Integral Attacks on SIMON64
-
摘要:
SIMON系列算法自提出以来便受到了广泛关注。积分分析方面,Wang,Fu和Chu等人给出了SIMON32和SIMON48算法的积分分析,该文在已有的分析结果上,进一步考虑了更长分组的SIMON64算法的积分分析。基于Xiang等人找到的18轮积分区分器,该文先利用中间相遇技术和部分和技术给出了25轮SIMON64/128算法的积分分析,接着利用等价密钥技术进一步降低了攻击过程中需要猜测的密钥量,并给出了26轮SIMON64/128算法的积分分析。通过进一步的分析,该文发现高版本的SIMON算法具有更好抵抗积分分析的能力。
Abstract:The SIMON block cipher receives extensive attention since its proposed. With respect to integral attacks, some integral attacks on SIMON32 and SIMON48 are presented by Wang, Fu and Chu et al. In this paper, on the basis of the existing analysis results, the integral attacks on SIMON64 are further studied. Based on known 18-round integral distinguisher presented by Xiang et al., the integral attacks on 25-round SIMON64/128 are presented using meet-in-the-middle and partial-sum techniques. Then the amount of subkeys that need to be guessed during the attack is further reduced by equivalent-subkey technique, and the improved integral attacks on 26-round SIMON64/128 are also presented. Through further analysis, it is found that the higher version of SIMON algorithm has better resistance to integral analysis.
-
Key words:
- Equivalent-subkey /
- SIMON 64 /
- Meet-in-the-middle /
- Partial-sum /
- Integral attacks
-
表 1 计算
$ \oplus \left( {{X_{18,\left\{ {31} \right\}}} \wedge {X_{18,\left\{ {24} \right\}}}} \right)$ 的复杂度步骤 猜测密钥(比特数) 统计状态(比特数) 时间复杂度 (1) ${K_{24,\left\{ {2\sim 5,8\sim 12,14\sim 19,21\sim 26,28\sim 30} \right\}}}$(24) ${X_{24,\left\{ {4\sim 6,10\sim 13,16\sim 20,23\sim 27,30,31} \right\}}}$(19),
${Y_{24,\left\{ {2\sim 5,8\sim 12,14\sim 19,21\sim 26,28\sim 30} \right\}}}$(24)${2^{24} } \cdot {2^{63} } \cdot \dfrac{ {24} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{81.94} }$ (2) ${K_{23,\left\{ {4\sim 6,10\sim 13,16\sim 20,23\sim 27,30,31} \right\}}}$(19) ${X_{2{\rm{3}},\left\{ {0,6,7,12\sim 14,18\sim 21,25\sim 28} \right\}}}$(14),
${Y_{23,\left\{ {4\sim 6,10\sim 13,16\sim 20,23\sim 27,30,31} \right\}}}$(19)${2^{43} } \cdot {2^{43} } \cdot \dfrac{ {19} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{80.61} }$ (3) ${K_{22,\left\{ {0,6,7,12\sim 14,18\sim 21,25\sim 28} \right\}}}$(14) ${X_{2{\rm{2}},\left\{ {8,14,15,20\sim 22,27\sim 29} \right\}}}$(9),
