Control Resource Optimization Mechanism of SDN Based on Traffic Engineering
-
摘要:
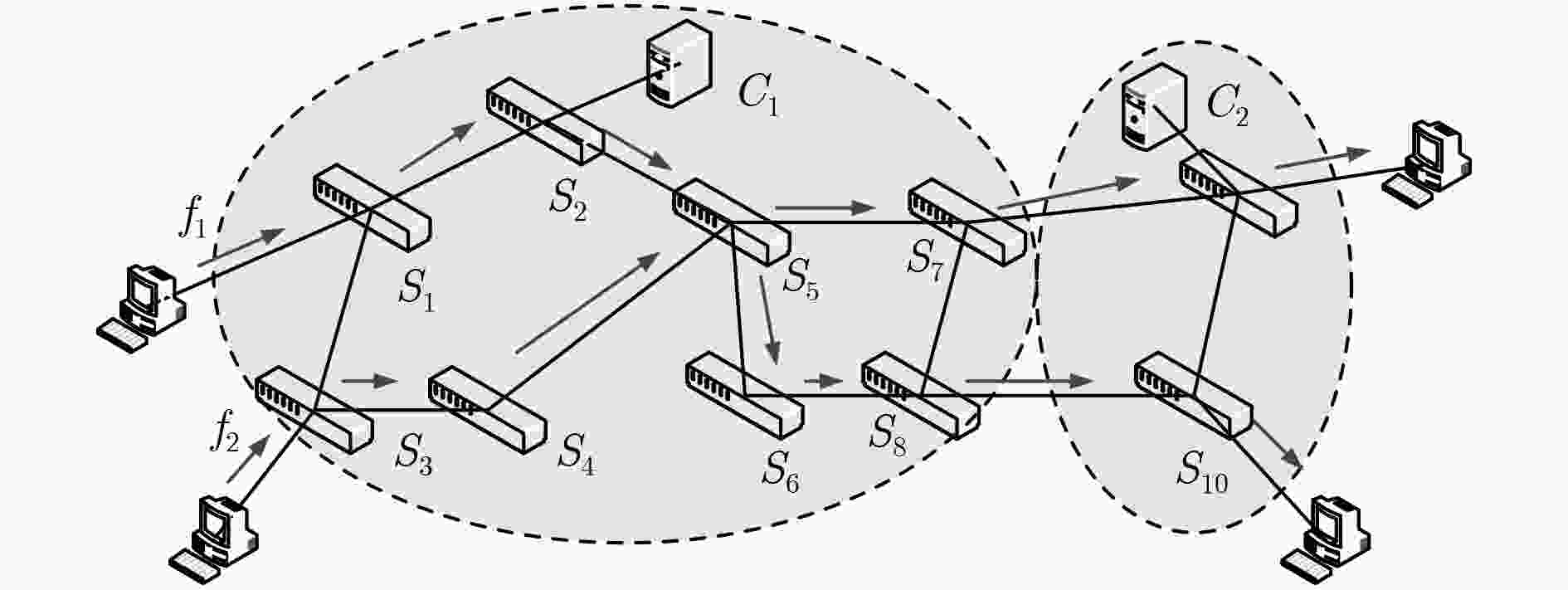
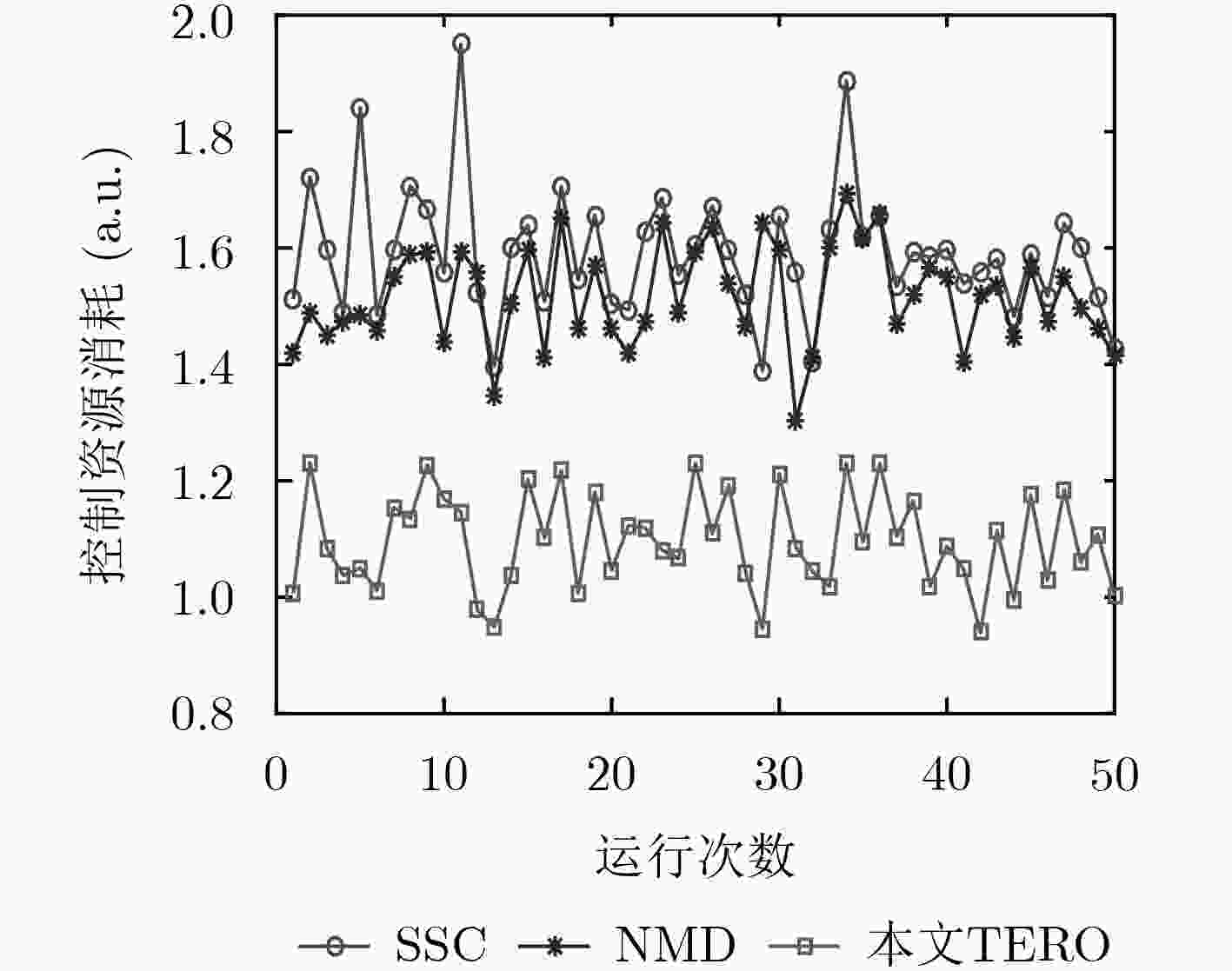
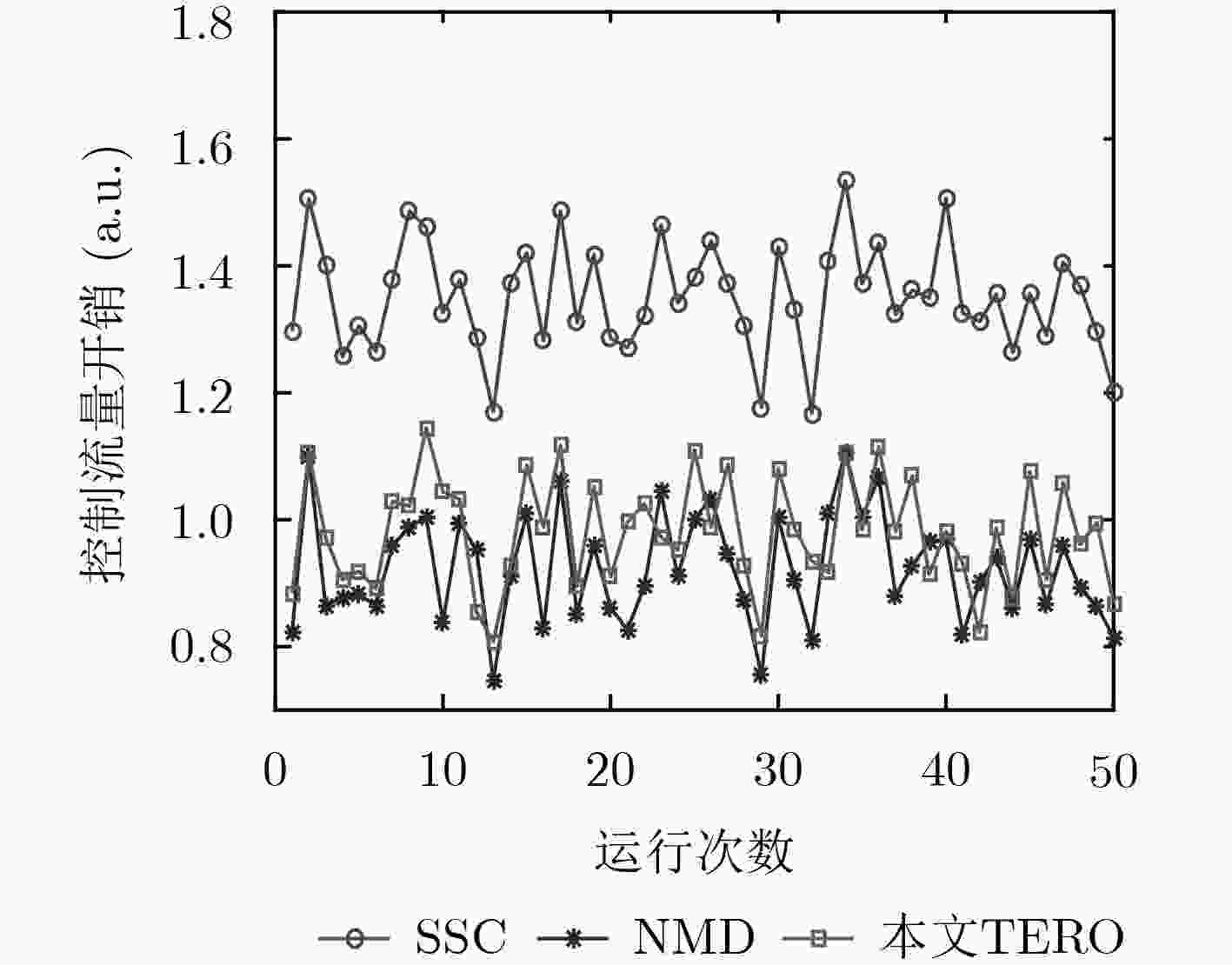
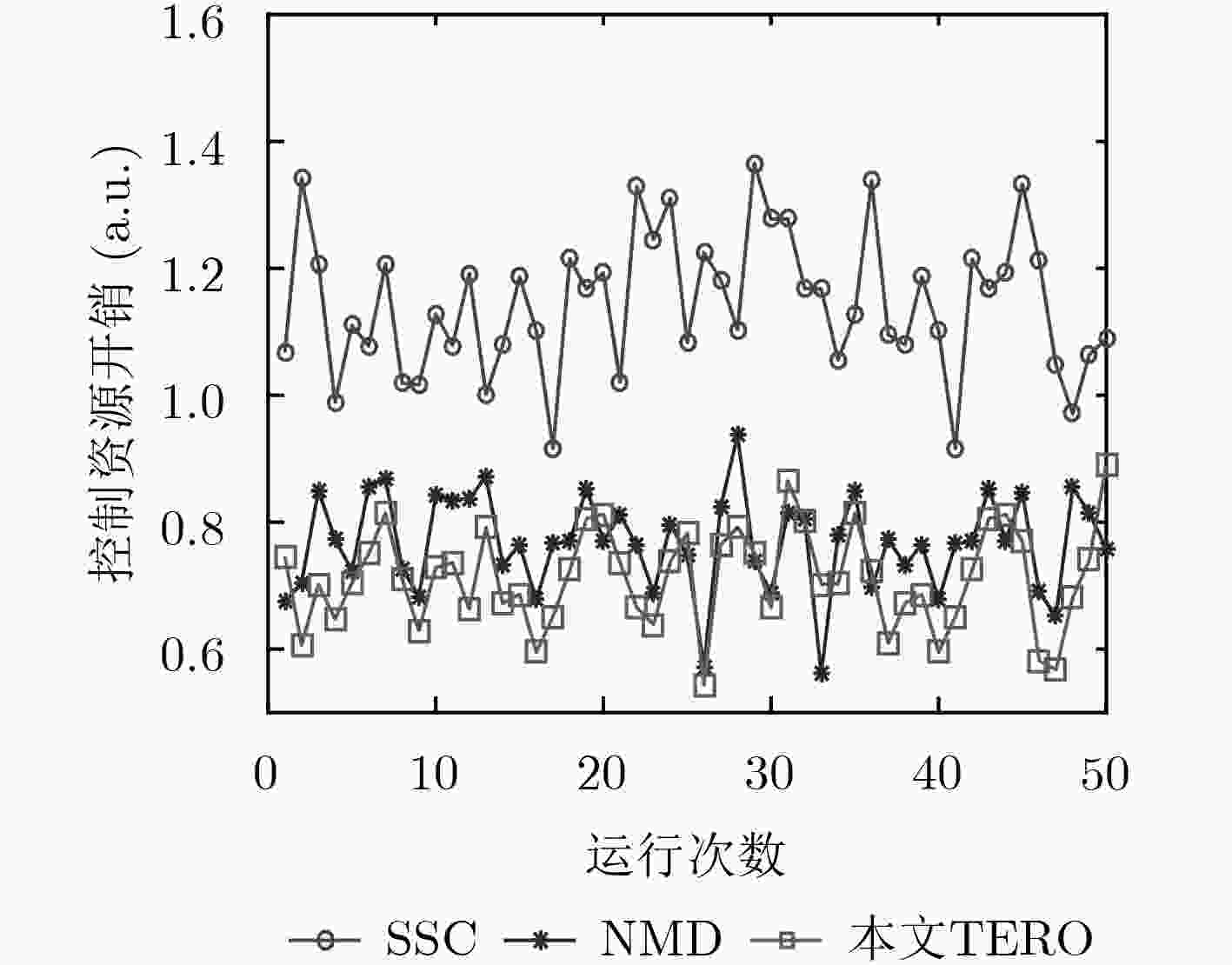
针对软件定义网络(SDN)分布式控制平面中由于网络分域管理所引发的控制扩张问题,该文提出了一种基于流量工程的SDN控制资源优化(TERO)机制。首先基于数据流的路径特征对流请求的控制资源消耗进行分析,指出通过调整控制器和交换机的关联关系可以降低控制资源消耗。然后将控制器关联过程分为两个阶段:先设计了最小集合覆盖算法来快速求解大规模网络中控制器关联问题;在此基础上,引入联合博弈策略来优化控制器和交换机的关联关系以减少控制资源消耗和控制流量开销。仿真结果表明,与现有的控制器和交换机就近关联机制相比,该文机制能在保证较低控制流量开销的前提下,节省约28%的控制资源消耗。
Abstract:In Software-Defined Networking (SDN) with distributed control plane, network expansion problems arise due to network domain management. To address this issue, a Traffic Engineering-based control Resource Optimization (TERO) mechanism of SDN is proposed. It analyzes the control resource consumption of flow requests processing with different path characteristics, and points out that the control resource consumption can be reduced by changing the association relationship between controllers and switches. The controller association mechanism is divided into two phases: firstly, a minimum set cover algorithm is designed to solve the controller association problem efficiently in large-scale network. Then, a coalitional game strategy is introduced to optimize the controller association relationship to reduce both control resource consumption and control traffic overhead. The simulation results demonstrate that while keeping control traffic overhead low, mechanism which in this paper can reduce control resource consumption by about 28% in comparison with the controller proximity mechanism.
-
表 1 最小集合覆盖算法执行过程
算法1 最小集合覆盖算法(Minimum Set Coverage) 输入: SDN网络拓扑邻接矩阵${\text{G}} = [{a_{ij}}]$;网络中流处理请求矩阵${\text{F}} = [{f_{ij}}]$;控制器所能关联的备选集合:${C_i} = \{ {S_1},{S_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{S_i}\} $;控制器的
容量及冗余因子:${\alpha _m}$, $\beta $输出:控制器-交换机之间的映射关系:${\text{X} } = [{x_{ij} }]$ (1) 初始化:控制器-交换机关联关系SC={·};已关联的交换机set_switches={·}; (2) 统计网络中端到端流量分布Flow_pair=Flow_sort(F); (3) while I in Flow_pair:遍历网络中流量 (4) Path_switch= Dijkstra(G, i);计算端到端流量的路径 (5) while Path_switch: 循环4个完备策略 (6) if Path_switch $ \subseteq $${C_i}$:若满足完备策略1, SC[${C_i}$]={Path_switch };流经过的所有交换机关联到${C_i}$ (7) if ${S_i}$$ \in $Path_switch AND ${S_i} \in $${C_j}$满足完备策略2, ${S_i} \to {C_j}$; ${S_i}$关联到${C_j}$ (8) if 存在${C_i} \subseteq {C_j}$:满足完备策略3,则$ \cup {S_i} \to {C_j}$;交换机${S_i}$优先关联到${C_j}$ (9) if Sn(${S_i}$)$ \subseteq $Sn(${S_j}$):满足完备策略4${S_i} \to \cup {\rm{ }}{C_j}$;交换机${S_i}$优先处理 (10) else 如果上述4个完备策略都不能满足:实行贪婪算法switch = max(Path_switch & ${C_i}$);寻找关联交换机较多的控制器SC[${C_i}$]=
{switch};将相应交换机关联到控制器${C_i}$上end if; end while; (11) end while; (12) SC={${C_j} = \{ {S_j},{S_{j + 1}}, ·\!·\!· {\rm{,}}{S_n}\} $;输出控制器-交换机映射关系 表 2 联合博弈策略执行过程
算法2 联合博弈策略Coalitional Game 输入:算法1输出的控制器-交换机之间的关联关系${\text{X}} = [{x_{ij} }]$ 输出: 控制器-交换机之间的关联关系$\text{X}' = [{x'_{ij} }]$ (1) 初始化$\text{X} = [{x_{ij} }]$, ${\alpha _m}$, $\beta $ (2) repeat (3) for each ${s_i}$ in $F$:寻找可能存在的交换机迁移 (4) Initial migration pair ${s_i}:{\rm{ }}{c_m} \to {C_n}$;找到满足两个条
