Correntropy-based Fusion Extreme Learning Machine forRepresentation Level Feature Fusion and Classification
-
摘要:
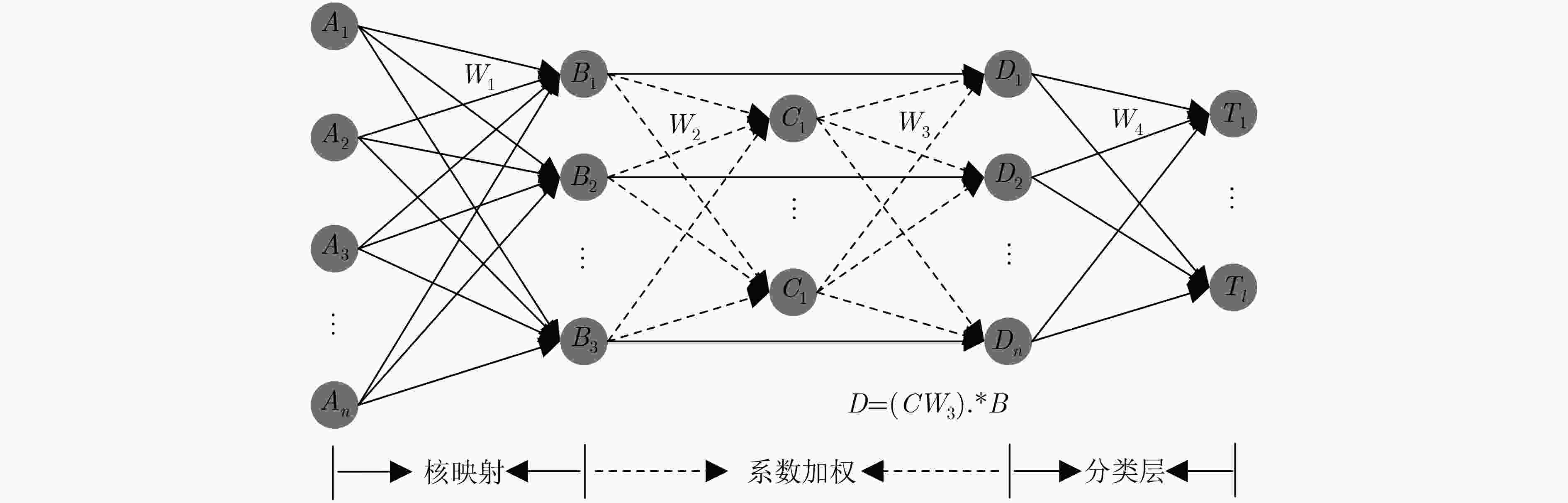
在极限学习机(ELM)网络结构和训练模式的基础上,该文提出了相关熵融合极限学习机(CF-ELM)。针对多数分类方法中表示级特征融合不充分的问题,该文将核映射与系数加权相结合,提出了能够有效融合表示级特征的融合极限学习机(F-ELM)。在此基础上,用相关熵损失函数替代均方误差(MSE)损失函数,推导出用于训练F-ELM各层权重矩阵的相关熵循环更新公式,以增强其分类能力与鲁棒性。为了检验方法的可行性,该文分别在数据库Caltech 101, MSRC和15 Scene上进行实验。实验结果证明,该文所提CF-ELM能够在原有基础上进一步融合表示级特征,从而提高分类正确率。
Abstract:Based on the network structure and training methods of the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM), Correntropy-based Fusion Extreme Learning Machine (CF-ELM) is proposed. Considering the problem that the fusion of representation level features is insufficient in most classification methods, the kernel mapping and coefficient weighting are combined to propose a Fusion Extreme Learning Machine (F-ELM), which can effectively fuse the representation level features. On this basis, the Mean Square Error (MSE) loss function is replaced by the correntropy-based loss function. A correntropy-based cycle update formula for training the weight matrices of the F-ELM is derived to enhance classification ability and robustness. Extensive experiments are performed on Caltech 101, MSRC and 15 Scene datasets respectively. The experimental results show that CF-ELM can further fuse the representation level features to improve the classification accuracy.
