Sparse and Low Rank Recovery Based Robust DOA Estimation Method
-
摘要:
该文针对有限次采样导致传统波达方向角(DOA)估计算法存在较大估计误差的问题,提出一种基于稀疏低秩分解(SLRD)的稳健DOA估计方法。首先,基于低秩矩阵分解方法,将接收信号协方差矩阵建模为低秩无噪协方差及稀疏噪声协方差矩阵之和;而后基于低秩恢复理论,构造关于信号和噪声协方差矩阵的凸优化问题;再者构建关于采样协方差矩阵估计误差的凸模型,并将此凸集显式包含进凸优化问题以改善信号协方差矩阵估计性能进而提高DOA估计精度及稳健性;最后基于所得最优无噪声协方差矩阵,利用最小方差无畸变响应(MVDR)方法实现DOA估计。此外,基于采样协方差矩阵估计误差服从渐进正态分布的统计特性,该文推导了一种误差参数因子选取准则以较好重构无噪声协方差矩阵。数值仿真表明,与传统常规波束形成(CBF)、最小方差无畸变响应(MVDR)、传统多重信号分类(MUSIC)及基于稀疏低秩分解的增强拉格朗日乘子(SLD-ALM)算法相比,有限次采样条件下所提算法具有较高DOA估计精度及较好稳健性能。
Abstract:Focusing on the problem of rather large estimation error in the traditional Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimation algorithm induced by finite subsampling, a robust DOA estimation method based on Sparseand Low Rank Decomposition (SLRD) is proposed in this paper. Following the low-rank matrix decomposition method, the received signal covariance matrix is firstly modeled as the sum of the low-rank noise-free covariance matrix and sparse noise covariance one. After that, the convex optimization problem associated with the signal and noise covariance matrix is constructed on the basis of the low rank recovery theory. Subsequently, a convex model of the estimation error of the sampling covariance matrix can be formulated, and this convex set is explicitly included into the convex optimization problem to improve the estimation performance of signal covariance matrix such that the estimation accuracy and robustness of DOA can be enhanced. Finally, with the obtained optimal noiseless covariance matrix, the DOA estimation can be implemented by employing the Minimum Variance Distortionless Response (MVDR) method. In addition, exploiting the statistical characteristics of the sampling covariance matrix estimation error subjecting to the asymptotic normal distribution, an error parameter factor selection criterion is deduced to reconstruct the noise-free covariance matrix preferably. Compared with the traditional Conventional BeamForming (CBF), Minimum Variance Distortionless Response(MVDR), MUltiple SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) and Sparse and Low-rank Decomposition based Augmented Lagrange Multiplier(SLD-ALM) algorithms, numerical simulations show that the proposed algorithm has higher DOA estimation accuracy and better robustness performance under finite sampling snapshot.
-
Key words:
- Direction Of Arrival (DOA) /
- Low rank recovery /
- Sparse /
- Convex optimization
-
表 1 误差参数对算法重构性能影响
误差参数($\eta $) 理想${R_{\rm s} }$对角线均值 理想$R$对角线均值 重构${R_{\rm s} }$对角线均值 重构$R$对角线均值 0.1 6.3246 7.4181 6.3110 7.3918 1 6.3246 7.3384 5.9738 7.0775 4 6.3246 7.3271 5.2290 6.2905 8 6.3246 7.3012 4.1855 5.2388 12 6.3246 7.2275 3.0957 4.1583 16 6.3246 7.3268 2.1294 3.1999 19 6.3246 7.3724 1.3133 2.4336 -
GUO Muran, ZHANG Y D, and CHEN Tao. DOA estimation using compressed sparse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(15): 4133–4146. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2847645 ZHENG Guimei. DOA estimation in MIMO radar with non-perfectly orthogonal waveforms[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(2): 414–417. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2622691 CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 ZHU Shaohao, YANG Kunde, MA Yuanliang, et al. Robust minimum variance distortionless response beamforming using subarray multistage processing for circular hydrophone arrays[C]. 2016 Techno-Ocean, Kobe, Japan, 2016: 692–696. doi: 10.1109/Techno-Ocean.2016.7890744. 李立欣, 白童童, 张会生, 等. 改进的双约束稳健Capon波束形成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 2014–2019. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151213LI Lixin, BAI Tongtong, ZHANG Huisheng, et al. Improved double constraint robust capon beamforming algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 2014–2019. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151213 VAN TREES H L. Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation and Modulation Theory[M]. New York: Wiley-Interscience, 2002. LIAO Bin, GUO Chongtao, HUANG Lei, et al. Matrix completion based direction-of-arrival estimation in nonuniform noise[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2016: 66–69. SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 HE Shun, YANG Zhiwei, and LIAO Guisheng. DOA estimation of wideband signals based on iterative spectral reconstruction[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28(6): 1039–1045. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.06.01 GU Yujie and LESHEM A. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3881–3885. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2194289 陈沛, 赵拥军, 刘成城. 基于稀疏重构的共形阵列稳健自适应波束形成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 301–308. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160436CHEN Pei, ZHAO Yongjun, and LIU Chengcheng. Robust adaptive beamforming algorithm for conformal arrays based on sparse reconstruction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 301–308. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160436 HU Rui, FU Yuli, CHEN Zhen, et al. Robust DOA estimation via sparse signal reconstruction with impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(6): 1333–1336. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2675407 HUANG Weibin and LI Hui. An improved DOA estimation algorithm based on sparse reconstruction[C]. The 11th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Guilin, China, 2016: 621–625. GU Yujie, GOODMAN N A, HONG Shaohua, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix sparse reconstruction[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 96: 375–381. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.10.009 HUANG Lei, ZHANG Jing, XU Xu, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming with a novel interference-plus-noise covariance matrix reconstruction method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(7): 1643–1650. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2015.2396002 韦娟, 计永祥, 牛俊儒. 