Multi-level Attention Feature Network for Few-shot Learning
-
摘要:
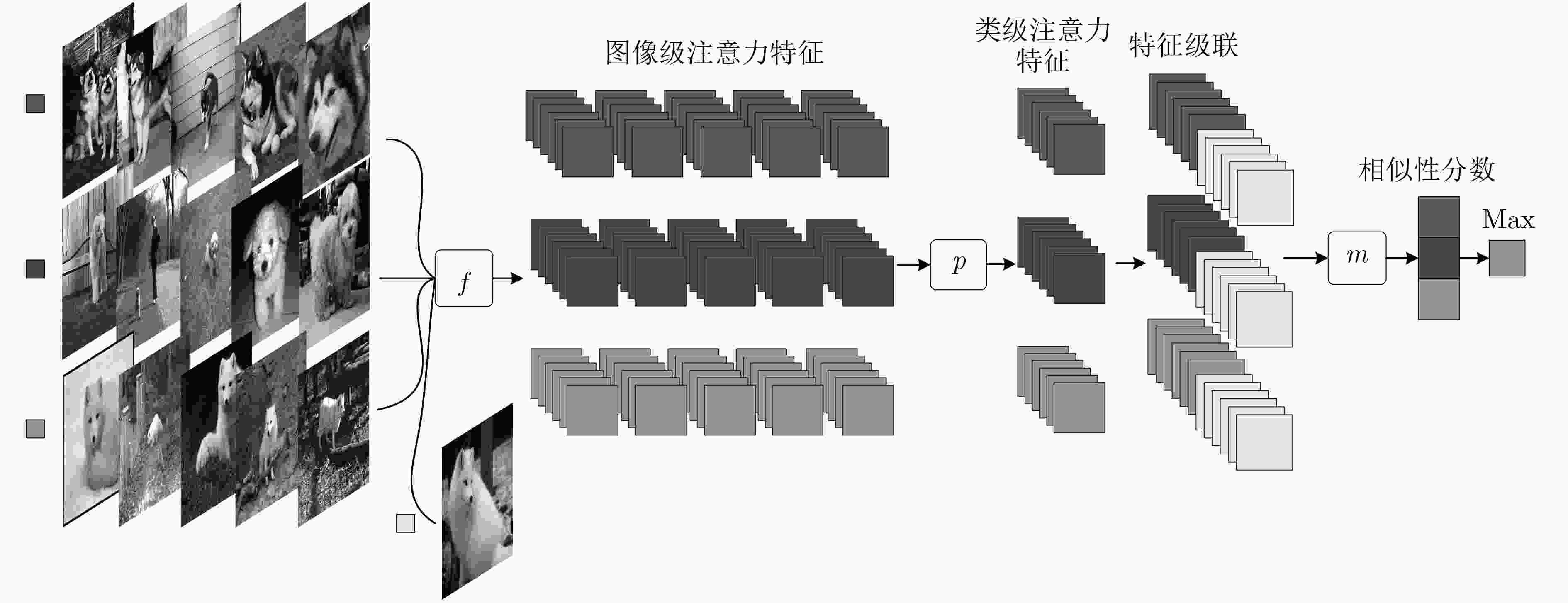
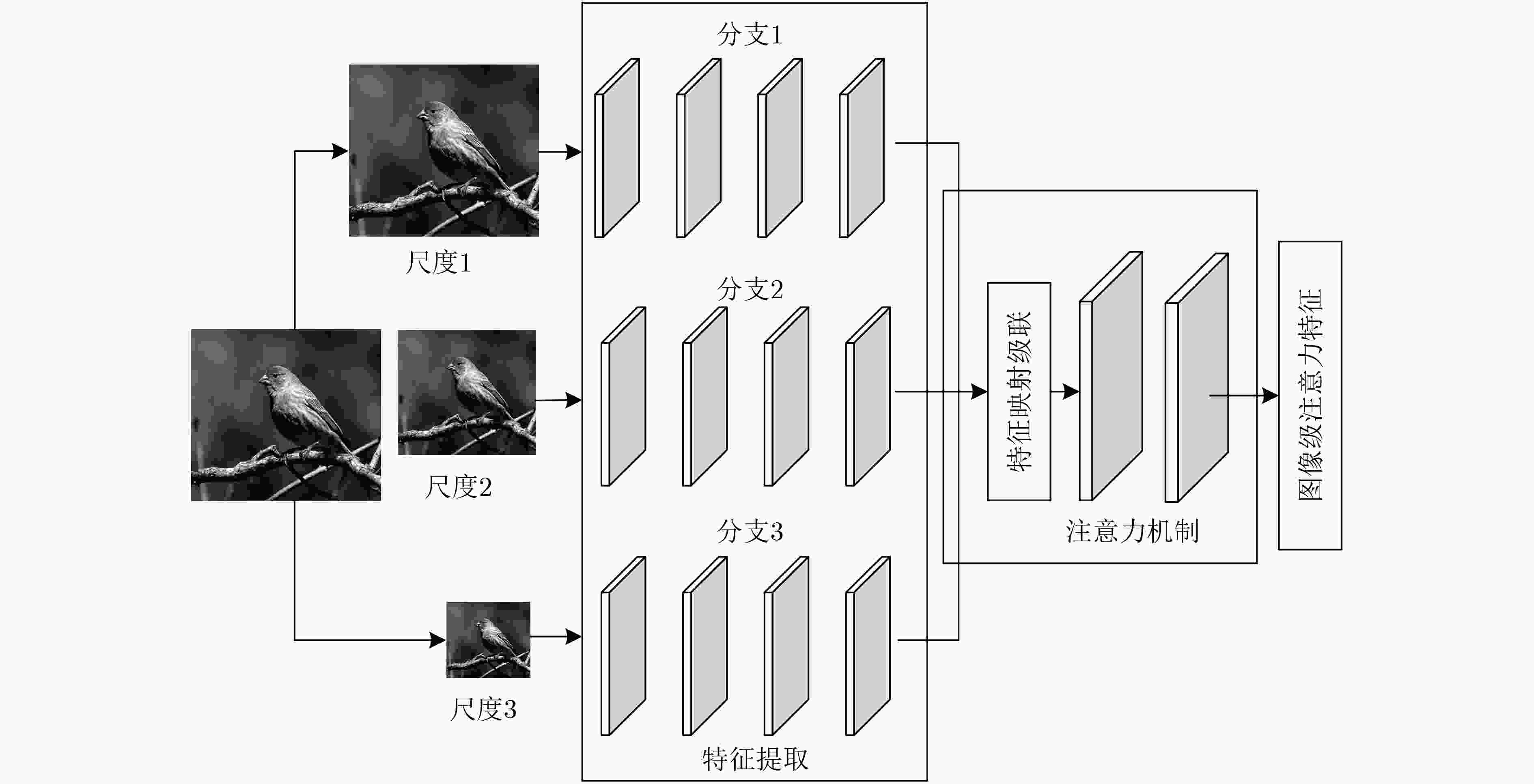
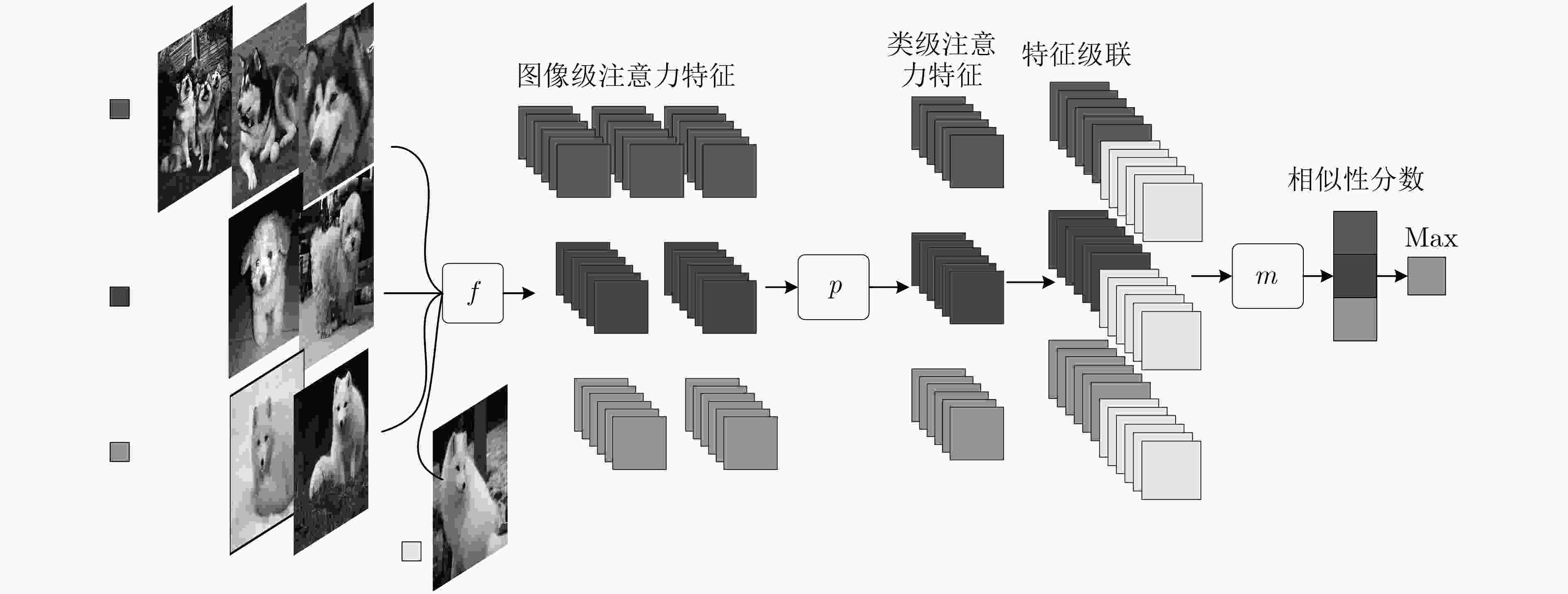
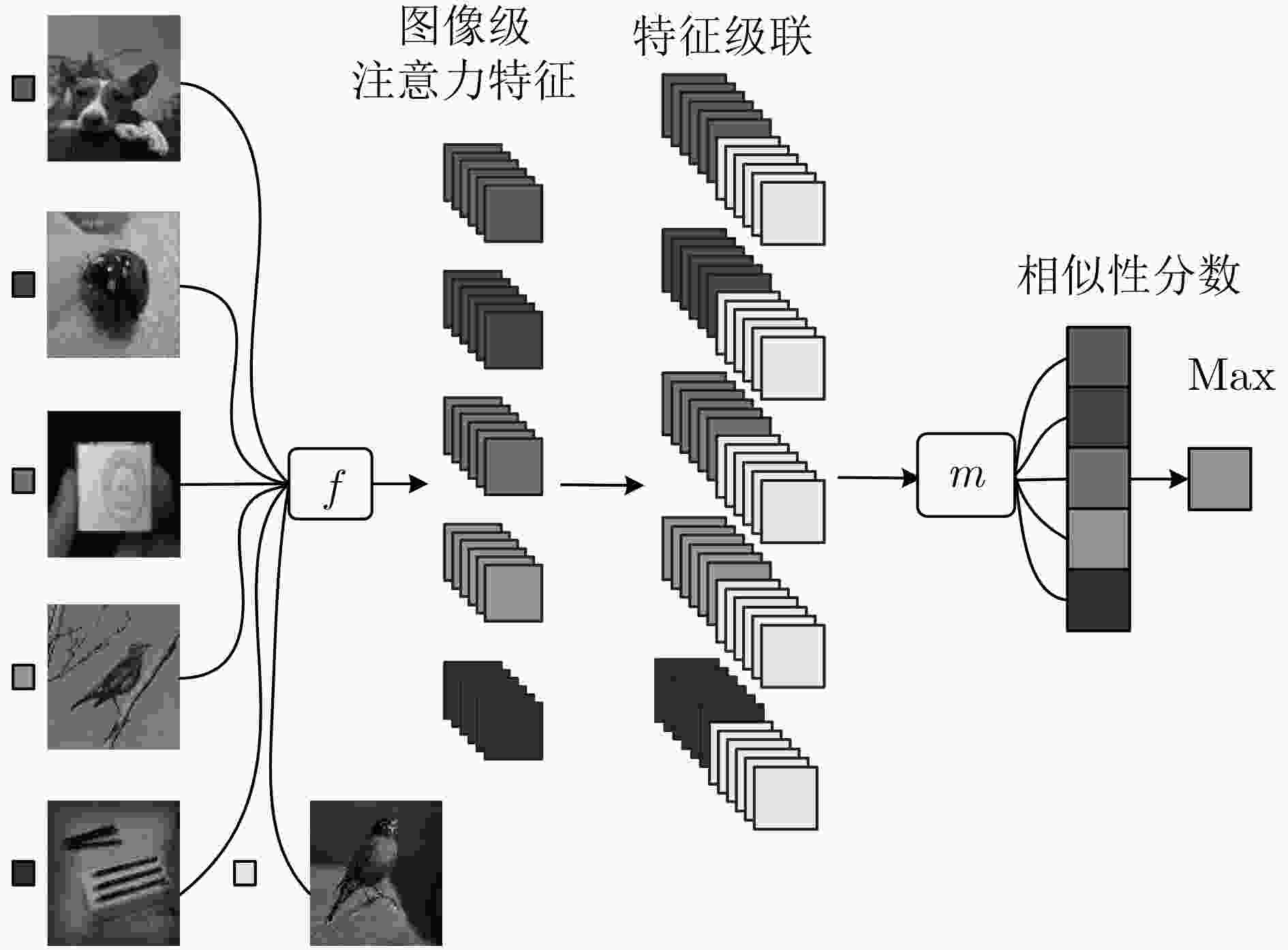
针对目前基于度量学习的小样本方法存在特征提取尺度单一,类特征学习不准确,相似性计算依赖标准度量等问题,该文提出多级注意力特征网络。首先对图像进行尺度处理获得多个尺度图像;其次通过图像级注意力机制融合所提取的多个尺度图像特征获取图像级注意力特征;在此基础上使用类级注意机制学习每个类的类级注意力特征。最后通过网络计算样本特征与每个类的类级注意力特征的相似性分数来预测分类。该文在Omniglot和MiniImageNet两个数据集上验证多级注意力特征网络的有效性。实验结果表明,相比于单一尺度图像特征和均值类原型,多级注意力特征网络进一步提高了小样本条件下的分类准确率。
Abstract:Existing few-shot methods have problems that feature extraction scale is single, the learned class representations are inaccurate, the similarity calculation still relies on standard metrics. In order to solve the above problems, multi-level attention feature network is proposed. Firstly, the multiple scale images are obtained by scale processing, the features of multiple scale images are extracted and the image-level attention features are obtained by the image-level attention mechanism to fusion them. Then, class-level attention features are learned by using the class-level attention mechanism. Finally, the classification is performed by using the network to compute the similarity scores between features. The proposed method is evaluated on the Omniglot dataset and the MiniImagenet dataset. The experimental results show that multi-level attention feature network can further improve the classification accuracy under small sample conditions compared to the single-scale image features and average prototypes.