${Y_{22,\left\{ {0,6,7,12\sim 14,18\sim 21,25\sim 28} \right\}}}$(14)${2^{57} } \cdot {2^{33} } \cdot \dfrac{ {14} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{84.16} }$ (4) ${K_{21,\left\{ {8,14,15,20\sim 22,27\sim 29} \right\}}}$(9) ${X_{2{\rm{1}},\left\{ {16,22,23,29,30} \right\}}}$(5),
${Y_{21,\left\{ {8,14,15,20\sim 22,27\sim 29} \right\}}}$(9)${2^{66} } \cdot {2^{23} } \cdot \dfrac{9}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{82.53} }$ (5) ${K_{20,\left\{ {16,22,23,29,30} \right\}}}$(5) ${X_{{\rm{20,}}\left\{ {{\rm{24,31}}} \right\}}}$(2), ${Y_{20,\left\{ {16,22,23,29,30} \right\}}}$(5) ${2^{71} } \cdot {2^{14} } \cdot \dfrac{5}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{77.68} }$ (6) ${K_{{\rm{19,}}\left\{ {{\rm{24,31}}} \right\}}}$(2) ${X_{18,\left\{ {24,31} \right\}}}$(2), ${X_{18,\left\{ {24} \right\}}} \wedge {X_{18,\left\{ {31} \right\}}}$(1) ${2^{73} } \cdot {2^7} \cdot \dfrac{3}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{71.95} }$ 表 2 计算
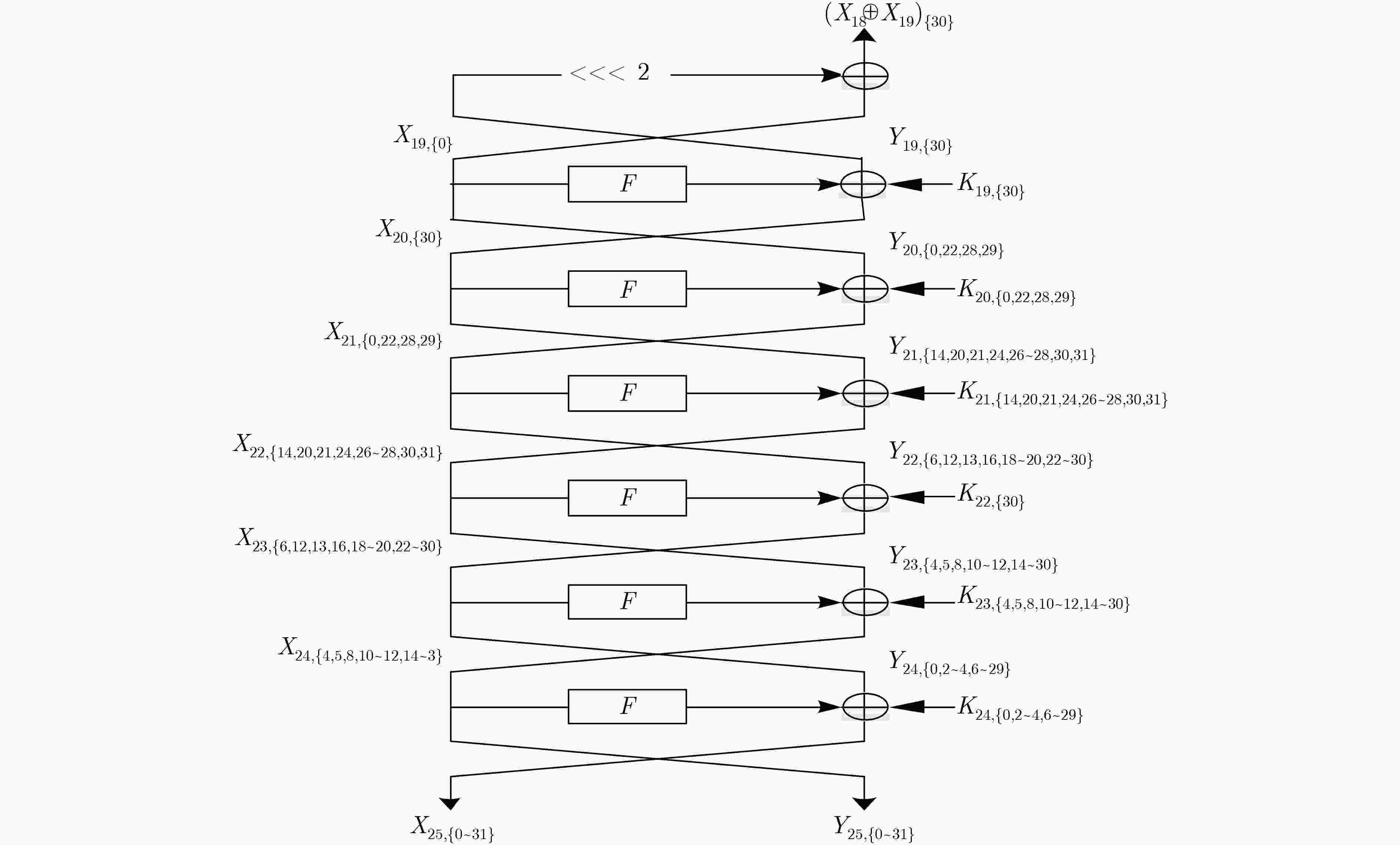
$ \oplus {\left( {{X_{18}} \oplus {X_{19}}} \right)_{\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$ 的复杂度步骤 猜测密钥(bit数) 统计状态(bit数) 时间复杂度 (1) ${K_{24,\left\{ {0,2\sim 4,6\sim 29} \right\}}}$(28) ${X_{2{\rm{4}},\left\{ {4,5,8,10\sim 12,14\sim 30} \right\}}}$(23), ${Y_{24,\left\{ {0,2\sim 4,6\sim 29} \right\}}}$(28) ${2^{28} } \cdot {2^{63} } \cdot \dfrac{ {28} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{86.17} }$ (2) ${K_{23,\left\{ {4,5,8,10\sim 12,14\sim 30} \right\}}}$(23) ${X_{2{\rm{3}},\left\{ {6,12,13,16,18\sim 20,22\sim 30} \right\}}}$(16), ${Y_{23,\left\{ {4,5,8,10\sim 12,14\sim 30} \right\}}}$(23) ${2^{51} } \cdot {2^{51} } \cdot \dfrac{ {23} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{96.88} }$ (3) ${K_{22,\left\{ {6,12,13,16,18\sim 20,22\sim 30} \right\}}}$(16) ${X_{2{\rm{2}},\left\{ {14,20,21,24,26\sim 28,30,31} \right\}}}$(9), ${Y_{22,\left\{ {6,12,13,16,18\sim 20,22\sim 30} \right\}}}$(16) ${2^{67} } \cdot {2^{39} } \cdot \dfrac{ {16} }{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{100.36} }$ (4) ${K_{21,\left\{ {14,20,21,24,26\sim 28,30,31} \right\}}}$(9) ${X_{2{\rm{1}},\left\{ {0,22,28,29} \right\}}}$(4), ${Y_{21,\left\{ {14,20,21,24,26\sim 28,30,31} \right\}}}$(9) ${2^{76} } \cdot {2^{25} } \cdot \dfrac{9}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{94.53} }$ (5) ${K_{20,\left\{ {0,22,28,29} \right\}}}$(4) ${X_{{\rm{20}},\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$(1), ${Y_{20,\left\{ {0,22,28,29} \right\}}}$(4) ${2^{80} } \cdot {2^{13} } \cdot \dfrac{4}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{85.36} }$ (6) ${K_{19,\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$(1) ${X_{{\rm{18,}}\left\{ {{\rm{31}}} \right\}}}$(1), $ \oplus {\left( {{X_{18}} \oplus {X_{19}}} \right)_{\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$ (1) ${2^{81} } \cdot {2^5} \cdot \dfrac{2}{ {32 \cdot 25} } \approx {2^{77.36} }$ 表 3 计算
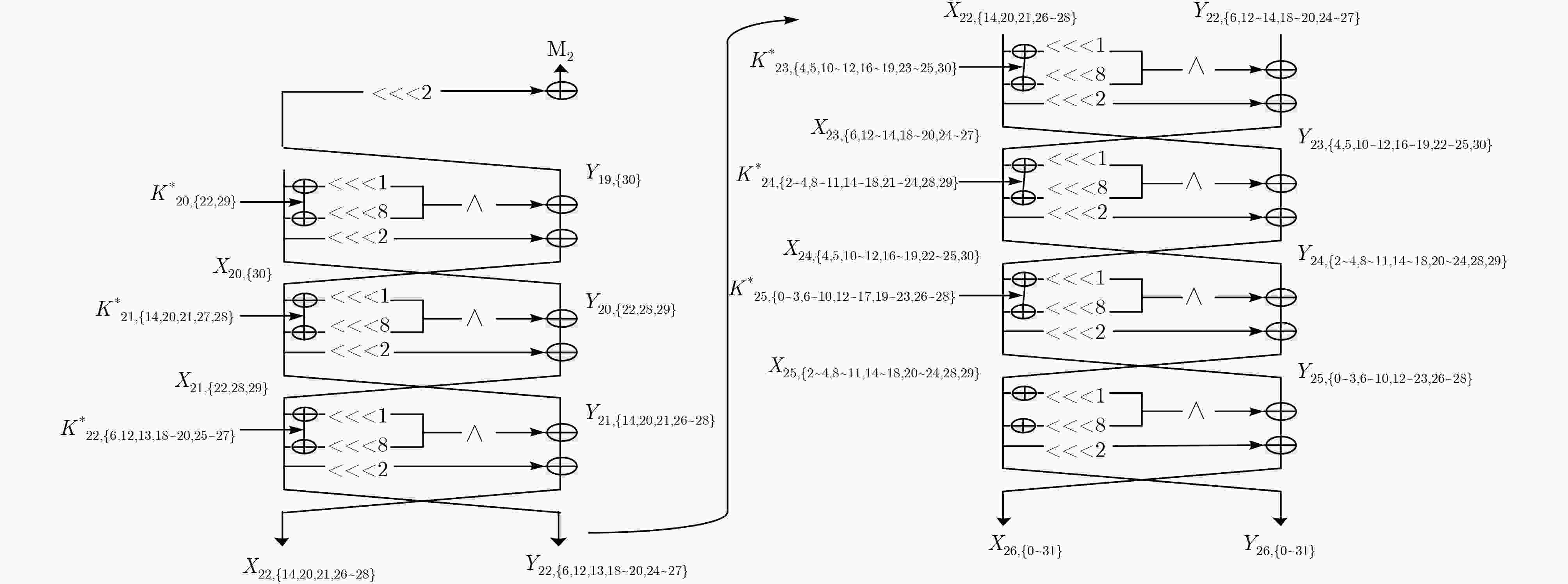
$ \oplus {M_1}$ 值的复杂度步骤 猜测密钥(比特数) 统计状态(比特数) 时间复杂度 (1) $ - $ ${X_{25,\left\{ {2\sim 5,8\sim 12,14\sim 19,21\sim 26,28\sim 30} \right\}}}$(24),
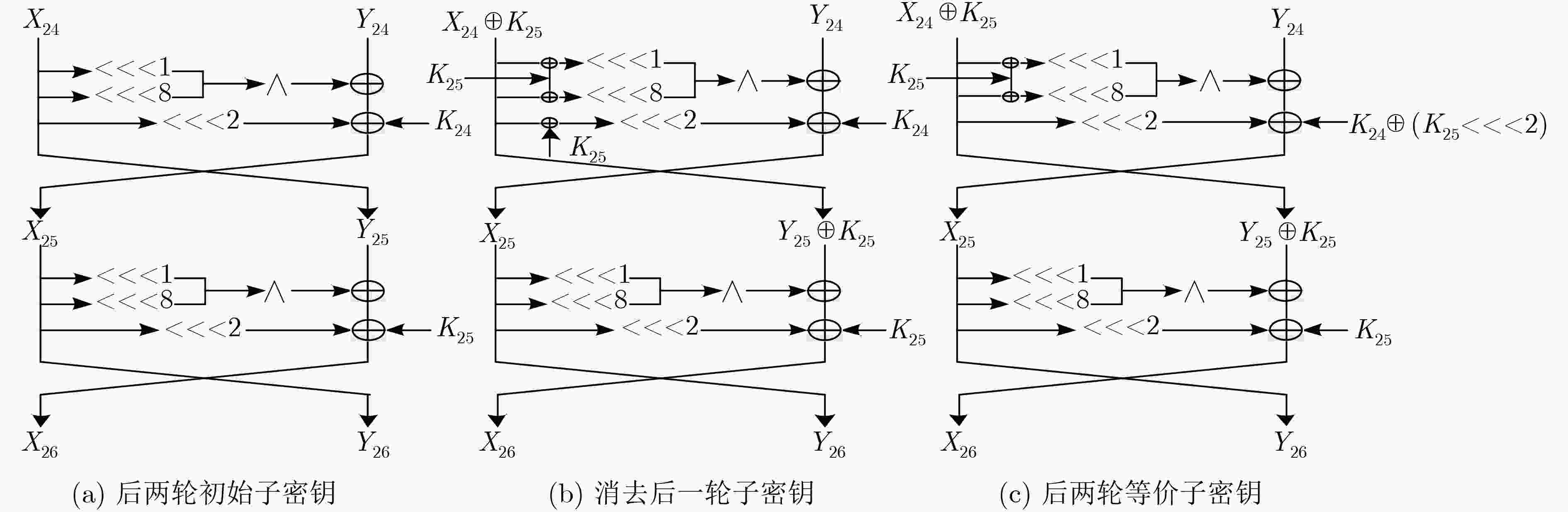
${Y_{25,\left\{ {0\sim 4,6\sim 29} \right\}}}$(29)${2^{63} } \cdot \dfrac{ {29} }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{58.16} }$ (2) $K_{25,\left\{ {0\sim 4,6\sim 11,13\sim 18,20\sim 29} \right\}}^{\rm{*}}$(27) ${X_{{\rm{24,}}\left\{ {{\rm{4\sim 6,10\sim 13,16\sim 20,23\sim 27,30,31}}} \right\}}}$(19),
${Y_{2{\rm{4}},\left\{ {2\sim 5,8\sim 12,14\sim 19,21\sim 26,28\sim 30} \right\}}}$(24)${2^{27} } \cdot {2^{53} } \cdot \dfrac{ {24} }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{74.89} }$ (3) $K_{{\rm{24,}}\left\{ {{\rm{2,5,9,12,16,19,23,26,30}}} \right\}}^{\rm{*}}$(9) ${X_{23,\left\{ {2,3,9,10,16,17,23,24,28} \right\}}}$(9),
${Y_{23,\left\{ {6,10,13,17,20,24,27,31} \right\}}}$(8), ${X_{24,\left\{ {4,11,18,25} \right\}}}$(4)${2^{36} } \cdot {2^{43} } \cdot \dfrac{8}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{72.30} }$ (4) $K_{24,\left\{ {3,10,17,24,28} \right\}}^*$(5) ${X_{23,\left\{ {0,3,4,6\sim 8,10\sim 15,17\sim 22,25\sim 29} \right\}}}$(23),
${Y_{23,\left\{ {4,11,18,25} \right\}}}$(4), ${X_{24,\left\{ {2,12,16,19,23,26,30} \right\}}}$(7)${2^{41} } \cdot {2^{21} } \cdot \dfrac{4}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{54.30} }$ (5) $K_{24,\left\{ {4,8,11,15,18,22,25,29} \right\}}^*$(8) ${X_{23,\left\{ {{\rm{0,6,}}7,12\sim 14,18\sim 21,25\sim 28} \right\}}}$(14),
