Indoor Localization Algorithm Based on Array Antenna and Sparse Bayesian Learning
-
摘要:
由于多径和非同源等因素的影响,传统基于蓝牙信号强度的室内定位方法的性能精度和稳定性都不高。针对基于蓝牙信号的复杂室内环境定位问题,该文提出基于低成本阵列天线的室内定位方法,该方法利用单通道轮采极化敏感阵列天线对蓝牙信号进行采样,然后结合暗室测量获得的准确阵列流形和极化快收敛稀疏贝叶斯学习(P-FCSBL)算法实现信源的角度估计,最后通过角度实现定位。该方法充分利用极化信息和角度信息来实现目标和多径信号的分离,同时对单信源的同时采样保证了估计的稳定性。最后通过实测数据处理验证了该方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 室内定位 /
- 极化快收敛稀疏贝叶斯学习 /
- 极化敏感阵列天线
Abstract:Due to the influence of many factors such as multipath and multi-source, the traditional indoor localization algorithms based on Bluetooth signal strength have low performance in accuracy and stability. In order to solve the location problem in complex indoor environment based on Bluetooth signal, an indoor localization algorithm based on low-cost array antenna is developed. The algorithm utilizes single-channel using switch-antenna polarization sensitive array to sample Bluetooth signal, then combines the accurate array manifold measured in dark room and the algorithm of Polarized Fast Converging Sparse Bayesian Learning (P-FCSBL) to estimate the source’s angle, and finally gets the target location by angle. This algorithm makes full use of polarization information and angle information to separate target and multipath signal, and simultaneous sampling of one source ensures estimation stability. Finally, the effectiveness of the method is verified by the real data.
-
初始化: $ {\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)^{\left( 1 \right)}}{\rm{ = }}{\widehat \sigma ^2}$ $ {{{v}}_i} = {{{S}}_i}{{{h}}_i},i = 1,2, ··· ,P$ $ {{D}} = \left[ {{{{v}}_1}\;{{{v}}_2}\; ··· \;{{{v}}_P}} \right]$ $ \gamma _i^{\left( 1 \right)} = \left| {{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{x}}} \right|/\left| {{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{{v}}_i}} \right|,i = 1,2, ··· ,P$ $ {{{C}}^{\left( 1 \right)}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i{\rm{ = }}1}^P {\gamma _i^{\left( 1 \right)}{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{{v}}_i} + {{\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)}^{\left( 1 \right)}}{{I}}} $ 迭代: $ {\mu ^{\left( j \right)}} = {{{\varGamma}} ^{\left( j \right)}}{{{D}}^{\rm{H}}}{\left( {{{{M}}^{\left( j \right)}}} \right)^{ - 1}}{{x}}$ $ {\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)^{\left( {j + 1} \right)}} = \left( {1/N} \right)\left[ {\left\| {{{x}} - {{D}}{{{\mu}} ^{\left( j \right)}}} \right\|_2^2 + {{\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)}^{\left( j \right)}}\displaystyle\sum\limits_1^P {\gamma _i^{\left( j \right)}{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{\left( {{{{C}}^{\left( j \right)}}} \right)}^{ - 1}}{{{v}}_i}} } \right]$ $ \gamma _i^{\left( {j + 1} \right)} = {\left| {\gamma _i^{\left( j \right)}{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{\left( {{{{C}}^{\left( j \right)}}} \right)}^{ - 1}}{{x}}} \right|^2},i = 1,2, ··· ,P$ $ {{{C}}^{\left( {j + 1} \right)}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i{\rm{ = }}1}^P {\gamma _i^{\left( {j + 1} \right)}{{v}}_i^{\rm{H}}{{{v}}_i} + {{\left( {{\sigma ^2}} \right)}^{\left( {j + 1} \right)}}{{I}}} $ 直到得到一个满足要求的稀疏解。 表 1 两次实验定位误差分析统计表
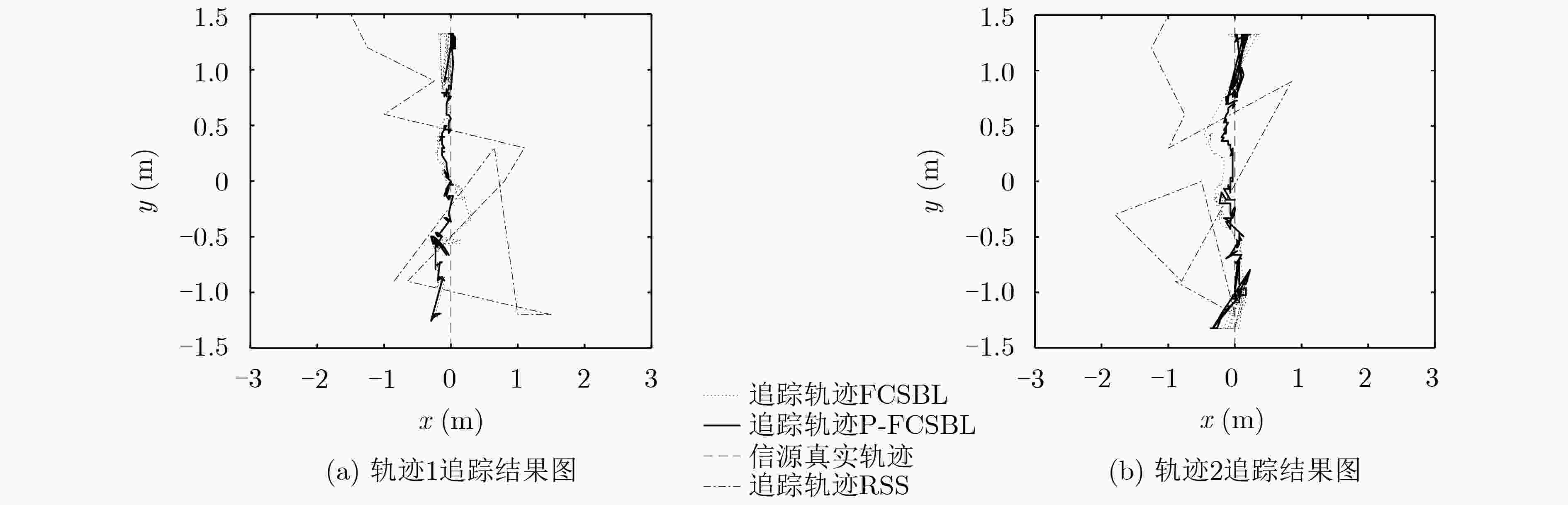
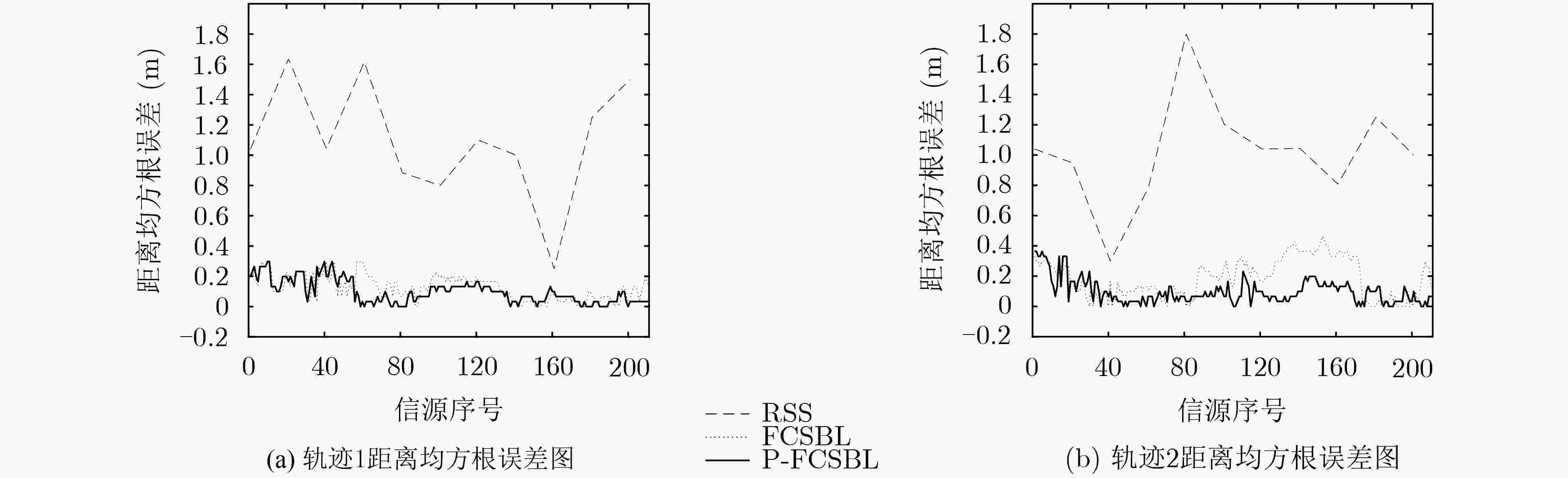
实验 平均定位误差(m) 误差≤0.2 m的占比(%) 误差≤0.4 m的占比(%)) 误差≤1 m的占比(%) 轨迹1 RSS 1.0858 0 3.48 36.32 轨迹2 RSS 1.0196 0 3.98 40.80 轨迹1 FCSBL 0.1247 87.16 100 100 轨迹2 FCSBL 0.1843 58.29 98.10 100 轨迹1 P-FCSBL 0.0930 90.79 100 100 轨迹2 P-FCSBL 0.0990 93.23 100 100 -
WANG Bang, CHEN Qiuyun, YANG L T, et al. Indoor smartphone localization via fingerprint crowdsourcing: Challenges and approaches[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2016, 23(3): 82–89. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2016.7498078 陈锐志, 陈亮. 基于智能手机的室内定位技术的发展现状和挑战[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1316–1326. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170383CHEN Ruizhi and CHEN Liang. Indoor positioning with smartphones: The state-of-the-art and the challenges[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1316–1326. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170383 周牧, 刘仪瑶, 杨小龙, 等. 基于Wi-Fi即时定位与映射像素模板匹配的室内运动地图构建与定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1050–1058. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170781ZHOU Mu, LIU Yiyao, YANG Xiaolong, et al. Indoor mobility map construction and localization based on Wi-Fi simultaneous localization and mapping pixel template matching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1050–1058. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170781 李方敏, 张韬, 刘凯, 等. 基于距离测量和位置指纹的室内定位方法研究[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(2): 339–350. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00339LI Fangmin, ZHANG Tao, LIU Kai, et al. An indoor positioning method based on range measuring and location fingerprinting[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(2): 339–350. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00339 SADOWSKI S and SPACHOS P. RSSI-based indoor localization with the internet of things[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 30149–30161. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2843325 ZHANG Meiyan and CAI Wenyu. Multivariate polynomial interpolation based indoor fingerprinting localization using Bluetooth[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2018, 2(4): 7001704. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2018.2878558 GU Yu and REN Fuji. Energy-efficient indoor localization of smart hand-held devices using Bluetooth[J]. IEEE Access, 2015, 3: 1450–1461. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2015.2441694 LOVÓN-MELGAREJO J, CASTILLO-CARA M, HUARCAYA-CANAL O, et al. Comparative study of supervised learning and metaheuristic algorithms for the development of Bluetooth-based indoor localization mechanisms[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 26123–26135. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899736 SUBEDI S, GANG H S, KO N Y, et al. Improving indoor fingerprinting positioning with affinity propagation clustering and weighted centroid fingerprint[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 31738–31750. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2902564 XIAO Chao, YANG Daiqin, CHEN Zhenzhong, et al. 3-D BLE indoor localization based on denoising autoencoder[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 12751–12760. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2720164 SUN Wei, XUE Min, YU Hongshan, et al. Augmentation of fingerprints for indoor WiFi localization based on Gaussian process regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(11): 10896–10905. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2870160 田增山, 王阳, 周牧, 等. 基于自适应渐消记忆的蓝牙序列匹配定位算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1381–1388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT18063TIAN Zengshan, WANG Yang, ZHOU Mu, et al. Adaptive fading memory based Bluetooth sequence matching localization algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1381–1388. doi: 10.11999/JEIT18063 GUO Xiansheng, LI Lin, ANSARI N, et al. Accurate WiFi localization by fusing a group of fingerprints via a global fusion profile[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 7314–7325. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2833029 YU Ning, ZHAN Xiaohong, ZHAO Shengnan, et al. A precise dead reckoning algorithm based on Bluetooth and multiple sensors[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(1): 336–351. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2784386 陈显舟, 陈周, 杨旭, 等. 阵列单通道轮采式快速高精度定位算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(8): 49–53. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.011CHEN Xianzhou, CHEN Zhou, YANG Xu, et al. Fast high-resolution passive localization algorithm based on single-channel using switch-antenna array[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(8): 49–53. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.08.011 WANG Zetao, XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, et al. Clutter suppression algorithm based on fast converging sparse Bayesian learning for airborne radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 130: 159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.06.023 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