-
表 1 不同尺度图像的特征提取网络分支结构
网络名 分支1 分支2 分支3 结构 $\left[ \begin{array}{l} {\rm C}:3 \times 3,64 \\ {\rm MP}:2 \times 2 \\ \end{array} \right]$ $\left[ \begin{array}{l} {\rm C}:3 \times 3,64 \\ {\rm MP}:2 \times 2 \\ \end{array} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ \begin{array}{l} {\rm C}:3 \times 3,64 \\ {\rm MP}:2 \times 2 \\ \end{array} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ $\left[ {{\rm C}:3 \times 3,64} \right]$ 表 2 Omniglot数据集上的小样本分类准确率(%)
方法 微调 5-way 分类准确率 20-way 分类准确率 1-shot 5-shot 1-shot 5-shot MANN 否 82.8 94.9 – – MATCHING NETS 是 97.9 98.7 93.5 98.7 PROTOTYPICAL NETS 否 98.8 99.7 96.0 98.9 MAML 是 98.7±0.4 99.9±0.1 95.8±0.3 98.9±0.2 RELATION NET 否 99.6±0.2 99.8±0.1 97.6±0.2 99.1±0.1 本文方法 否 99.6 99.7 97.8 99.2 表 3 MiniIamgenet数据集上的小样本分类准确率(%)
方法 微调 5-way分类准确率 1-shot 5-shot MATCHING NETS 否 43.56±0.84 53.11±0.73 META-LEARN LSTM 否 43.44±0.77 60.60±0.71 MAML 是 48.70±1.84 63.11±0.92 PROTOTYPICAL NETS 否 49.42±0.78 68.20±0.66 RELATION NETS 否 50.44±0.82 65.32±0.70 本文方法 否 53.18±0.80 66.72±0.71 本文方法(L2正则化) 否 54.56±0.81 67.39±0.68 表 4 MiniImageNet数据集上类特征方法的对比(%)
类特征 5-way 5-shot 分类准确率 本文方法(均值类原型) 65.80±0.65 本文方法(求和) 65.56±0.66 本文方法(类级注意力特征) 66.43±0.68 表 5 MiniImageNet数据集上图像特征方法的对比(%)
图像特征 5-way 分类准确率 1-shot 5-shot 本文方法(单尺度特征) 52.20±0.82 66.43±0.68 本文方法(两尺度特征) 53.93±0.79 66.89±0.71 本文方法(图像级注意力特征) 54.56±0.81 67.39±0.68 表 6 MiniImageNet数据集上多尺度方式对比(%)
多尺度方法 5-way 分类准确率 1-shot 5-shot 特征金字塔网络 53.42±0.76 66.50±0.69 不同卷积核 53.27±0.83 66.29±0.66 本文方法 54.56±0.81 67.39±0.68 表 7 MiniImageNet数据集上相似性度量方法的对比(%)
度量方式 5-way 分类准确率 1-shot 5-shot 本文方法(欧氏距离) 48.43±0.78 63.52±0.71 本文方法(余弦相似度) 46.54±0.82 60.50±0.70 本文方法(网络计算) 54.56±0.81 67.39±0.68 -
GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. HE Di, XIA Yingce, QIN Tao, et al. Dual learning for machine translation[C]. The 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 820–828. LI Feifei, FERGUS R, and PERONA P. One-shot learning of object categories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(4): 594–611. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.79 MEHROTRA A and DUKKIPATI A. Generative adversarial residual pairwise networks for one shot learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.08033, 2017. DIXIT M, KWITT R, NIETHAMMER M, et al. AGA: Attribute-guided augmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7455–7463. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.355. HARIHARAN B and GIRSHICK R. Low-shot visual recognition by shrinking and hallucinating features[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 3037–3046. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.328. FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126–1135. RAVI S and LAROCHELLE H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning[EB/OL]. https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJY0-Kcll, 2017. SANTORO A, BARTUNOV S, BOTVINICK M, et al. Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 1842–1850. KOCH G. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition[EB/OL]. http://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~gkoch/files/msc-thesis.pdf, 2015. VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. The 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3630–3638. SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. The 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. SUNG F, YANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1199–1208. doi: 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00131. WANG Peng, LIU Lingqiao, and SHEN Chunhua. Multi-attention network for one shot learning[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6212–6220. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.658. HILLIARD N, HODAS N O, and CORLEY C D. Dynamic input structure and network assembly for few-shot learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.06819v1, 2017. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