${Y_{{\rm{23,}}\left\{ {{\rm{4\sim 6,10\sim 13,16\sim 20,23\sim 27,30,31}}} \right\}}}$(19)${2^{49} } \cdot {2^{34} } \cdot \dfrac{ {19} }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{77.55} }$ (6) $K_{23,\left\{ {4,11,18,25} \right\}}^*$(4) ${X_{22,\left\{ {4,5,11,12,18,19,25,26,30} \right\}}}$(9),
${Y_{{\rm{22,}}\left\{ {{\rm{12,19,26}}} \right\}}}$(3), ${X_{{\rm{23,}}\left\{ {{\rm{6,13,20,27}}} \right\}}}$(4)${2^{53} } \cdot {2^{33} } \cdot \dfrac{3}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{77.88} }$ (7) $K_{23,\left\{ {5,12,19,26} \right\}}^*$(4) ${X_{22,\left\{ {5,6,8,10,12\sim 17,19\sim 24,26\sim 31} \right\}}}$(22),
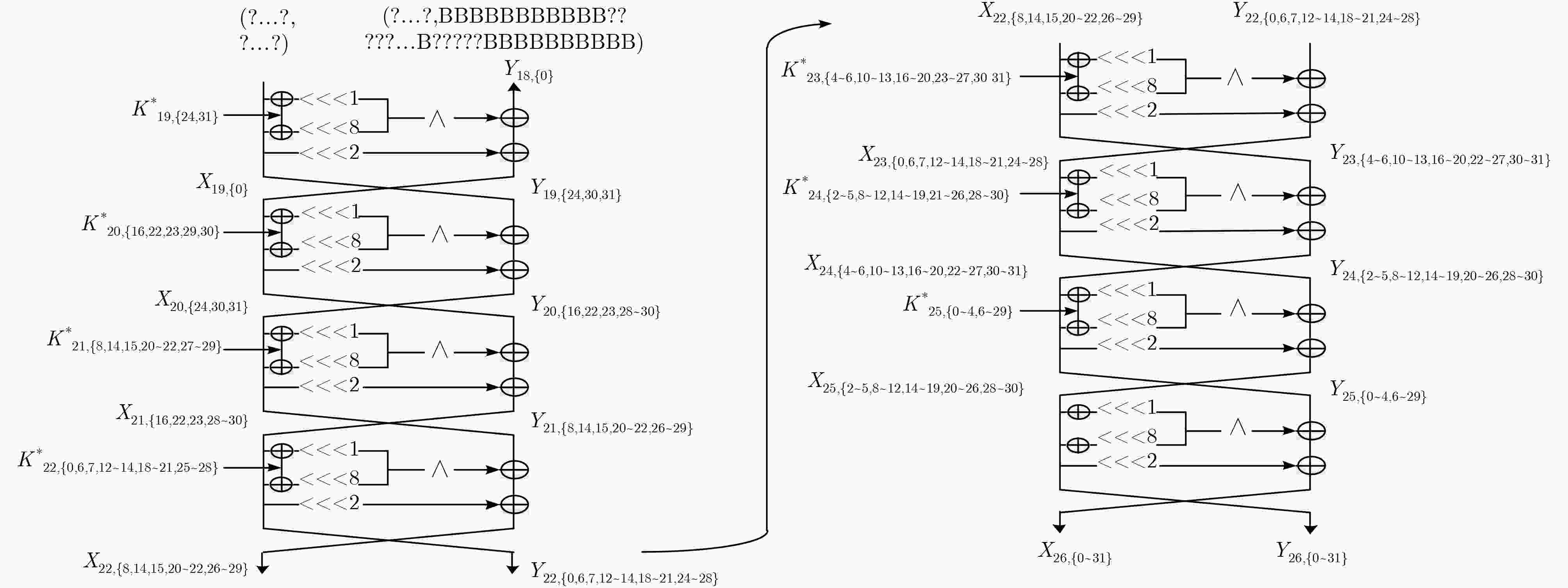
${Y_{22,\left\{ {6,13,20,27} \right\}}}$(4), ${X_{23,\left\{ {0,7,14,18,21,25,28} \right\}}}$(7)${2^{57} } \cdot {2^{16} } \cdot \dfrac{4}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{65.30} }$ (8) $K_{23,\left\{ {6,10,13,17,20,24,27,31} \right\}}^*$(8) ${X_{22,\left\{ {8,14,15,20\sim 22,27\sim 29} \right\}}}$(9),
${Y_{22,\left\{ {0,6,7,12\sim 14,18\sim 21,25\sim 28} \right\}}}$(14)${2^{65} } \cdot {2^{33} } \cdot \dfrac{ {14} }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{92.11} }$ (9) $K_{22,\left\{ {0,7,14,21,28} \right\}}^*$(5) ${X_{21,\left\{ {6,12,13,19,20,27,28} \right\}}}$(7),
${Y_{21,\left\{ {8,15,22,29} \right\}}}$(4), ${X_{22,\left\{ {14,21,28} \right\}}}$(3)${2^{70} } \cdot {2^{23} } \cdot \dfrac{4}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{85.30} }$ (10) $K_{22,\left\{ {6,13,20,27} \right\}}^*$(4) ${X_{21,\left\{ {12,16,18,19,22,23,25,26,29,30} \right\}}}$(10),
${Y_{21,\left\{ {14,21,28} \right\}}}$(3), ${X_{22,\left\{ {20,27} \right\}}}$(2)${2^{74} } \cdot {2^{14} } \cdot \dfrac{3}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{79.88} }$ (11) $K_{22,\left\{ {12,19,26} \right\}}^*$(4) ${X_{21,\left\{ {16,22,23,29,30} \right\}}}$(5),
${Y_{21,\left\{ {8,14,15,20\sim 22,27\sim 29} \right\}}}$(9)${2^{77} } \cdot {2^{15} } \cdot \dfrac{9}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{85.47} }$ (12) $K_{21,\left\{ {8,15,22,29} \right\}}^*$(4) ${X_{20,\left\{ {14,20,21,24,27,28,31} \right\}}}$(7),
${Y_{20,\left\{ {16,23,30} \right\}}}$(3), ${X_{21,\left\{ {22,29} \right\}}}$(2)${2^{81} } \cdot {2^{14} } \cdot \dfrac{3}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{86.88} }$ (13) $K_{21,\left\{ {14,21,28} \right\}}^*$(3) ${X_{20,\left\{ {24,31} \right\}}}$(2), ${Y_{20,\left\{ {16,22,23,29,30} \right\}}}$(5) ${2^{84} } \cdot {2^{12} } \cdot \dfrac{5}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{88.62} }$ (14) $K_{20,\left\{ {16,23,30} \right\}}^*$(3) ${X_{19,\left\{ 0 \right\}}}$(1), ${Y_{19,\left\{ {24,31} \right\}}}$(2) ${2^{ {\rm{87} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{\rm{7} } } \cdot \dfrac{ {\rm{2} } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{85} }{\rm{.30} } } }$ (15) $K_{19,\left\{ {24,31} \right\}}^*$(2) $\left( {{X_{18,\left\{ {31} \right\}}} \wedge {X_{18,\left\{ {{\rm{24}}} \right\}}}} \right) \oplus {X_{19,\left\{ 0 \right\}}}$(1) ${2^{ {\rm{89} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{\rm{3} } } \cdot \dfrac{ {\rm{1} } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{82} }{\rm{.30} } } }$ 表 4 计算
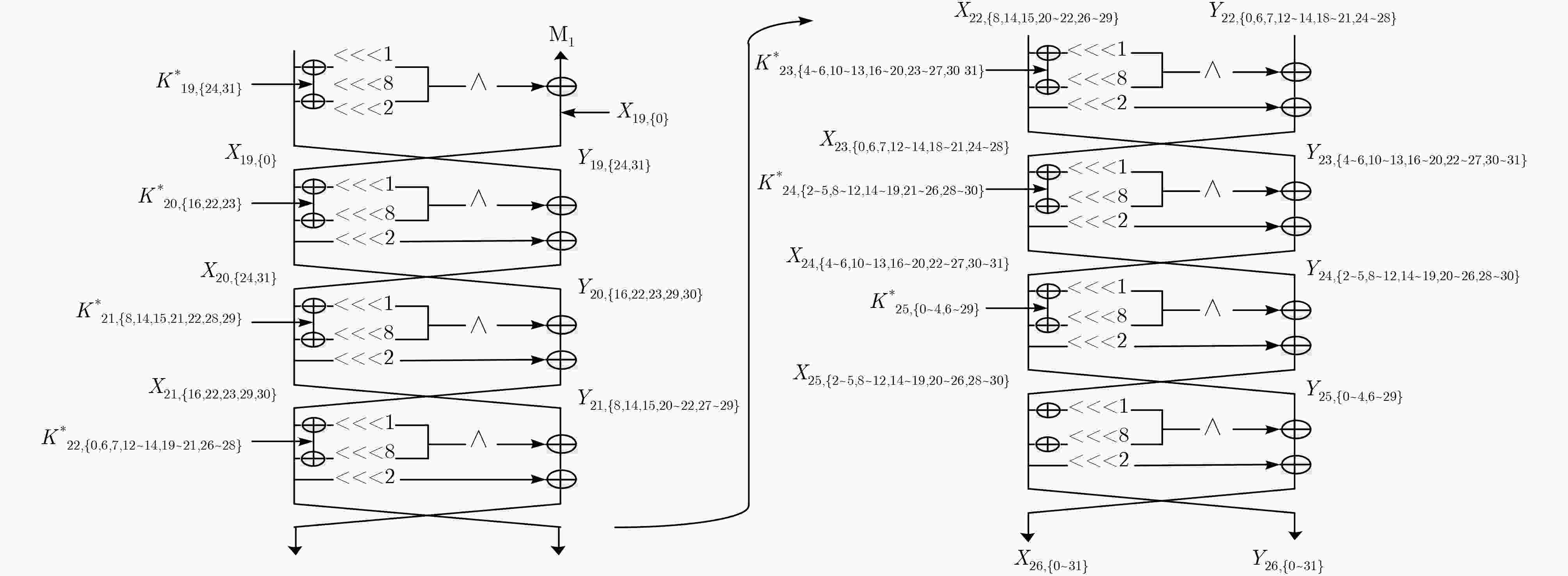
$ \oplus {M_{\rm{2}}}$ 值的复杂度步骤 猜测密钥(比特数) 统计状态(比特数) 时间复杂度 (1) $ - $ ${X_{25,\left\{ {2\sim 4,8\sim 11,14\sim 18,20\sim 24,28,29} \right\}}}$(19),
${Y_{25,\left\{ {0\sim 3,6\sim 10,12\sim 23,26\sim 28} \right\}}}$(24)${2^{63} } \cdot \dfrac{ { {\rm{24} } } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{5{\rm{7} }{\rm{.89} } } }$ (2) $K_{25\left\{ {0\sim 3,6\sim 10,12\sim 17,19\sim 23,26\sim 28} \right\}}^*$(22) ${X_{24,\left\{ {4,5,10\sim 12,16\sim 19,22\sim 25,30} \right\}}}$(14),
${Y_{24,\left\{ {2\sim 4,8\sim 11,14\sim 18,20\sim 24,28,29} \right\}}}$(19)${2^{ {\rm{22} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{ {\rm{43} } } } \cdot \dfrac{ { {\rm{19} } } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{59} }{\rm{.55} } } }$ (3) $K_{24\left\{ {2\sim 4,8\sim 11,14\sim 18,21\sim 24,28,29} \right\}}^*$(18) ${X_{23,\left\{ {6,12,13,18\sim 20,24\sim 27} \right\}}}$(10),
${Y_{23,\left\{ {4,5,10\sim 12,16\sim 19,22\sim 25,30} \right\}}}$(14)${2^{ {\rm{40} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{ {\rm{33} } } } \cdot \dfrac{ { {\rm{14} } } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{67} }{\rm{.11} } } }$ (4) $K_{23,\left\{ {4,5,10\sim 12,16\sim 19,23\sim 25,30} \right\}}^*$(13) ${X_{22,\left\{ {14,20,21,26\sim 28} \right\}}}$(6), ${Y_{22,\left\{ {6,12,13,18\sim 20,24\sim 27} \right\}}}$(10) ${2^{ {\rm{5} }3} } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{ {\rm{24} } } } \cdot \dfrac{ { {\rm{1} }0} }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{70} }{\rm{.63} } } }$ (5) $K_{22\left\{ {6,12,13,18\sim 20,25\sim 27} \right\}}^*$(9) ${X_{21,\left\{ {22,28,29} \right\}}}$(3), ${Y_{21,\left\{ {14,20,21,26\sim 28} \right\}}}$(6) ${2^{6{\rm{2} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{ {\rm{16} } } } \cdot \dfrac{ {\rm{6} } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{70} }{\rm{.89} } } }$ (6) $K_{21\left\{ {14,20,21,27,28} \right\}}^*$(5) ${X_{20,\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$(1), ${Y_{20,\left\{ {22,28,29} \right\}}}$(3) ${2^{6{\rm{7} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{\rm{9} } } \cdot \dfrac{3}{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{67} }{\rm{.89} } } }$ (6) $K_{20\left\{ {22,29} \right\}}^*$(2) $ \oplus {Y_{19,\left\{ {30} \right\}}}$(1) ${2^{6{\rm{9} } } } \cdot { {\rm{2} }^{\rm{4} } } \cdot \dfrac{ {\rm{1} } }{ {32 \cdot 26} } \approx {2^{ {\rm{63} }{\rm{.30} } } } $ 表 5 SIMON算法的积分分析(分组长度64/96/128-bit)
算法 区分器轮数 数据量(CP) 攻击轮数 猜测密钥量(bit) 攻击复杂度(E) SIMON64/96 18 ${{\rm{2}}^{63}}$ 25 73 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{95}}}}$ SIMON64/128 18 ${{\rm{2}}^{63}}$ 26 102 ${{\rm{2}}^{127}}$ SIMON96/96 22 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{95}}}}$ 28 64 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{95}}}}$ SIMON96/144 22 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{95}}}}$ 30 138 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{95}}}}$ SIMON128/128 26 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ 33 98 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ SIMON128/192 26 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ 35 187 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ SIMON128/256 26 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ 36 241 ${{\rm{2}}^{{\rm{127}}}}$ -
KNUDSEN L and WAGNER D. Integral cryptanalysis[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Leuven, Belgium, 2002: 112–127. DAEMEN J, KNUDSEN L, and RIJMEN V. The block cipher Square[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Haifa, Israel, 1997: 149–165. FERGUSON N, KELSEY J, LUCKS S, et al. Improved cryptanalysis of rijndael[C]. The 7th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, New York, USA, 2001: 213–230. TODO Y. Integral cryptanalysis on full MISTY1[C]. The 35th Annual Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2015: 413–432. BEAULIEU R, SHORS D, SMITH J, et al. The SIMON and SPECK families of lightweight block ciphers[EB/OL]. https: //eprint.iacr.org/2013/404, 2013. ABED F, LIST E, LUCKS S, et al. Differential cryptanalysis of round-reduced SIMON and SPECK[C]. The 21st International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, London, UK, 2015: 525–545. BIRYUKOV A, ROY A, and VELICHKOV V. Differential analysis of block ciphers SIMON and SPECK[C]. The 21st International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, London, UK, 2015: 546–570. KÖLBL S, LEANDER G, and TIESSEN T. Observations on the SIMON block cipher family[C]. The 35th Annual Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2015: 161–185. QIAO Kexin, HU Lei, and SUN Siwei. Differential analysis on simeck and simon with dynamic key-guessing techniques[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Rome, Italy, 2017: 64–85. LIU Zhengbin, LI Yongqiang, and WANG Mingsheng. Optimal differential trails in SIMON-like ciphers[J]. IACR Transactions on Symmetric Cryptology, 2017(1): 358–379. doi: 10.13154/tosc.v2017.i1.358-379 WANG Ning, WANG Xiaoyun, JIA Keting, et al. Differential attacks on reduced SIMON versions with dynamic key-guessing techniques[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(9): 098103. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9231-5 ALIZADEH J, ALKHZAIMI H A, AREF M R, et al. Cryptanalysis of SIMON variants with connections[C]. The 10th International Workshop on Radio Frequency Identification: Security and Privacy Issues, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2014: 90–107. ABDELRAHEEM N A, ALIZADEH J, ALKHZAIMI H A, et al. Improved linear cryptanalysis of reduced-round SIMON[EB/OL]. https: //eprint.iacr.org/2014/681, 2014. CHEN Huaifeng and WANG Xiaoyun. Improved linear hull attack on round-reduced Simon with dynamic key-guessing techniques[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Fast Software Encryption, Bochum, Germany, 2016: 428–449. WANG Qingju, LIU Zhiqiang, VARICI K, et al. Cryptanalysis of reduced-round SIMON32 and SIMON48[C]. The 15th International Conference on Cryptology in India, New Delhi, India, 2014: 143–160. BOURA C, NAYA-PLASENCIA M, and SUDER V. Scrutinizing and improving impossible differential attacks: Applications to CLEFIA, Camellia, LBlock and Simon[C]. The 20th International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Kaoshiung, China, 2014: 179–199. 陈展, 王宁. SIMON算法的不可能差分分析[J]. 密码学报, 2015, 2(6): 505–514. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000097CHEN Zhan and WANG Ning. Impossible differential cryptanalysis of reduced-round SIMON[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2015, 2(6): 505–514. doi: 10.13868/j.cnki.jcr.000097 YU Xiaoli, WU Wenling, SHI Zhenqing, et al. Zero-correlation linear cryptanalysis of reduced-round SIMON[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2015, 30(6): 1358–1369. doi: 10.1007/s11390-015-1603-5 XIANG Zejun, ZHANG Wentao, BAO Zhenzhen, et al. Applying MILP method to searching integral distinguishers based on division property for 6 lightweight block ciphers[C]. The 22nd International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2016: 648–678. FU Kai, SUN Ling, and WANG Meiqin. New integral attacks on SIMON[J]. IET Information Security, 2017, 11(5): 277–286. doi: 10.1049/iet-ifs.2016.0241 CHU Zhihui, CHEN Huaifeng, WANG Xiaoyun, et al. Improved integral attacks on SIMON32 and SIMON48 with dynamic key-guessing techniques[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2018: 5160237. doi: 10.1155/2018/5160237 -





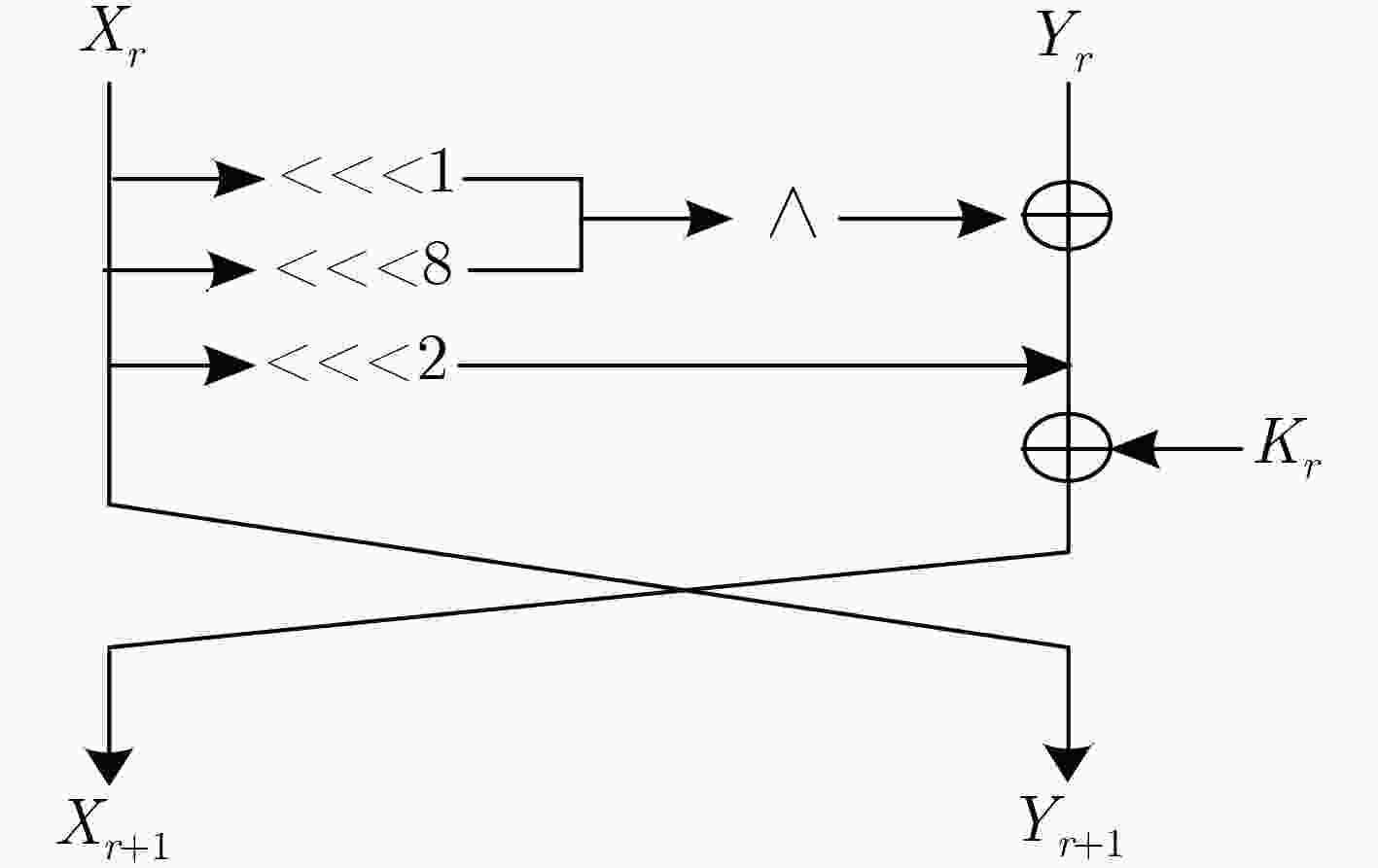
 下载:
下载:
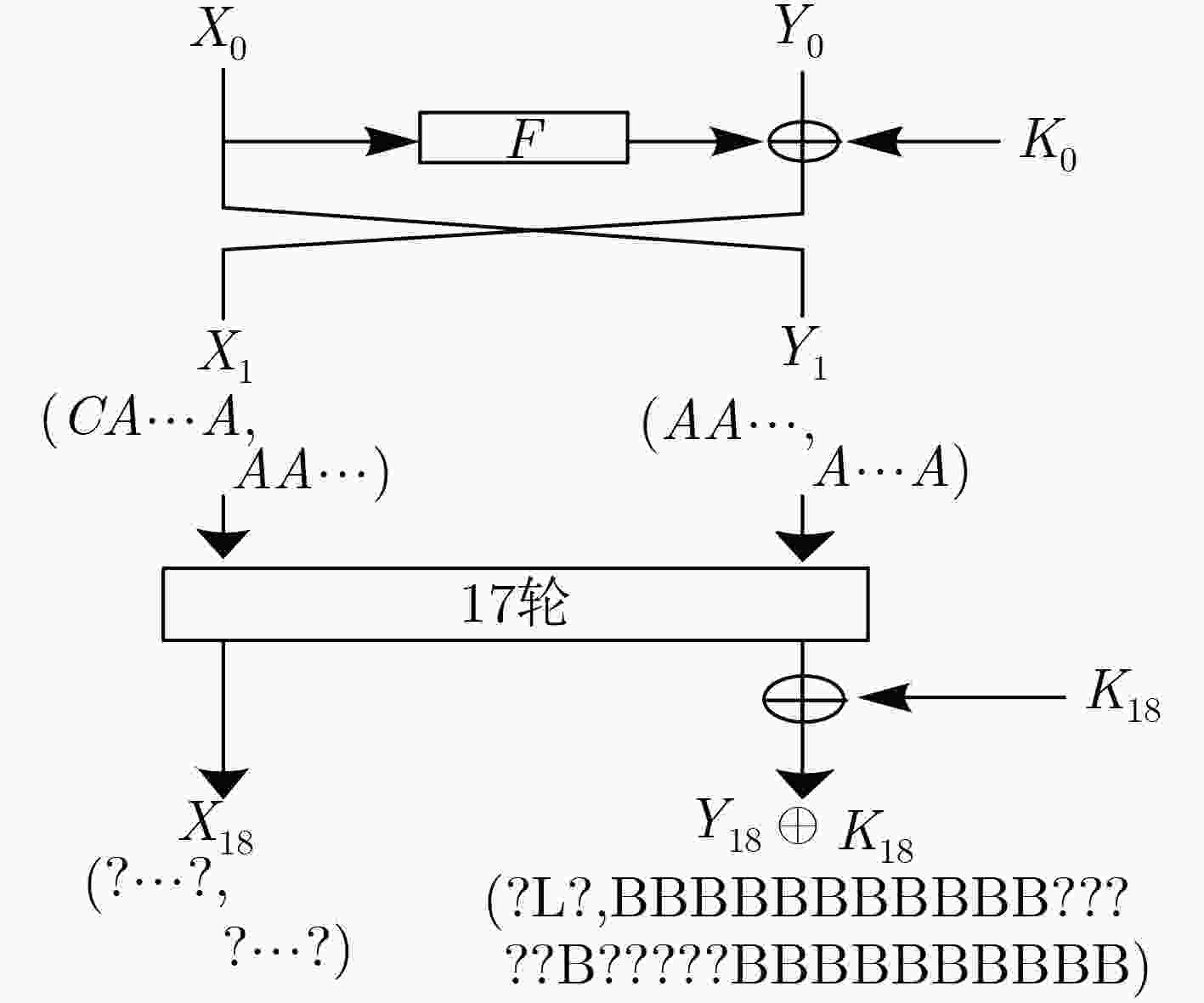
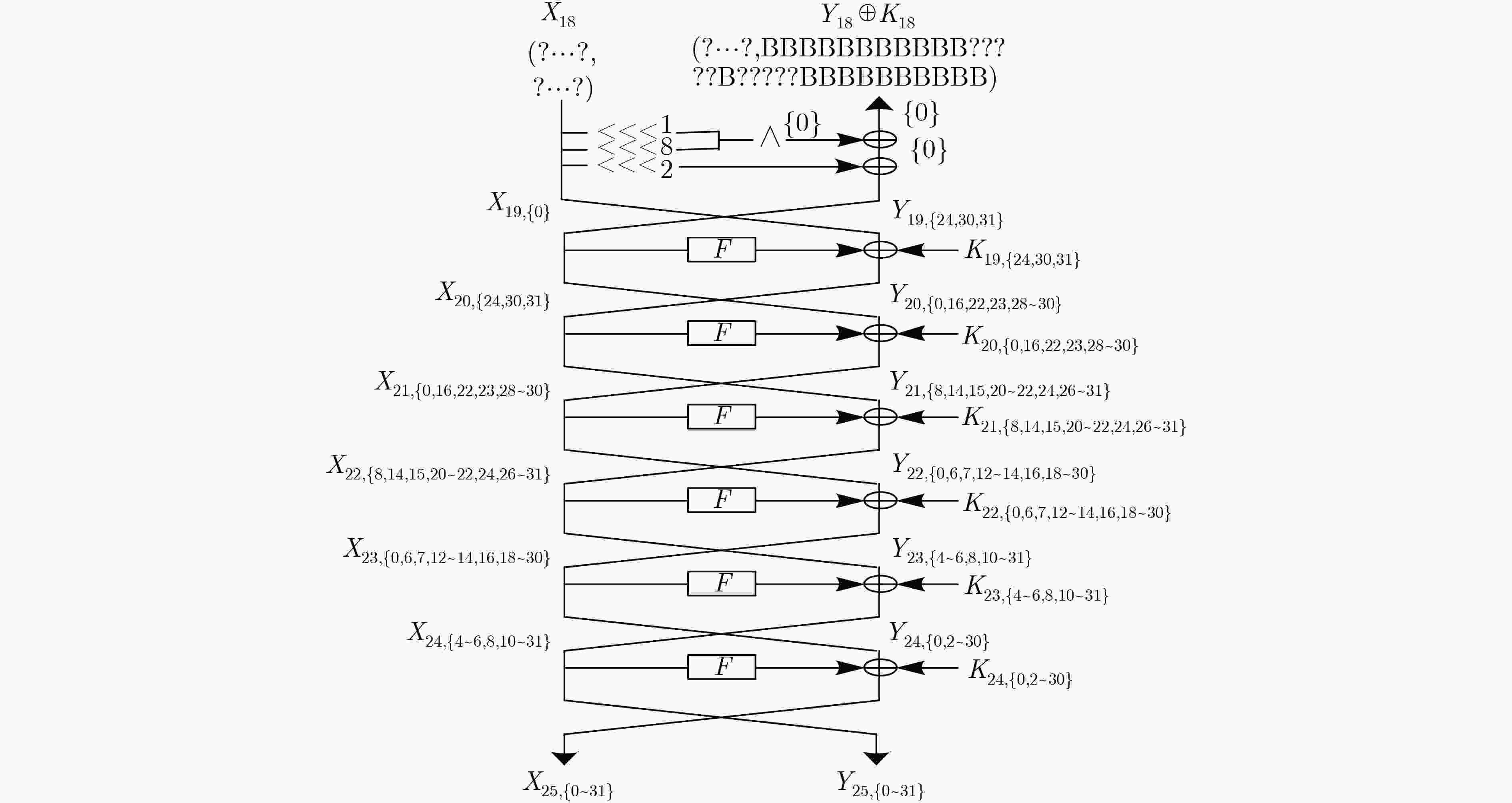
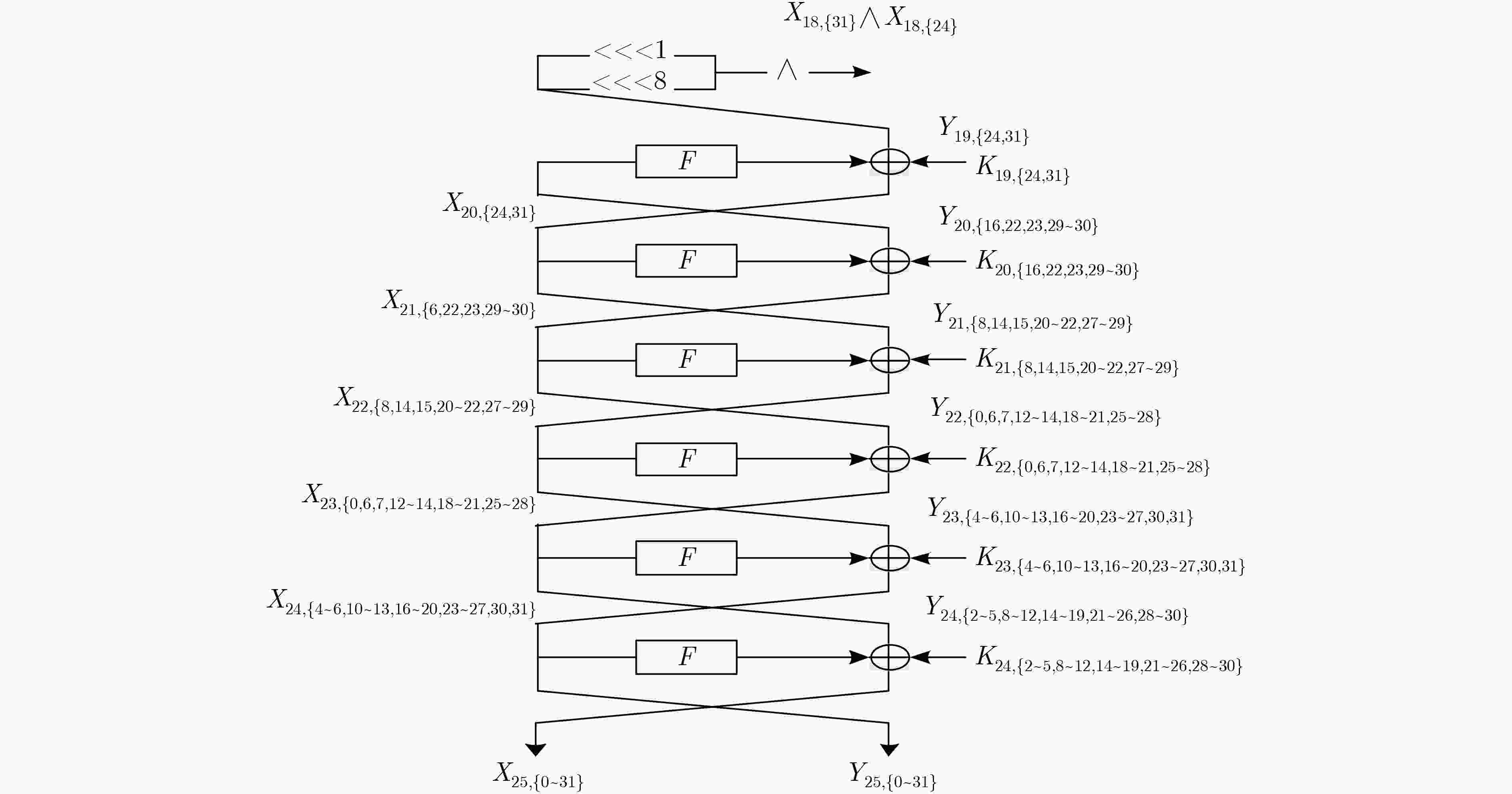










 下载:
下载:
