Minimal Surface Filter Driven by Curvature Difference
-
摘要:
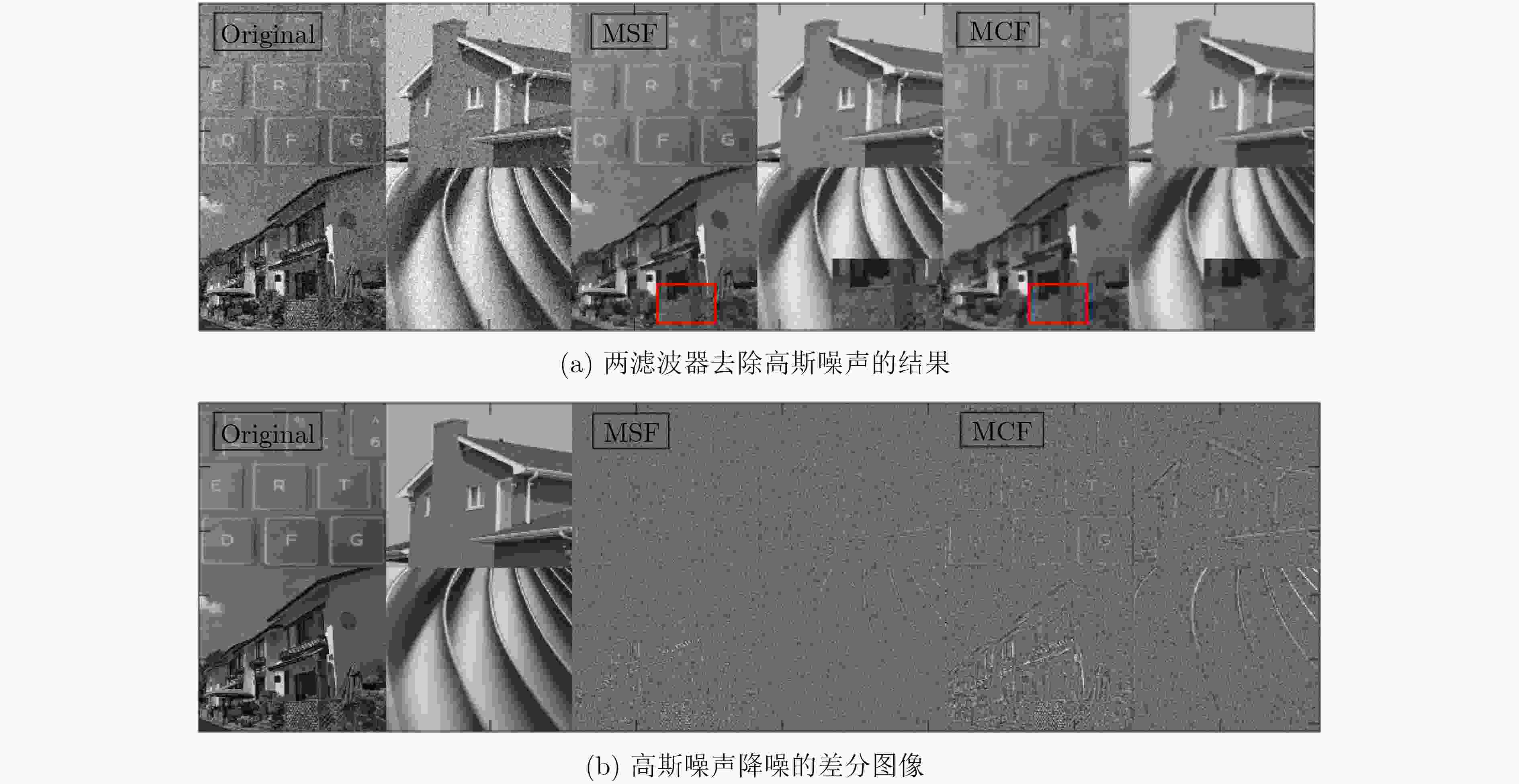
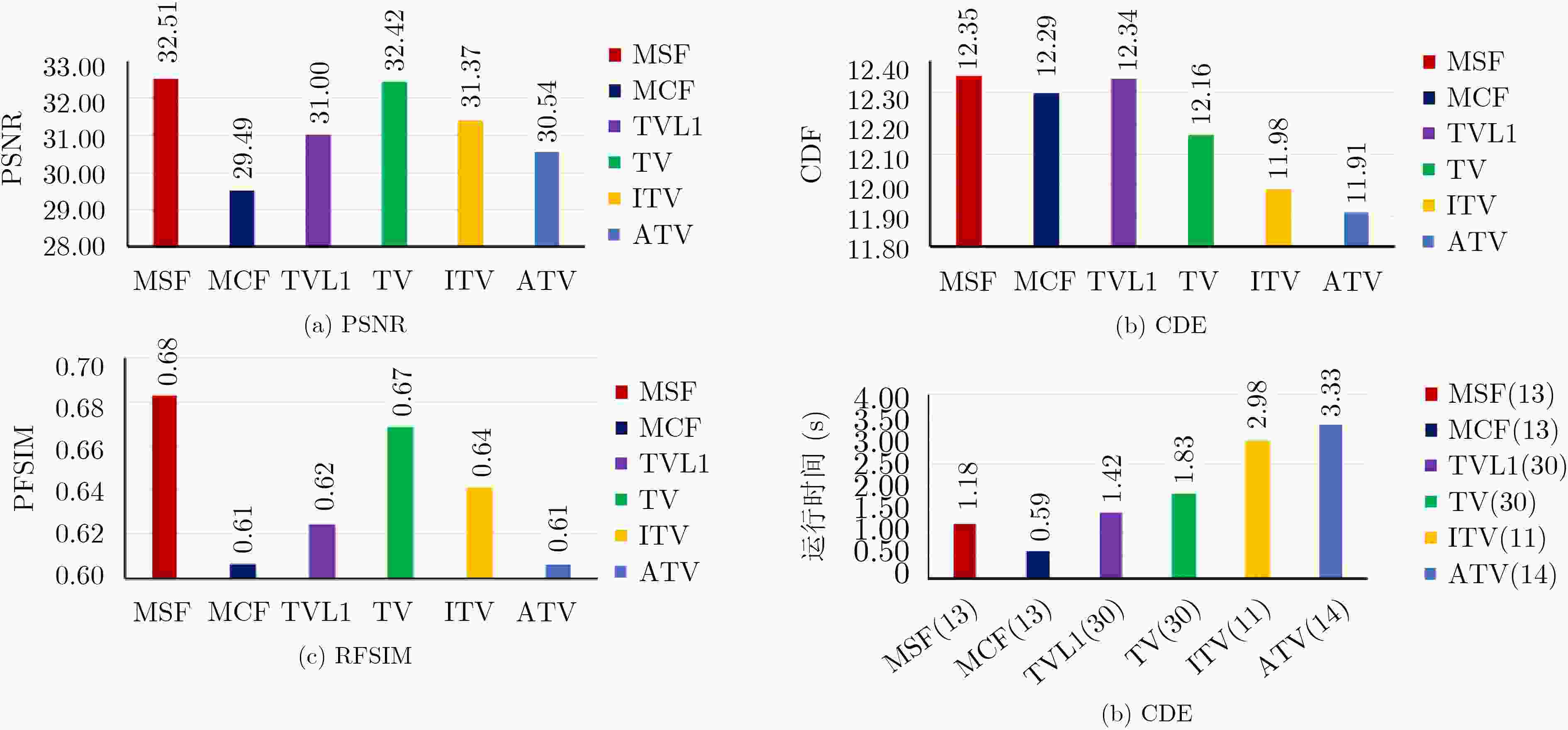
为提高全变分图像降噪模型的降噪性能和边缘保持性能,该文提出一种曲率差分驱动的极小曲面滤波器。首先,在平均曲率滤波器模型基础上,引入自适应曲率差分边缘探测函数,建立曲率差分驱动的极小曲面滤波器模型;接着,从微分几何理论角度,阐述该能量泛函模型的物理意义和平均曲率能量减小方法;最后,在离散的图像域,通过迭代的方式使图像每个像素邻域内的曲面向极小曲面迭代进化,实现能量泛函的平均曲率能量极小化,从而能量泛函的总能量也完成极小化。实验表明,该滤波器不仅能去除高斯噪声、椒盐噪声,还能去除这两类噪声构成的混合噪声,其降噪性能和边缘保持性能优于同类型的其他5种全变分算法。
Abstract:To improve performance of denoising and edge preservation of the total variational image denoising model, a curvature difference driven minimal surface filter is proposed. Firstly, the presented filter model is constructed by adding an adaptive edge detection function of curvature difference to the mean curvature filter model. After that, from the perspective of differential geometry theory, the physical meaning of the energy functional model and the method of reducing the average curvature energy are elaborated. Finally, in the discrete image domain, the surface in the neighborhood of each pixel of the image is iteratively evolved to the minimal surface to minimize the average curvature energy of the energy functional, so that the total energy of the energy functional is also minimized. Experiments show that the filter can not only remove Gauss noise and salt and pepper noise, but also remove the mixed noise composed of these two kinds of noise. Its performance of noise reduction and edge preservation is better than the other five total variational algorithms of the same kind.
-
Key words:
- Image denoising /
- Filter /
- Energy functional /
- Mean curvature /
- Minimal surface
-
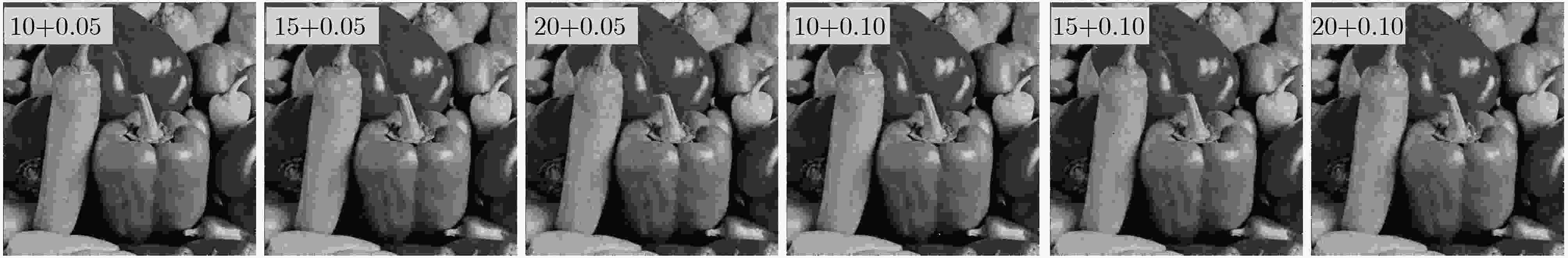
表 1 降噪图像的评价指标数据
噪声类型 图像 滤波器 噪声方差噪声密度 迭代次数 PSNR.N PSNR.D CDE RFSIM 高斯噪声 Lena MSF 10 10 28.1111 32.5290 12.3499 0.6873 20 20 22.1472 28.8819 12.3575 0.5065 MCF 10 10 28.1111 31.2486 12.3128 0.6063 20 20 22.1472 28.7087 12.3020 0.4644 House MSF 5 7 34.1560 35.9549 11.0543 0.6838 10 10 28.1072 32.4532 11.0582 0.5043 20 20 22.1129 28.5565 11.0600 0.3117 MCF 5 7 34.1560 33.1901 11.0436 0.5879 10 10 28.1072 31.1816 11.0491 0.4750 20 20 22.1129 28.3753 11.0487 0.3315 椒盐噪声 peppers MSF 0.05 4 18.2659 34.3401 12.3245 0.8842 0.10 9 15.3176 32.0921 12.3229 0.8271 MCF 0.05 4 18.2659 30.1227 12.3089 0.7940 0.10 9 15.3176 30.5087 12.2877 0.7083 -
RUDIN L I, OSHER S, and FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1/4): 259–268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F DING Meng, HUANG Tingzhu, WANG Si, et al. Total variation with overlapping group sparsity for deblurring images under Cauchy noise[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 341: 128–147. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2018.08.014 SHEN Zhengwei and CHENG Lishuang. Convex composite wavelet frame and total variation-based image deblurring using nonconvex penalty functions[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2017, 26(5): 053005. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.26.5.053005 郭从洲, 秦志远, 时文俊. 基于能量泛函和视觉特性的全变分图像降噪模型[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2014, 19(9): 1282–1287. doi: 10.11834/jig.20140904GUO Congzhou, QIN Zhiyuan, and SHI Wenjun. TV image denoising model based on energy functionals and HVS[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2014, 19(9): 1282–1287. doi: 10.11834/jig.20140904 LIU Zexian, LIU Hongwei, and WANG Xiping. Accelerated augmented Lagrangian method for total variation minimization[J]. Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2019, 38(2): 50–64. doi: 10.1007/s40314-019-0787-7 GAO Tianling, WANG Xiaofei, LIU Qiang, et al. A fixed-point algorithm for second-order total variation models in image denoising[J]. Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2019, 38(1): 8–22. doi: 10.1007/s40314-019-0763-2 ZOU Jian, SHEN Marui, ZHANG Ya, et al. Total variation denoising with non-convex regularizers[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 4422–4431. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2888944 BEN SAID A, HADJIDJ R, and FOUFOU S. Total variation for image denoising based on a novel smart edge detector: An application to medical images[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2019, 61(1): 106–121. doi: 10.1007/s10851-018-0829-6 LI Mingqiang, HAN Congying, WANG Ruxin, et al. Shrinking gradient descent algorithms for total variation regularized image denoising[J]. Computational Optimization and Applications, 2017, 68(3): 643–660. doi: 10.1007/s10589-017-9931-8 王宇, 汤心溢, 罗易雪, 等. 自适应Split Bregman迭代的红外图像降噪算法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2014, 33(5): 546–551. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2014.00546WANG Yu, TANG Xinyi, LUO Yixue, et al. IR image denoising algorithm based on adaptive split bregman method[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2014, 33(5): 546–551. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1010.2014.00546 FIRSOV D and LUI S H. Domain decomposition methods in image denoising using Gaussian curvature[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 193(2): 460–473. doi: 10.1016/j.cam.2005.05.032 JIDESH P and GEORGE S. Gauss curvature-driven image inpainting for image reconstruction[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2014, 37(1): 122–133. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2012.751332 ZHU Wei and CHAN T. Image denoising using mean curvature of image surface[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2012, 5(1): 1–32. doi: 10.1137/110822268 GONG Yuanhao. Spectrally regularized surfaces[D]. [Ph.D dissertation], ETH-Zürich, 2015: 127–165. doi: 10.3929/ethz-a-010438292. GONG Yuanhao and SBALZARINI I F. Curvature filters efficiently reduce certain variational energies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1786–1798. doi: 10.1109/tip.2017.2658954 BAI Yunjiao, ZHANG Quan, HONG Shangguan, et al. Patch similarity modulus and difference curvature based fourth-order partial differential equation for image denoising[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: 636295. doi: 10.1155/2015/636295 YIN Xuehui and ZHOU Shangbo. Image structure-preserving denoising based on difference curvature driven fractional nonlinear diffusion[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: 930984. doi: 10.1155/2015/930984 DONOHO D L and JOHNSTONE J M. Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage[J]. Biometrika, 1994, 81(3): 425–455. doi: 10.1093/biomet/81.3.425 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
