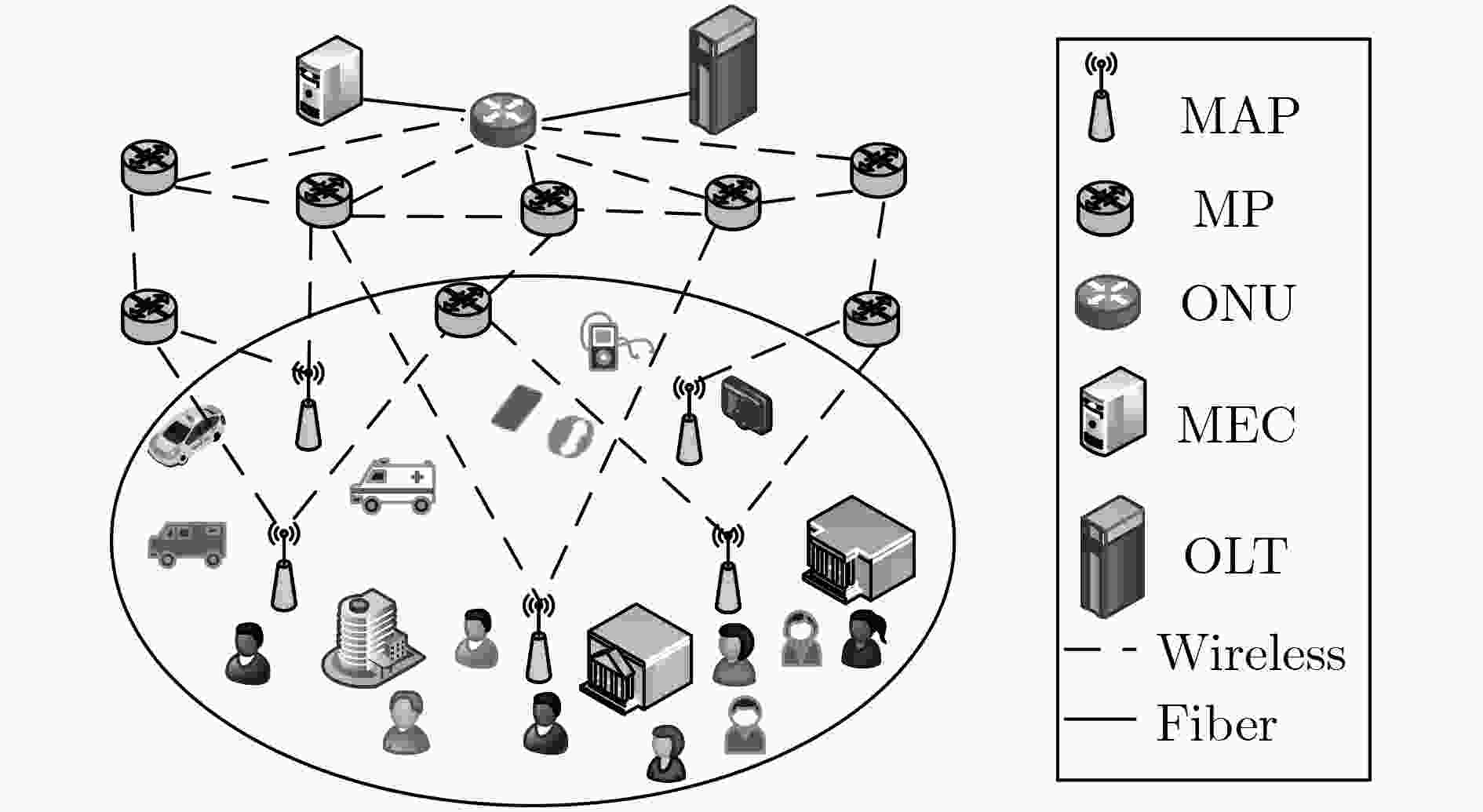
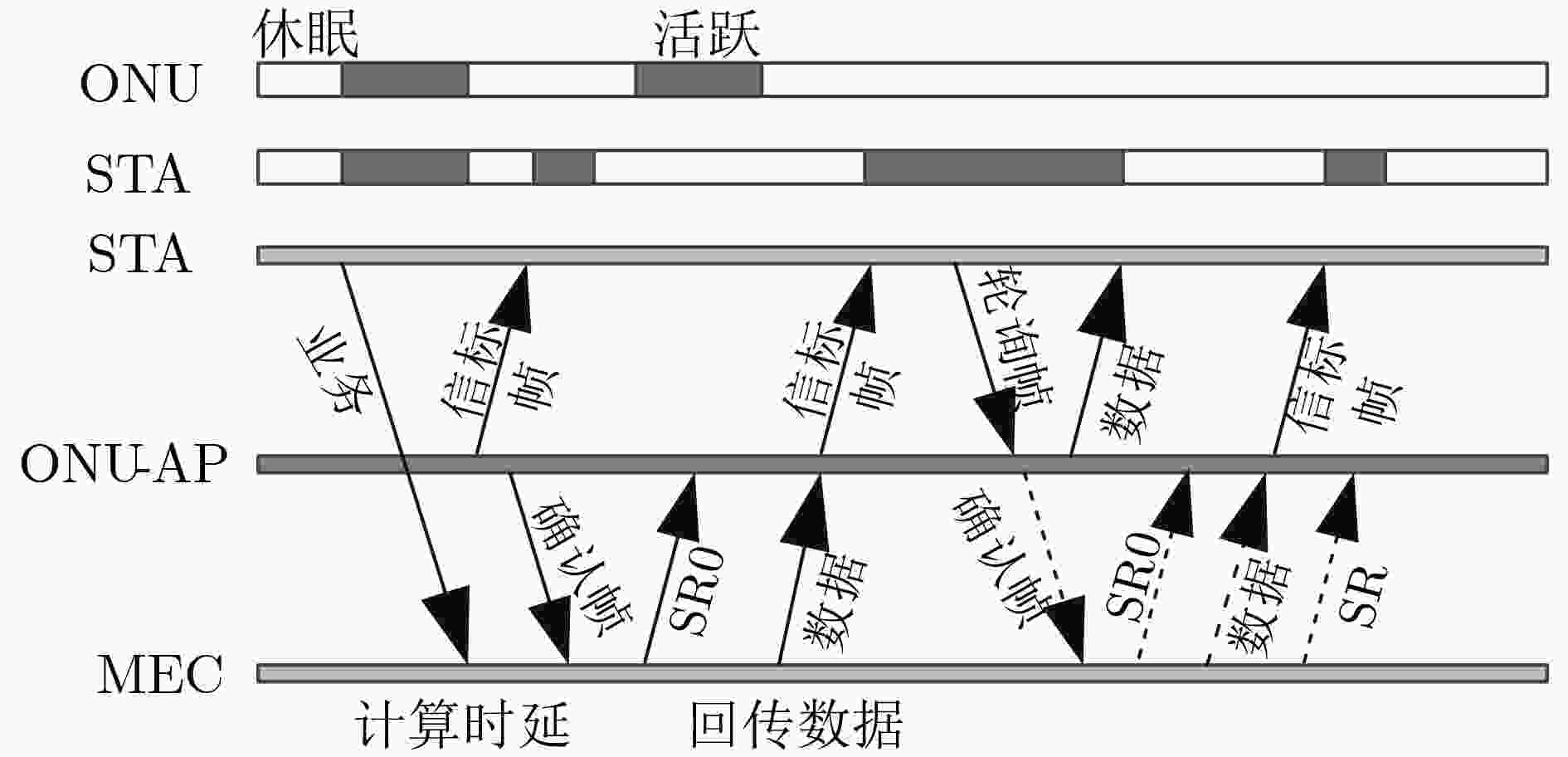
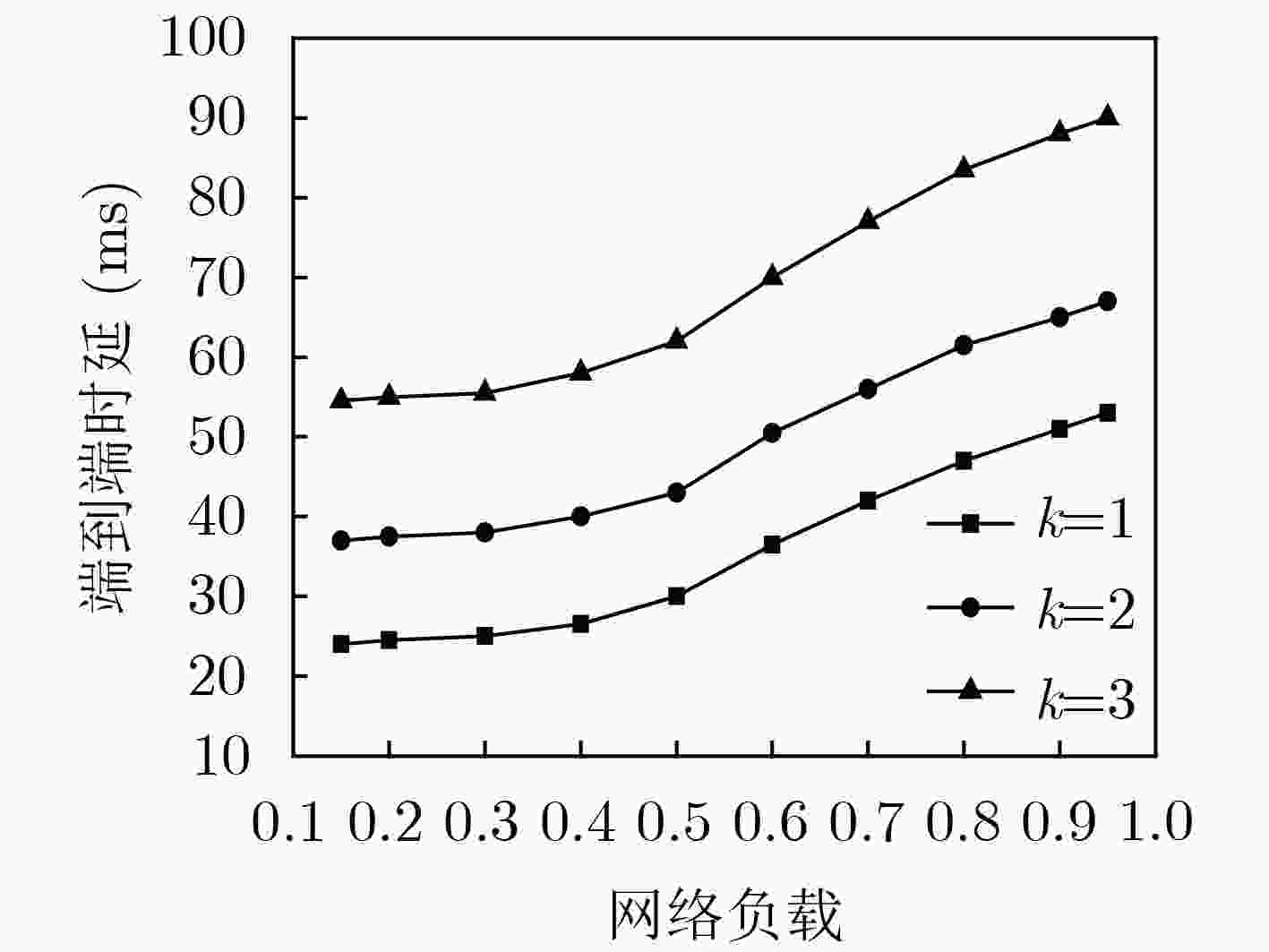
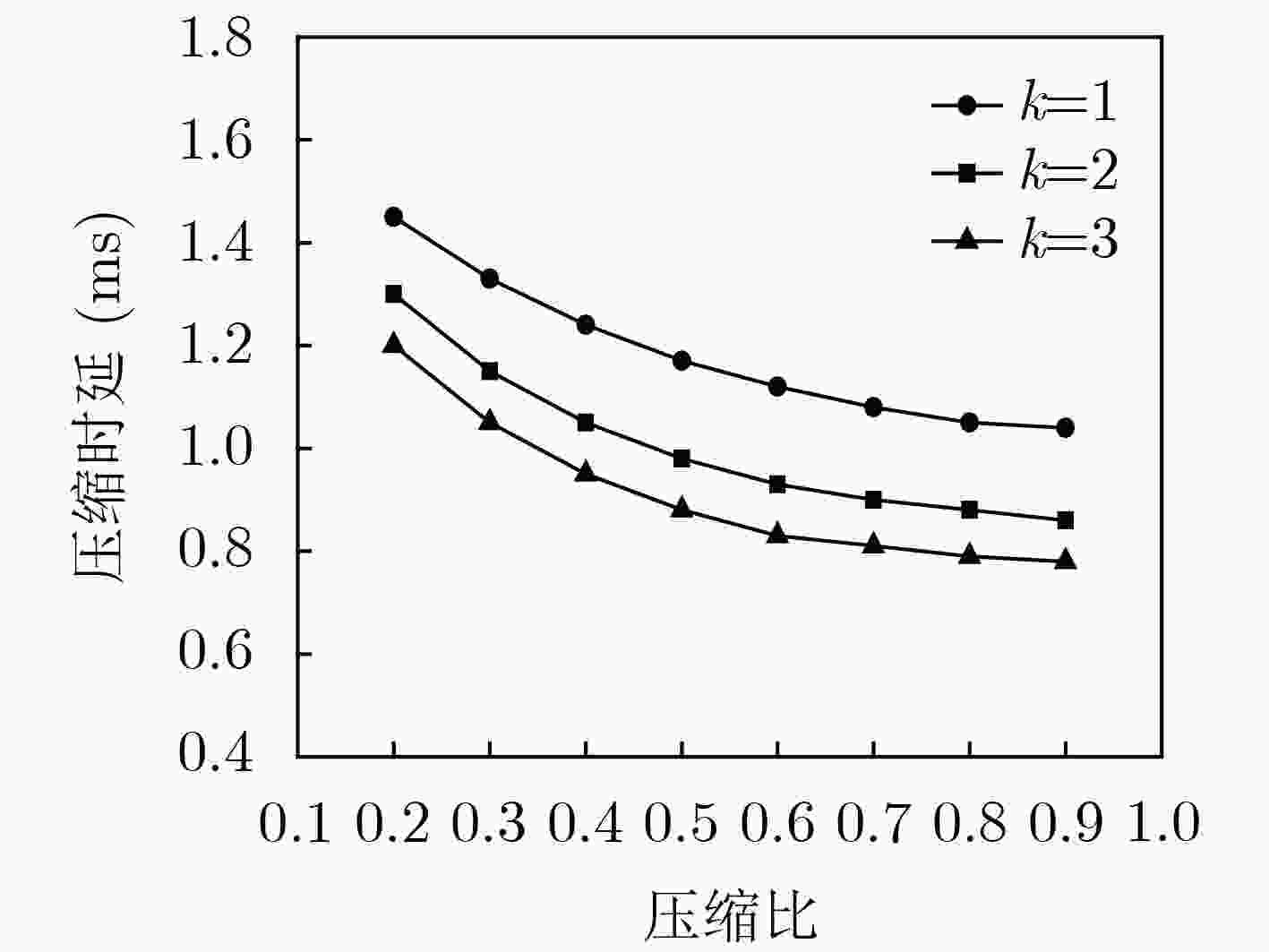
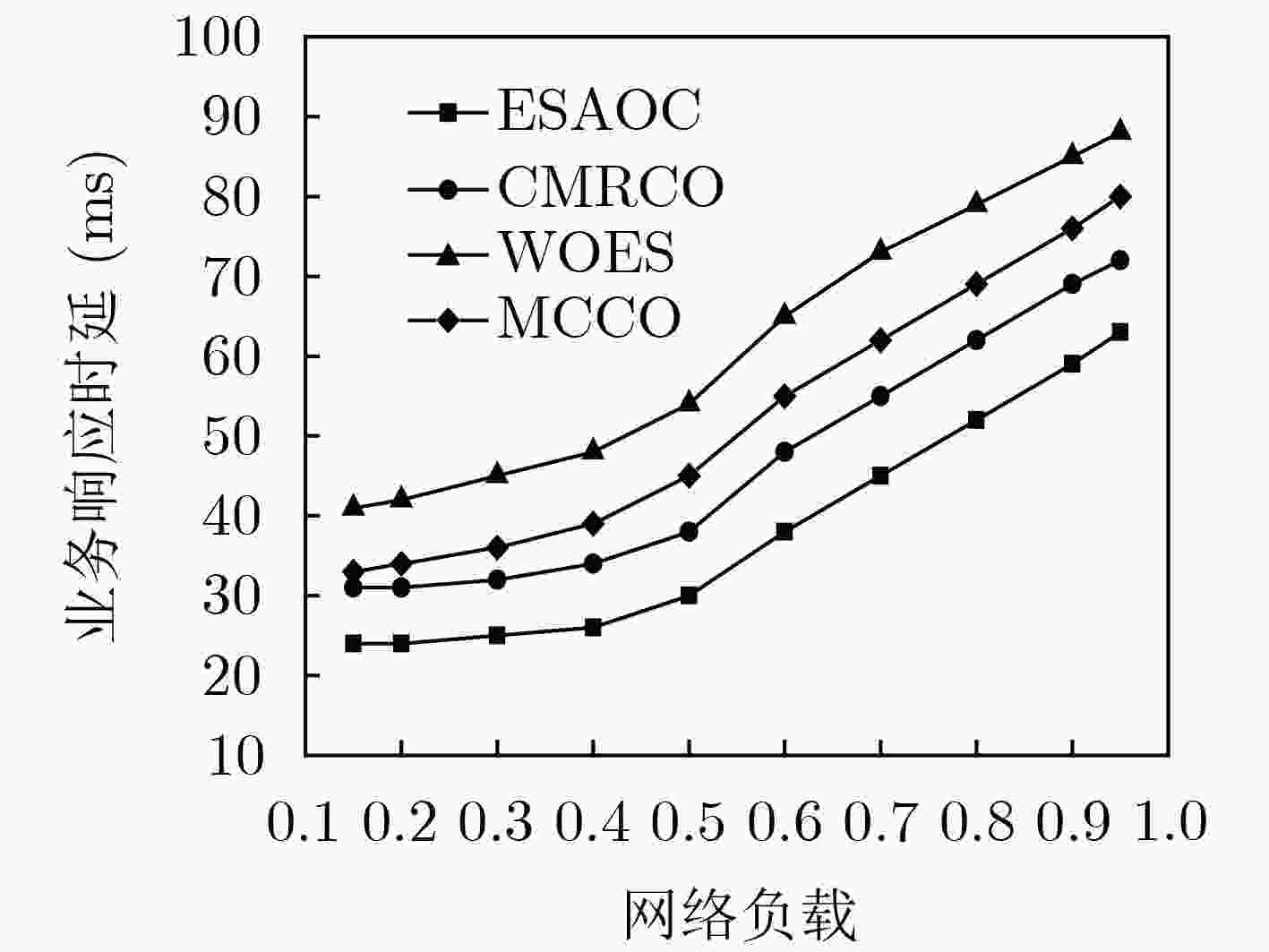
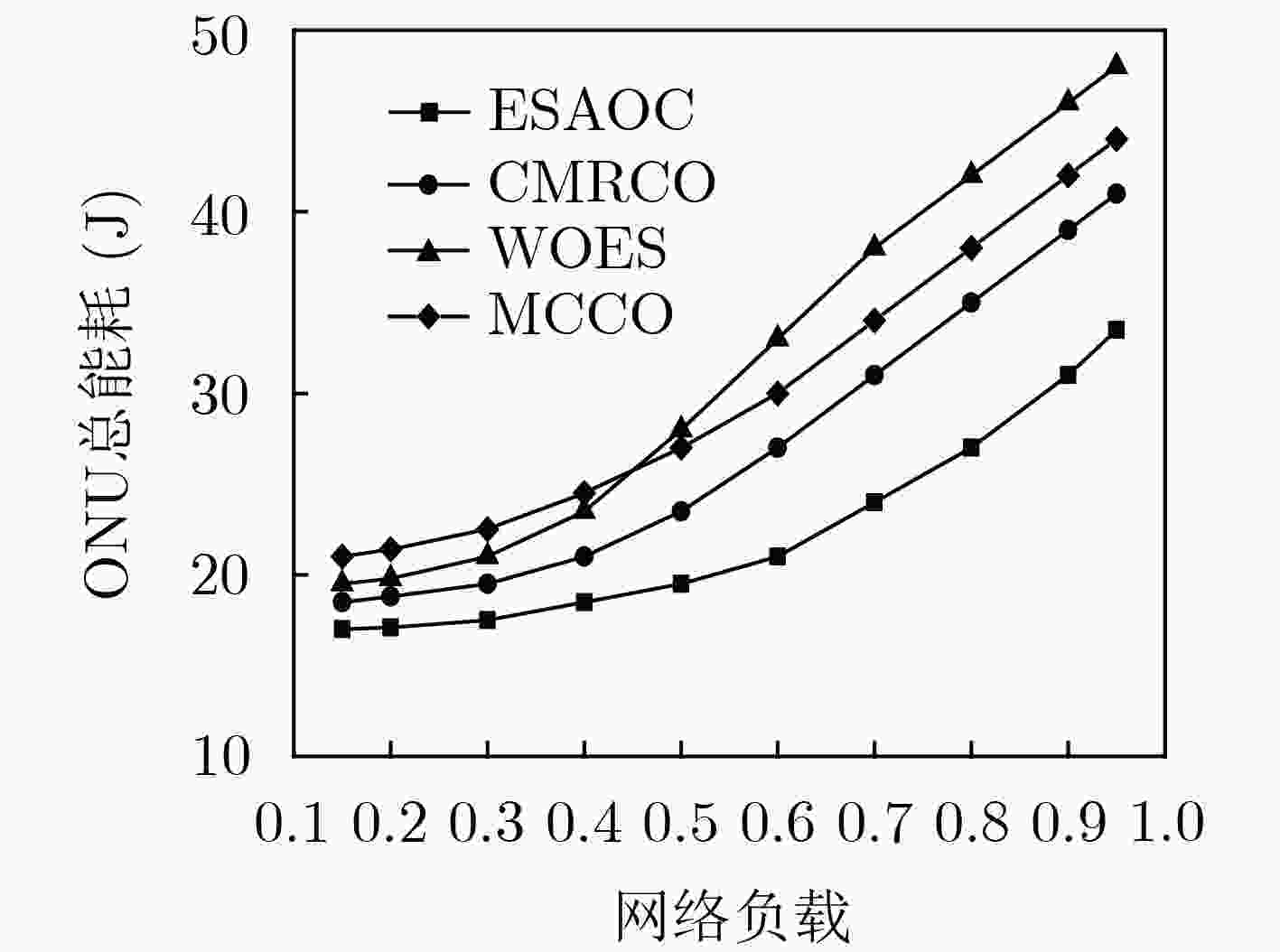
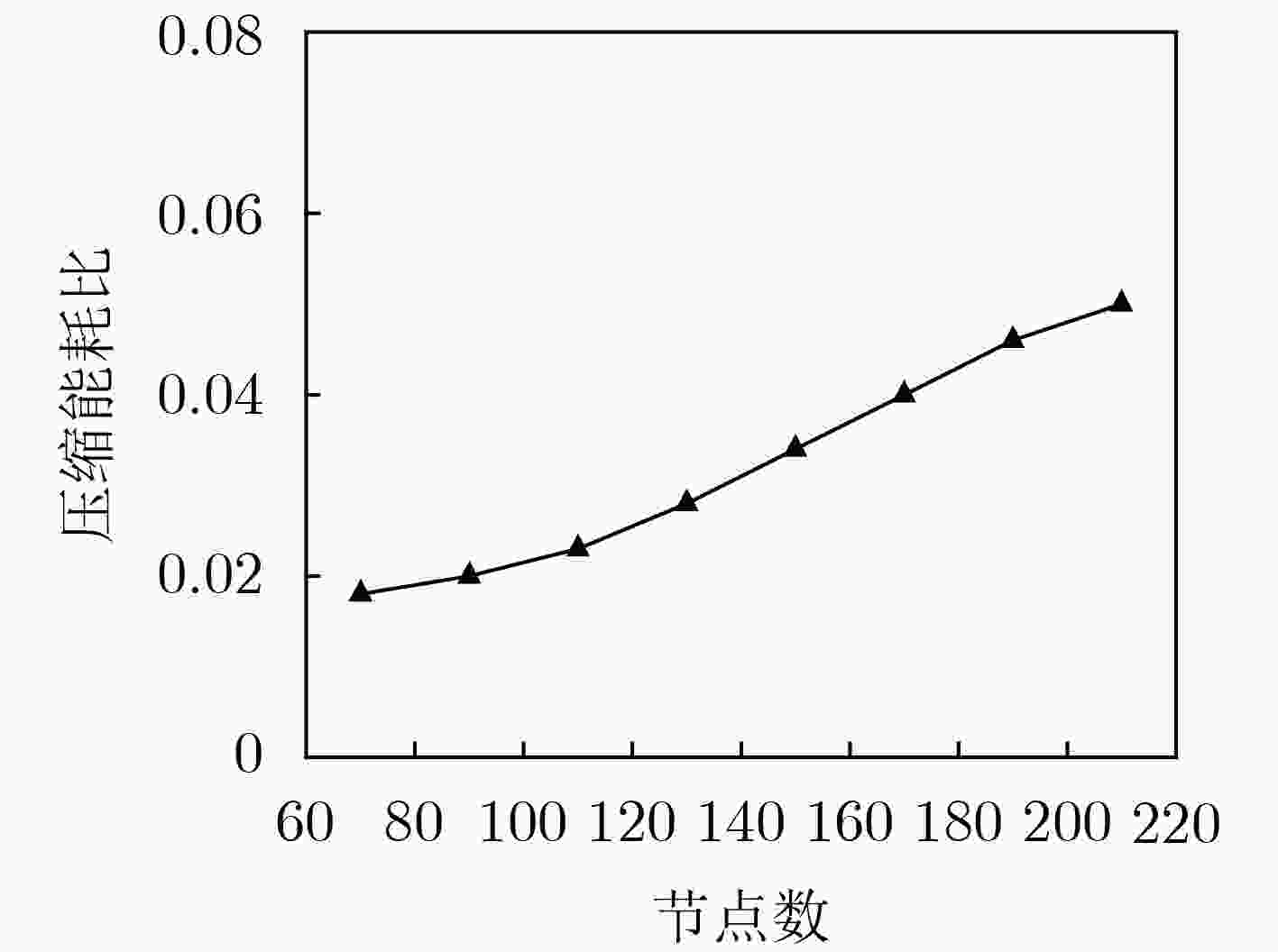
针对云增强型光纤-无线(FiWi)网络能耗以及卸载的通信开销过大问题,该文提出一种自适应卸载压缩节能机制(ESAOC),针对不同类型的业务属性和最大的容忍时延,结合光网络单元的负载变化和无线网状网的流量情况,通过统计的方式获得不同优先级卸载数据的平均到达率,再结合各个节点的压缩时延,动态调整业务的卸载压缩比,以降低卸载的通信开销;同时,建立排队模型分析卸载业务在MEC服务器的排队时延,协同调度无线侧中继节点,进而对光网络单元和终端设备进行协同休眠调度,最大化休眠时长,提高系统能源效率。结果表明,所提方法在有效降低整个网络能耗的同时能够保证卸载业务的时延性能。
Abstract:In cloudlet enhanced Fiber-Wireless (FiWi) network, there is a problem that energy consumption and communication overhead of offloading are too large. An Energy Saving mechanism with Adaptive Offloading Compression (ESAOC) is proposed. According to the different types of service attributes and the maximum tolerant delay, combined with the load changes of the optical network unit and the traffic of the wireless mesh network, the ratio of the offloading compression of service is dynamically adjusted to reduce the communication overhead of the offloading by the average arrival rate of the offloaded data of different priorities obtained by means of statistical methods and combined with the delay of compression of each node. At the same time, a queuing model is established to analyze the delay of the offloading service in the MEC server and cooperatively schedule the relay node in wireless mesh network, thereby performing the schedule of collaborative sleeping on the optical network units and the terminal devices to maximize the duration of sleeping and improving the energy efficiency of system. The results show that the proposed mechanism can effectively reduce the network energy consumption while ensuring the delay performance of offloading service.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
参数设定 参数数值 网络区域(m2) 500×500 ONU数目N(个) 8 Mesh节点数目${N_w}$(个) 20 STA数目W(个) 50 ONU活跃状态能耗(W) 5.05 ONU休眠状态能耗(W) 0.75 平均卸载分组大小(kb) 128.5 节点处理能力$\tau $(ns/b) 0.35 压缩参数$\beta $ 5 压缩能耗系数$\varepsilon $(nJ/b) 8 ${R_{\rm{mes} }}$(Mbit/s) 6900 ${R_{\rm{O}} }$(Gbit/s) 1 ${T_{\rm{O} \to {\rm{M}} }}$(μs) 50 ONU保护时隙(μs) 40 控制帧时隙(μs) 0.5 ${\xi _0}$(cycles/bit) 500 ${f_0}$(cycles/s) $3.2 \times {10^9}$ -
吴大鹏, 李雪, 李红霞. 基于TWDM-PON与C-RAN的QoE感知视频协作缓存与传输机制[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(3): 80–91. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019066WU Dapeng, LI Xue, and LI Hongxia. QoE-aware video cooperative caching and transmission mechanism based on TWDM-PON and C-RAN[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(3): 80–91. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2019066 王汝言, 徐宁宁, 吴大鹏. 能耗和时延感知的虚拟化云无线接入网络资源分配机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 83–90. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180063WANG Ruyan, XU Ningning, and WU Dapeng. Energy consumption and delay-aware resource allocation mechanism for virtualization cloud radio access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 83–90. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180063 AGIWAL M, ROY A, and SAXENA N. Next generation 5G wireless networks: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(3): 1617–1655. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2532458 XU Yi and MAO Shiwen. A survey of mobile cloud computing for rich media applications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2013, 20(3): 46–53. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2013.6549282 吴大鹏, 吴光锴, 王汝言. 带有上行数据帧聚合的光无线融合接入网络节能机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 690–696. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170508WU Dapeng, WU Guangkai, and WANG Ruyan. Energy-saving mechanism of integrated fiber-wireless access network with uplink data frame aggregation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 690–696. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170508 RIMAL B P, VAN D P, and MAIER M. Mobile edge computing empowered fiber-wireless access networks in the 5G era[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(2): 192–200. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600156CM LI Xiaoyang, YOU Changsheng, ANDREEV S, et al. Wirelessly powered crowd sensing: Joint power transfer, sensing, compression, and transmission[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(2): 391–406. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2872379 KOLO J G, SHANMUGAM S A, LIM D W G, et al. Fast and efficient lossless adaptive compression scheme for wireless sensor networks[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2015, 41: 275–287. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2014.06.008 LIU Luning, CHEN Xin, LU Zhaoming, et al. Mobile-edge computing framework with data compression for wireless network in energy internet[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2019, 24(3): 271–280. doi: 10.26599/TST.2018.9010124 XU Ding, LI Qun, and ZHU Hongbo. Energy-saving computation offloading by joint data compression and resource allocation for mobile-edge computing[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(4): 704–707. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2897630 ZHANG Wei, WEN Yonggang, ZHANG Yingjun, et al. Mobile cloud computing with voltage scaling and data compression[C]. The 18th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Sapporo, Japan, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC.2017.8227788. REN Jinke, YU Guanding, CAI Yunlong, et al. Latency optimization for resource allocation in mobile-edge computation offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(8): 5506–5519. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2845360 ALVI S A, ZHOU Xiangyun, and DURRANI S. Optimal compression and transmission rate control for node-lifetime maximization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(11): 7774–7788. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2870870 HU Weizheng, ZHANG Wei, HU Han, et al. Toward joint compression-transmission optimization for green wearable devices: An energy-delay tradeoff[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(4): 1006–1018. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2704605 ZHAO Tianchu, ZHOU Sheng, GUO Xueying, et al. A cooperative scheduling scheme of local cloud and internet cloud for delay-aware mobile cloud computing[C]. 2015 IEEE Globecom Workshops, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOMW.2015.7414063. LIU Yejun, GUO Lei, ZHANG Lincong, et al. A new integrated energy-saving scheme in green Fiber-Wireless (FiWi) access network[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2014, 57(6): 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11432-013-4958-7 RIMAL B P, VAN D P, and MAIER M. Mobile-edge computing vs. centralized cloud computing in fiber-wireless access networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/INFCOMW.2016.7562226. CHOWDHURY M and MAIER M. Collaborative computing for advanced tactile internet human-to-robot (H2R) communications in integrated FiWi multirobot infrastructures[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(6): 2142–2158. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2761599 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
