Estimation of Volume Target Length in Alpha Distribution Noise
-
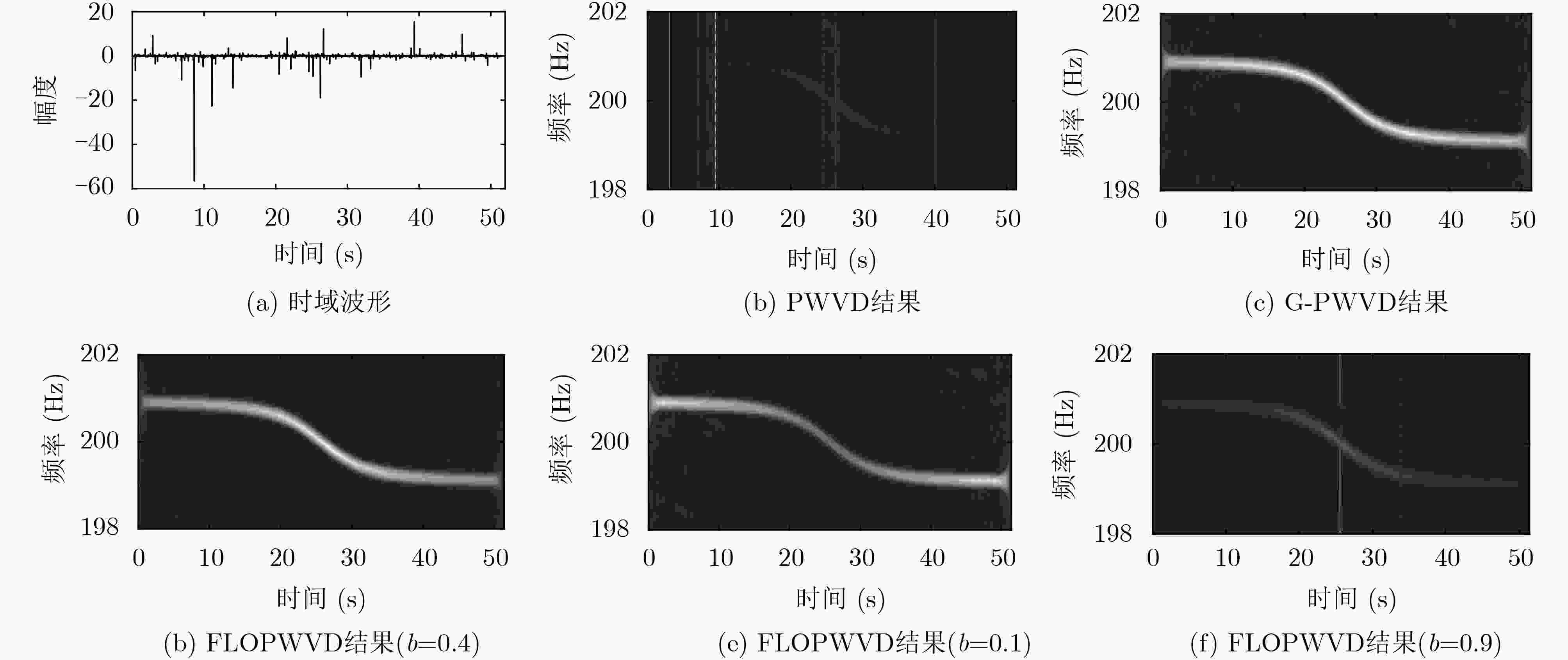
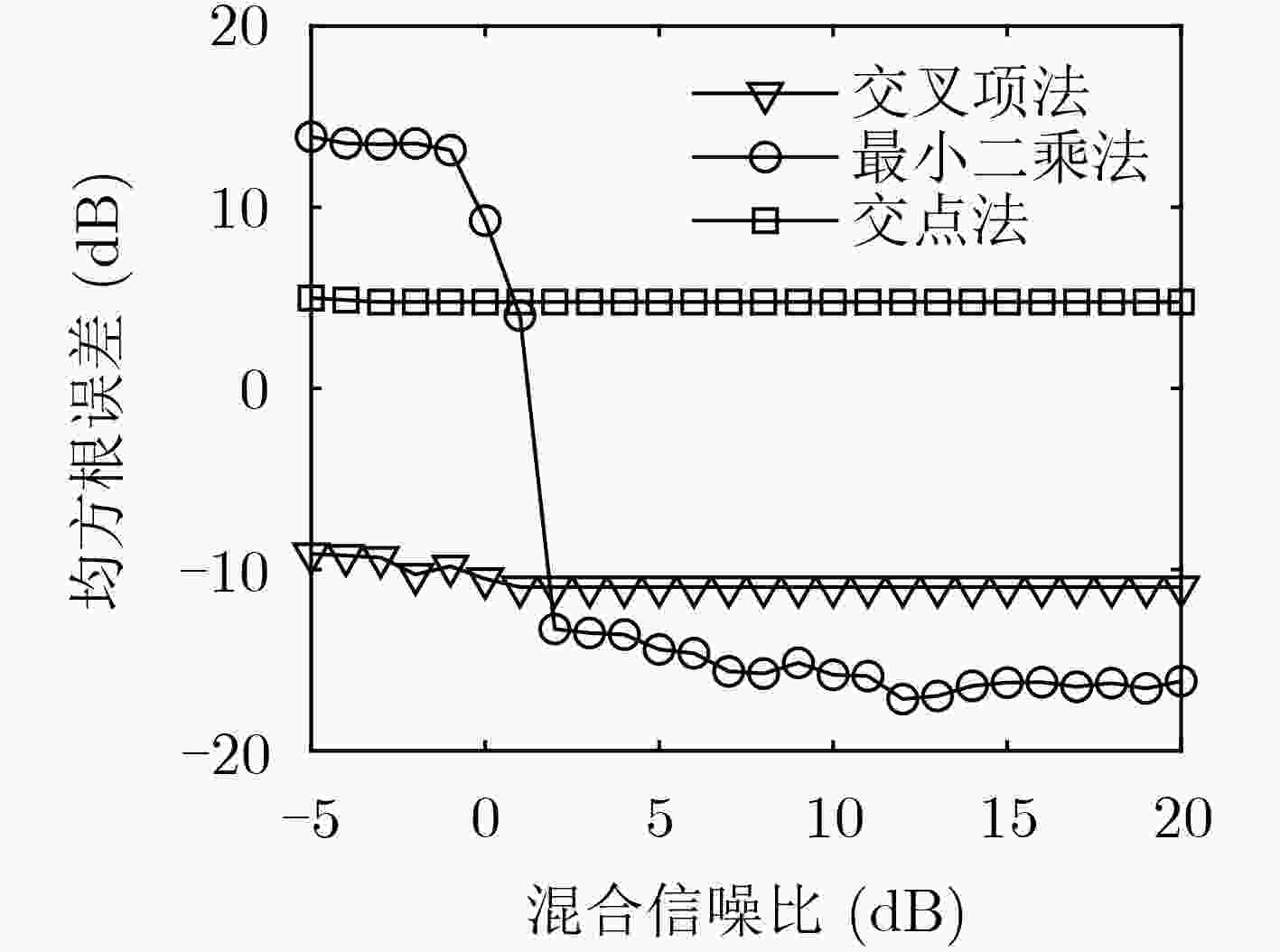
摘要: 为了解决Alpha稳定分布噪声环境下运动舰船目标的长度估计问题,该文借鉴非线性变换抑制脉冲噪声以及多普勒目标运动特性估计思想,提出基于广义时频分析(G-TFA)和最小二乘估计的运动目标长度估计方法。该方法首先利用G-TFA获取Alpha稳定分布噪声环境下运动目标的多普勒频率,然后利用最小二乘方法估计出目标航速和不同位置的横正时刻,最后利用上述估计结果计算目标长度。以广义Winger-Ville分布(G-WVD)为例,从理论上推导了G-TFA在Alpha稳定分布噪声环境下具有提取目标多普勒特征的能力,并通过仿真实验验证了该算法在中低混合信噪比下的稳健性。与现有算法相比,该文所提算法不需要估计噪声特征指数,算法性能优于基于传统时频分析的估计方法。
-
关键词:
- 目标长度估计 /
- 横正时刻估计 /
- Alpha稳定分布噪声 /
- 广义时频分析 /
- 多普勒分析
Abstract: In order to estimate the length of moving ship targets in Alpha stable distribution noise, a moving target length estimation method based on Generalized Time-Frequency Analysis (G-TFA) and least squares estimation is proposed, which utilizes nonlinear transform to suppress impulsive noise and Doppler effect to estimate target motion characteristics. The method uses G-TFA to obtain the Doppler frequency of moving targets in a stable distributed noise environment. Then, the least squares method is used to estimate the target speed and the closest point of approach time of different positions. Finally, the target length is calculated using the above estimation results. Taking Generalized Winger-Ville Distribution (G-WVD) as an example, the ability of G-TFA to extract Doppler features in Alpha stable distributed noise is theoretically derived. The robustness of the proposed method under low-to-medium mixed signal-to-noise ratio is verified by simulation experiments. Compared with the existing methods, the proposed method does not need to estimate the noise characteristic index, and the performance is better than the methods based on the traditional time-frequency analysis. -
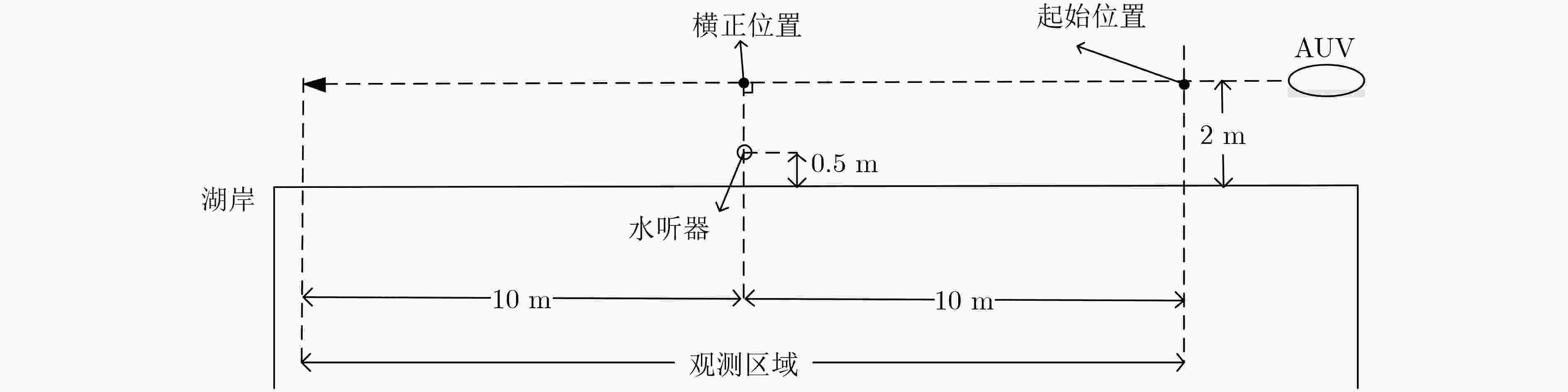
表 1 实验条件
被测目标 天和防务TH-B050R型AUV 采集设备 Ocean Sonics公司icListen HF智能水听器 测试地点 信息工程大学中心校区人工湖,测试区域水深1.5 m左右 测试环境 有雨并伴有4~5级风 表 2 最小二乘参数估计结果
横正距离(m) 横正时刻(s) 速度(m/s) 记录值 1.50 12.58 0.795 估计值 1.56 12.52 0.748 表 3 横正距离50 m的识别结果
目标类型 识别类型 大 中 小 错误 大 142 10 0 4 中 11 233 3 2 小 0 6 87 3 -
李余兴, 李亚安, 陈晓. 基于EEMD的舰船辐射噪声特征提取方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(5): 114–119. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.05.018LI Yuxing, LI Yaan, and CHEN Xiao. Ships’ radiated noise feature extraction based on EEMD[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(5): 114–119. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.05.018 YAN Jiaquan, SUN Haixin, CHEN Hailan, et al. Resonance-based time-frequency manifold for feature extraction of ship-radiated noise[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4): 936. doi: 10.3390/s18040936 相敬林, 刘勋. 舰船做为体积声源的源强度谱纵向分布特性[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2002, 24(2): 5–9, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2002.02.002XIANG Jinglin and LIU Xun. The longitudinal distribution of source intensity spectrum of ship-radiated noise[J]. Journal of Detection &Control, 2002, 24(2): 5–9, 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2002.02.002 周有, 韩鹏, 相敬林. 舰船作为体积目标时噪声通过特性的仿真[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2005, 27(2): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2005.02.017ZHOU You, HAN Peng, and XIANG Jinglin. Simulation of radiated noise of the ship as a volume target[J]. Journal of Detection &Control, 2005, 27(2): 61–64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1194.2005.02.017 陈韶华, 李世智, 陈川. 子带通过特性分析用于体积目标识别的研究[C]. 中国声学学会2007年青年学术会议论文集(下), 武汉, 2007: 211–212.CHEN Shaohua, LI Shizhi, and CHEN Chuan. Volume target recognition with subband passage signature analysis[C]. China Acoustics Society 2007 Youth Conference, Wuhan, China, 2007: 211–212. 刘勋, 相敬林, 张文军, 等. 自适应舰船被动跟踪与尺度估计的实验研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2002, 23(1): 54–58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2002.01.013LIU Xun, XIANG Jinglin, ZHANG Wenjun, et al. Experimental study on the adaptive passive tracking and size estimation of ships[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2002, 23(1): 54–58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2002.01.013 石杰, 相敬林, 陈韶华, 等. 七元非典型声强向量阵对舰船的被动定向和尺度估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(6): 1483–1486.SHI Jie, XIANG Jinglin, CHEN Shaohua, et al. The bearing and size estimation of Volume target based on a vector sound intensity array[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(6): 1483–1486. 王笑. 目标舰船尺度特性估计算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国舰船研究院, 2015.WANG Xiao. Research on the scale estimates algorithm of the Ship target characteristic[D]. [Master dissertation], China Ship Research and Development Academy, 2015. 张揽月, 丁丹丹, 杨德森, 等. 阵元随机均匀分布球面阵列联合噪声源定位方法[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(1): 014303. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.014303ZHANG Lanyue, DING Dandan, YANG Desen, et al. Noise source identification by using near field acoustic holograpy and focused beamforming based on spherical microphone array with random unifrom distribution of elements[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(1): 014303. doi: 10.7498/aps.66.014303 俞孟萨, 庞业珍. 舰船辐射声场及声源特性测量方法研究综述[J]. 船舶力学, 2017, 21(1): 107–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2017.01.013YU Mengsa and PANG Yezhen. A review of measurement methods of radiation acoustic field and acoustic source characteristics for ships[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2017, 21(1): 107–126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2017.01.013 CHITRE M, POTTER J, and HENG O S. Underwater acoustic channel characterisation for medium-range shallow water communications[C]. OCEANS '04 MTS/IEEE TECHNO-OCEAN '04, Kobe, Japan, 2004: 40–45. 张安清, 邱天爽, 章新华. α稳定分布的水声信号处理新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(8): 1201–1204.ZHANG Anqing, QIU Tianshuang, and ZHAND Xinhua. A new underwater acoustic signals processing approach to α-stable distribution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2005, 27(8): 1201–1204. FERGUSON B G. Doppler effect for sound emitted by a moving airborne source and received by acoustic sensors located above and below the sea surface[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1993, 94(6): 3244–3247. doi: 10.1121/1.407230 XU Lingji and YANG Yixin. Parameter estimation of underwater moving sources by using matched Wigner transform[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 101: 5–14. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.07.020 GRIFFITH D W, GONZALEZ J G, and ARCE G R. Robust time-frequency representations for signals in α-stable noise using fractional lower-order statistics[C]. 1997 IEEE Signal Processing Workshop on Higher-Order Statistics, Banff, Canada, 1997: 415–419. 张俊林, 王彬, 汪洋, 等. 一种α稳定分布噪声下OFDM信号调制识别与参数估计算法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(6): 1390–1396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.06.017ZHANG Junlin, WANG Bin, WANG Yang, et al. An algorithm for recognition and parameters estimation of OFDM in alpha stable distribution noise[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(6): 1390–1396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.06.017 LI Qin, YUAN Bingchen, and MING Xing. Simulation technique of radiated noise from underwater target and its implement of simulator[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics and Intelligent Transportation System, Shenzhen, China, 2009: 357–360. 罗建, 赵亚磊, 黄仁可. 作为体积目标的舰船辐射噪声建模[J]. 数字海洋与水下攻防, 2018, 1(2): 38–42.LUO Jian, ZHAO Yalei, and HUANG Renke. Modelling of ship-radiated noise as volume targets[J]. Digital Ocean &Underwater Warfare, 2018, 1(2): 38–42. -





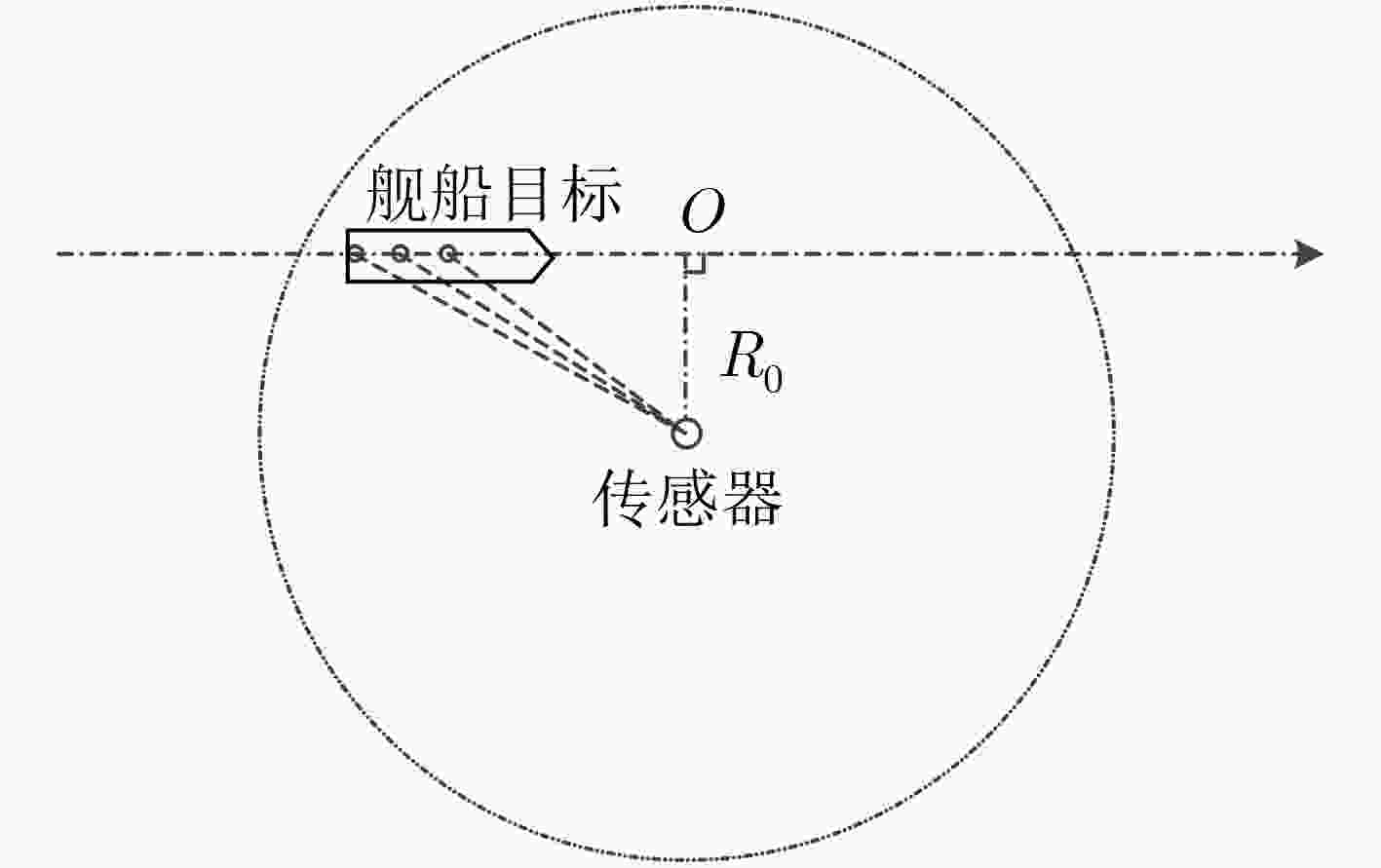
 下载:
下载:
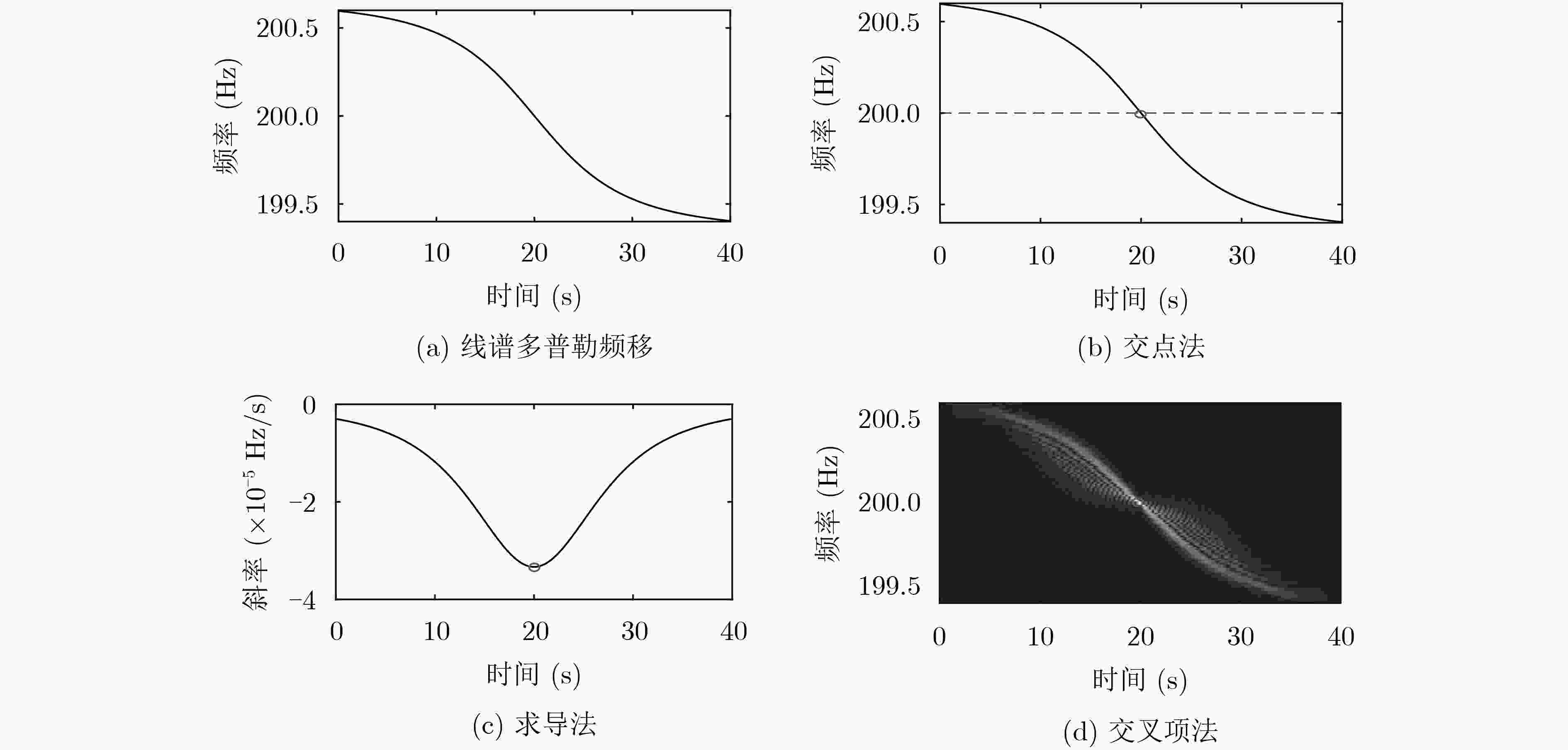
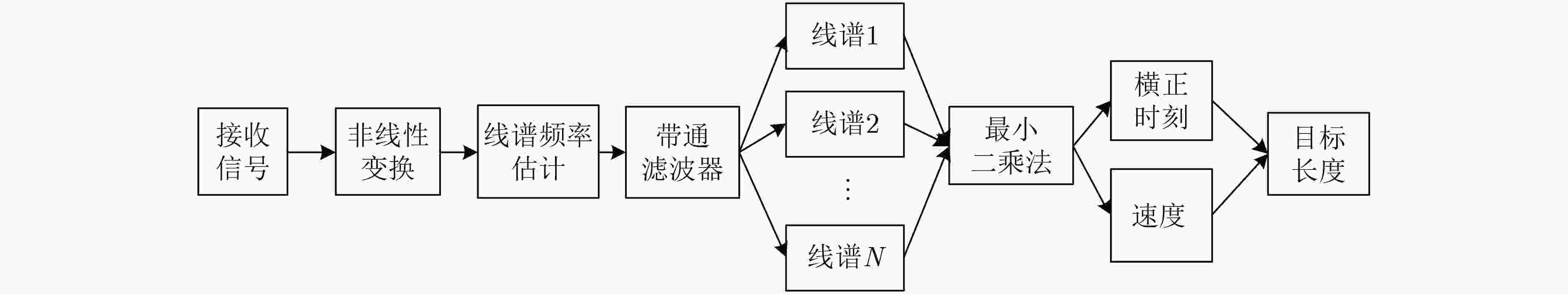





 下载:
下载:
