A Deep Convolutional Network for Saliency Object Detection with Balanced Accuracy and High Efficiency
-
摘要:
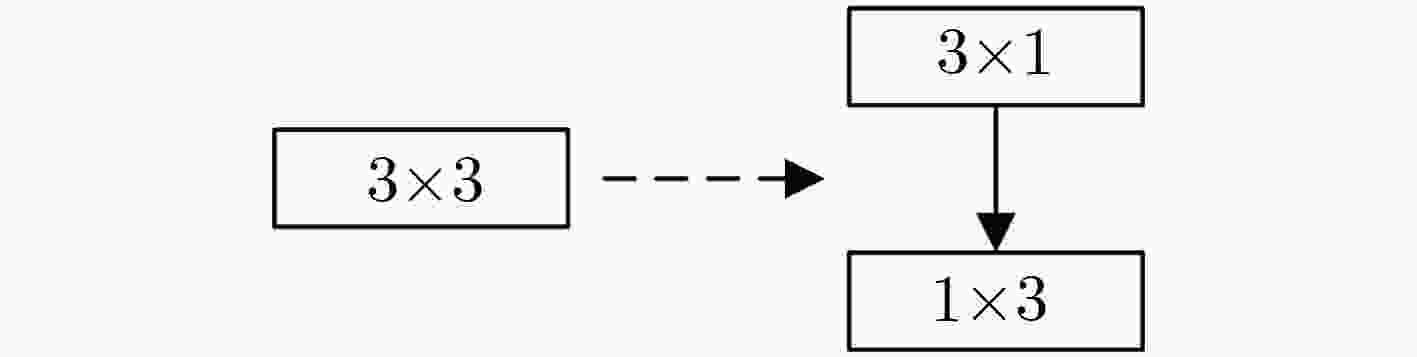
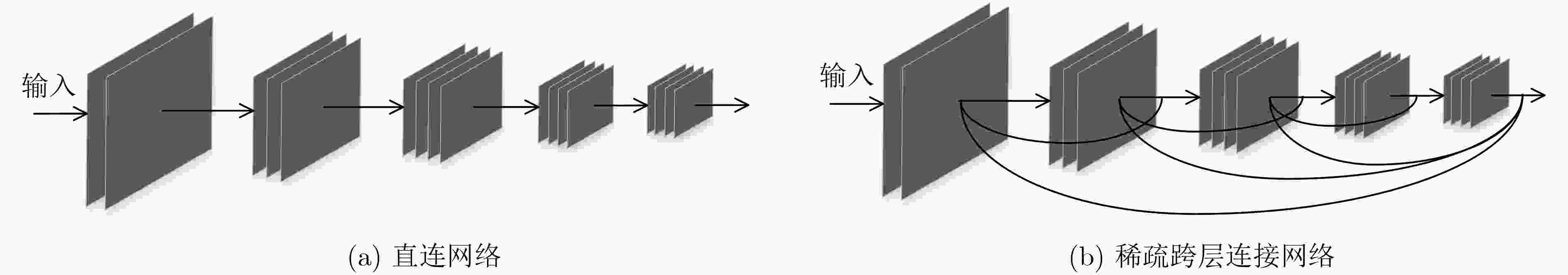
当前的显著性目标检测算法在准确性和高效性两方面不能实现良好的平衡,针对这一问题,该文提出了一种新的平衡准确性以及高效性的显著性目标检测深度卷积网络模型。首先,通过将传统的卷积替换为可分解卷积,大幅减少计算量,提高检测效率。其次,为了更好地利用不同尺度的特征,采用了稀疏跨层连接结构及多尺度融合结构来提高模型检测精度。广泛的评价表明,与现有方法相比,所提的算法在效率和精度上都取得了领先的性能。
Abstract:It is difficult for current salient object detection algorithms to reach a good balance performance between accuracy and efficiency. To solve this problem, a deep convolutional network for saliency object detection with balanced accuracy and high efficiency is produced. First, through replacing the traditional convolution with the decomposed convolution, the computational complexity is greatly reduced and the detection efficiency of the model is improved. Second, in order to make better use of the characteristics of different scales, sparse cross-layer connection structure and multi-scale fusion structure are adopted to improve the detection precision. A wide range of evaluations show that compared with the existing methods, the proposed algorithm achieves the leading performance in efficiency and accuracy.
-
表 1 不同卷积结构对比
结构 参数量(106) 准确率(%) 使用时间(s) 2维卷积 5.16 89.3 0.026 分解卷积 3.75 89.7 0.017 表 2 不同卷积结构对比
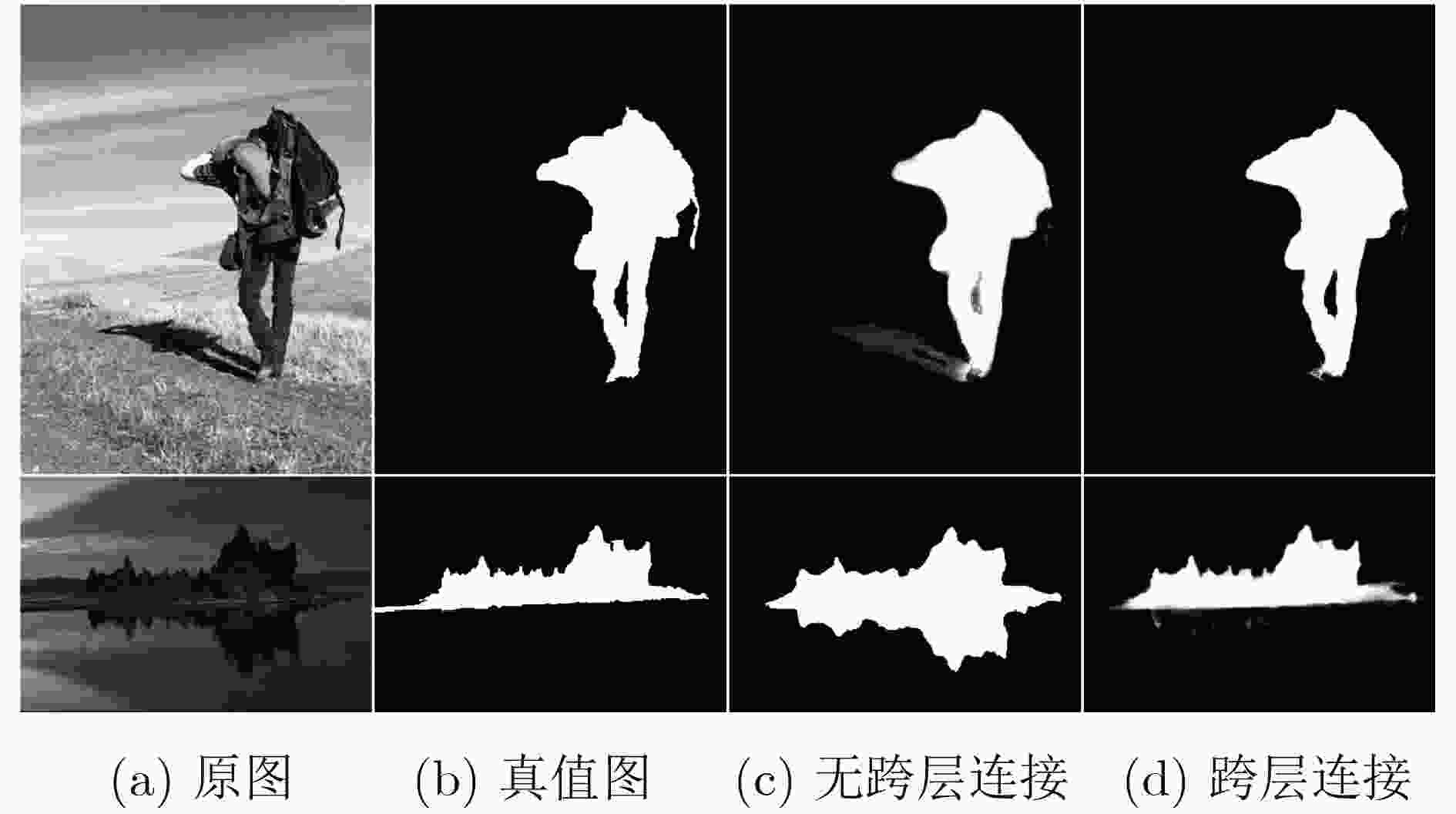
结构 准确率(%) 使用时间(s) 无跨层连接 89.7 0.017 跨层连接 91.7 0.023 表 3 整体网络结构详表
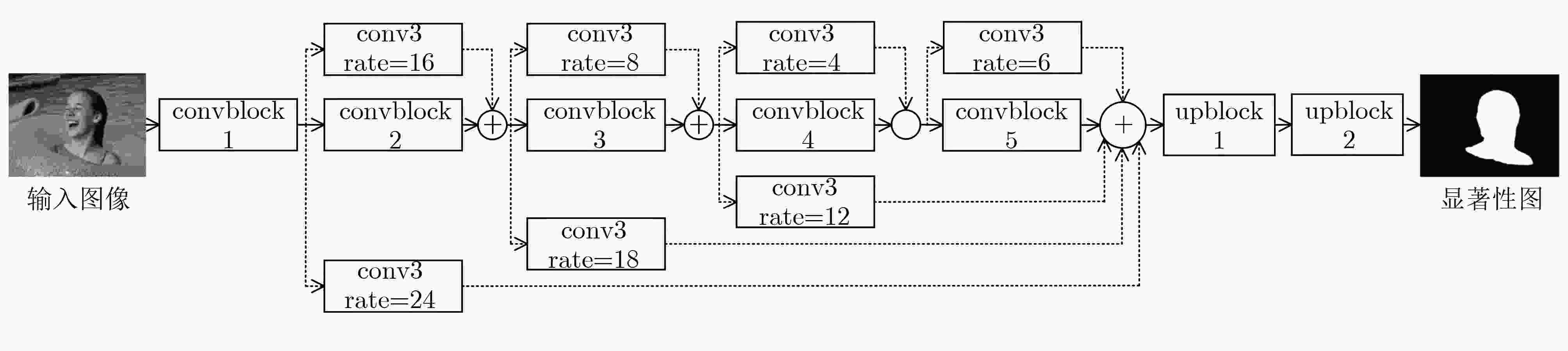
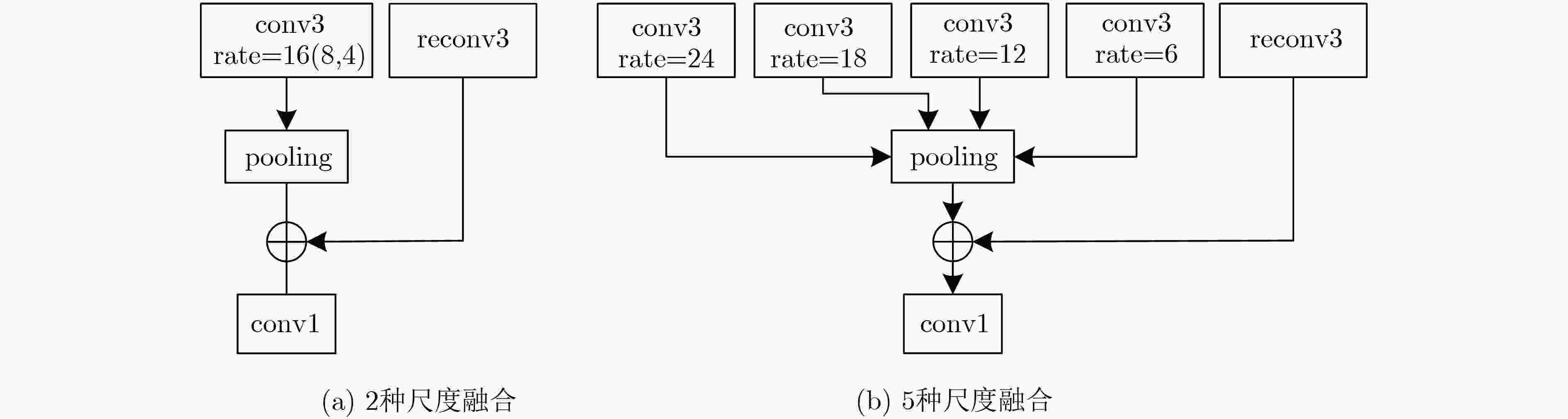
结构 名称 类型 输出尺寸 输出编号 结构 名称 类型 输出尺寸 输出编号 convblock1 reconv$ \times $2 448$ \times $448$ \times $16 1 cross-layer conv3 rate=12 224$ \times $224$ \times $256 $5" $ cross-layer conv3 rate=16 448$ \times $448$ \times $32 $1' $ convblock4 maxpool 下采样 cross-layer conv3 rate=24 448$ \times $448$ \times $256 $1'' $ reconv$ \times $3 56$ \times $56$ \times $128 6 convblock2 maxpool 下采样 concat3 融合 56$ \times $56$ \times $256 $(5'+6) $ reconv$ \times $2 224$ \times $224$ \times $32 2 conv1 降维 56$ \times $56$ \times $128 7 concat1 融合 224$ \times $224$ \times $64 $(1'+2) $ cross-layer conv3 rate=6 56$ \times $56$ \times $256 $7'' $ conv1 降维 224$ \times $224$ \times $32 3 convblock5 maxpool 下采样 cross-layer conv3 rate=8 224$ \times $224$ \times $64 $3′ $ reconv$ \times $3 28$ \times $28$ \times $256 8 cross-layer conv3 rate=18 224$ \times $224$ \times $256 $3" $ concat4 融合 28$ \times $28$ \times $1280 $(1''+3''+5''+7''+8) $ convblock3 maxpool 下采样 conv1 降维 28$ \times $28$ \times $256 9 reconv$ \times $3 112$ \times $112$ \times $64 4 upblock1 deconv 上采样 concat2 融合 112$ \times $112$ \times $128 $(3'+4) $ reconv$ \times $3 112$ \times $112$ \times $64 conv1 降维 112$ \times $112$ \times $64 5 upblock2 deconv 上采样 448$ \times $448$ \times $2 final ross-layer conv3 rate=4 224$ \times $224$ \times $128 $5' $ 表 4 F-measure(F-m)和MAE得分表
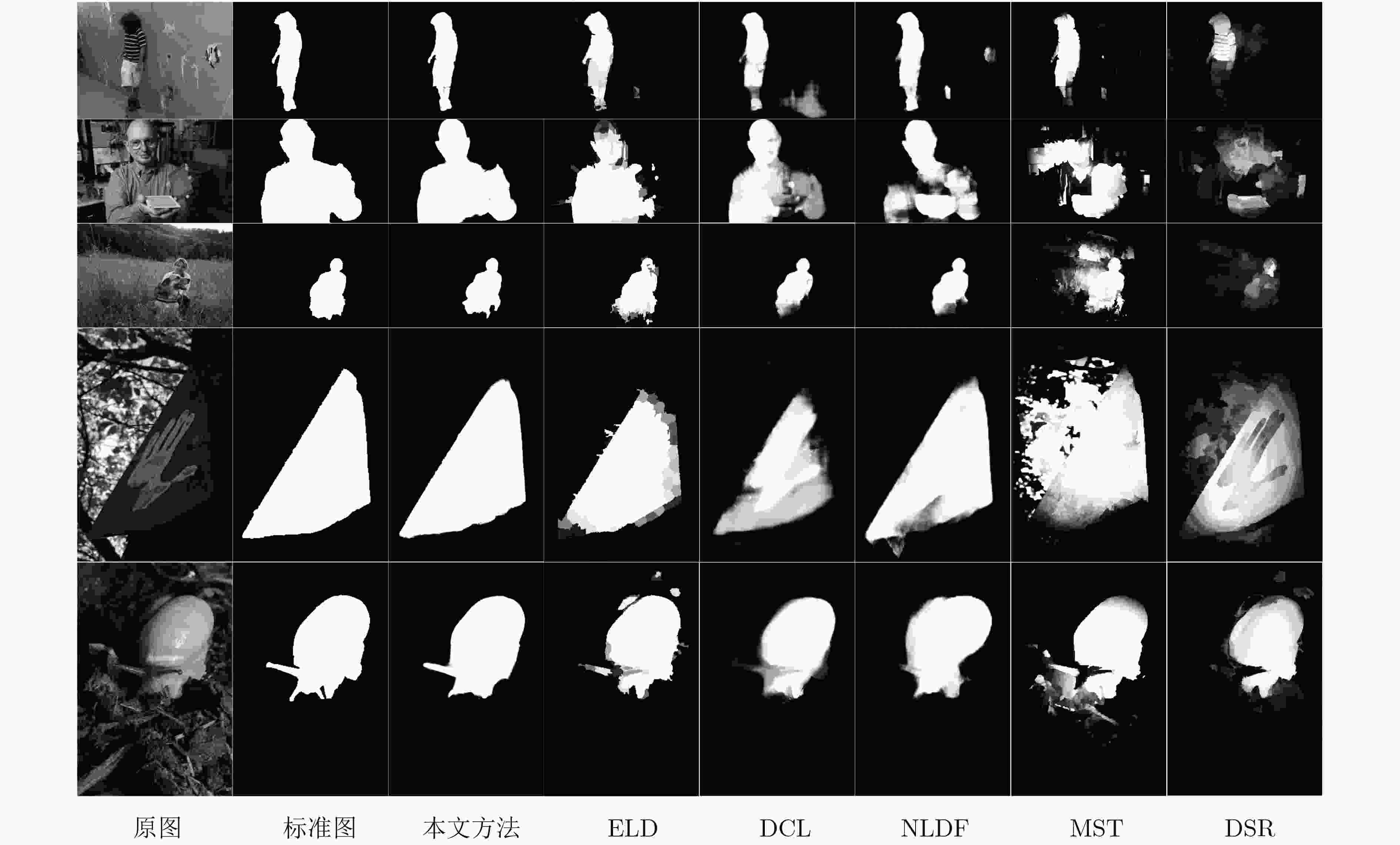
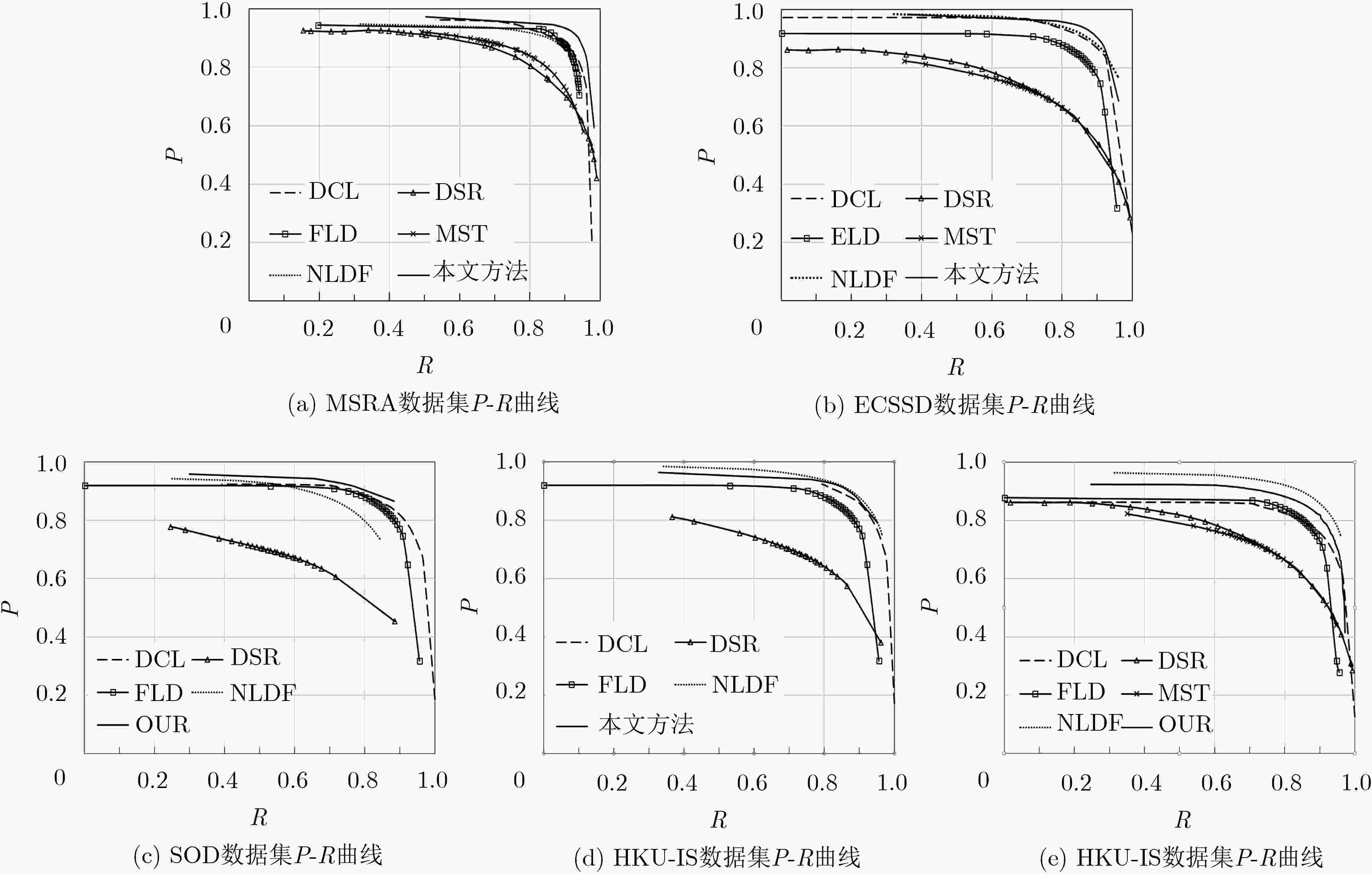
算法 MSRA ECSSD PASCAL-S SOD HKU-IS F-m MAE F-m MAE F-m MAE F-m MAE F-m MAE 本文方法 0.914 0.045 0.893 0.060 0.814 0.113 0.832 0.119 0.893 0.036 DCL 0.905 0.052 0.890 0.088 0.805 0.125 0.820 0.139 0.885 0.072 ELD 0.904 0.062 0.867 0.080 0.771 0.121 0.760 0.154 0.839 0.074 NLDF 0.911 0.048 0.905 0.063 0.831 0.099 0.810 0.143 0.902 0.048 MST 0.839 0.128 0.653 0.171 0.584 0.236 – – – – DSR 0.812 0.119 0.737 0.173 0.646 0.204 0.655 0.234 0.735 0.140 表 5 不同算法处理时间对比(s)
模型 本文方法 DCL ELD NLDF MST DSR 时间 0.023 1.200 0.300 0.080 0.025 13.580 环境 GTX1080 GTX1080 GTX1080 Titan X i7 CPU i7 CPU 尺寸 448$ \times $448 300$ \times $400 400$ \times $300 300$ \times $400 300$ \times $400 400$ \times $300 -
WANG Lijun, LU Huchuan, RUAN Xiang, et al. Deep networks for saliency detection via local estimation and global search[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3183–3192. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298938. LI Guanbin and YU Yizhou. Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5455–5463. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299184. LEE G, TAI Y W, and KIM J. Deep saliency with encoded low level distance map and high level features[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 660–668. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.78. LIU Nian and HAN Junwei. DHSNet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 678–686. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.80. WANG Linzhao, WANG Lijun, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 825–841. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_50. ZHANG Xinsheng, GAO Teng, and GAO Dongdong. A new deep spatial transformer convolutional neural network for image saliency detection[J]. Design Automation for Embedded Systems, 2018, 22(3): 243–256. doi: 10.1007/s10617-018-9209-0 ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Tong, DAI Yuchao, et al. Deep unsupervised saliency detection: A multiple noisy labeling perspective[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9029–9038. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00941. CAO Feilong, LIU Yuehua, and WANG Dianhui. Efficient saliency detection using convolutional neural networks with feature selection[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 456: 34–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.05.006 ZHU Dandan, DAI Lei, LUO Ye, et al. Multi-scale adversarial feature learning for saliency detection[J]. Symmetry, 2018, 10(10): 457–471. doi: 10.3390/sym10100457 ZENG Yu, ZHUGE Yunzhi, LU Huchuan, et al. Multi-source weak supervision for saliency detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6067–6076. SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. 2014, arXiv: 1409.1556. ALVAREZ J and PETERSSON L. DecomposeMe: Simplifying convNets for end-to-end learning[J]. 2016, arXiv: 1606.05426v1. LIU Tie, YUAN Zejian, SUN Jian, et al. Learning to detect a salient object[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(2): 353–367. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.70 YAN Qiong, XU Li, SHI Jianping, et al. Hierarchical saliency detection[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 1155–1162. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.153. LI Yin, HOU Xiaodi, KOCH C, et al. The secrets of salient object segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 280–287. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.43. MOVAHEDI V and ELDER J H. Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 49–56. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2010.5543739. LI Guanbin and YU Yizhou. Deep contrast learning for salient object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 478–487. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.58. LUO Zhiming, MISHRA A, ACHKAR A, et al. Non-local deep features for salient object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6593–6601. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.698. TU W C, HE Shengfeng, YANG Qingxiong, et al. Real-time salient object detection with a minimum spanning tree[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2334–2342. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.256. LI Xiaohui, LU Huchuan, ZHANG Lihe, et al. Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 2976–2983. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.370. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
