Indoor Through-the-wall Passive Human Target Detection Algorithm
-
摘要:
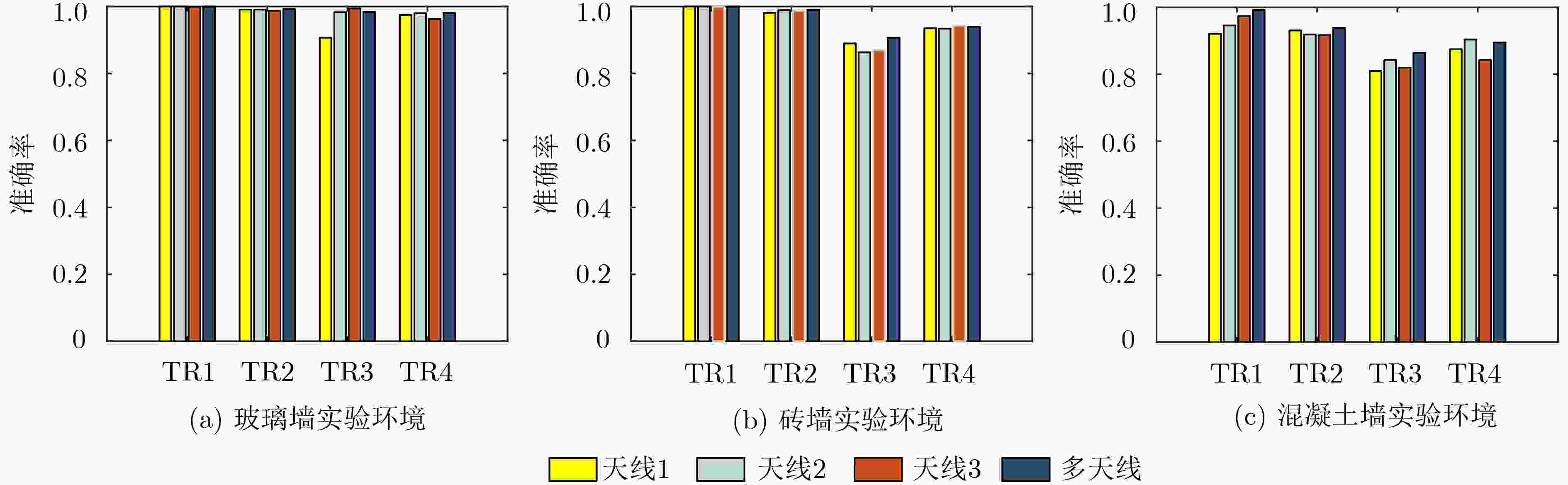
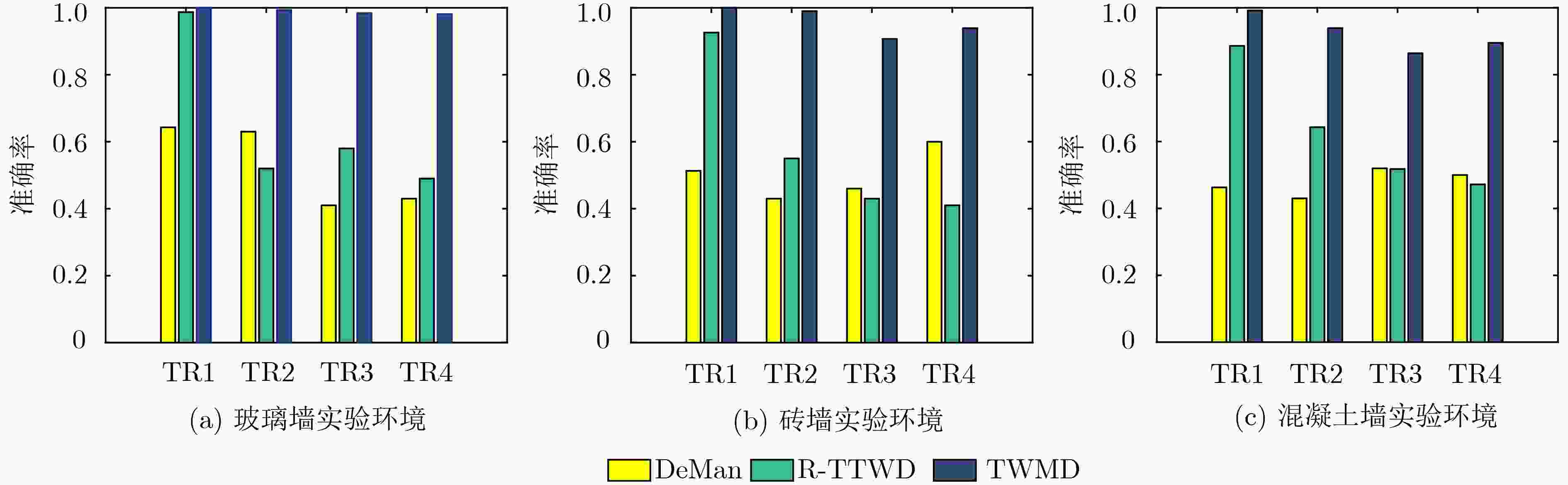
穿墙场景下,由于墙体造成信号严重衰减,接收信号中目标反射信号的能量大幅下降,接收信号淹没在收发机直射信号和室内家具反射信号中,难以检测墙后目标。针对上述问题,该文提出一种新颖的基于多维信号特征融合的穿墙多人体目标检测算法(TWMD)。先对接收到的信道状态信息(CSI)进行预处理以消除相位误差和幅值噪声,再利用CSI的时序相关性和子载波相关性从相关系数矩阵中提取多维信号特征,最后使用BP神经网络完成特征与检测结果之间的映射。实验结果表明,该算法在玻璃墙、砖墙和混凝土墙环境的识别精度分别在0.98, 0.90, 0.85以上。根据所统计的4000个各类样本的检测结果,与现有基于单一信号特征的检测算法相比,该文算法在对不同数量运动目标的检测上,获得了平均0.45的精度提升。
Abstract:In through-the-wall scene, due to the serious attenuation of signal caused by wall, the energy of target reflection signal in the received signal decreases significantly and the received signal is submerged in the direct signal of the transceiver and the reflection signal of indoor furniture, making the target behind wall is hard to be detected. In view of the above problems, a novel Through-the-Wall Multiple human targets Detection (TWMD) algorithm based on multidimensional signal features fusion is proposed. Firstly, the received Channel State Information(CSI) is preprocessed to eliminate the phase error and amplitude noise, and the multidimensional signal features are fully extracted from the correlation coefficient matrix by using time correlation and subcarrier correlation of CSI. Finally, the mapping between features and detection results is established by BP neural network. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of this algorithm in the environment with glass wall, brick wall and concrete wall is above 0.98, 0.90, 0.85, respectively. According to the detection results of 4000 samples, compared with the existing detection algorithms based on single signal feature, the proposed algorithm achieves an average accuracy improvement of 0.45 in the detection of different number of moving targets.
-
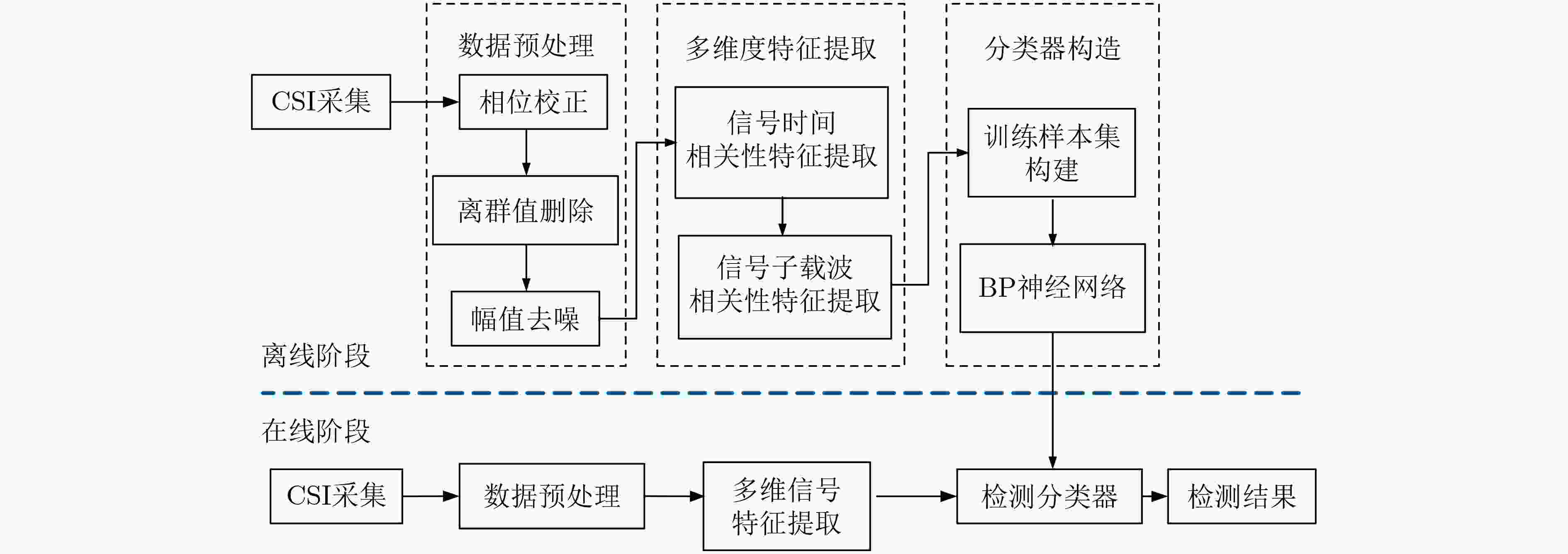
表 1 本文所提基于多维特征的目标检测算法
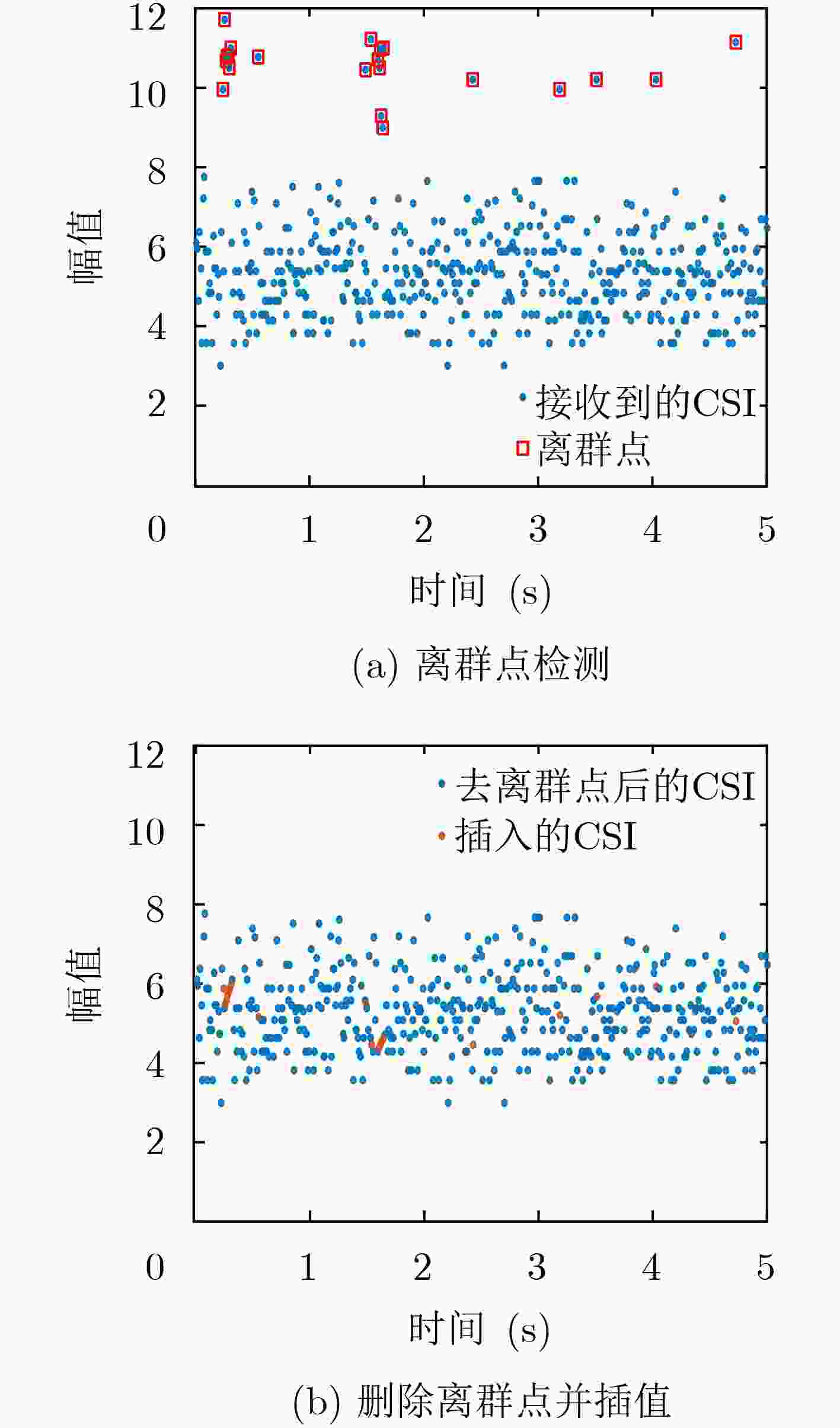
输入:天线1的CSI接收矩阵${{{H}}_1}$,天线2的CSI接收矩阵${{{H}}_2}$,天线3 的CSI接收矩阵${{{H}}_3}$。 输出:输出特征${{F}}''$。 初始化: 天线个数$N{\rm{ = }}3$;输出特征${{F}}''{\rm{ = 0}}$。 算法步骤: (1) for $i$=1, 2, $···,N$ (2) 用式(4)校正${{{H}}_i}$的相位,得到${{\theta }}$; (3) 用离群值删除与小波去噪对${{{H}}_i}$的幅值进行预处理,得到
$\left\| {{\tilde{ H}}} \right\|$;(4) 用式(6)、式(7)计算$\left\| {{\tilde{ H}}} \right\|$的相关系数矩阵${{A}}$; (5) 对${{A}}$进行矩阵分解,得到第1个和第2个大特征值
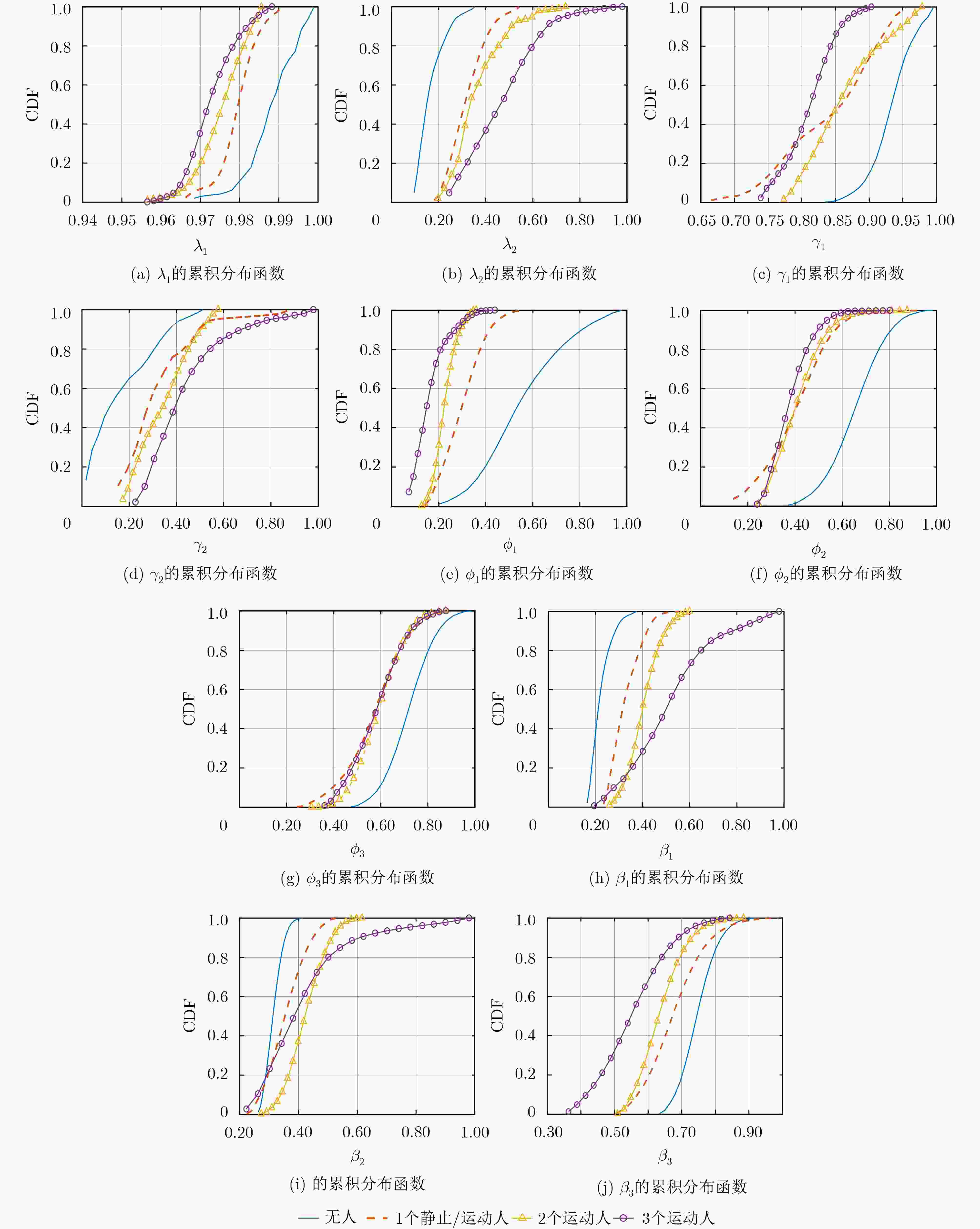
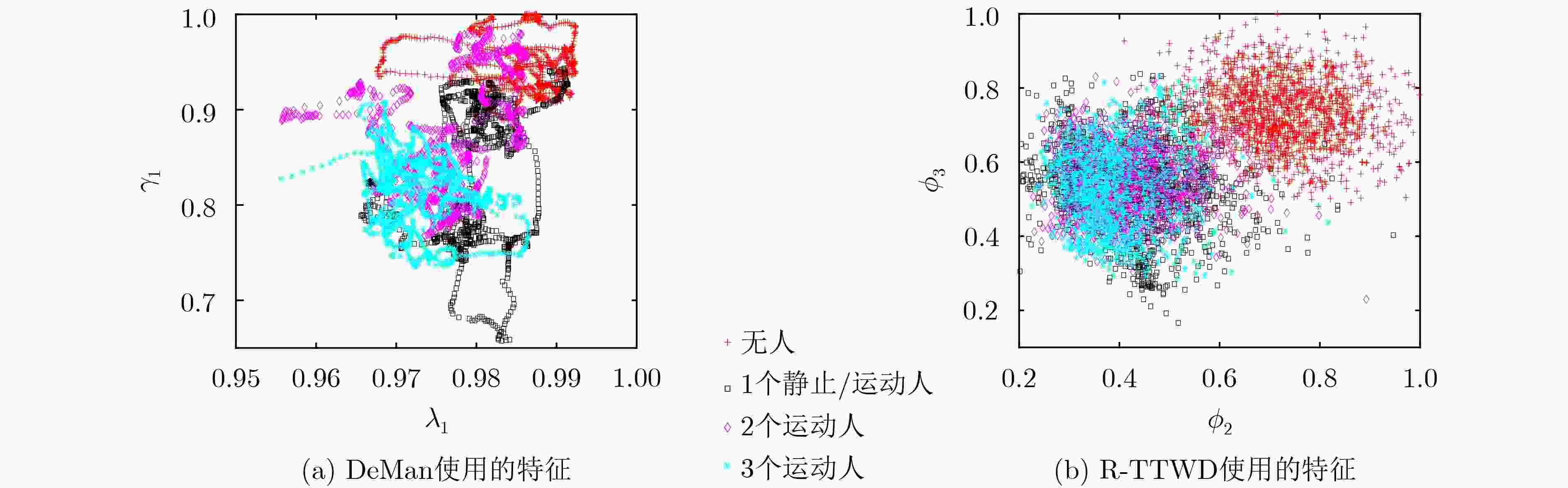
${\lambda _1},\,{\lambda _2}$;(6) 用式(8)计算${{\theta }}$的相关系数矩阵${{C}}$; (7) 对${{C}}$进行矩阵分解,提取第1个和第2个大特征值
${\gamma _1},\;{\gamma _2}$;(8) 用式(10)计算子载波相关系数矩阵${{S}}$; (9) 对${{S}}$进行分解,提取前3个大特征值对应的特征向量
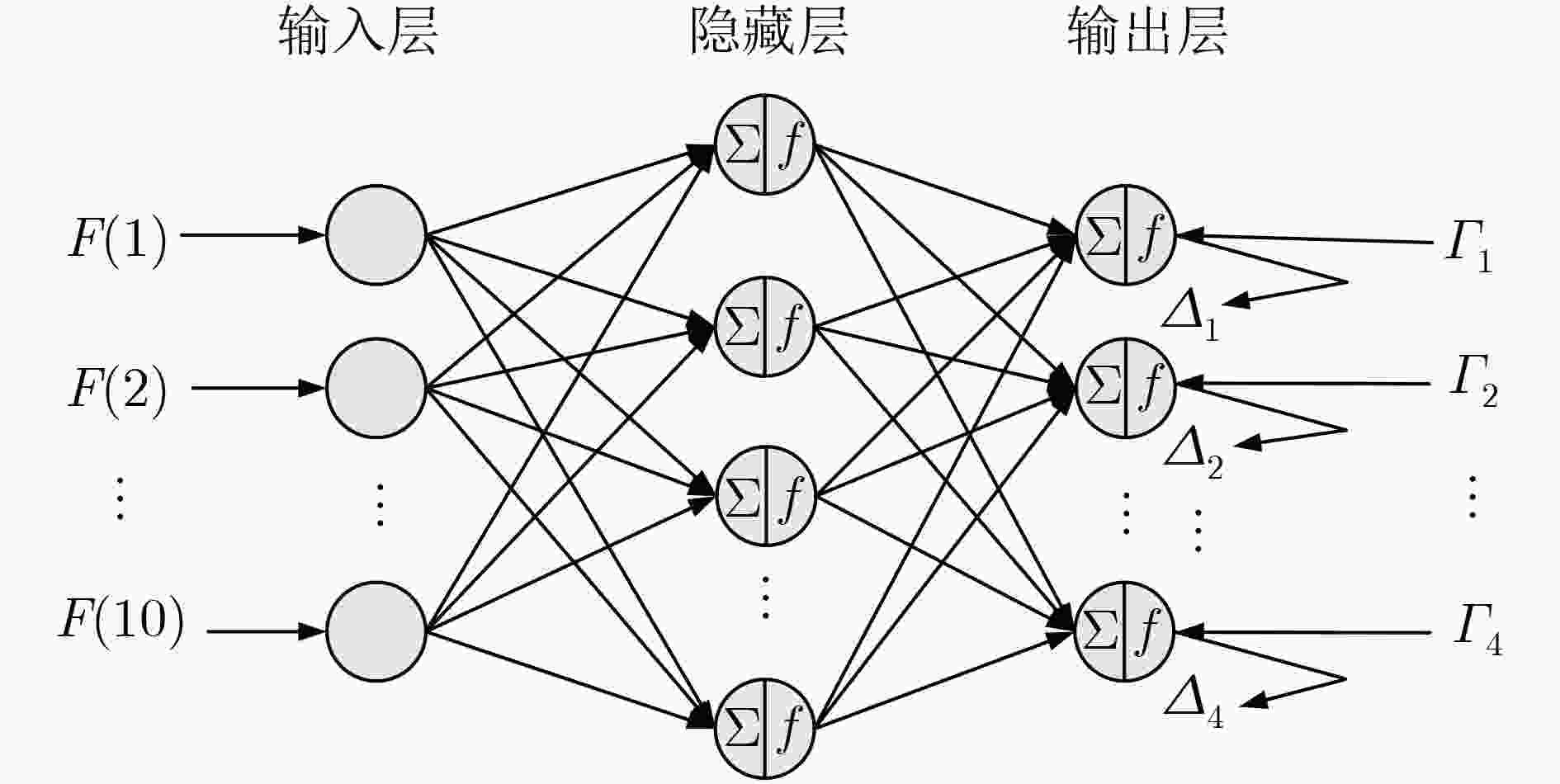
${{{e}}_1},\,{{{e}}_2}, \,{{{e}}_3}$;(10) for $j$=1, 2, 3 (11) 用式(11)计算特征向量1阶差分均值${\phi _j}$; (12) end for (13) 对$\left\| {{\tilde{ H}}} \right\|$的分布标准化得到${{Z}}$; (14) for $k$=1, 2, 3 (15) 将${{Z}}$投影到${{{e}}_k}$上,得到${{{p}}_k}$; (16) 计算${{{p}}_k}$的方差,得到${\beta _i}$; (17) end for (18) 构建样本空间${{{F}}_i}$; (19) 将${{{F}}_i}$输入到神经网络模型,得到输出特征${{{F'}}_i}$; (20) end for (21) for $l$=1, 2, $···, N$ (22) ${{F''}} = {{F''}} + {{{F'}}_l}$; (23) end for 表 2 收发机参数设置
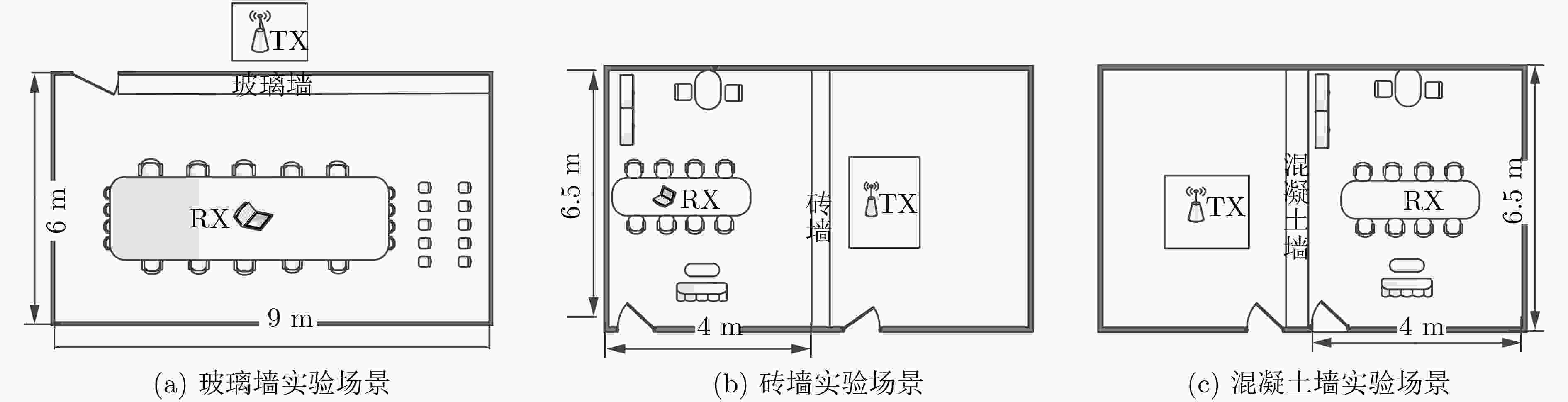
参数 发射机 接收机 模式 Injection Monitor 信道编号 149(5.749 GHz) 带宽 40 MHz 发包速率 500 包/s 子载波个数 30 子载波编号 –58, –54, ···, 54, 58 发射功率 15 dBm -
ADIB F, MAO Hongzi, KABELAC Z, et al. Smart homes that monitor breathing and heart rate[C]. The 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Korea, 2015: 837–846. doi: 10.1145/2702123.2702200. ZHANG Dongheng, HU Yang, CHEN Yan, et al. BreathTrack: Tracking indoor human breath status via commodity WiFi[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3899–3911. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2893330 ABDELNASSER H, HARRAS K, and YOUSSEF M. A ubiquitous WiFi-based fine-grained gesture recognition system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 18(11): 2474–2487. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2879075 DUAN Shihong, YU Tianqing, and HE Jie. WiDriver: Driver activity recognition system based on WiFi CSI[J]. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 2018, 25(2): 146–156. doi: 10.1007/s10776-018-0389-0 XIA Lu, CHEN C C, and AGGARWAL J K. Human detection using depth information by Kinect[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2011 WORKSHOPS, Colorado Springs, USA, 2011: 15–22. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2011.5981811. KOSBA A E, SAEED A, and YOUSSEF M. RASID: A robust WLAN device-free passive motion detection system[C]. 2012 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Lugano, Switzerland, 2012: 180–189. doi: 10.1109/PerCom.2012.6199865. YANG Lei, LIN Qiongzheng, LI Xiangyang, et al. See through walls with COTS RFID system[C]. The 21st Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Paris, France, 2015: 487–499. doi: 10.1145/2789168.2790100. XIAO Jiang, WU Kaishun, Yi Youwen, et al. FIMD: Fine-grained device-free motion detection[C]. The 18th IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Singapore, 2012: 229–235. doi: 10.1109/ICPADS.2012.40. XI Wei, ZHAO Jizhong, LI Xiangyang, et al. Electronic frog eye: Counting crowd using WiFi[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2014 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, Canada, 2014: 361–369. doi: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2014.6847958. QIAN Kun, WU Chenshu, YANG Zheng, et al. PADS: Passive detection of moving targets with dynamic speed using PHY layer information[C]. The 20th IEEE International Conference on Parallel And Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Taipei, China, 2014: 183–190. doi: 10.1109/PADSW.2014.7097784. WU Chenshu, YANG Zheng, ZHOU Zimu, et al. Non-Invasive Detection of Moving and Stationary Human With WiFi[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(11): 2329–2342. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2430294 ZHOU Zimu, YANG Zheng, WU Chenshu, et al. Omnidirectional coverage for device-free passive human detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(7): 1819–1829. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.274 ADIB F and KATABI D. See through walls with WiFi![J]. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2013, 43(4): 75–86. doi: 10.1145/2534169.2486039 DI DOMENICO S, DE SANCTIS M, CIANCA E, et al. WiFi-based through-the-wall presence detection of stationary and moving humans analyzing the Doppler spectrum[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2018, 33(5/6): 14–19. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2018.170124 ZHU Hai, XIAO Fu, SUN Lijuan, et al. R-TTWD: Robust device-free through-the-wall detection of moving human with WiFi[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(5): 1090–1103. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2679578 LI Fan, XU Cheng, LIU Yang, et al. Mo-sleep: Unobtrusive sleep and movement monitoring via Wi-Fi signal[C]. The 35th IEEE International Performance Computing and Communications Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 173–180. doi: 10.1109/PCCC.2016.7820634. 李姣军, 余景鹏, 陶金, 等. 一维信号的小波去噪[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2016, 30(12): 83–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2016.12.013LI Jiaojun, YU Jingpeng, TAO Jin, et al. Review of one-Dimensional signal wavelet de-noising[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology:Natural Science, 2016, 30(12): 83–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8425(z).2016.12.013 LE CUN Y, BOSER B, DENKER J S, et al. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network[C]. The Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2, San Francisco, USA, 1990: 396–404. -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
