Social Attribute Aware Task Scheduling Strategy in Edge Computing
-
摘要:
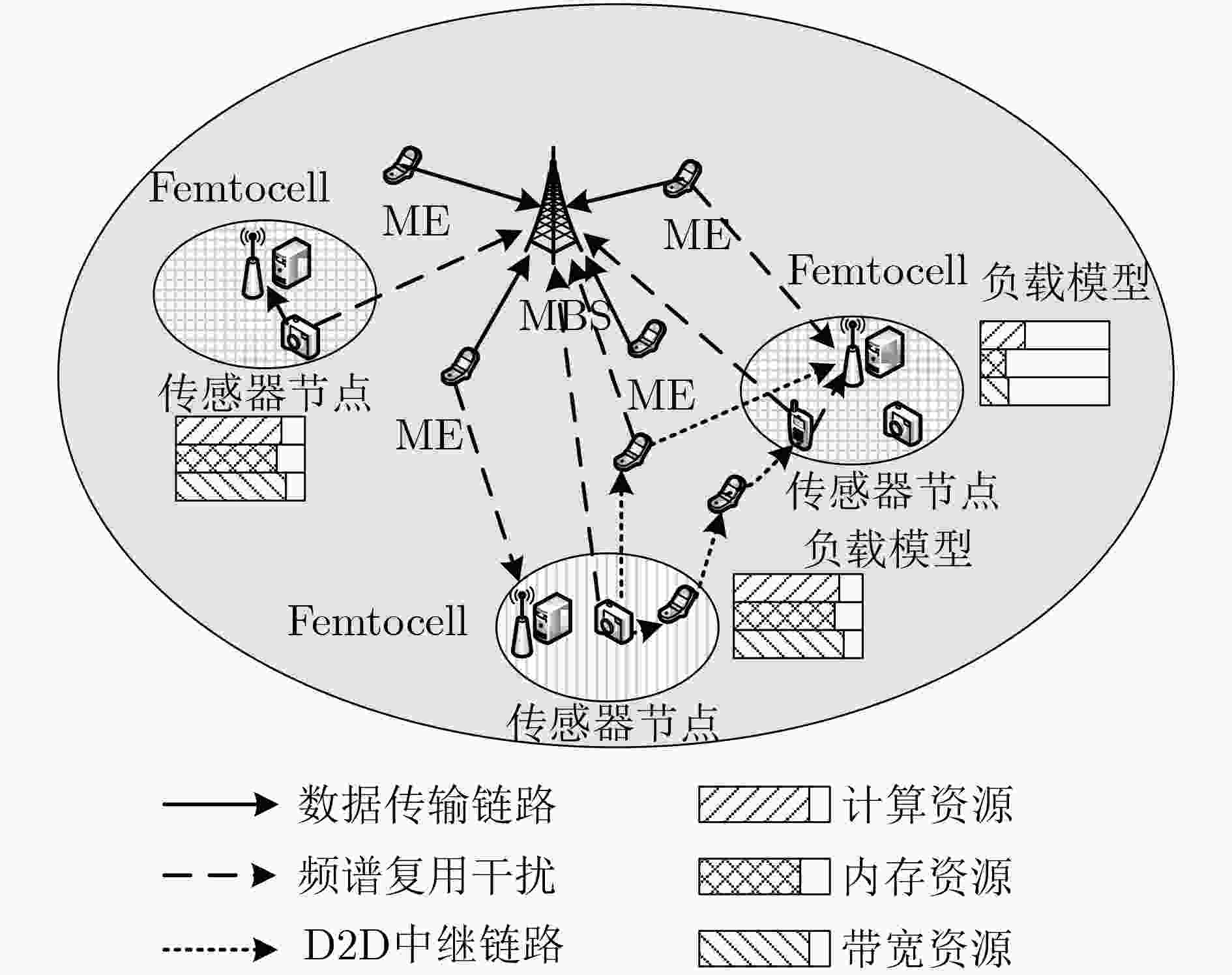
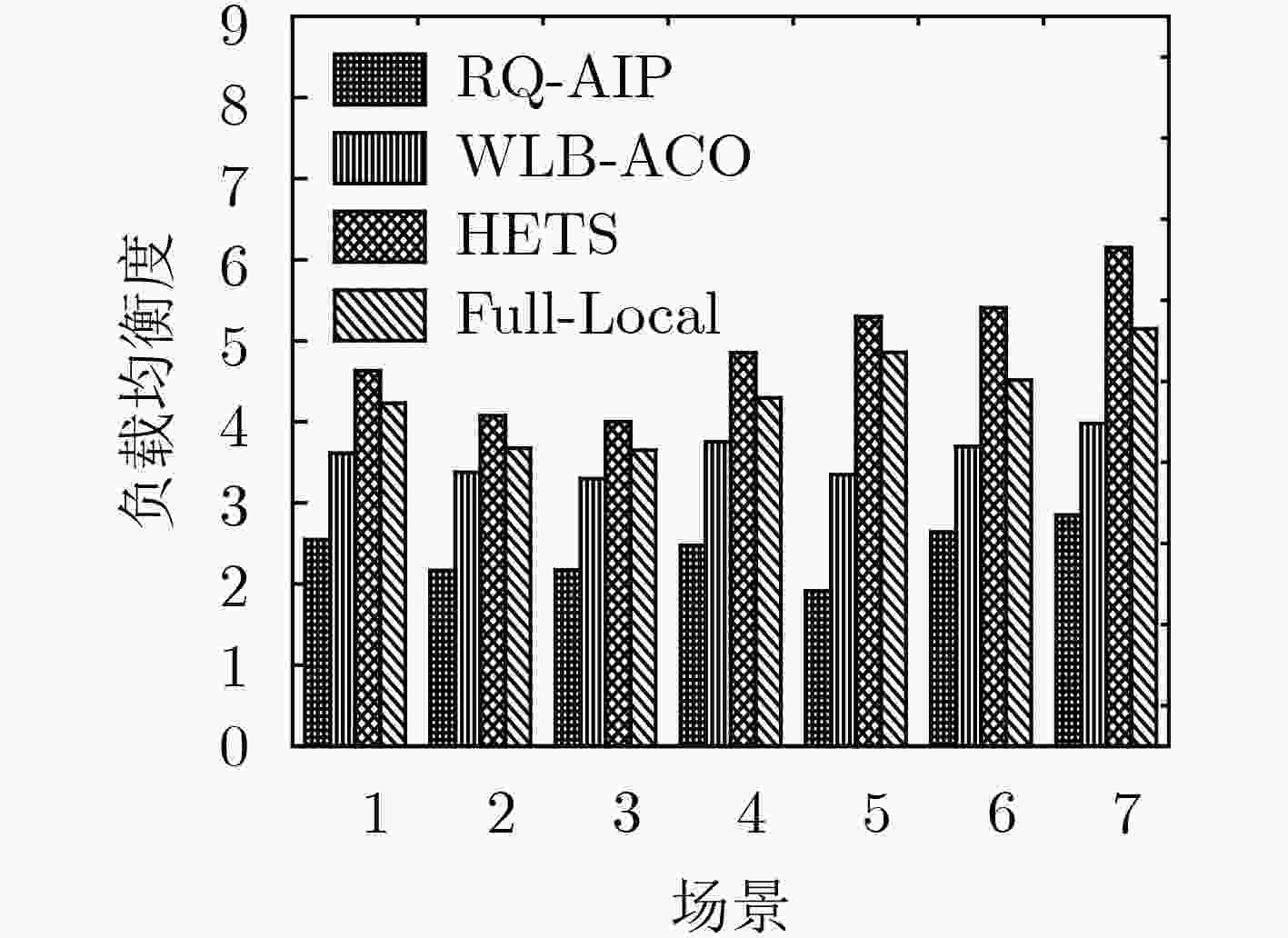
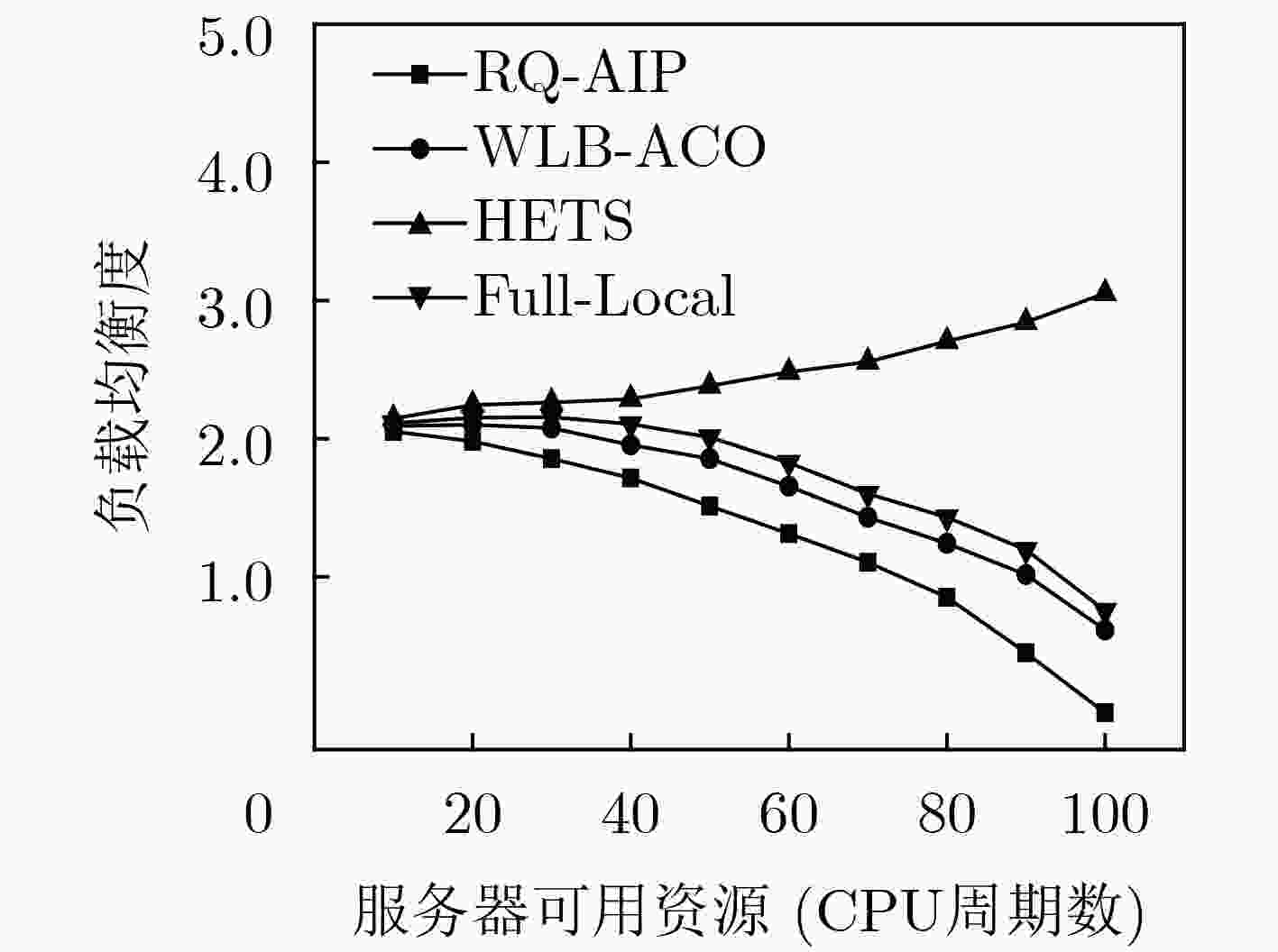
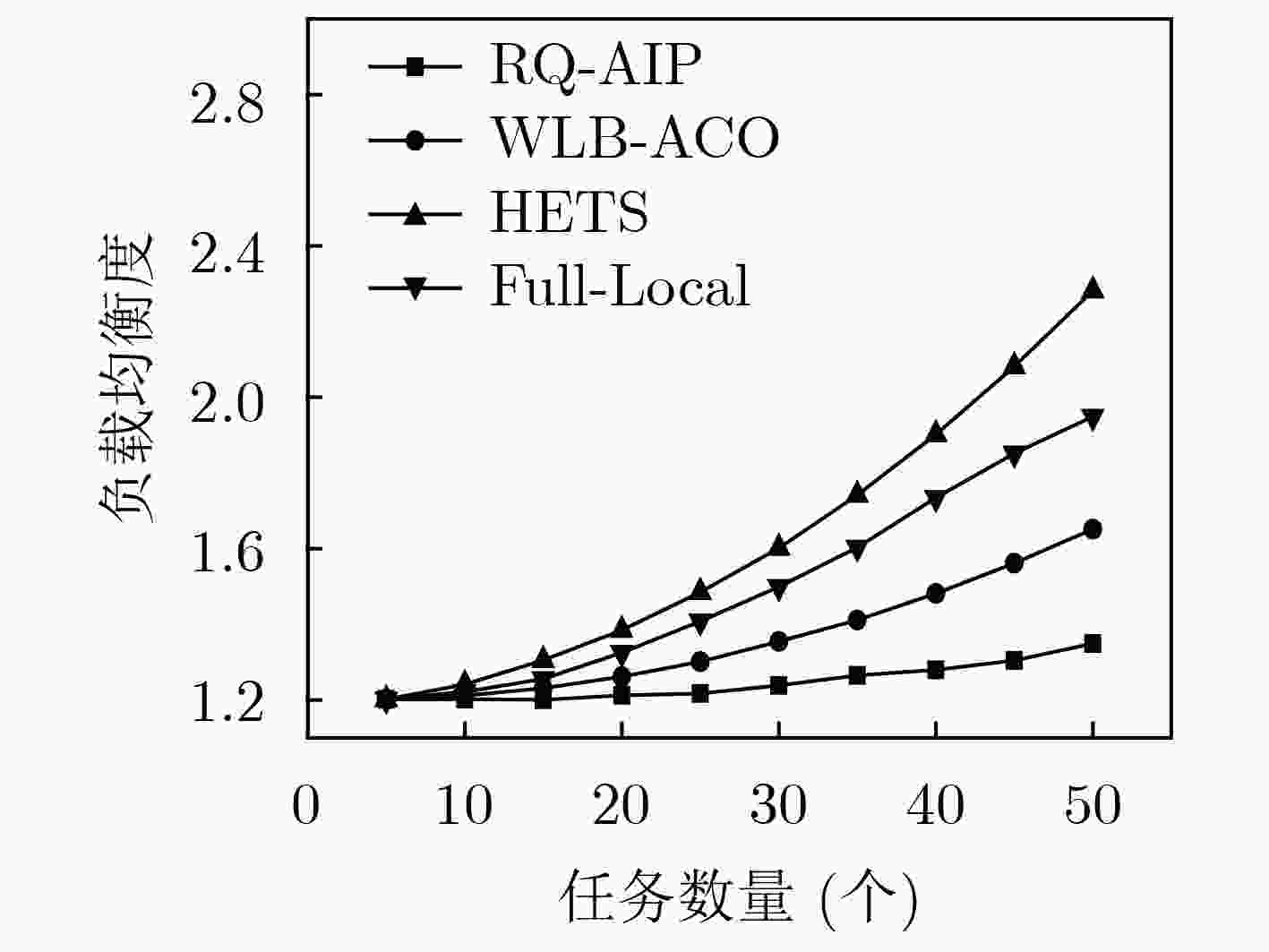
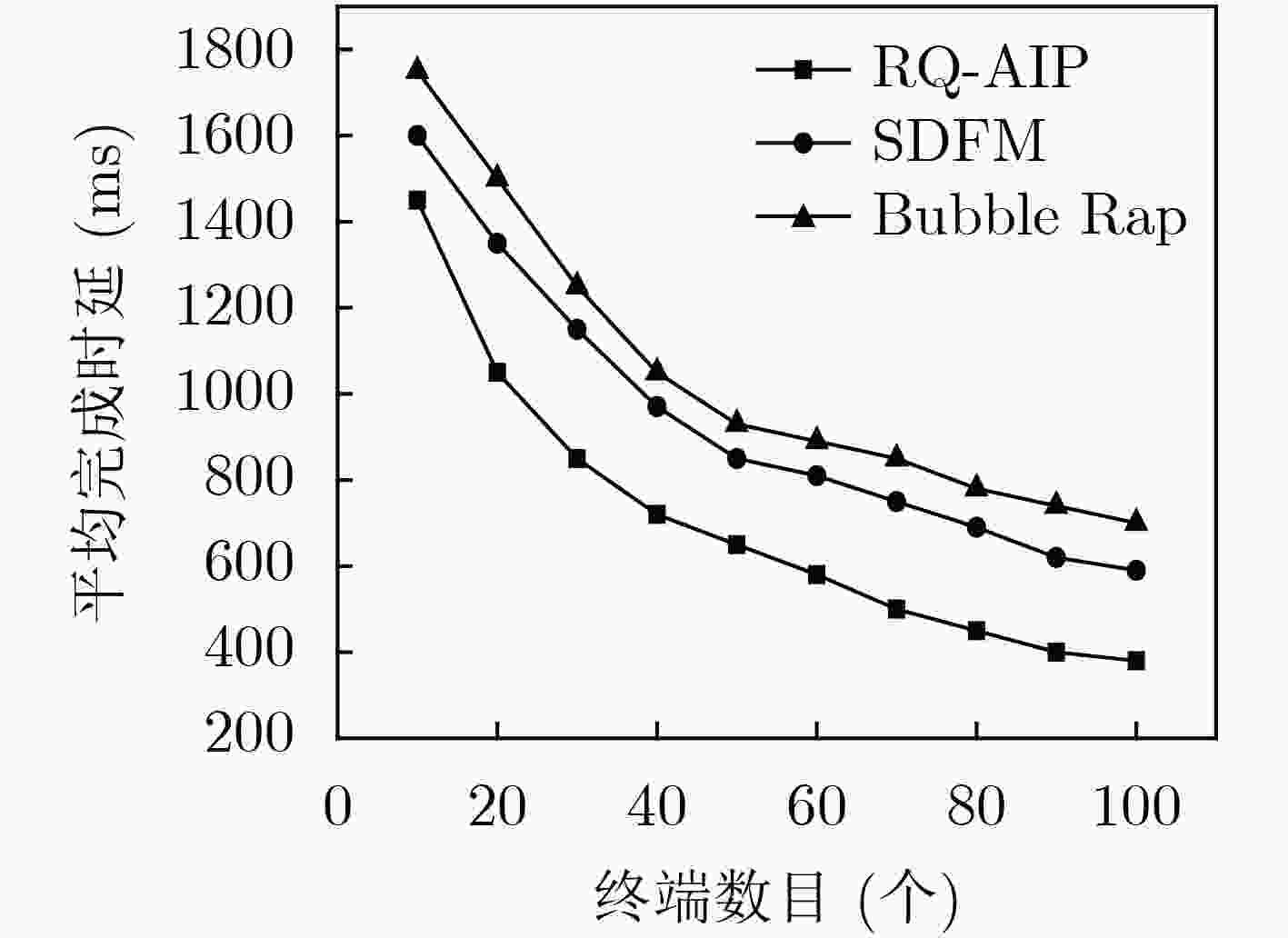
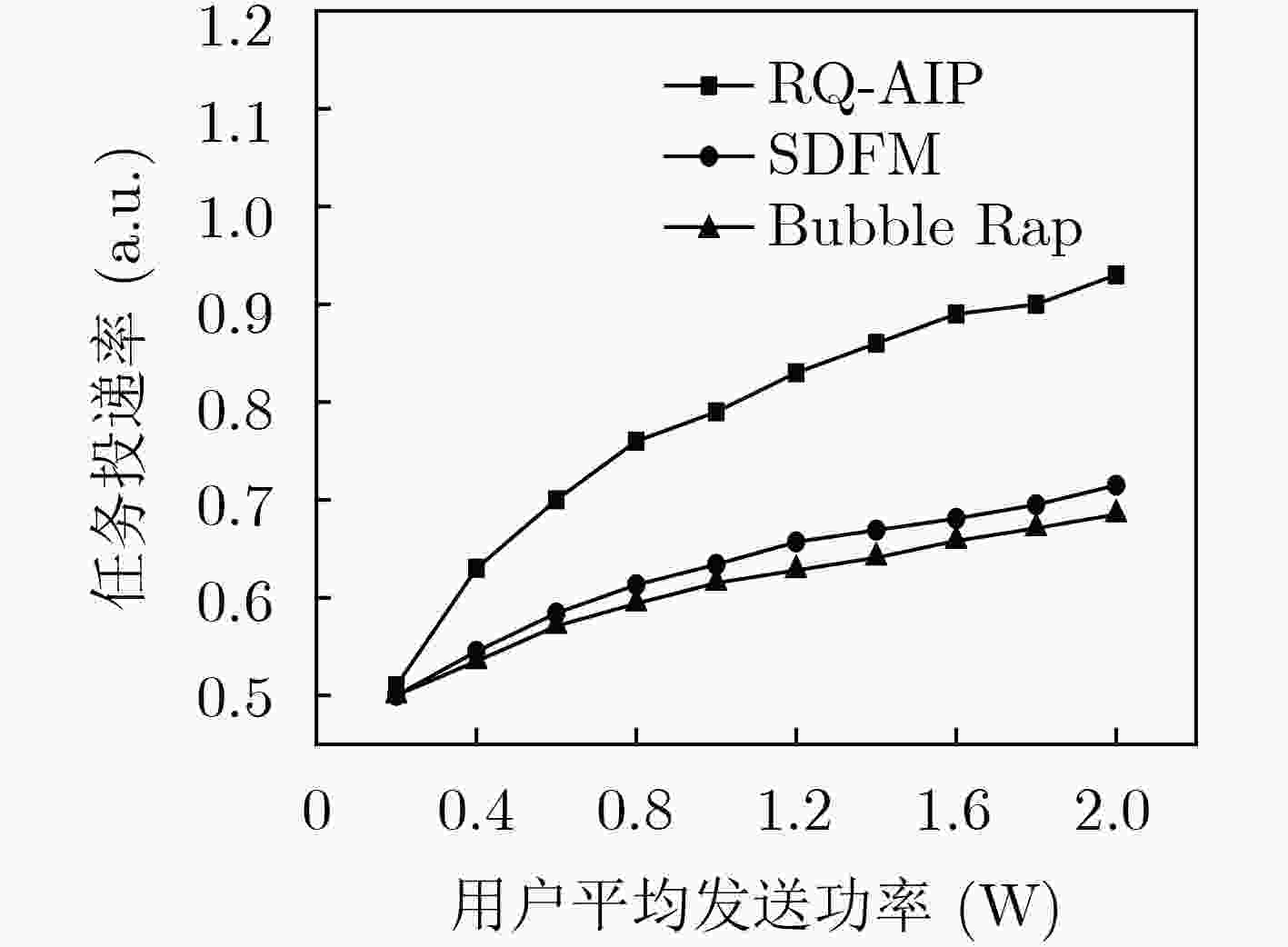
边缘计算服务器的负载不均衡将严重影响服务能力,该文提出一种适用于边缘计算场景的任务调度策略(RQ-AIP)。首先,根据服务器的负载分布情况衡量整个网络的负载均衡度,结合强化学习方法为任务匹配合适的边缘服务器,以满足传感器节点任务的资源差异化需求;进而,构造任务时延和终端发射功率的映射关系来满足物理域的约束,结合终端用户社会属性,为任务不断地选择合适的中继终端,通过终端辅助调度的方式实现网络的负载均衡。仿真结果表明,所提出的策略与其他负载均衡策略相比能有效地缓解边缘服务器之间的负载和核心网的流量,降低任务处理时延。
Abstract:Unbalanced load on the edge computing server will seriously affect service capabilities, a task scheduling strategy Reinforced Q-learning-Automatic Intent Picking (RQ-AIP) for edge computing scenarios is proposed. Firstly, the load balance of the entire network is measured based on the load distribution of the server. By combining the reinforcement learning method, the appropriate edge server is matched for the task to meet the resource differentiation needs of sensor node tasks. Then, a mapping relationship between task delay and terminal transmit power is constructed to satisfy the constraints of the physical domain. Combining the social attributes of terminal, the appropriate relay terminal is continuously selected for the task to achieve the load balancing of network by terminal-assisted scheduling. Simulation results show that compared with other load balancing strategies, the proposed strategy can effectively alleviate the load between the edge servers and the traffic of the core network, reduce task processing latency.
-
Key words:
- Computer network /
- Edge computing /
- Social attribute /
- Load balancing
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
参数设定 参数数值 任务到达率(个/s) [0, 4] 任务所需内存(GB) [1, 10] 任务所需CPU周期(MHz) 50 任务时延(s) [200, 1500] 边缘服务器CPU频率(GHz) 3 无线信道带宽(MHz) 5 边缘服务器数量(个) 5 学习因子 0.5 终端发射功率(W) [0.1, 2] 噪声功率(dBm/Hz) –170 -
KUMAR K, LIU Jibang, LU Y H, et al. A survey of computation offloading for mobile systems[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2013, 18(1): 129–140. doi: 10.1007/s11036-012-0368-0 ZENG Deze, GU Lin, GUO Song, et al. Joint optimization of task scheduling and image placement in fog computing supported software-defined embedded system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2016, 65(12): 3702–3712. doi: 10.1109/TC.2016.2536019 MAO Yuyi, ZHANG Jun, and LETAIEF K B. Dynamic computation offloading for mobile-edge computing with energy harvesting devices[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3590–3605. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2611964 CHEN Xu, JIAO Lei, LI Wenzhong, et al. Efficient multi-user computation offloading for mobile-edge cloud computing[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2016, 24(5): 2795–2808. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2015.2487344 MACH P and BECVAR Z. Mobile edge computing: A survey on architecture and computation offloading[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(3): 1628–1656. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2682318 SAHNI Y, CAO Jiannong, and LEI Yang. Data-aware task allocation for achieving low latency in collaborative edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3512–3524. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2886757 LI Tianze, WU Muqing, ZHAO Min, et al. An overhead-optimizing task scheduling strategy for ad-hoc based mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 5609–5622. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2678102 SCHÄFER D, EDINGER J, ECKRICH J, et al. Hybrid task scheduling for mobile devices in edge and cloud environments[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, Athens, Greece, 2018: 669–674. doi: 10.1109/PERCOMW.2018.8480201. THAM C K and CHATTOPADHYAY R. A load balancing scheme for sensing and analytics on a mobile edge computing network[C]. The 18th IEEE International Symposium on A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks, Macau, China, 2017: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/WoWMoM.2017.7974307. CHEN Lixing, ZHOU Sheng, and XU Jie. Computation peer offloading for energy-constrained mobile edge computing in small-cell networks[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2018, 26(4): 1619–1632. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2018.2841758 YOUNES H, BOUATTANE O, YOUSSFI M, et al. New load balancing framework based on mobile AGENT and ant-colony optimization technique[C]. 2017 Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision, Fez, Morocco, 2017: 1–6. MASOOD A, MUNIR E U, RAFIQUE M M, et al. HETS: Heterogeneous edge and task scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous computing systems[C]. The 17th IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, New York, USA, 2015: 1865–1870. doi: 10.1109/HPCC-CSS-ICESS.2015.295. TIAN Rui, JIAO Zhenzhen, BIAN Guiyun, et al. A social-based data forwarding mechanism for V2V communication in VANETs[C]. The 10th International Conference on Communications and Networking in China, Shanghai, China, 2015: 595–599. doi: 10.1109/CHINACOM.2015.7498007. Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2015–2020[EB/OL]. https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/m/en_in/innovation/enterprise/assets/mobile-white-paper-c11-520862.pdf, 2016. ZHAO Pengtao, TIAN Hui, QIN Cheng, et al. Energy-saving offloading by jointly allocating radio and computational resources for mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 11255–11268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2710056 PAN Hui, CROWCROFT J, and YONEKI E. BUBBLE Rap: Social-based forwarding in delay-tolerant networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2011, 10(11): 1576–1589. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2010.246 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