件的交换机迁移对end for (5) for each $ {c_m}$:对于每一个控制器 (6) ${L_{ij}}$=${f_{ij}}{d_{kl}}{x_{ik}}{x_{jl}} + \delta {c_{ik}}$;计算每条数据流的资源消耗 (7) if ${s_i}:{\rm{ }}{c_m} \to {C_n}$ and ${\theta _n} \le \alpha \times \beta $;保证控制器不过载,
寻找可能的交换机迁移(8) ${L'_{ij}}$=${f_{ij}}{d_{kl}}{x'_{ik}}{x'_{jl}} + \delta {c'_{ik}}$;假设迁移,计算新的资源
消耗(9) if ${L'_{ij}} \le {L_{ij}}$: 若交换机迁移前后,资源消耗减少了,
则接受迁移(10) ${s_i} \to {c_j}$;实施交换机迁移${L_{ij}} = {L'_{ij}}$;更新的资源
消耗(11) end if; end for; (12) 直到系统没有任何交换机要求迁移,则算法收敛 表 3 实验拓扑数据
网络拓扑 节点数 链路数 控制器数 距离阈值 ARNES 34 47 4 3 ChinaNet 42 66 5 4 Interllifiber 73 93 6 5 Interoute 110 149 7 6 -
ZHANG Yuan, CUI Lin, WANG Wei, et al. A survey on software defined networking with multiple controllers[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 103: 101–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.11.015 KARAKUS M and DURRESI A. A survey: Control plane scalability issues and approaches in Software-Defined Networking (SDN)[J]. Computer Networks, 2016, 112: 279–293. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2016.11.017 XU Yang, CELLO M, WANG I C, et al. Dynamic switch migration in distributed software-defined networks to achieve controller load balance[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(3): 515–529. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2894237 MUQADDAS A S, GIACCONE P, BIANCO A, et al. Inter-controller traffic to support consistency in ONOS clusters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2017, 14(4): 1018–1031. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2017.2723477 BENSON T, AKELLA A, and MALTZ D A. Network traffic characteristics of data centers in the wild[C]. The 10th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, Melbourne, Australia, 2010: 267–280. WANG Tao, LIU Fangming, GUO Jian, et al. Dynamic SDN controller assignment in data center networks: Stable matching with transfers[C]. The 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 1–9. 胡涛, 张建辉, 邬江, 等. SDN中基于分布式决策的控制器负载均衡机制[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(10): 2316–2324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.10.002 CUI Jie, LU Qianzhe, ZHONG Hong, et al. A load-balancing mechnism for distributed SDN control using response time[J]. Thansactions on Network and Service Management, 2018, 15(4): 1197–1206. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2018.2876369 伊鹏, 刘邦舟, 王文博, 等. 一种考虑软件定义网络控制节点故障的控制器部署和交换机迁移方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(8): 1972–1978. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161216YI Peng, LIU Bangzhou, WANG Wenbo, et al. Controller placement and switch immigration strategy for SDN controller failure[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(8): 1972–1978. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161216 ZHOU Yang, ZHENG Kangfeng, NI Wei, et al. Elastic switch migration for control plane load balancing in SDN[J]. IEEE Access, 2018(6): 3909–3919. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2795576 张少军, 兰巨龙, 江逸茗, 等. 流特征感知的软件定义网络控制器动态关联机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2050–2056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171149ZHANG Shaojun, LAN Julong, JIANG Yiming, et al. Flow characteristics aware dynamic controller assignment in software-defined networking[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2050–2056. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171149 SALMAN O, ELHAJJ I H, KAYSSI A, et al. SDN controllers: A comparative study[C]. The 18th Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, Lemesos, Cyprus, 2016: 1–6. PAL C, VEENA S, RUSTAGI R P, et al. Implementation of simplified custom topology framework in Mininet[C]. 2014 Asia-Pacific Conference on Computer Aided System Engineering, South Kuta, Indonesia, 2014: 48–53. doi: 10.1109/APCASE.2014.6924470. KNIGHT S, NGUYEN H X, FALKNER N, et al. The internet topology zoo[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(9): 1765–1775. doi: 10.1109/jsac.2011.111002 LIAO Jianxin, SUN Haifeng, WANG Jingyu, et al. Density cluster based approach for controller placement problem in large-scale software defined networkings[J]. Computer Networks, 2017, 112: 24–35. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2016.10.014 YAO Guang, BI Jun, LI Yuliang, et al. On the capacitated controller placement problem in software defined networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(8): 1339–1342. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2332341 -





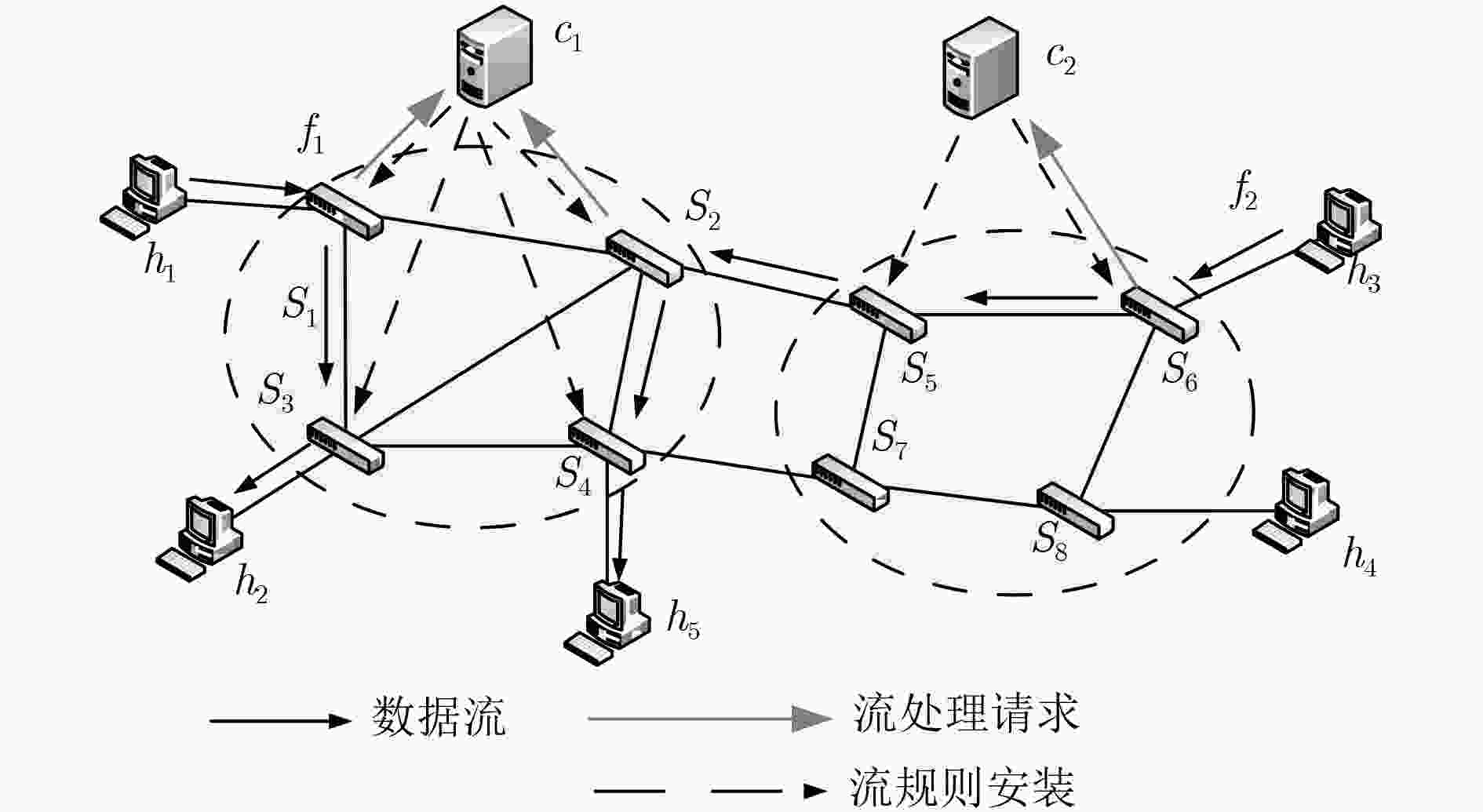
 下载:
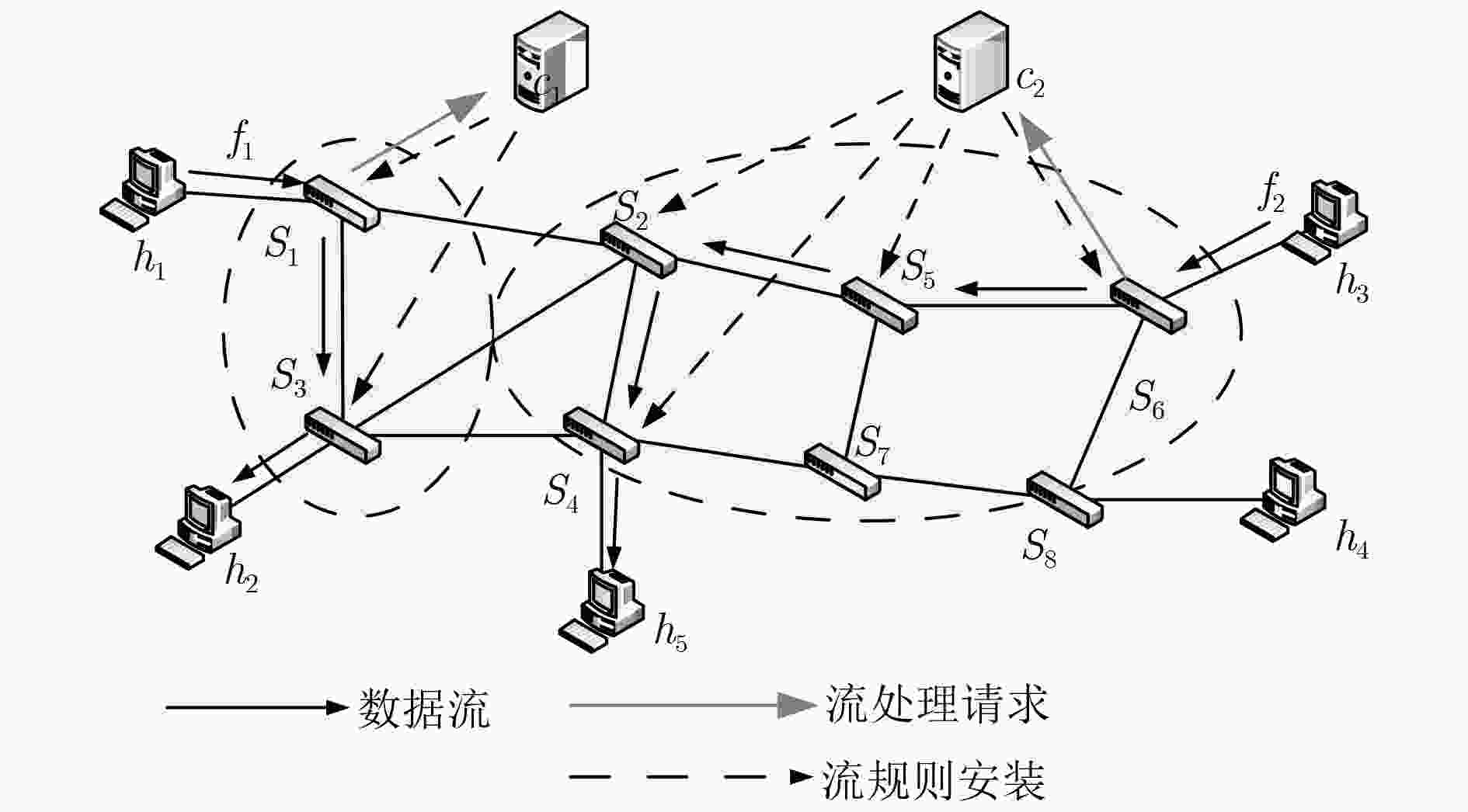
下载:
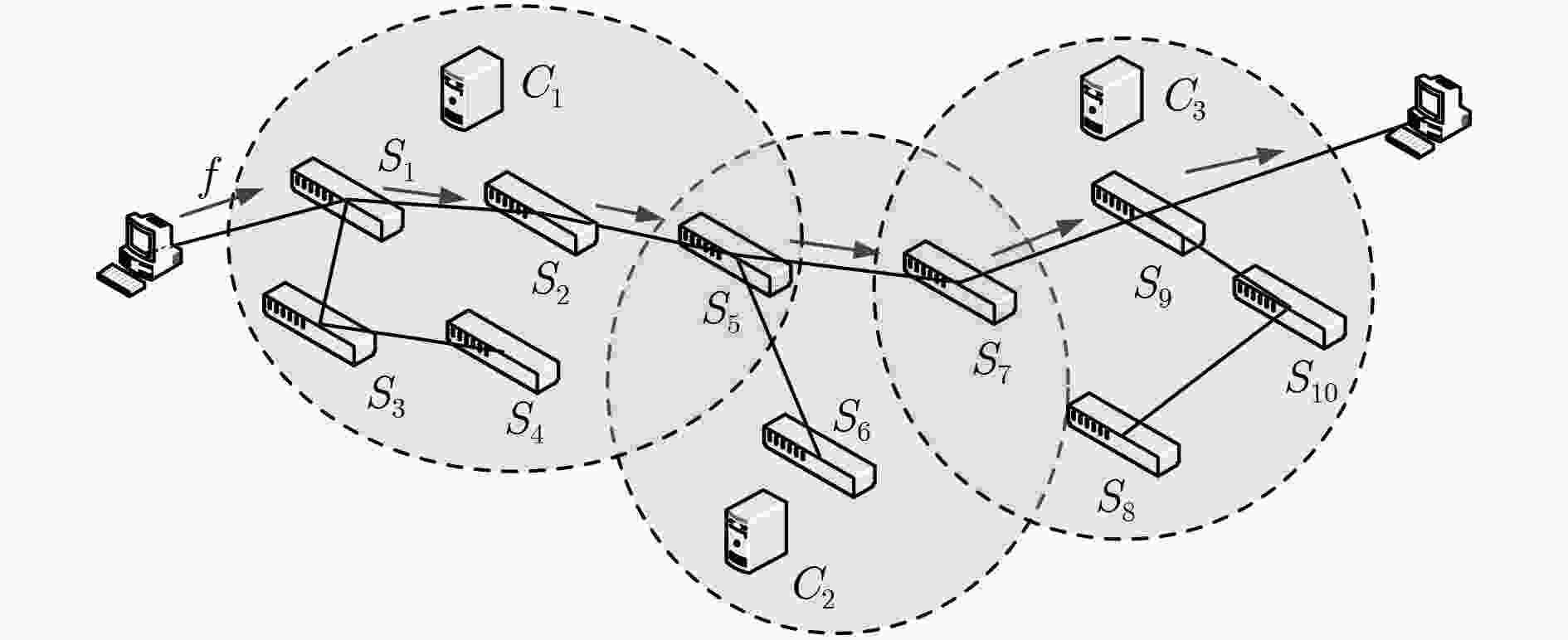
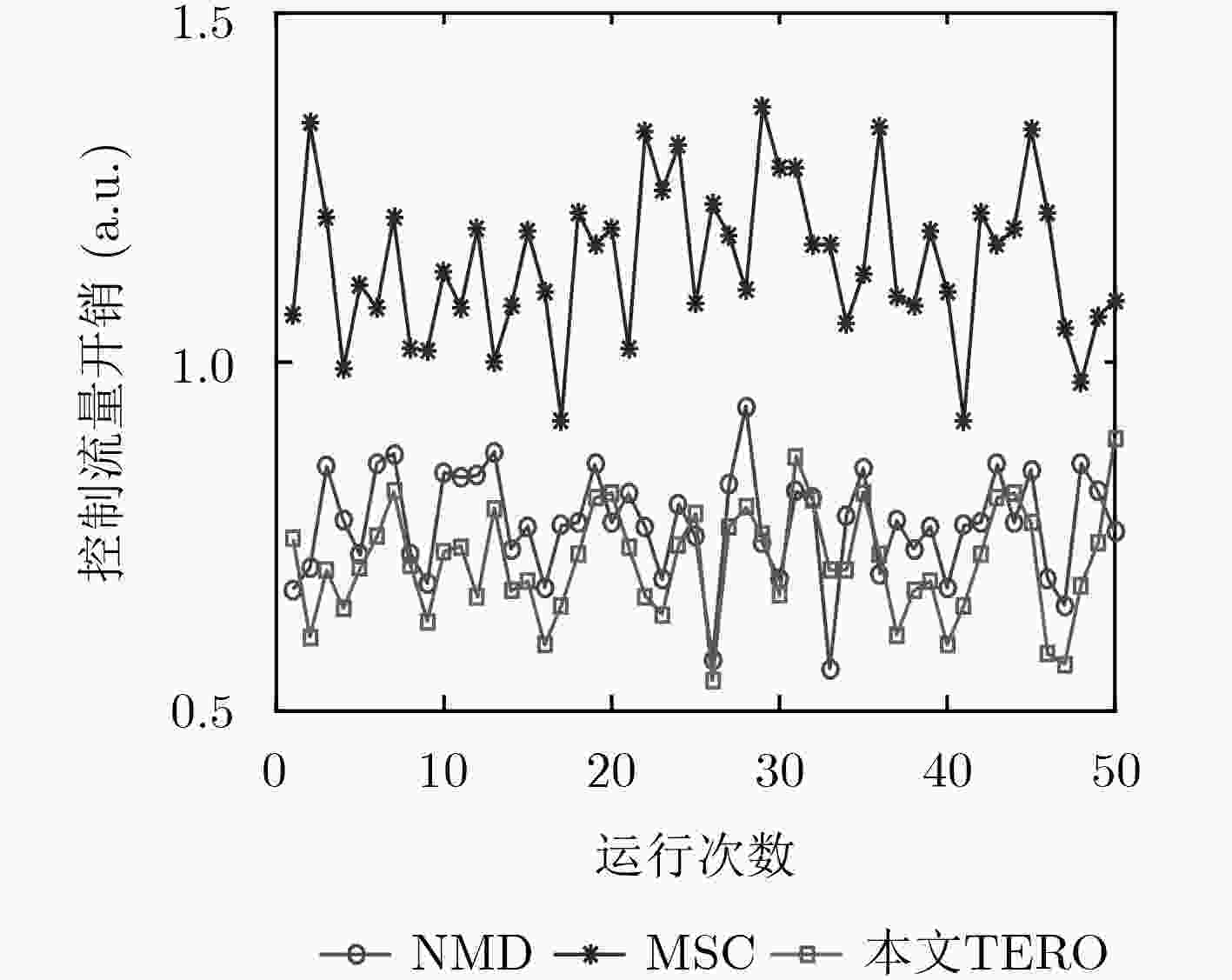
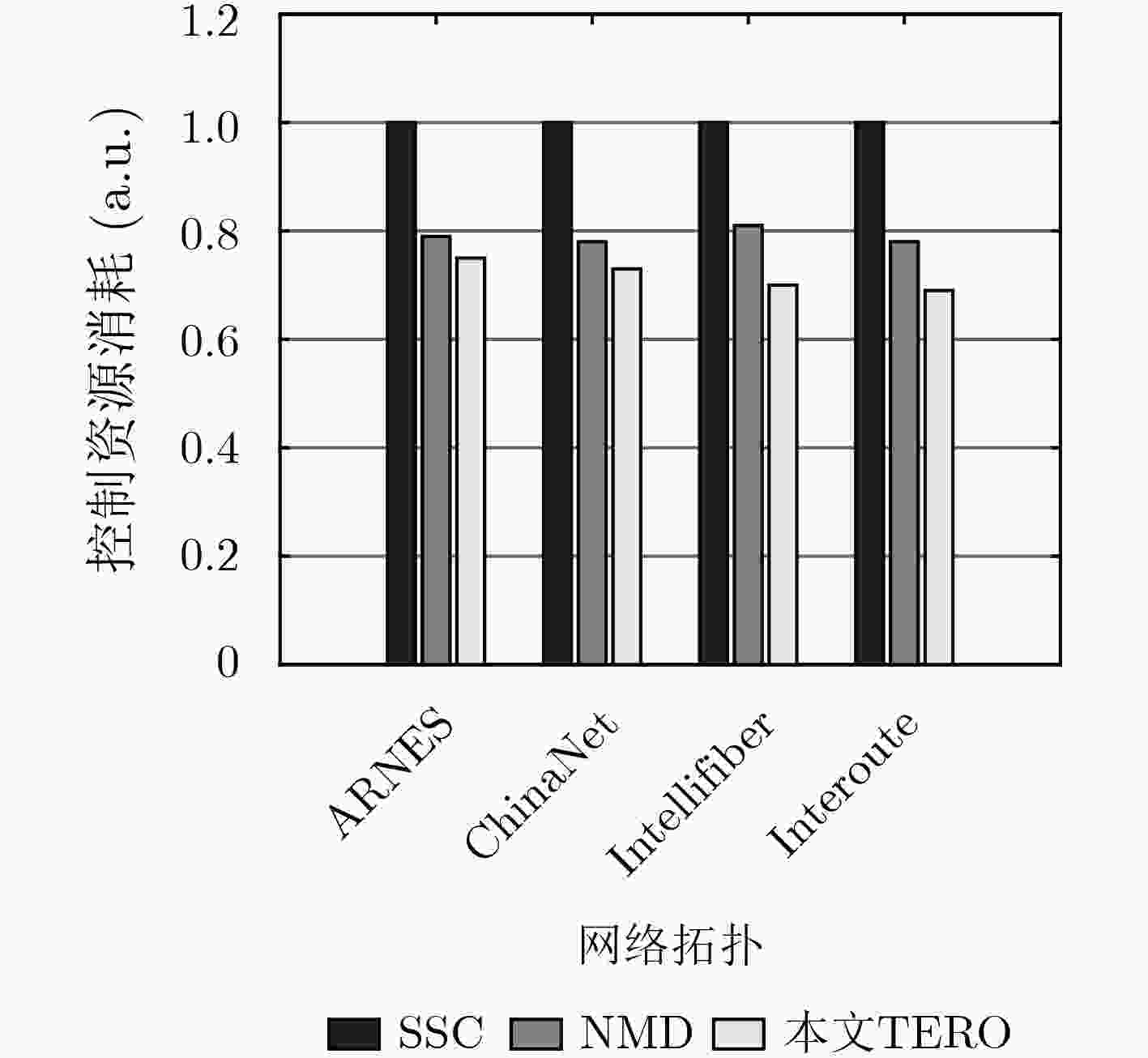
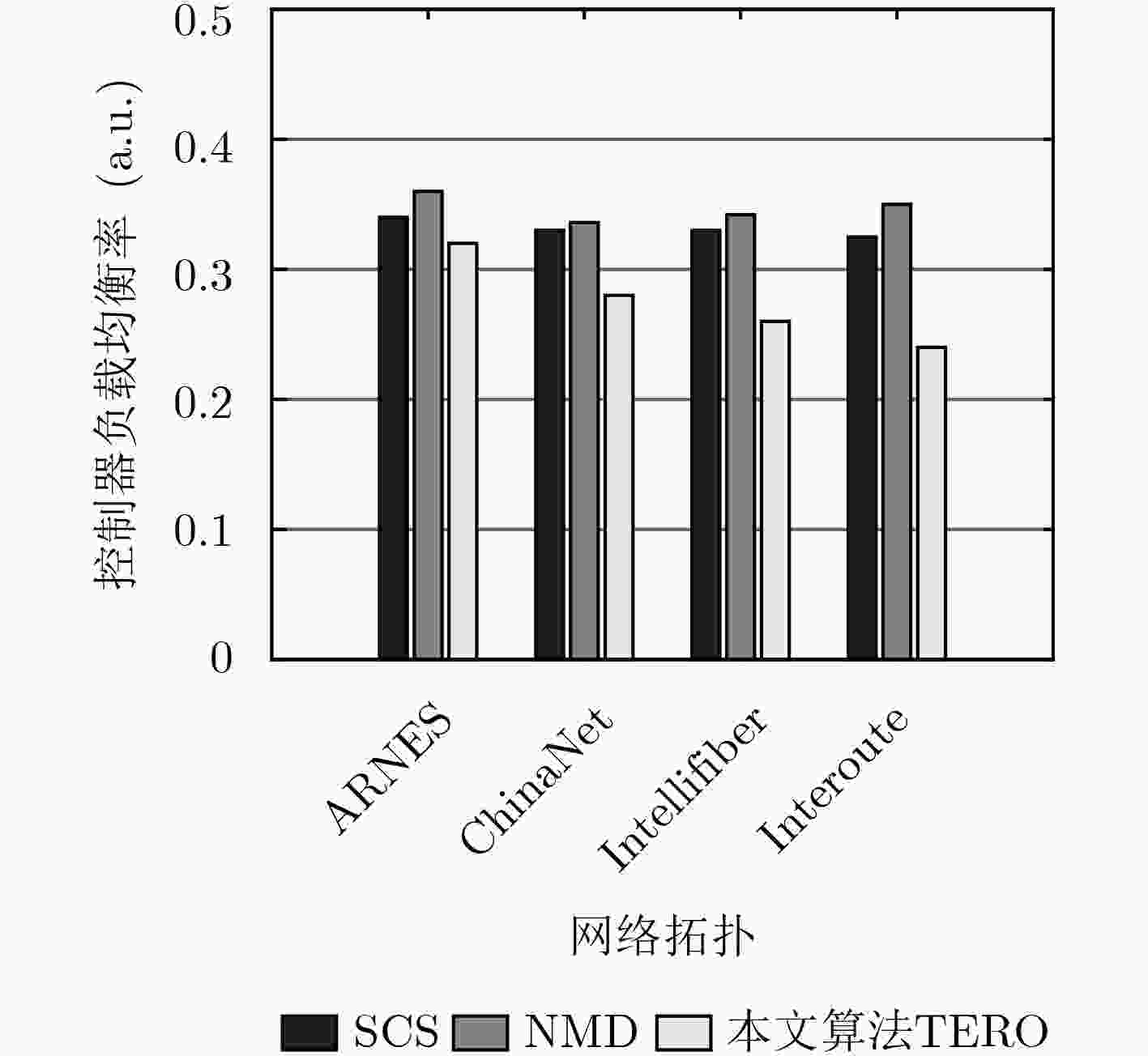


 下载:
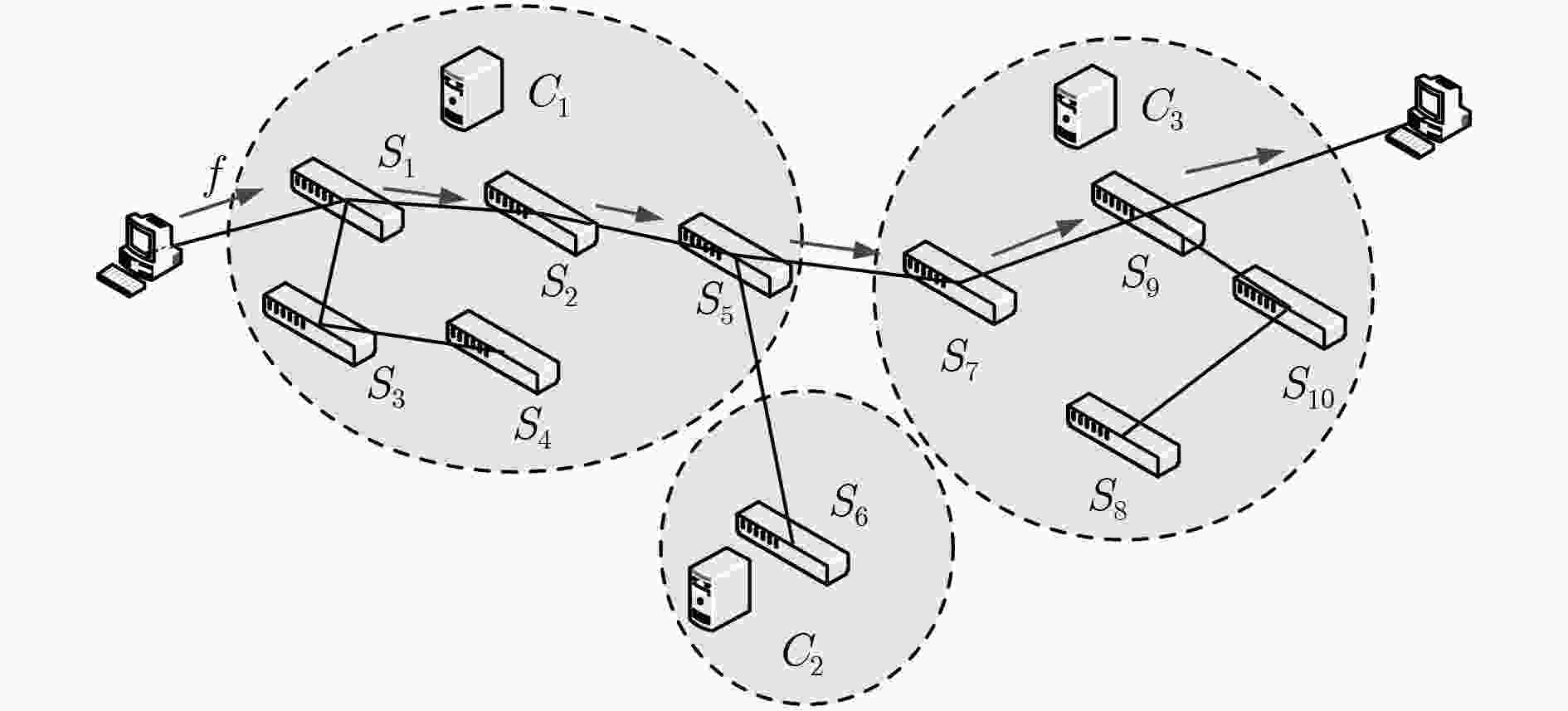
下载:
