An Offloading Mechanism Based on Software Defined Network and Mobile Edge Computing in Vehicular Networks
-
摘要:
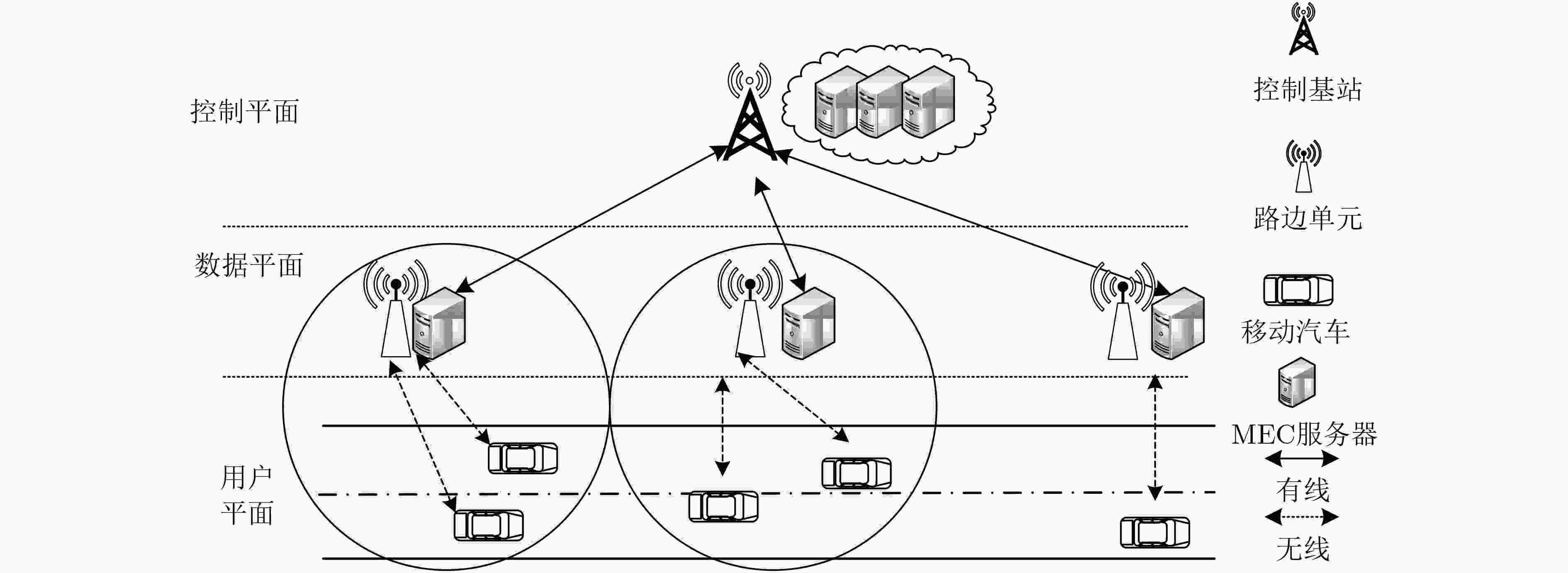
在新兴的车联网络中,汽车终端请求卸载的任务对网络带宽、卸载时延等有着更加严苛的需求,而新型通信网络研究中移动边缘计算(MEC)的提出更好地解决了这一挑战。该文着重解决的是汽车终端进行任务卸载时卸载对象的匹配问题。文中引入了软件定义车载网络(SDN-V)对全局变量统一调度,实现了资源控制管理、设备信息采集以及任务信息分析。基于用户任务的差异化性质,定义了重要度的模型,在此基础上,通过设计任务卸载优先级机制算法,实现任务优先级划分。针对多目标优化模型,采用乘子法对非凸优化模型进行求解。仿真结果表明,与其他卸载策略相比,该文所提卸载机制对时延和能耗优化效果明显,能够最大程度地保证用户的效益。
Abstract:In the emerging vehicular networks, the task of the car terminal requesting offloading has more stringent requirements for network bandwidth and offload delay, and the proposed Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) in the new communication network research solves better this challenge. This paper focuses on matching the offloaded objects when the car terminal performs the task offloading. By introducing the Software-Defined in-Vehicle Network (SDN-V) to schedule uniformly global variables, which realizes resource control management, device information collection and task information analysis. Based on the differentiated nature of user tasks, a model of importance is defined. On this basis, task priority is divided by designing the task to offload the priority mechanism. For the multi-objective optimization model, the non-convex optimization model is solved by the multiplier method. The simulation results show that compared with other offloading strategies, the proposed offloading mechanism has obvious effects on delay and energy consumption optimization, which can guarantee the benefit of users to the greatest extent.
-
表 1 任务卸载优先级机制
(1) 输入:车辆$i$的请求信息为$\{ {C_i},{S_i},t_{{Q_i}}^{\max }\} $,定义$\zeta $的取值,$i \in \{ 1\; 2\; ··· \; n\} $, ${\rm{Im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{i}}}{\rm{ = \{ im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{1}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{2}}}\; ···\; {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{{n}}}\; {\rm{\} }}$ (2) 输出:降序排列的重要度${\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_i}$ (3) for $i = 1;i < n;i + + $ (4) 将${C_i},t_{{Q_i}}^{\max }$代入式(9)求出${\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_i}$ (5) ${\rm{Im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{i}}}={\rm{\{ im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{1}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{2}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} ···\; {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{{i}}}{\rm{\} }}$ (6) for $i = 1:n$ do (7) if ${{{\rm Imp}(i) < {\rm Imp}(i + 1)}}$; ${{\rm temp} = {\rm Imp}(i + 1)}$; ${{{\rm Imp}(i + 1) = {\rm Imp}(i)}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} ;{{{\rm Imp}(i) = {\rm temp}}}$ (8) end 表 2 基于Q-学习的任务卸载策略机制
(1) 输入:车辆$i$的请求信息$\{ {Q_i},{T_i}\} $, ${\tau _{\rm{1}}},{\tau _2},({\rm{0 < }}{\tau _{\rm{1}}} < {\tau _{\rm{2}}})$, $i \in \{ 1\; 2\; ··· \; n\} $, ${\rm{Im}}{{\rm{p}}_{{i}}}{\rm{ = \{ im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{1}}}{\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{\rm{2}}}\; ···\; {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_{{i}}}{\rm{\} }}$ (2) 输出:${x_i}$, ${\psi _i}$ (3) if ${\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_i} < {\tau _{\rm{1}}}$:${x_i}=0$;${\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_i} > {\tau _2}$:${x_i}{\rm{ = 1}}$ (4) elif ${\tau _{\rm{1}}} < {\rm{im}}{{\rm{p}}_i} < {\tau _{\rm{2}}}$:初始化$g$, ${x_{ij}} = 1$, $\varsigma $, $p$, $\hat Q\left( {{a_i}} \right) = 0,\; {\kern 1pt} t = 0$最大收敛时间${t_{c - \max }}$ (5) while ${\kern 1pt} t < {t_{c - \max }} + 1$:按照时延约束对车辆用户排序 (6) for $i = 1:N\; {\kern 1pt} {\kern 1pt} $ do (7) 根据贪婪方法选择行为${a_i}$、根据式(15)求出用户奖励 (8) 更新$\hat { Q}$数值矩阵通过${\hat Q_{t + 1}}\left( {s,a} \right) \leftarrow \left( {1 - \varsigma } \right){\hat Q_t}\left( {s,a} \right) + \varsigma \left( {g + \eta \mathop {\max }\limits_{a'} {{\hat Q}_t}\left( {s',a'} \right)} \right)$, $p \leftarrow \left( {p/\sqrt t } \right)$ (9) end for;$t = t + 1$;end while (10) 利用${\psi _i}$更新目标优化式(7) (11) end 表 3 模拟参数表
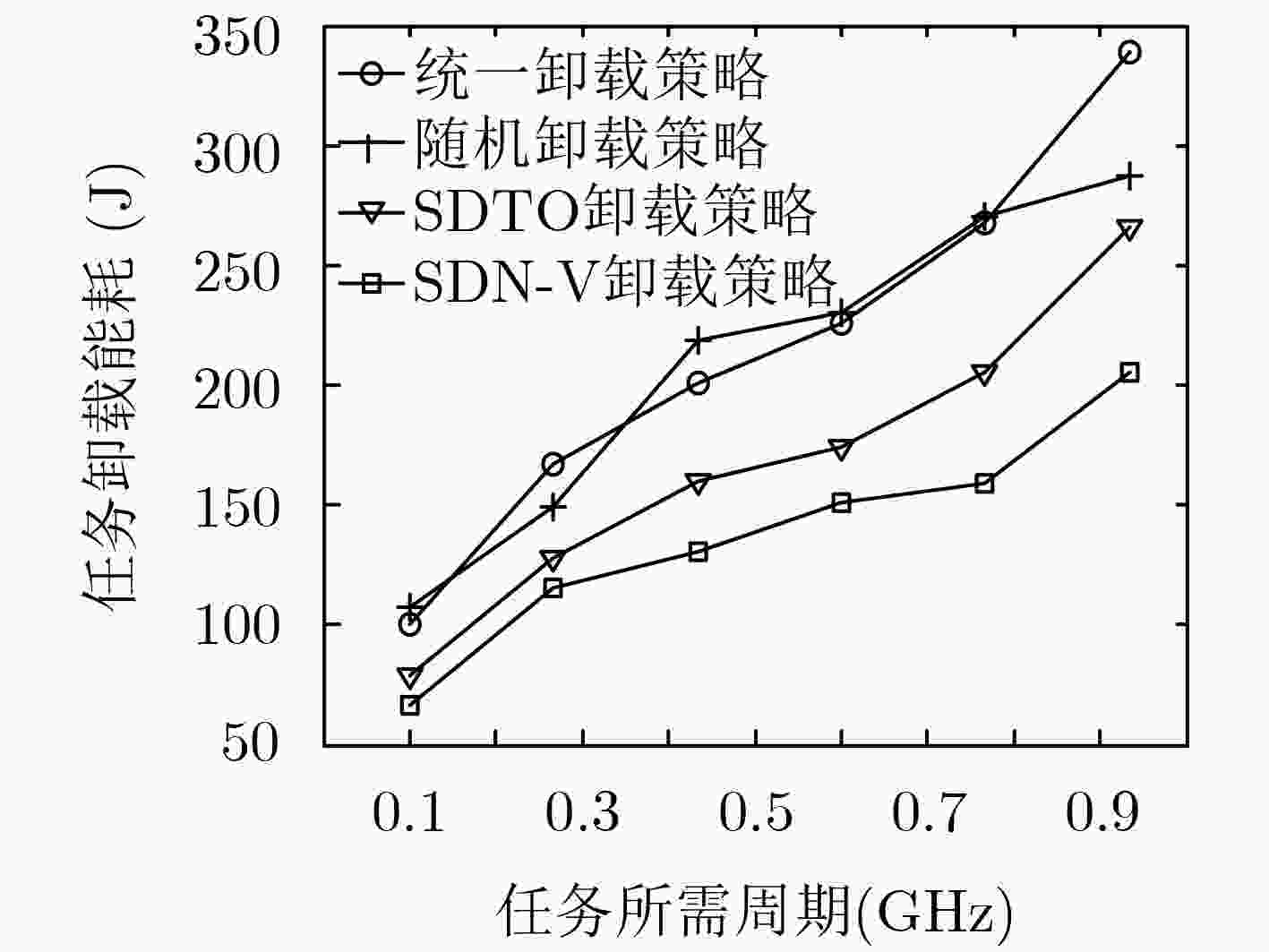
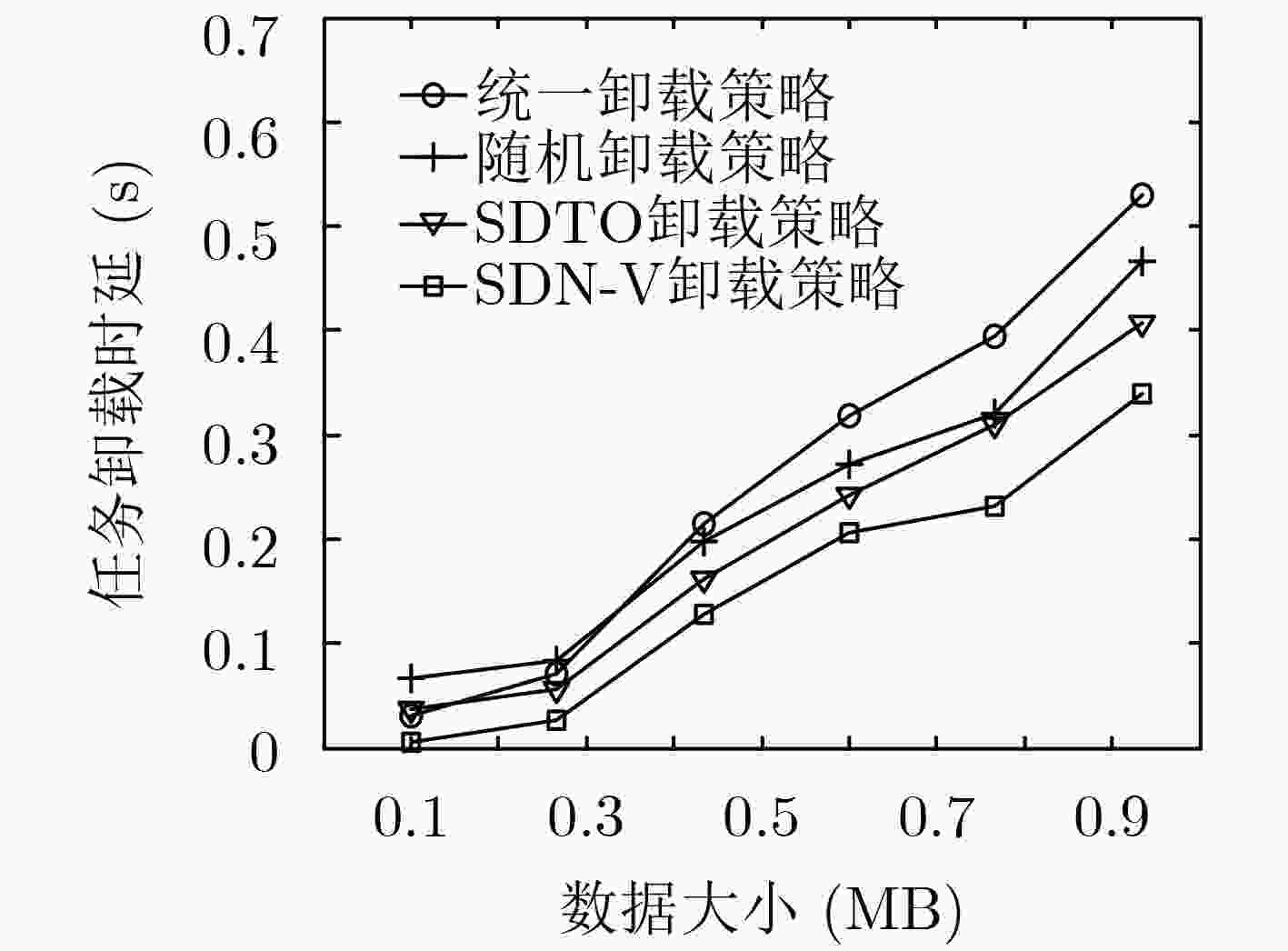
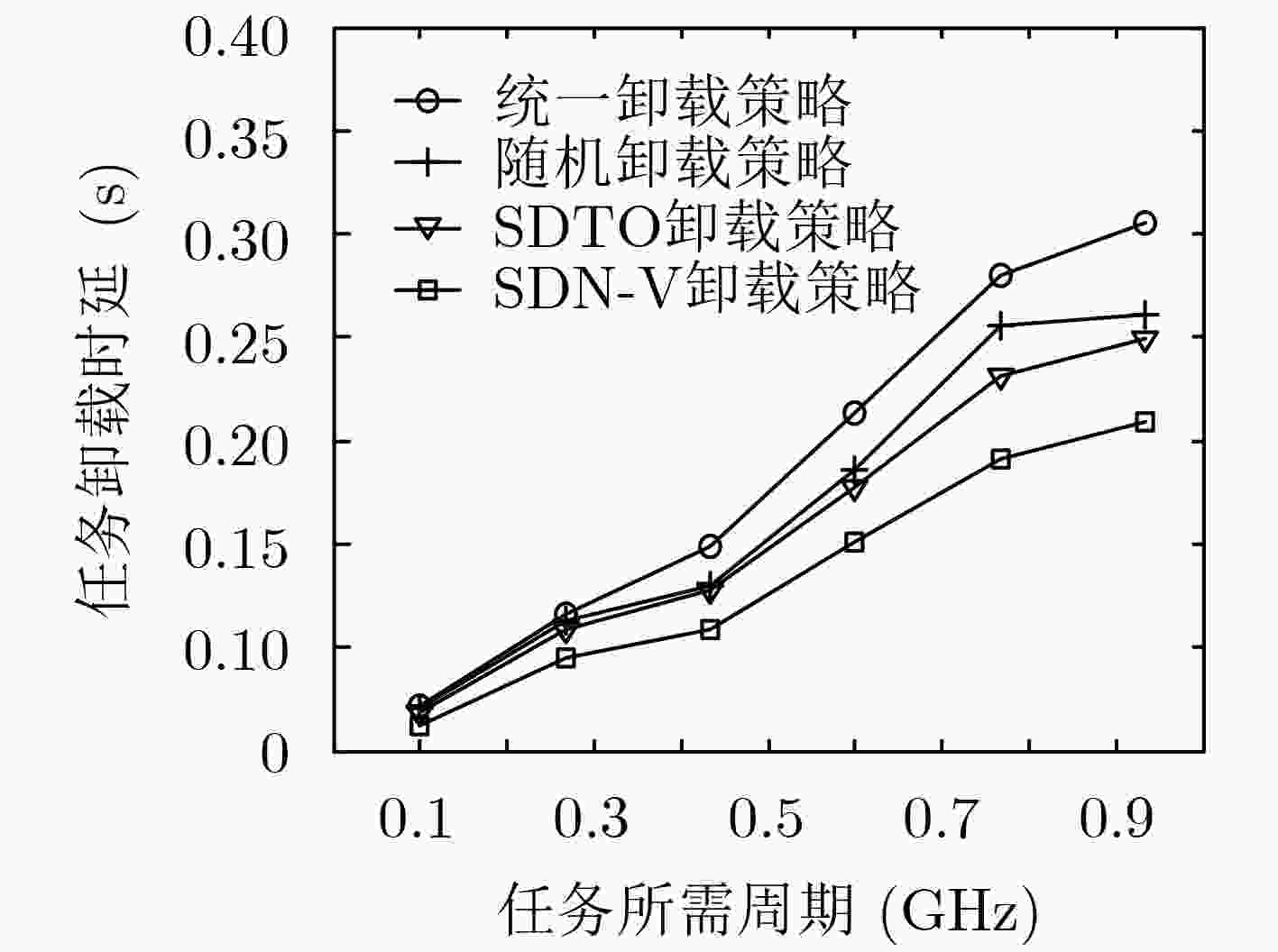
参数 数值 计算任务${Q_i}$ 1~50 MB 传输带宽$W$ 100 MHz 汽车用户发射功率${p_i}$ 0.2 W 任务所需CPU周期数${C_i}$ 0.1~1 GHz MEC服务器CPU周期频率${f_{\rm b}}$ 6 GHz 车辆用户的CPU周期频率${f_v}$ 0.5~1 GHz 高斯噪声${\sigma ^2}$ –100 dBm 信道传输距离${d_{mn}}$ 5~500 m 汽车CPU能耗功率系数${p_{{v} } }$ 80 W/GHz 电池最大容量 20 kWh -
程刚, 郭达. 车联网现状与发展研究[J]. 移动通信, 2011, 35(17): 23–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2011.17.004CHENG Gang, and GUO Da. Research on the status and development of internet of vehicles[J]. Mobile Communications, 2011, 35(17): 23–26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1010.2011.17.004 齐彦丽, 周一青, 刘玲, 等. 融合移动边缘计算的未来5G移动通信网络[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2018, 55(3): 478–486. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170801QI Yanli, ZHOU Yiqing, LIU Ling, et al. MEC coordinated future 5G mobile wireless networks[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2018, 55(3): 478–486. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2018.20170801 LI Yong, JIN Depeng, HUI Pan, et al. Optimal base station scheduling for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 34(1): 27–40. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2452415 AMEMIYA K, AKIYAMA Y, KOBAYASHI K, et al. On-site evaluation of a software cellular based MEC system with downlink slicing technology[C]. The 7th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Networking, Tokyo, Japan, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/CloudNet.2018.8549380. WANG Hansong, LI Xi, JI Hong, et al. Dynamic offloading scheduling scheme for MEC-enabled vehicular networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, Beijing, China, 2018: 206–210. doi: 10.1109/ICCChinaW.2018.8674508. YU Rong, DING Jiefei, HUANG Xumin, et al. Optimal resource sharing in 5G-enabled vehicular networks: A matrix game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(10): 7844–7856. doi: 10.1109/tvt.2016.2536441 鲍楠, 左加阔, 胡晗, 等. 基于SDN的网络资源选择多目标优化算法[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40(2): 51–59. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000?436x.2019031BAO Nan, ZUO Jiakuo, HU Han, et al. SDN based network resource selection multi-objective optimization algorithm[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40(2): 51–59. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000?436x.2019031 CHEN Min and HAO Yixue. Task offloading for mobile edge computing in software defined ultra-dense network[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(3): 587–597. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2815360 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Optimal delay constrained offloading for vehicular edge computing networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2017.7997360. HU Bo, CHEN Jianye, and LI fengcun. Dynamic service allocation algorithm in mobile edge computing[C]. 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence, Jeju, South Korea, 2017: 104–109. doi: 10.1109/ICTC.2017.8190951. LI Baozhu, ZHAO Xuhui, HAN Shiyuan, et al. New SDN-based architecture for integrated vehicular cloud computing networking[C]. 2018 International Conference on Selected Topics in Mobile and Wireless Networking, Tangier, Morocco, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MoWNet.2018.8428935. HUANG Xumin, YU Rong, KANG Jiawen, et al. Distributed reputation management for secure and efficient vehicular edge computing and networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 25408–25420. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2769878 TRAN T X and POMPILI D. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 856–868. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2881191 JAIN R and PAUL S. Network virtualization and software defined networking for cloud computing: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2013, 51(11): 24–31. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6658648 WILHELMI F, BELLALTA B, CANO C, et al. Implications of decentralized Q-learning resource allocation in wireless networks[C]. The 28th IEEE Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, Montreal, Canada, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2017.8292321. -





 下载:
下载:

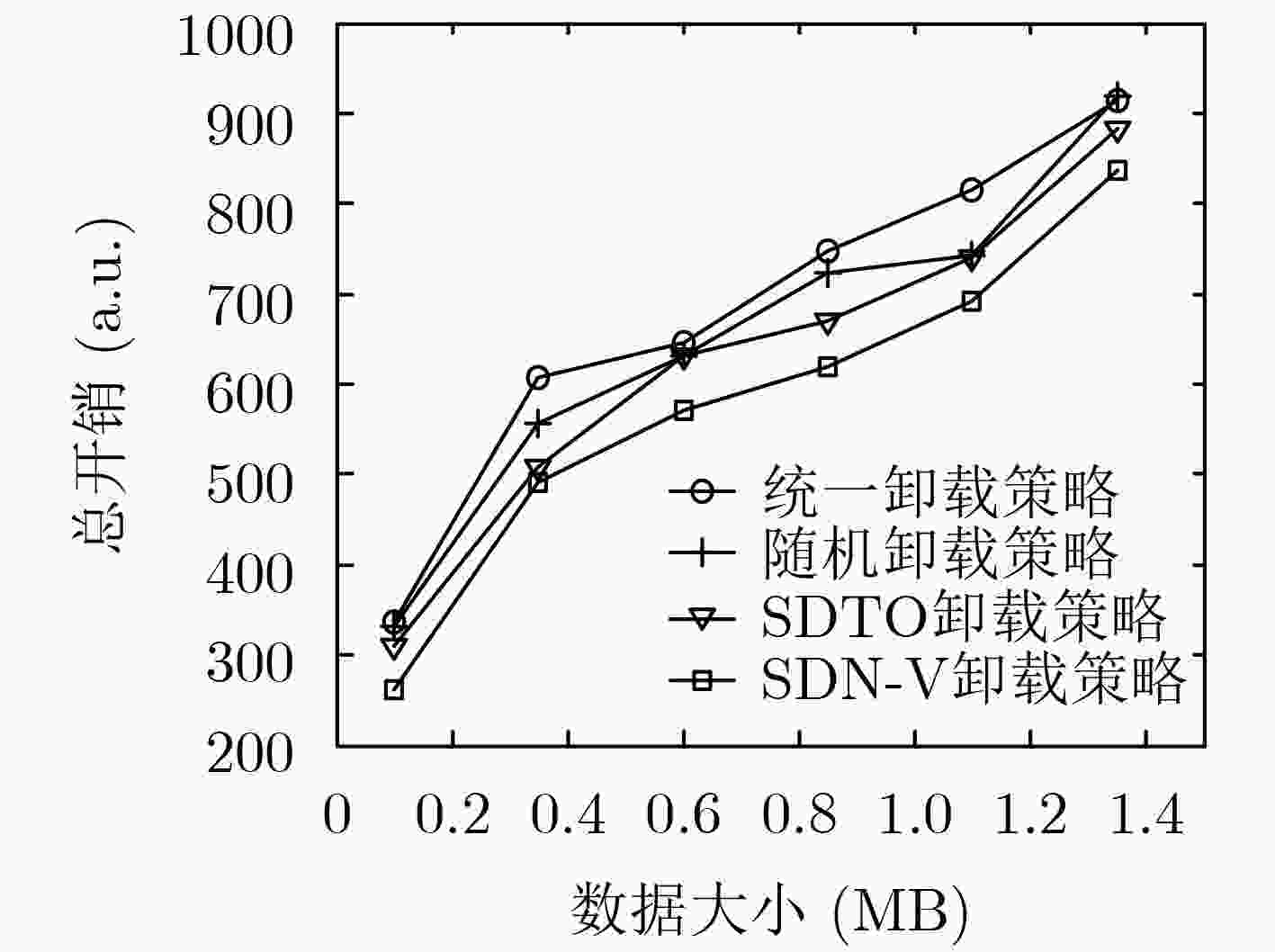
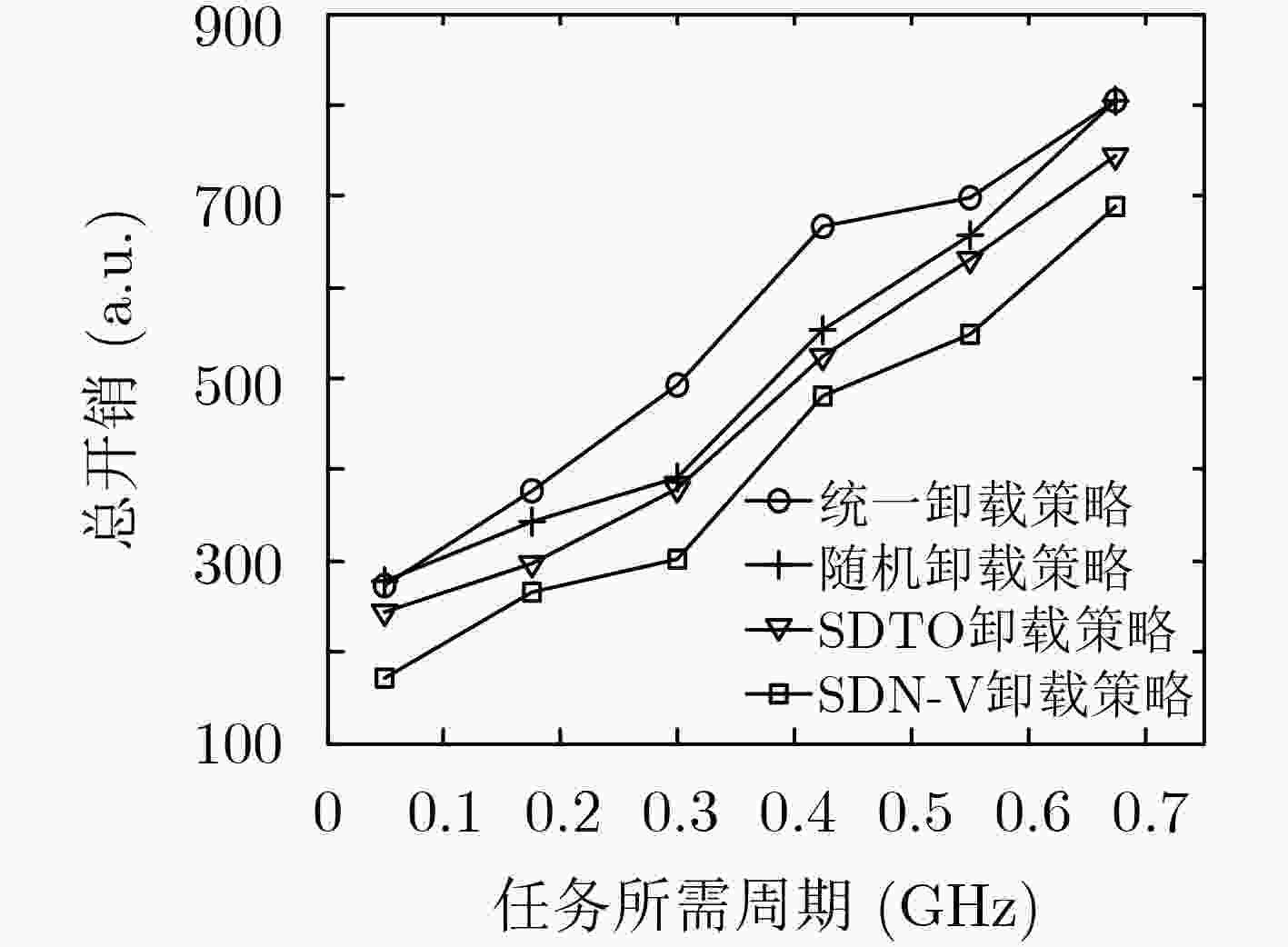


 下载:
下载:
