RGBD Image Co-saliency Object Detection Based on Sample Selection
-
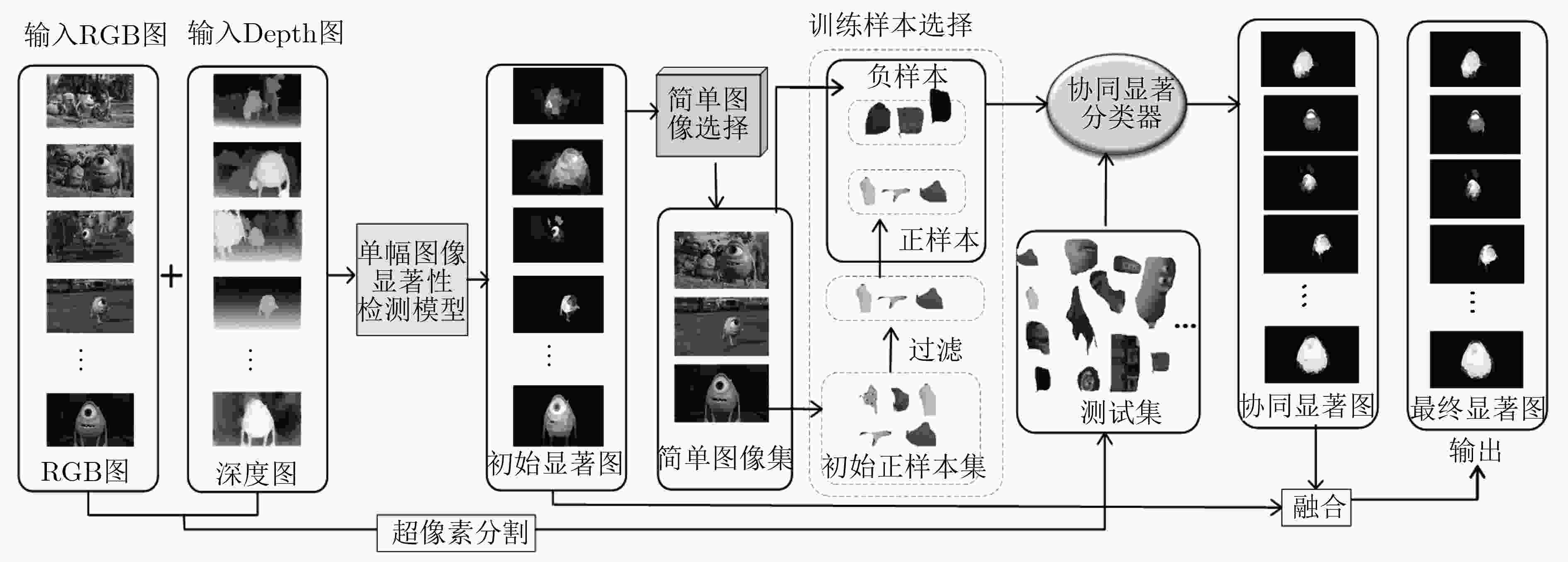
摘要: 协同显著目标检测的目的是在包含两张及以上相关图像的图像组中检测共同显著的物体。该文提出一种利用机器学习的方法对协同显著目标进行检测。首先,基于4个评分指标从图像组中选择部分显著目标易于检测的简单图像,构成简单图像集;接着,基于协同一致性的原则,从简单图像集中提取正负样本,并用深度学习模型提取的高维语义特征表示正负样本;再者,利用正负样本训练的协同显著分类器对图像中的超像素进行分类,得到协同显著目标区域;最后,经过一个平滑融合的操作,得到最终的协同显著图。在公开数据集上的测试结果表明,所提算法在检测精度和检测效率上优于目前的主流算法,并具有较强的鲁棒性。Abstract: Co-saliency object detection aims to discover common and salient objects in an image group which contains two or more relevant images. In this paper, a method of using machine learning is proposed to detect co-saliency objects. Firstly, some simple images are selected to form a simple image set based on four scoring indicators. Secondly, positive and negative samples are extracted from the simple images set based on co-coherence characteristics, and high-dimensional semantic features are extracted by the deep learning model which receives RGBD four-channels input. Thirdly, the co-saliency classifier is trained by positive and negative samples, and co-saliency maps are generated by testing all the superpixels in the images by the co-saliency classifier. Finally, a smooth fusion operation is adopted to generate the final co-saliency map. Experimental results on the public benchmark dataset show that the proposed algorithm is superior to the state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and efficiency, and it is robust.
-
Key words:
- Object detection /
- Co-saliency object /
- RGBD images /
- Deep learning /
- Classifier
-
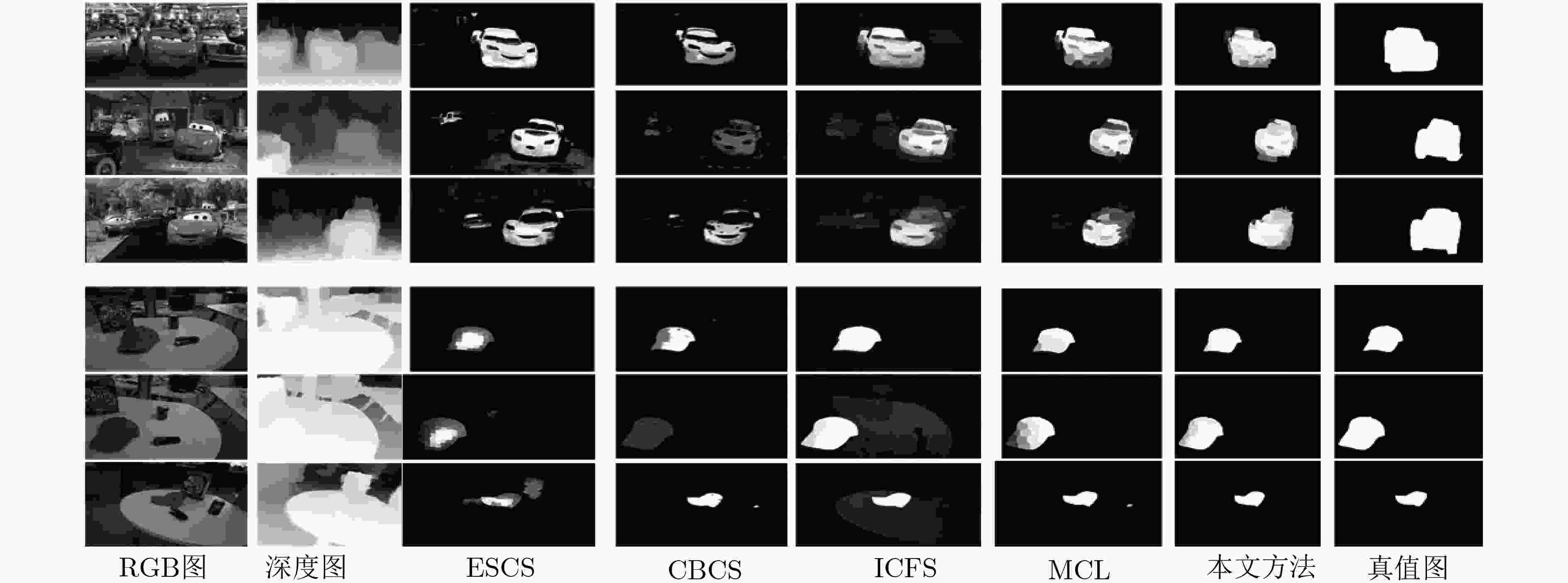
表 1 不同算法在两个数据集上的测试结果对比
RGBD CoSal150 RGBD CoSeg183 S-measure F-measure MAE S-measure F-measure MAE ESCS 0.625 0.587 0.218 0.636 0.414 0.156 CBCS 0.572 0.582 0.215 0.622 0.365 0.116 ICFS 0.710 0.764 0.179 0.630 0.443 0.163 MCL 0.766 0.810 0.137 0.689 0.488 0.098 本文方法 0.849 0.881 0.089 0.708 0.502 0.081 表 2 不同模块在两个数据集上的测试结果对比
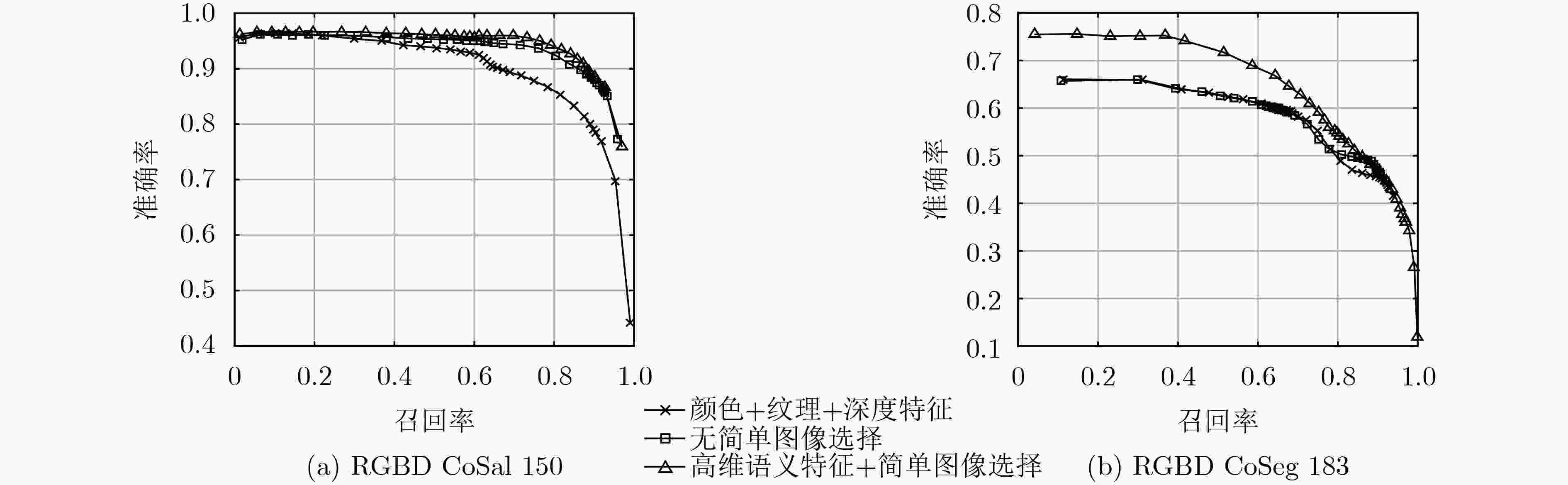
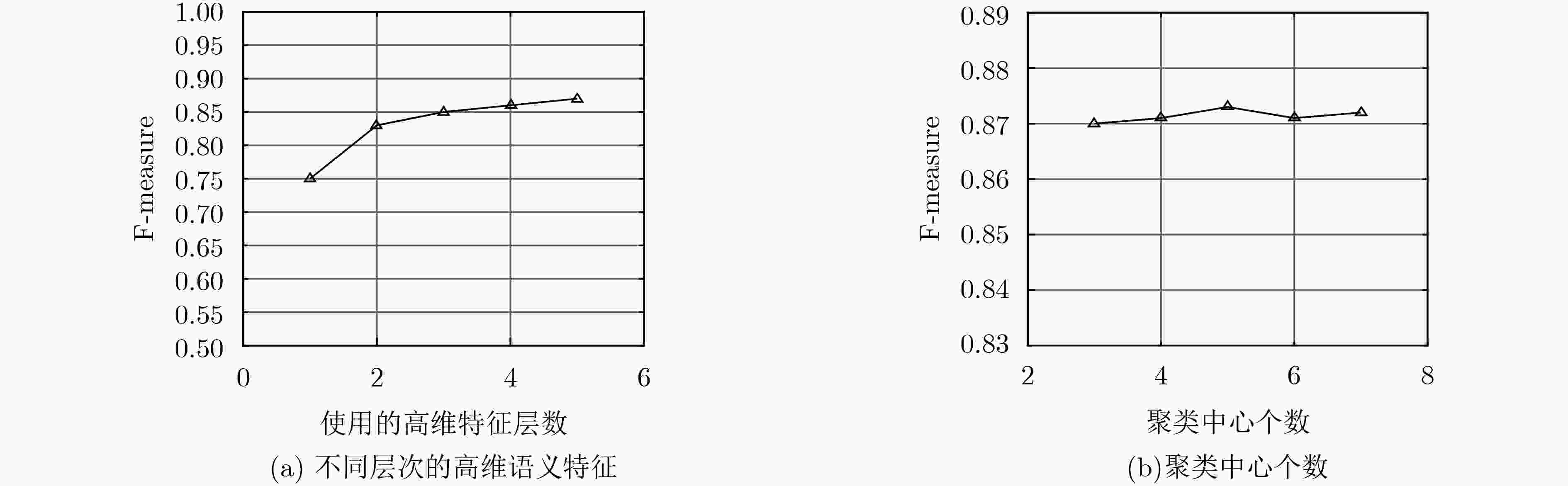
RGBD CoSal150 RGBD CoSeg183 S-measure F-measure MAE S-measure F-measure MAE 颜色+纹理特征 0.816 0.817 0.131 0.661 0.473 0.143 无简单图像选择 0.832 0.837 0.117 0.702 0.477 0.090 高维语义特征+简单图像选择 0.849 0.881 0.089 0.708 0.502 0.081 表 3 不同方法平均每副图运行时间比较(s)
方法 ESCS CBCS ICFS MCL 本文方法 时间 2.84 2.43 42.67 41.03 8.76 -
WANG Wenguan, SHEN Jianbing, LI Xuelong, et al. Robust video object cosegmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(10): 3137–3148. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2438550 LEI Jianjun, WU Min, ZHANG Changqing, et al. Depth-preserving stereo image retargeting based on pixel fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 19(7): 1442–1453. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2660440 LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, CONG Runmin, et al. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664–5677. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 CAO Xiaochun, ZHANG Changqing, FU Huazhu, et al. Saliency-aware nonparametric foreground annotation based on weakly labeled data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(6): 1253–1265. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2488637 PANG Yanwei, ZHU Hailong, LI Xuelong, et al. Motion blur detection with an indicator function for surveillance machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(9): 5592–5601. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2564938 LEI Jianjun, LIU Jianying, ZHANG Hailong, et al. Motion and structure information based adaptive weighted depth video estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2015, 61(3): 416–424. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2015.2437197 YANG Jingyu, GAN Ziqiao, LI Kun, et al. Graph-based segmentation for RGB-D data using 3-D geometry enhanced superpixels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(5): 927–940. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2340032 SONG Hangke, LIU Zhi, XIE Yufeng, et al. RGBD co-saliency detection via bagging-based clustering[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1722–1726. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2615293 CONG Runmin, LEI Jianjun, FU Huazhu, et al. Co-saliency detection for RGBD images based on multi-constraint feature matching and cross label propagation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(2): 568–579. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2763819 CONG Runmin, LEI Jianjun, FU Huazhu, et al. An iterative co-saliency framework for RGBD images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(1): 233–246. doi: 10.1109/tcyb.2017.2771488 CHEN M, VELASCO-FORERO S, TSANG I, et al. Objects co-segmentation: Propagated from simpler images[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 1682–1686. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2015.7178257. ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 GUO Jingfan, REN Tongwei, and BEI Jia. Salient object detection for RGB-D image via saliency evolution[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Seattle, USA, 2016: 1–6. CONG Runmin, LEI Jianjun, ZHANG Changqing, et al. Saliency detection for stereoscopic images based on depth confidence analysis and multiple cues fusion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(6): 819–823. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2016.2557347 MAI Long and LIU Feng. Comparing salient object detection results without ground truth[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 76–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_6. LI Lina, LIU Zhi, and ZHANG Jian. Unsupervised image co-segmentation via guidance of simple images[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 1650–1661. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.10.002 CONG Runmin, LEI Jianjun, FU Huazhu, et al. HSCS: Hierarchical Sparsity based co-saliency detection for RGBD images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(7): 1660–1771. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2884481 ARTHUR D and VASSILVITSKII S. k-means++: The advantages of careful seeding[C]. The Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, New Orleans, USA, 2007: 1027–1035. HUANG Posheng, SHEN C H, and HSIAO H F. RGBD salient object detection using spatially coherent deep learning framework[C]. The 23rd IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 2018: 1–5. LIU Zhengyi, SHI Song, DUAN Quntao, et al. Salient object detection for RGB-D image by single stream recurrent convolution neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 363: 46–57. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.07.012 HAN Junwei, CHENG Gong, LI Zhenpeng, et al. A unified metric learning-based framework for co-saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(10): 2473–2483. doi: 10.1109/tcsvt.2017.2706264 QIN Yao, FENG Mengyang, LU Huchuan, et al. Hierarchical cellular automata for visual saliency[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2018, 126(7): 751–770. doi: 10.1007/s11263-017-1062-2 OTSU N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1979, 9(1): 62–66. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076 BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, JIANG Huaizu, et al. Salient object detection: A benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5706–5722. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2487833 WANG Wenguan, SHEN Jianbing, and SHAO Ling. Consistent video saliency using local gradient flow optimization and global refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4185–4196. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2460013 FAN Dengping, CHENG Mingming, LIU Yun, et al. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 4558–4567. LI Yijun, FU Keren, LIU Zhi, et al. Efficient saliency-model-guided visual co-saliency detection[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(5): 588–592. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2364896 FU Huazhu, CAO Xiaochun, and TU Zhuowen. Cluster-based co-saliency detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(10): 3766–3778. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2260166 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