一种新的稀疏重构的DOA估计算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 45(5): 13–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.05.003WEI Juan, JI Yongxiang, and NIU Junru. Novel algorithm for DOA estimation based on the sparse reconstruction[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2018, 45(5): 13–18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2018.05.003 CHEN Yong, WANG Fang, WAN Jianwei, et al. Sparse and low-rank decomposition of covariance matrix for efficient DOA estimation[C]. The 9th IEEE International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Guangzhou, China, 2017: 957–961. WANG Xianpeng, ZHU Yanghui, HUANG Mengxing, et al. Unitary matrix completion-based DOA estimation of noncircular signals in nonuniform noise[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 73719–73728. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2920707 CANDES E J and PLAN Y. Matrix completion with noise[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6): 925–936. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2009.2035722 HE Zhenqing, SHI Zhiping, and HUANG Lei. Covariance sparsity-aware DOA estimation for nonuniform noise[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2014, 28: 75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2014.02.013 BLANCHARD P and BRÜNING E. Constrained Minimization Problems (Method of Lagrange Multipliers)[M]. BLANCHARD P and BRÜNING E. Mathematical Methods in Physics. Cham: Birkhäuser, 2015: 537–546. LEE S, YOON Y J, LEE J E, et al. Two-stage DOA estimation method for low SNR signals in automotive radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(11): 1613–1619. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0221 TIAN Ye, SUN Xiaoying, and ZHAO Shishun. DOA and power estimation using a sparse representation of second-order statistics vector and ${\ell _0} $ -norm approximation[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 105: 98–108. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2014.05.014HU Yao, ZHANG Debing, YE Jieping, et al. Fast and accurate matrix completion via truncated nuclear norm regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(9): 2117–2130. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2012.271 MALIOUTOV D, ÇETIN M, and WILLSKY A S. A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3010–3022. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.850882 WRIGHT J, GANESH A, RAO S, et al. Robust principal component analysis: Exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices[J]. arXiv: 0905.0233, 2009. HAN Le and LIU Xiaolan. Convex relaxation algorithm for a structured simultaneous low-rank and sparse recovery problem[J]. Journal of the Operations Research Society of China, 2015, 3(3): 363–379. doi: 10.1007/s40305-015-0089-8 WANG Xianpeng, WANG Luyun, LI Xiumei, et al. Nuclear norm minimization framework for DOA estimation in MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 135: 147–152. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.12.031 LUO Xiaoyu, FEI Xiaochao, GAN Lu, et al. Direction-of-arrival estimation using an array covariance vector and a reweighted norm[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2015, E98.A(9): 1964–1967. doi: 10.1587/transfun.E98.A.1964 LIAO Bin, GUO Chongtao, and SO H. Direction-of-arrival estimation in nonuniform noise via low-rank matrix decomposition[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, London, UK, 2017: 1–4. OTTERSTEN B, STOICA P, and ROY R. Covariance matching estimation techniques for array signal processing applications[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 1998, 8(3): 185–210. doi: 10.1006/dspr.1998.0316 HORN R A and JOHNSON C R. Matrix Analysis[M]. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1985: 1-162. ARLOT S and CELISSE A. A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection[J]. Statistics Surveys, 2010, 4: 40–79. doi: 10.1214/09-SS054 DAS A. Theoretical and experimental comparison of off-grid sparse Bayesian direction-of-arrival estimation algorithms[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 18075–18087. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2747153 -





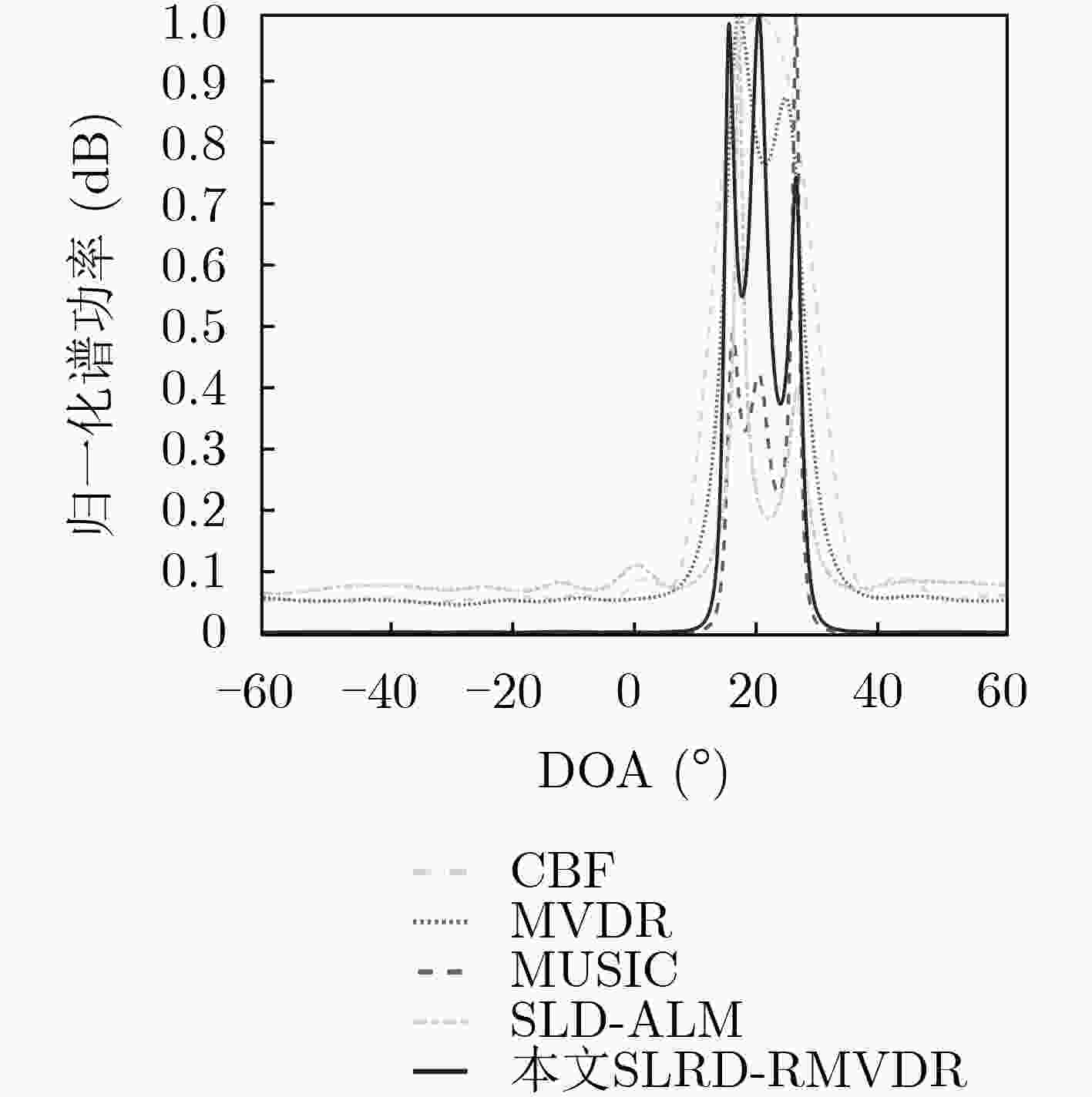
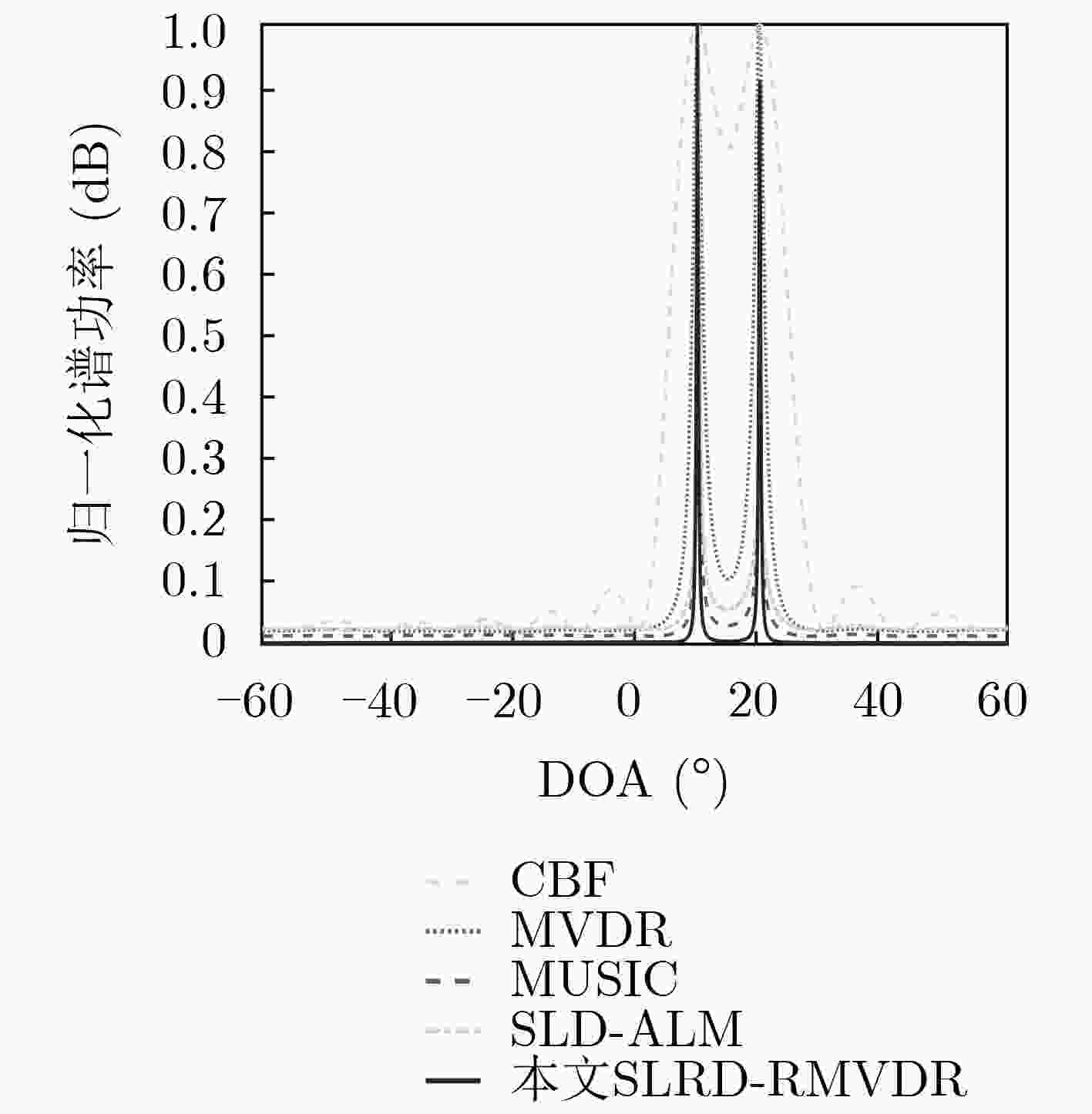
 下载:
下载:
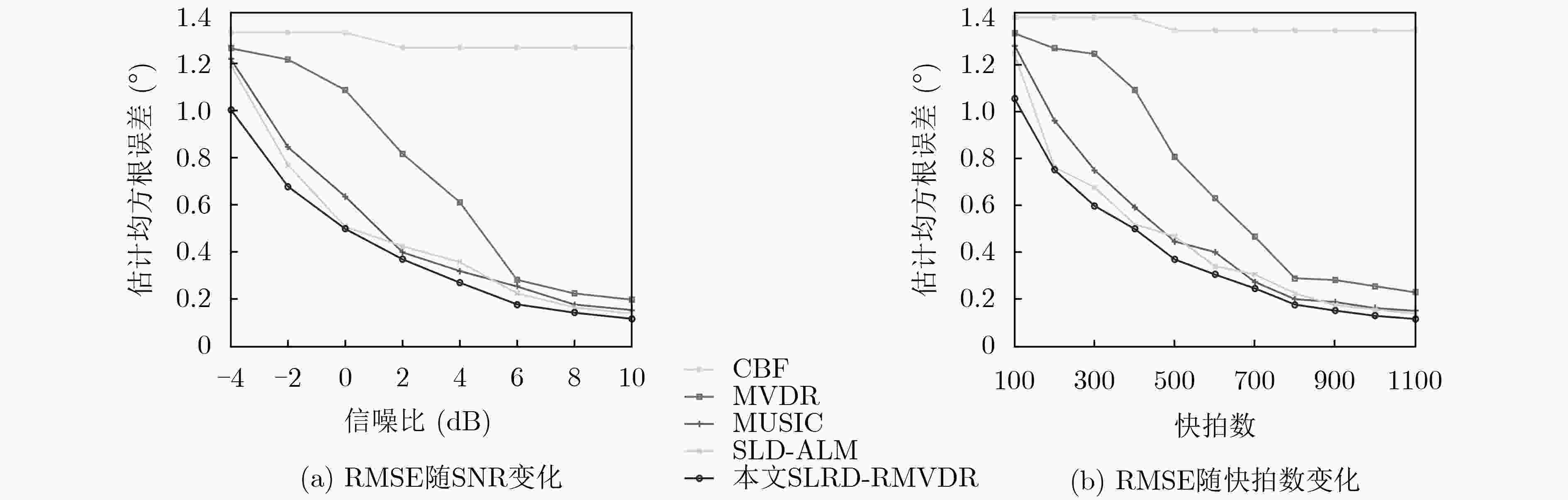
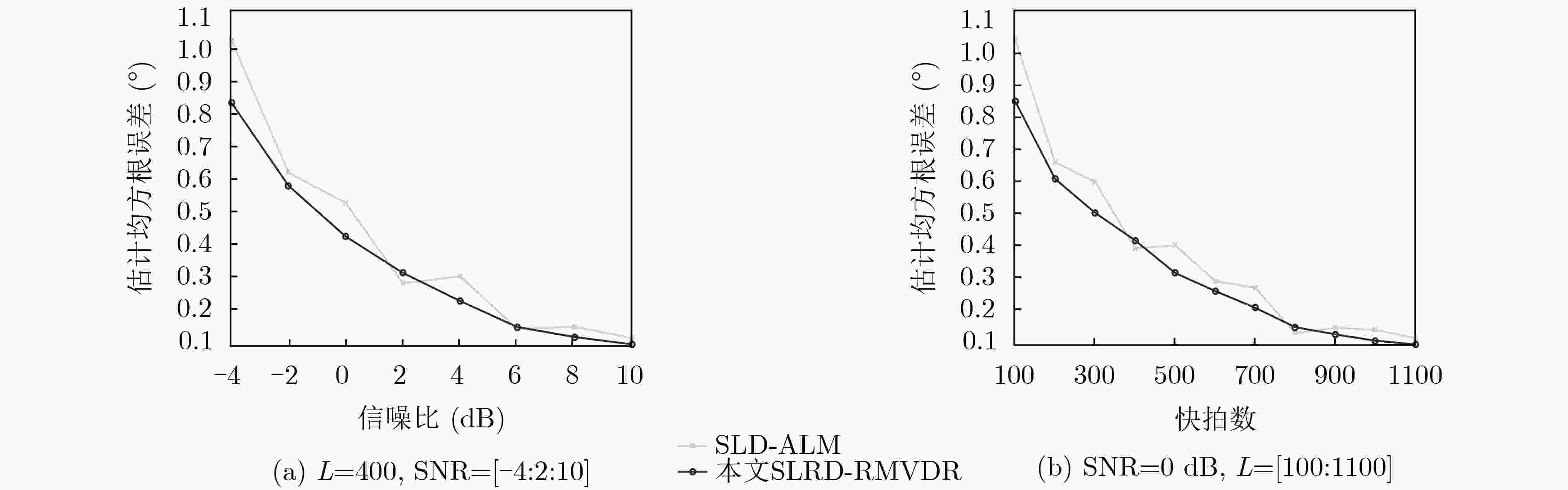



 下载:
下载:
