A Source-location Privacy Preservation Method Based on Hilbert-filling-curve Routing Protocol in Marine Wireless Sensor Networks
-
摘要:
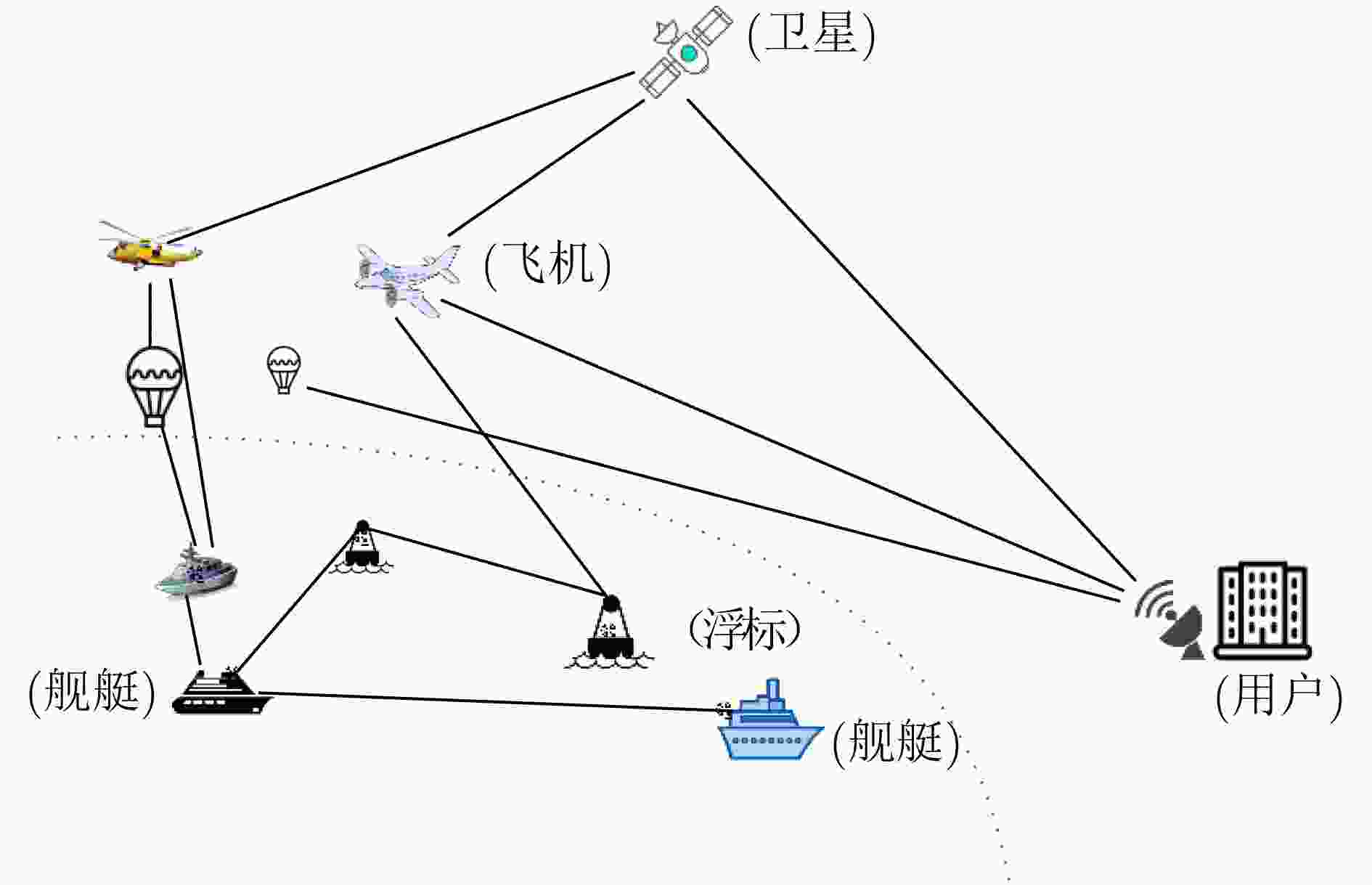
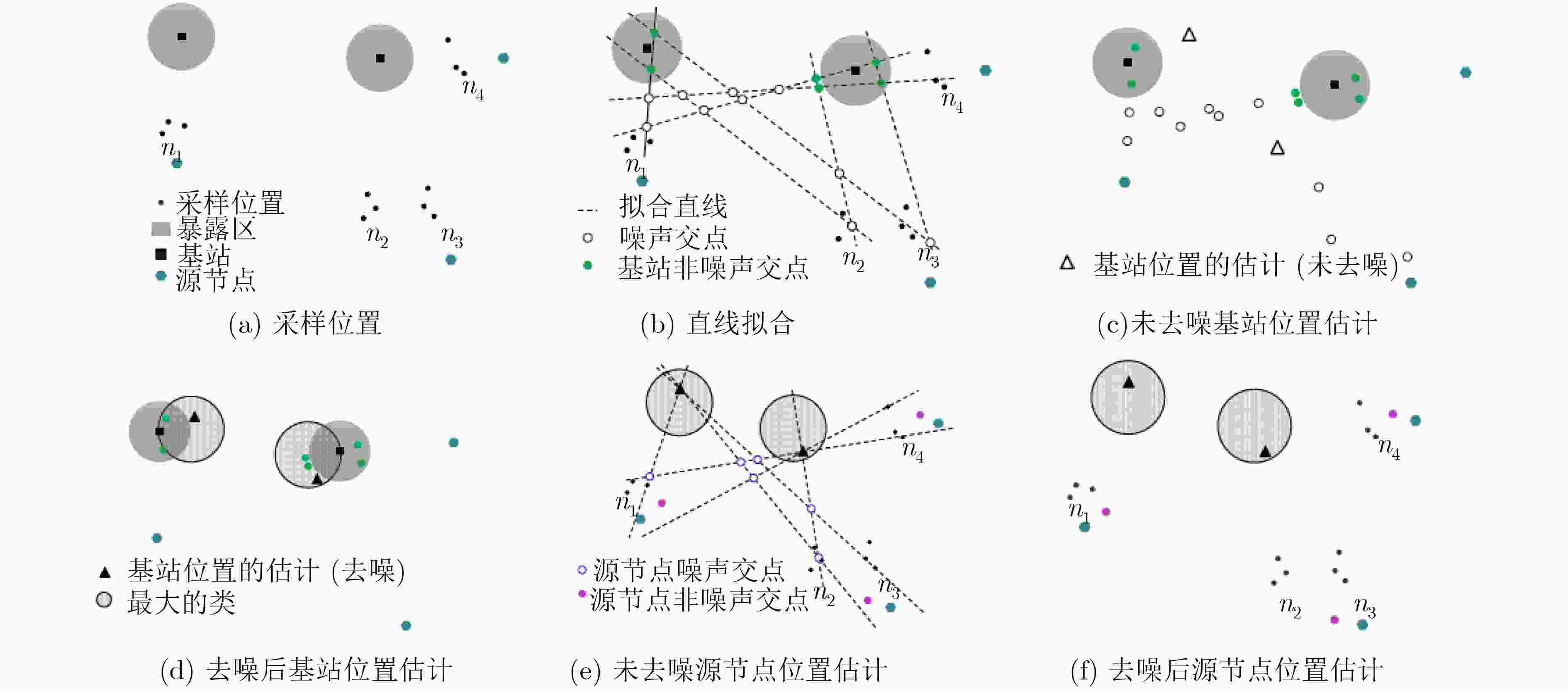
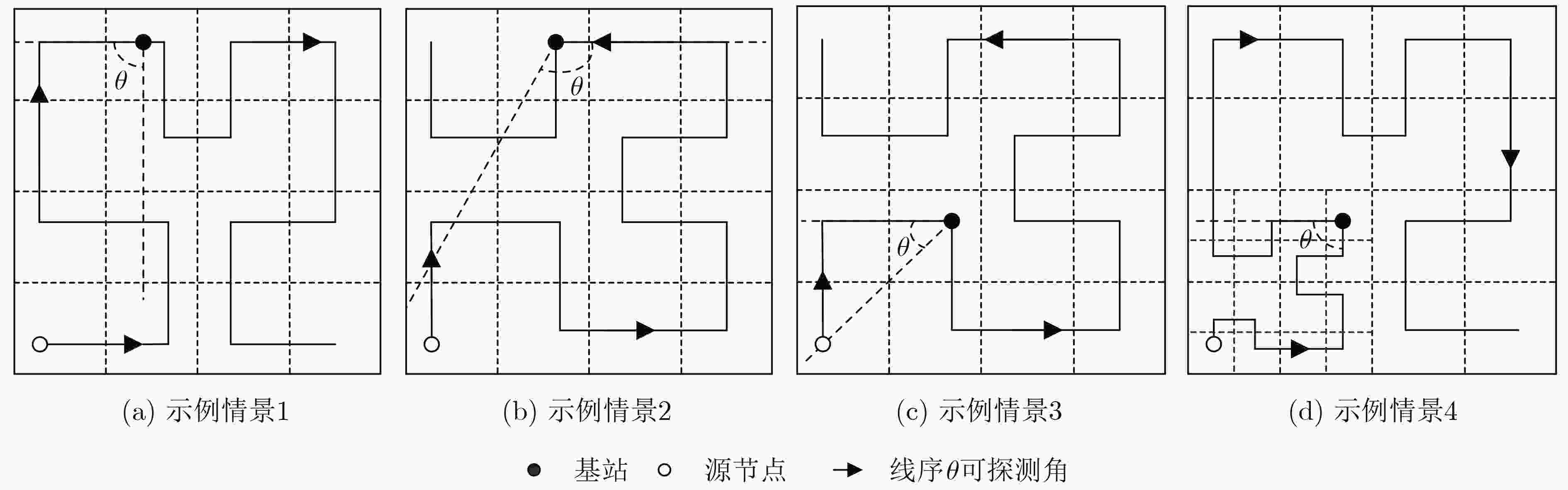
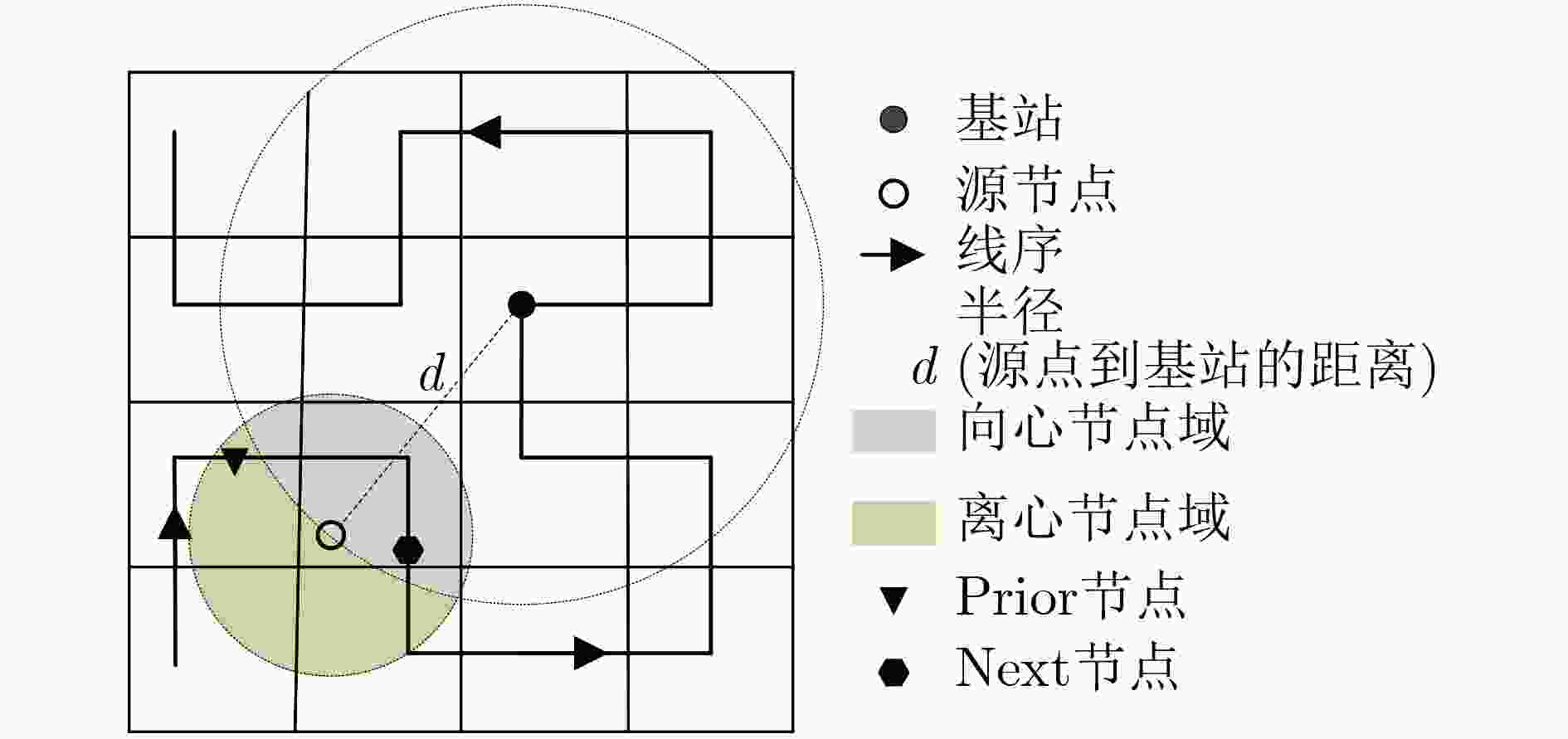
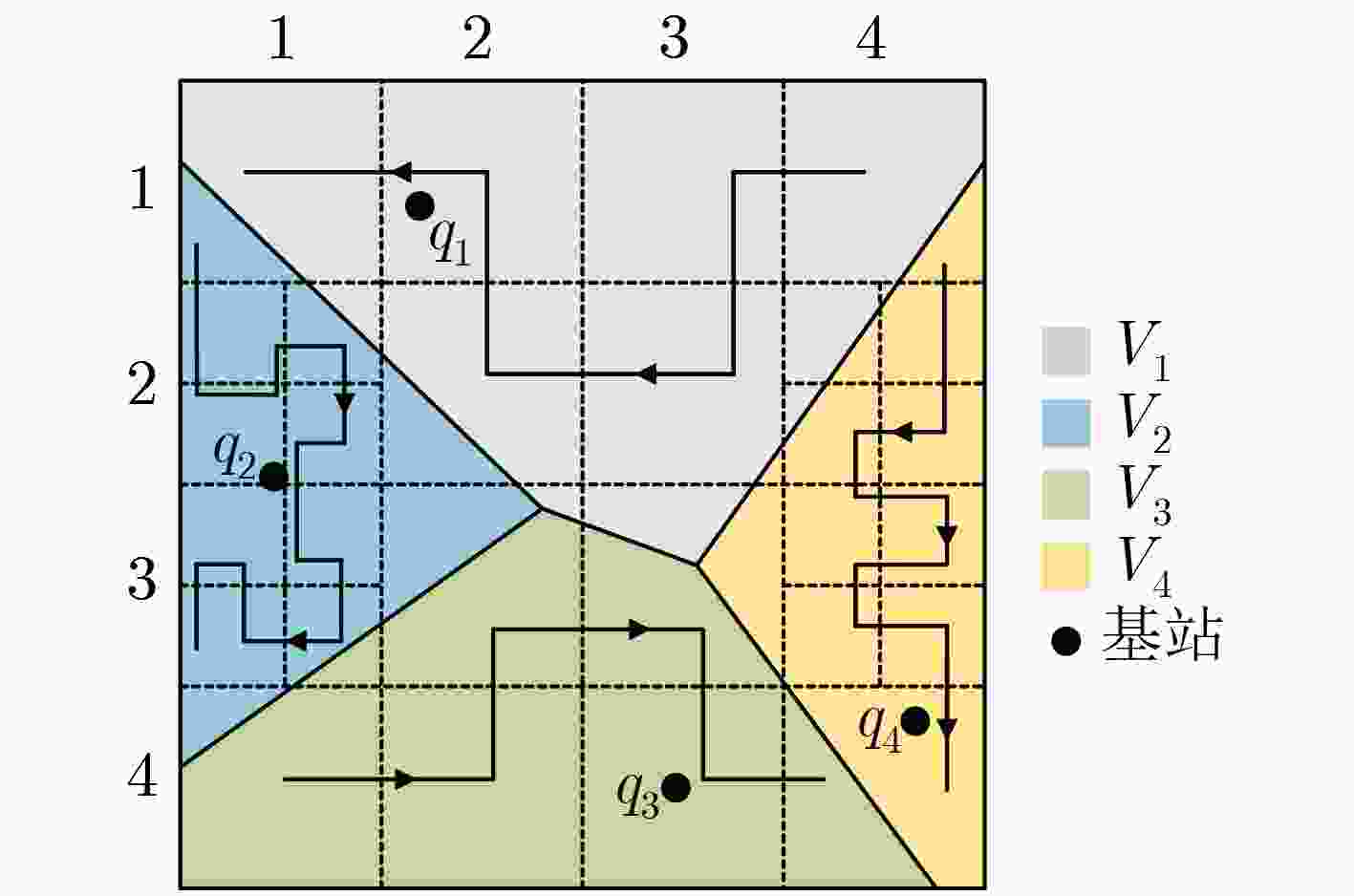
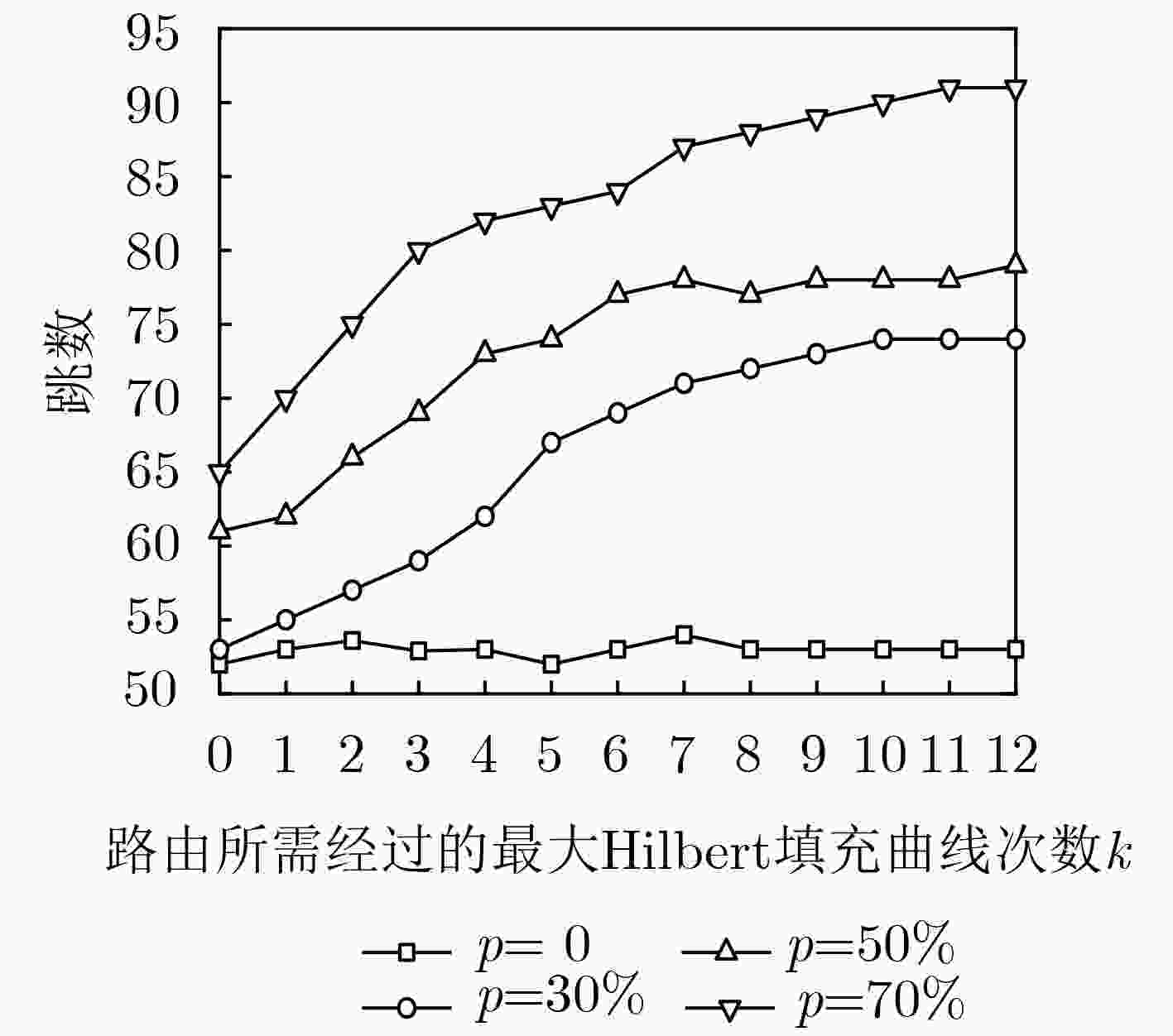
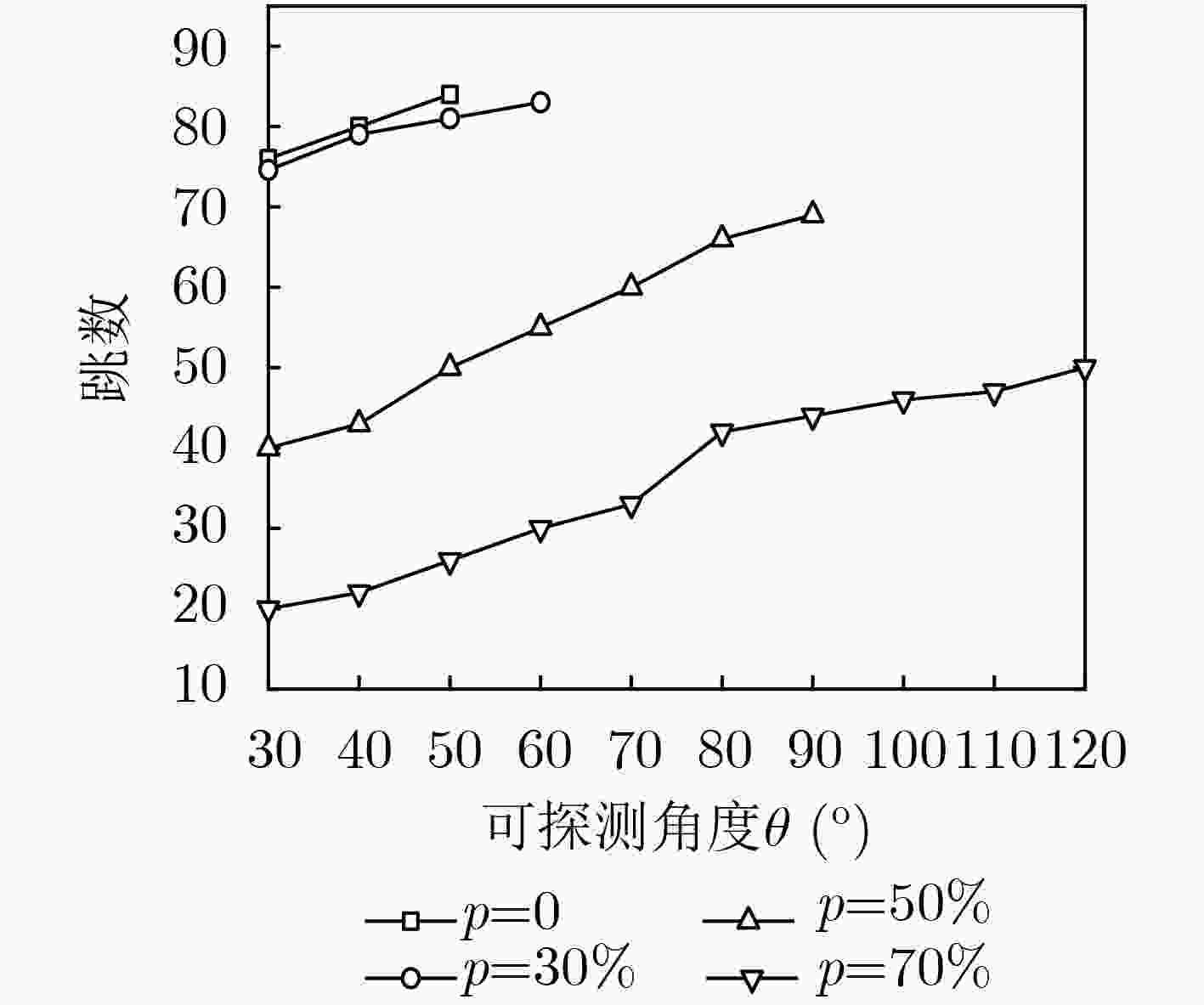
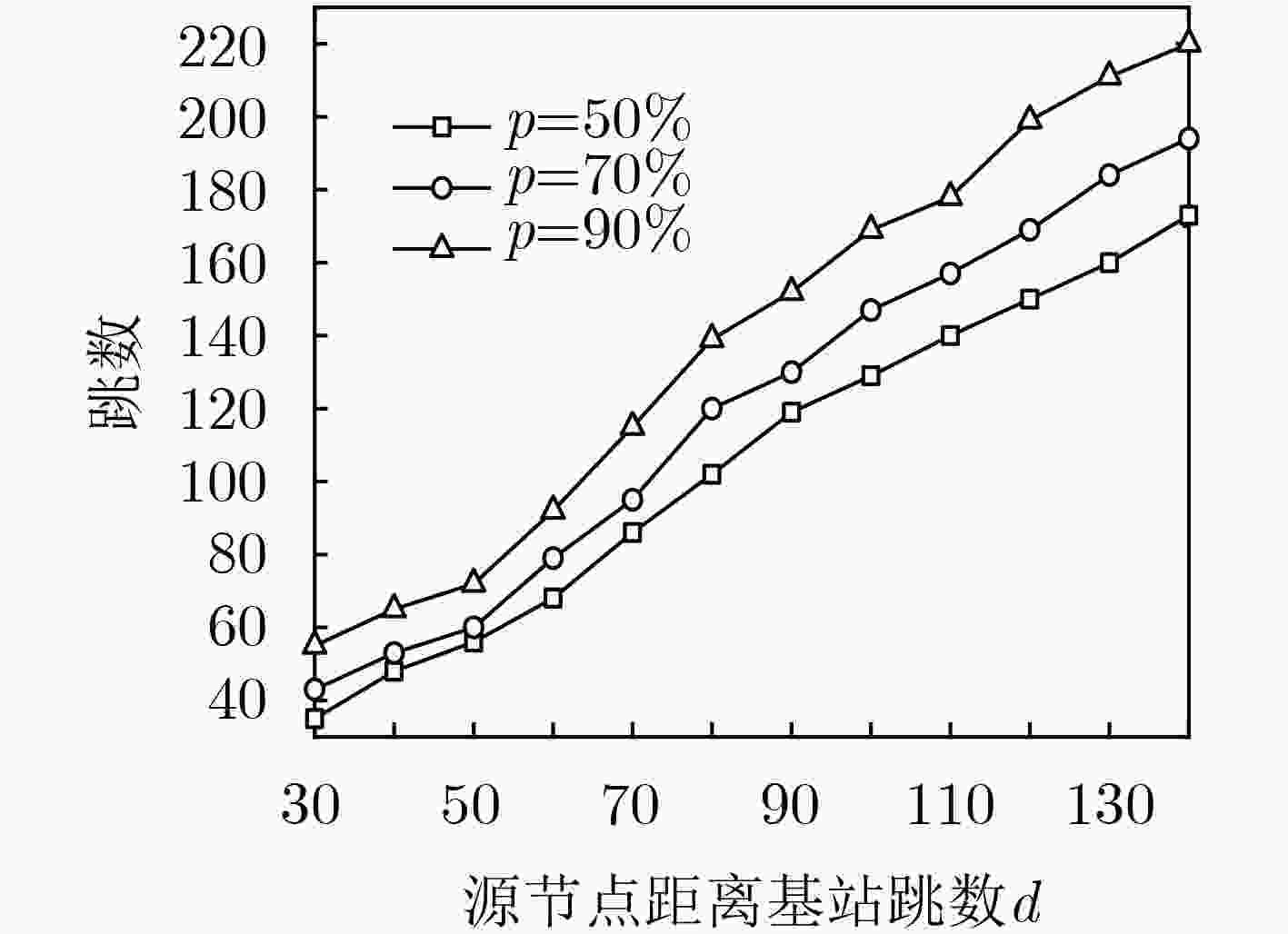
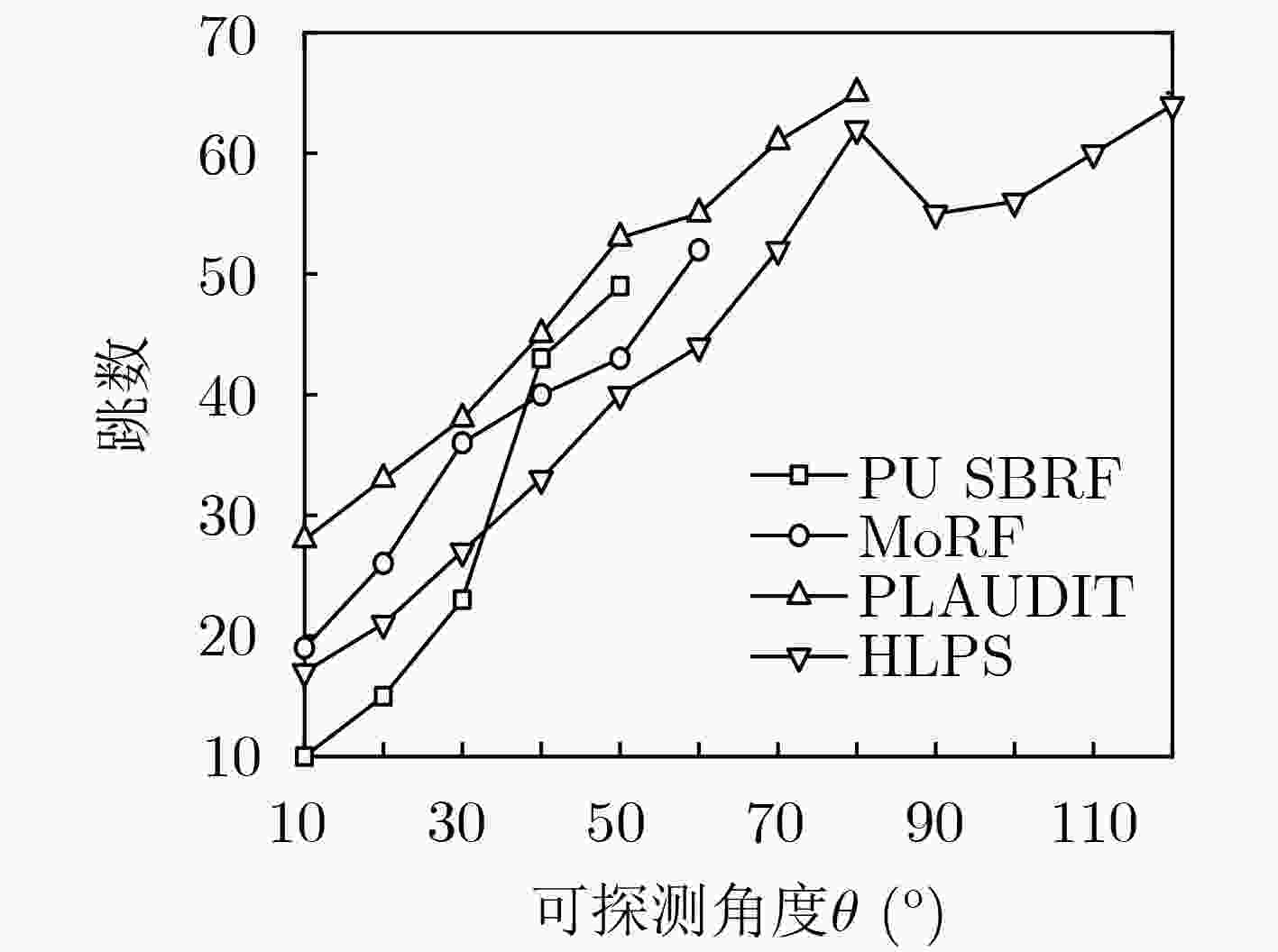
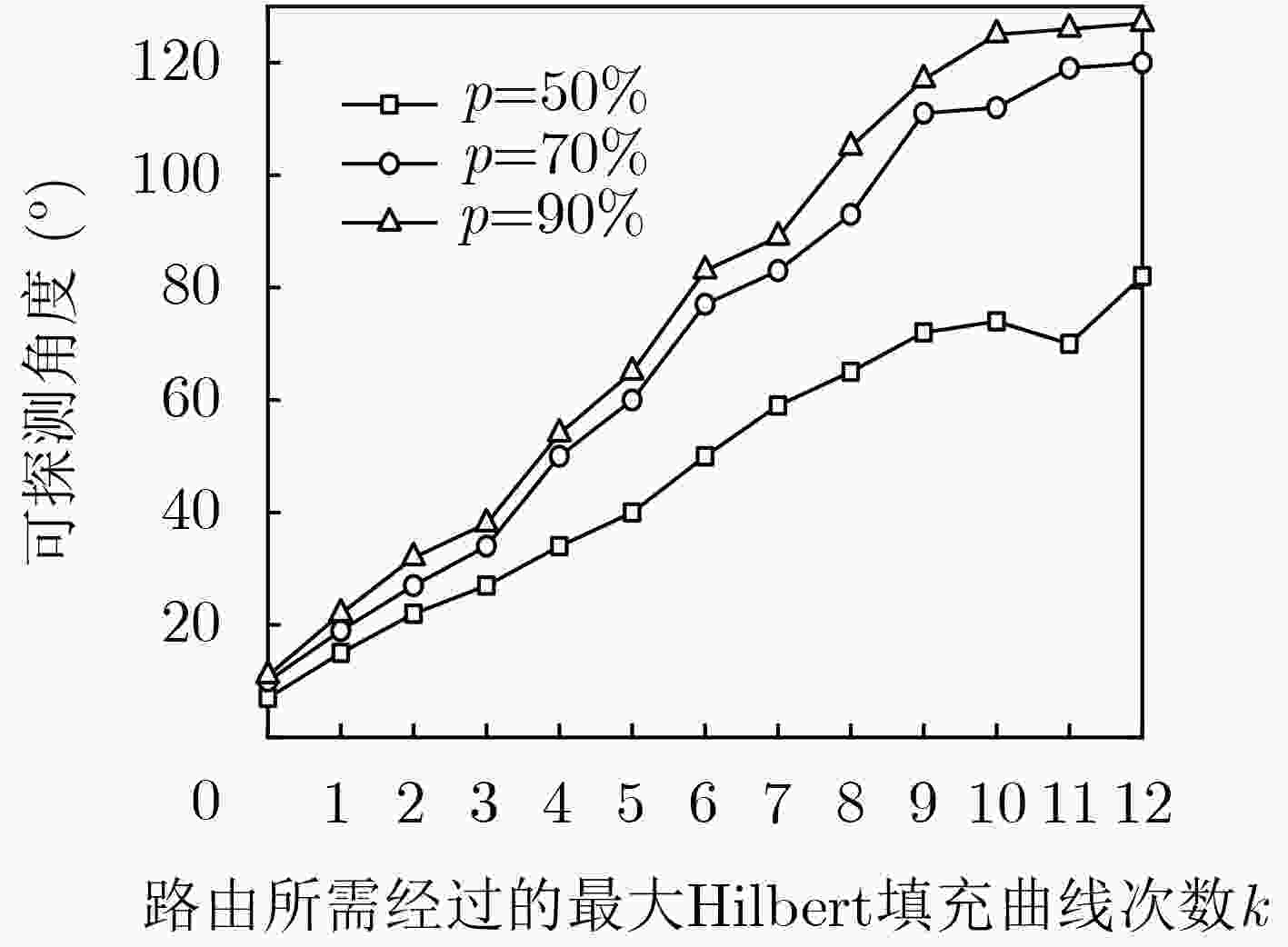
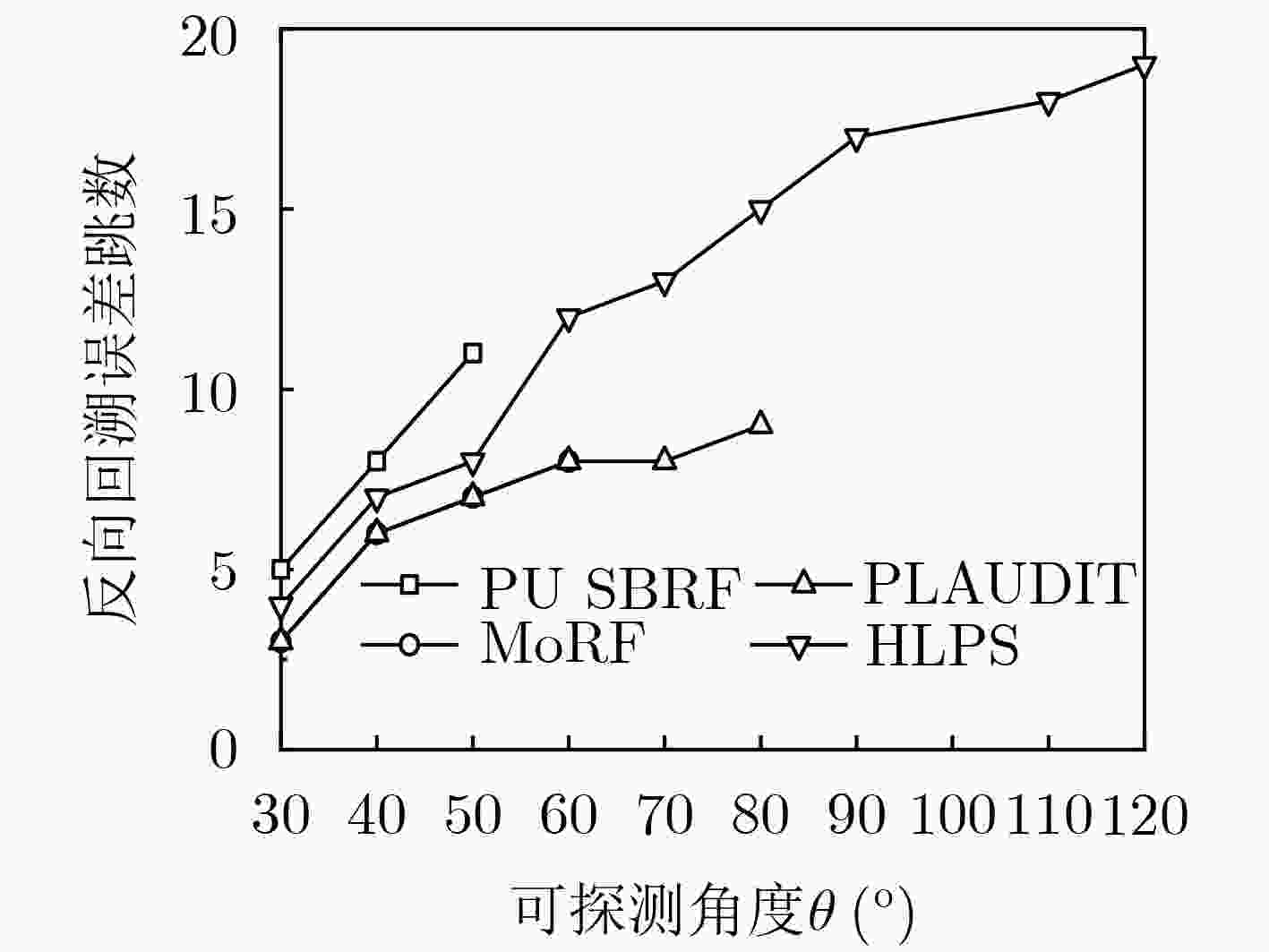
节点位置保护对于海洋无线传感器网络(MWSNs)至关重要,尤其是对于无人值守的环境。然而,由于大多数静态部署,传感器的能量、存储和通信能力的限制,MWSNs容易受到各种位置(和衍生)攻击的影响。该文从攻击和防御两个方面研究节点位置隐私保护问题。首先,针对两种重要节点(包括基站和源节点)提出了一种新的二相定位攻击,它可以在少量的本地无线传输监视中找到基站节点,反向跟踪源节点的位置。与现有方法不同,提出的攻击根据传输方向确定节点位置,从而突破现有的防御。然后,为了抵御这种攻击,该文设计了一种基于Hilbert填充曲线的传感器网络路由节点位置隐私保护方法(HLPS)。攻防理论分析与对抗实验表明,该方法能够保护目标节点的位置隐私,具有较小的通信和计算开销。
-
关键词:
- 海上无线传感网 /
- 网络安全 /
- 网络位置隐私保护 /
- Hilbert填充曲线
Abstract:Source node location protection is critical to the Marine Wireless Sensor Networks (MWSNs), especially for unattended environment. However, due to most of the static deployment and the limitations in energy, storage and communication capabilities of the sensors, MWSNs are vulnerable to various location (and derivative) attacks. In this work, the node location privacy protection issues are studied from both aspects of attacks and defenses. First, a new two-phase location attack is proposed for two important types of nodes (including base station and source node). It can locate a base station node within few amounts of local wireless transmission monitoring, and then reversely traces the location of the source node. Different from existing methods, the proposed attack determines the node location based on the transmission direction, which can break through existing defenses. Then, to defend against such attack, a Hilbert-filling-curve-based Location-privacy Protection Scheme (HLPS) is designed for MWSNs. The theory analysis and confrontation experiment of attack and defense show that the proposed scheme owns capable of protecting the location privacy of the target node with moderate communication and computation overhead.
-
WALID E, THOMAS N, EOIN O, et al. Trust security mechanism for maritime wireless sensor networks[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2017, 29(23): e3945. doi: 10.1002/cpe.3945 陈娟, 方滨兴, 殷丽华, 等. 传感器网络中基于源节点有限洪泛的源位置隐私保护协议[J]. 计算机学报, 2010, 33(9): 1736–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.01736CHEN Juan, FANG Binxing, YIN Lihua, et al. A source-location privacy preservation protocol in wireless sensor networks using source-based restricted flooding[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2010, 33(9): 1736–1747. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.01736 BAROUTIS N and YOUNIS M. Using fake sinks and deceptive relays to boost base-station anonymity in wireless sensor network[C]. The 40th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Clearwater Beach, USA, 2015: 109–116. doi: 10.1109/LCN.2015.7366289. DI PIETRO R and VIEJO A. Location privacy and resilience in wireless sensor networks querying[J]. Computer Communications, 2011, 34(3): 515–523. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2010.05.014 AL-MISTARIHI M F, TANASH I M, YASEEN F S, et al. Protecting source location privacy in a clustered wireless sensor networks against local eavesdroppers[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(1): 42–54. doi: 10.1007/s11036-018-1189-6 NGAI E C H and RODHE I. On providing location privacy for mobile sinks in wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Networks, 2013, 19(1): 115–130. doi: 10.1007/s11276-012-0454-z WANG Jian, WANG Fengyu, CAO Zhenzhong, et al. Sink location privacy protection under direction attack in wireless sensor networks[J]. Wireless Networks, 2017, 23(2): 579–591. doi: 10.1007/s11276-015-1179-6 彭志宇, 李善平. 移动环境下LBS位置隐私保护[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(5): 1211–1216. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01050PENG Zhiyu and LI Shanping. Protecting location privacy in location-based services in mobile environments[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(5): 1211–1216. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01050 LONG Jun, LIU Anfeng, DONG Mianxiong, et al. An energy-efficient and sink-location privacy enhanced scheme for WSNs through ring based routing[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2015, 81–82: 47–65. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2015.04.003 LIU Anfeng, LIU Xiao, TANG Zhipeng, et al. Preserving smart sink-location privacy with delay guaranteed routing scheme for WSNs[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2017, 16(3): 68. doi: 10.1145/2990500 BAROUTIS N and YOUNIS M. Load-conscious maximization of base-station location privacy in wireless sensor networks[J]. Computer Networks, 2017, 124: 126–139. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2017.06.021 LIN Xiaodong, LU Rongxing, LIANG Xiaohui, et al. STAP: A social-tier-assisted packet forwarding protocol for achieving receiver-location privacy preservation in VANETs[C]. 2011 IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 2011: 2147–2155. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2011.5935026. FAN Yanfei, JIANG Yixin, ZHU Haojin, et al. An efficient privacy-preserving scheme against traffic analysis attacks in network coding[C]. The 28th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2009: 2213–2221. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2009.5062146. HU Ling, KU W S, BAKIRAS S, et al. Spatial query integrity with voronoi neighbors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2013, 25(4): 863–876. doi: 10.1109/tkde.2011.267 KALNIS P, GHINITA G, MOURATIDIS K, et al. Preventing location-based identity inference in anonymous spatial queries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2007, 19(12): 1719–1733. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2007.190662 WANG Weiping, CHEN Liang, and WANG Jianxin. A source-location privacy protocol in WSN based on locational angle[C]. 2008 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Beijing, China, 2008: 1630–1634. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2008.315. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