-
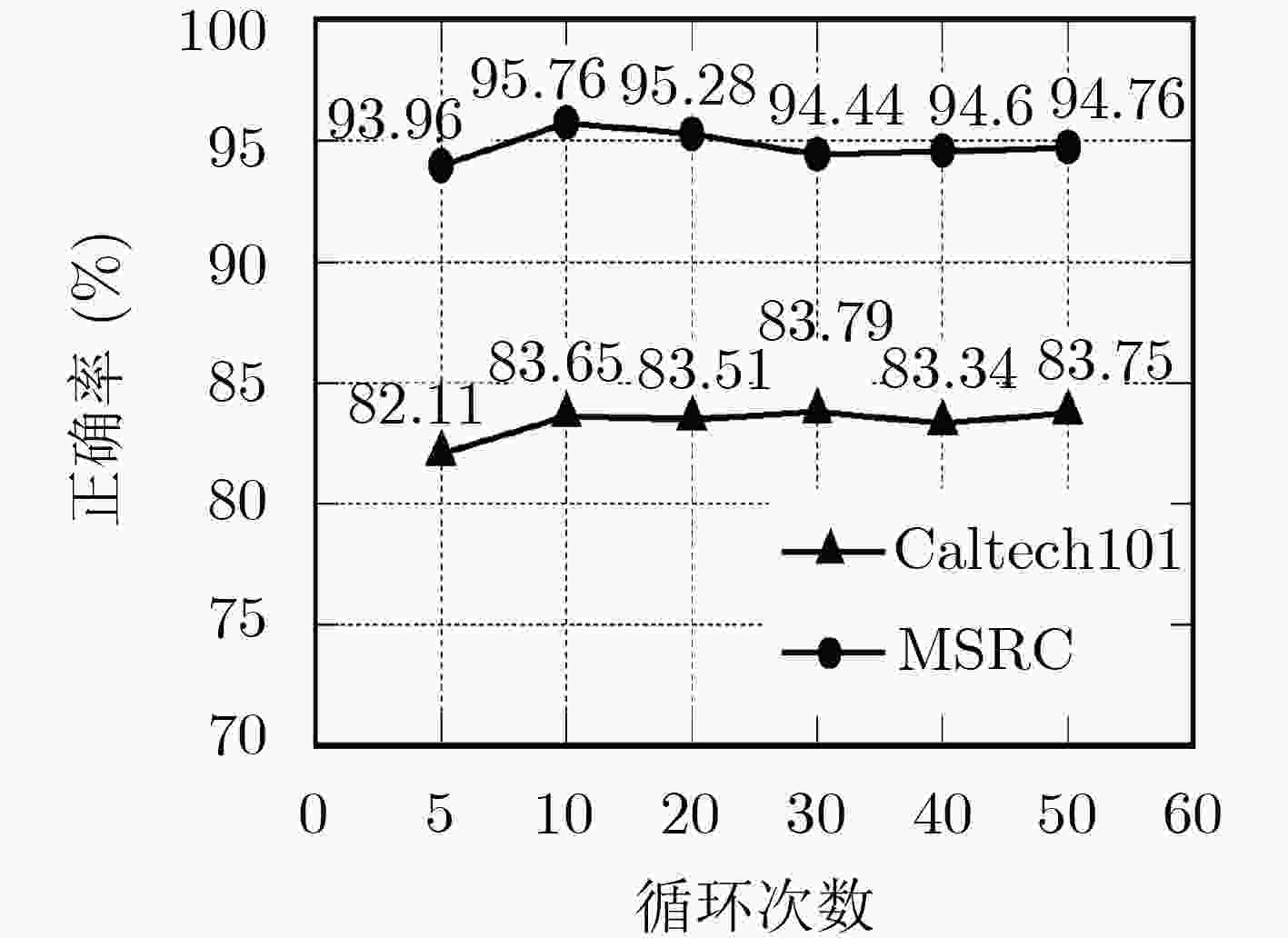
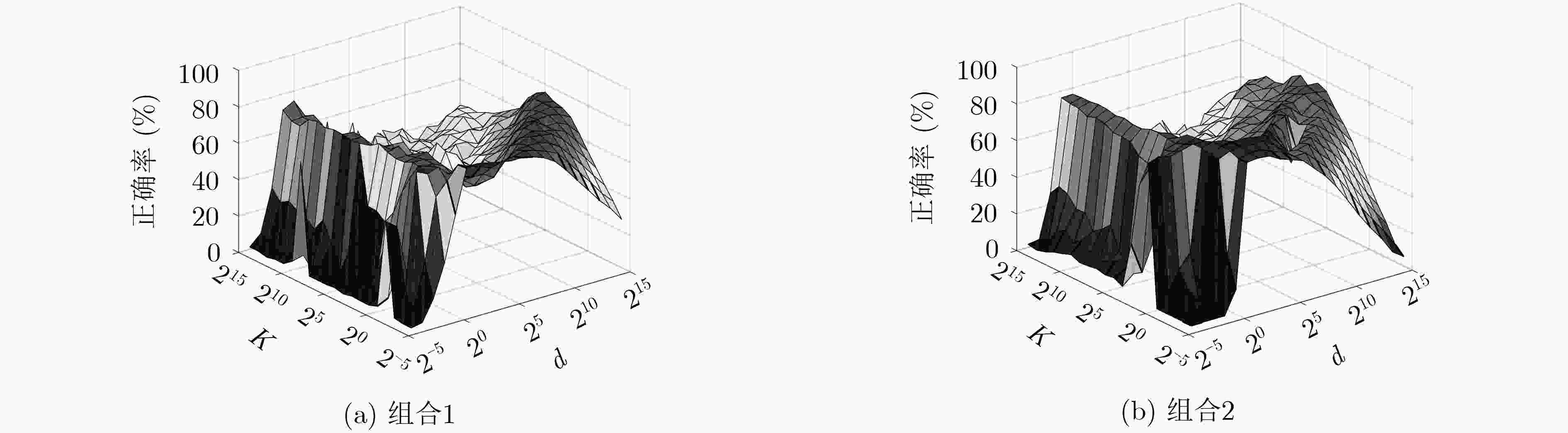
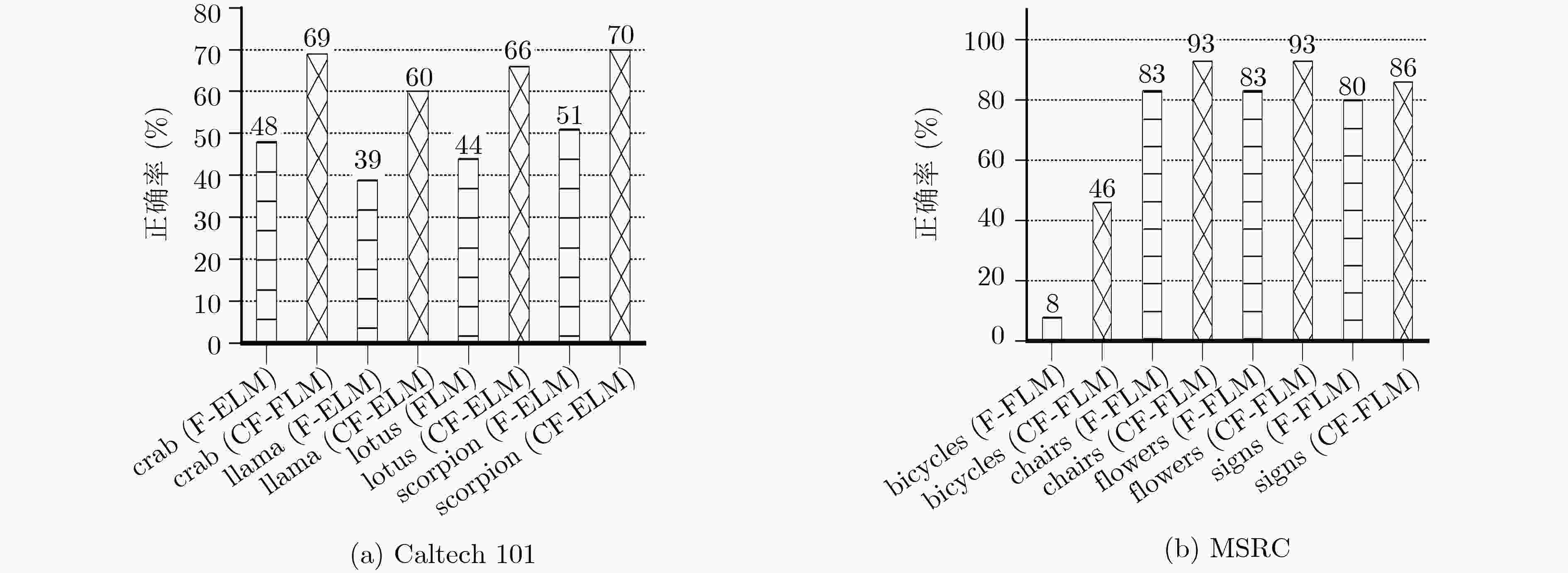
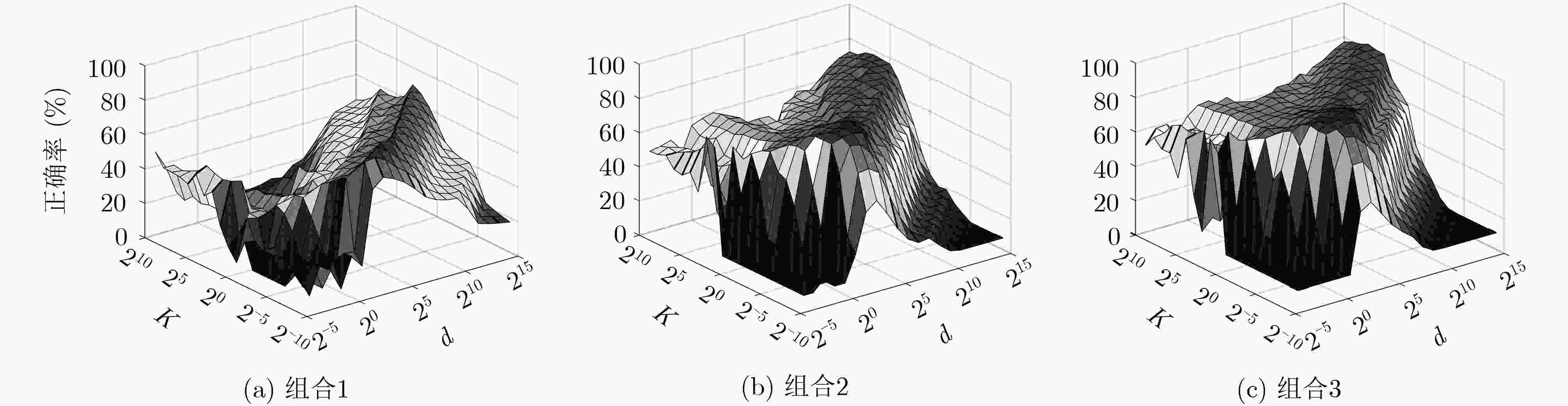
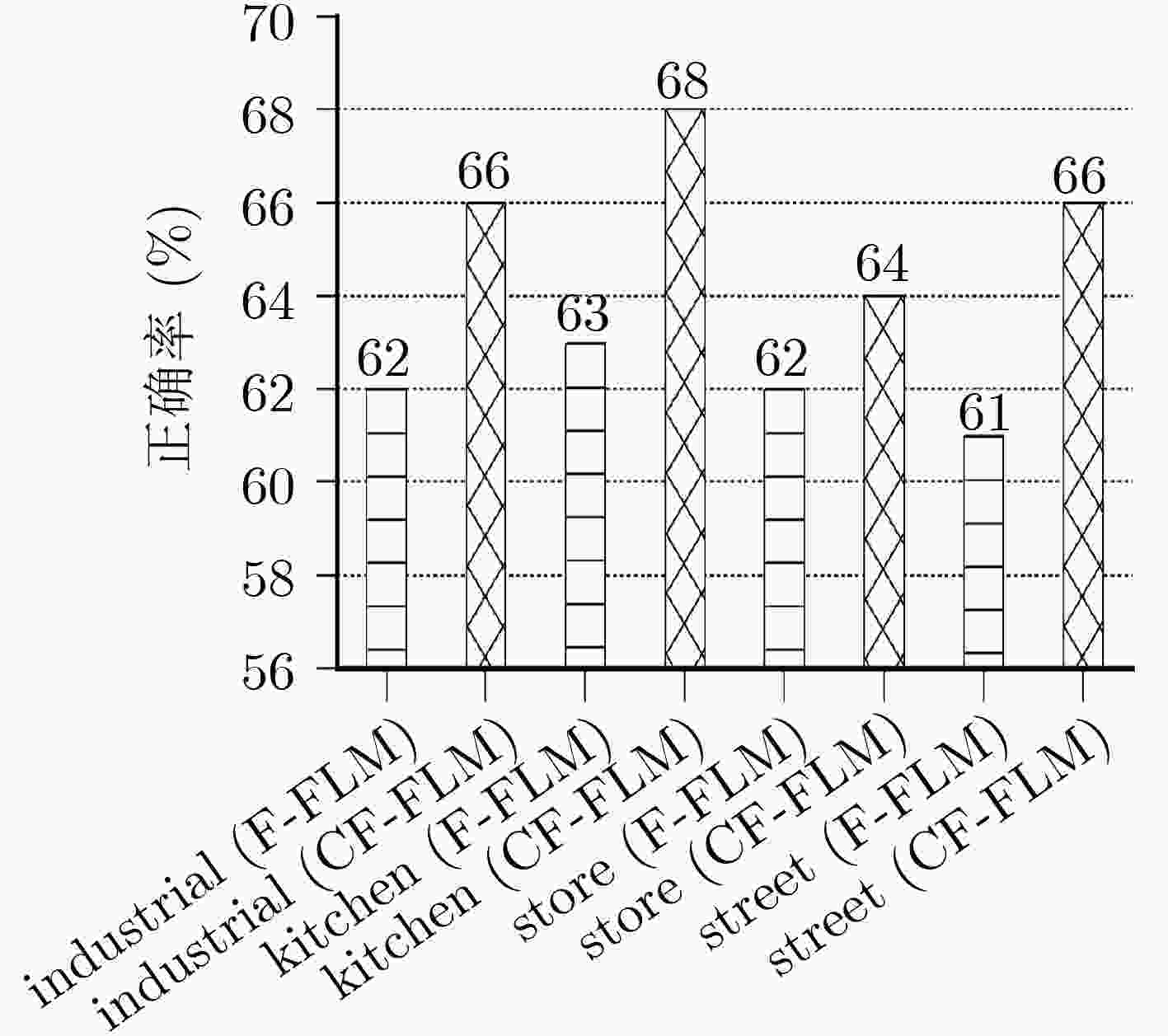
表 1 Caltech 101与MSRC的正确率与训练时间
组合方法 SVM KELM F-ELM CF-ELM 组合1 组合2 组合3 组合1 组合2 组合3 组合1 组合2 组合3 组合1 组合2 组合3 Caltech 101 (%) 72.04 77.93 – 79.43 78.84 – 80.31 80.19 – 80.59 83.65 – 训练时间(s) 862.16 540.30 – 860.37 538.56 – 861.76 539.77 – 902.13 569.80 – MSRC (%) 90.26 88.57 94.13 91.42 90.42 91.74 91.74 90.58 93.49 90.95 92.06 95.76 训练时间(s) 79.59 17.11 17.11 79.51 17.01 17.01 79.54 17.04 17.04 80.68 18.20 18.20 表 2 Caltech 101的结果比较
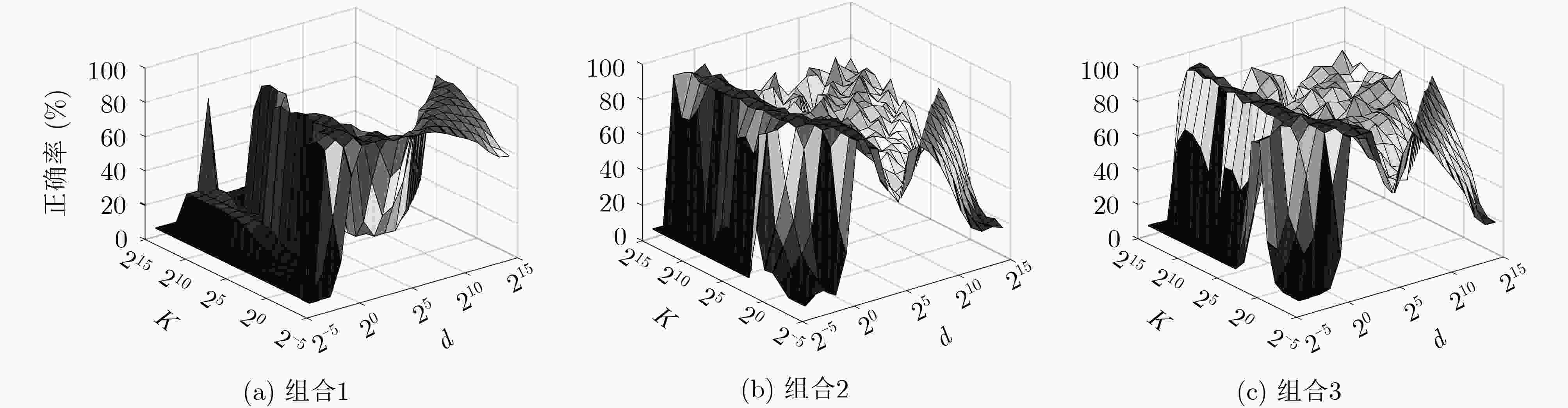
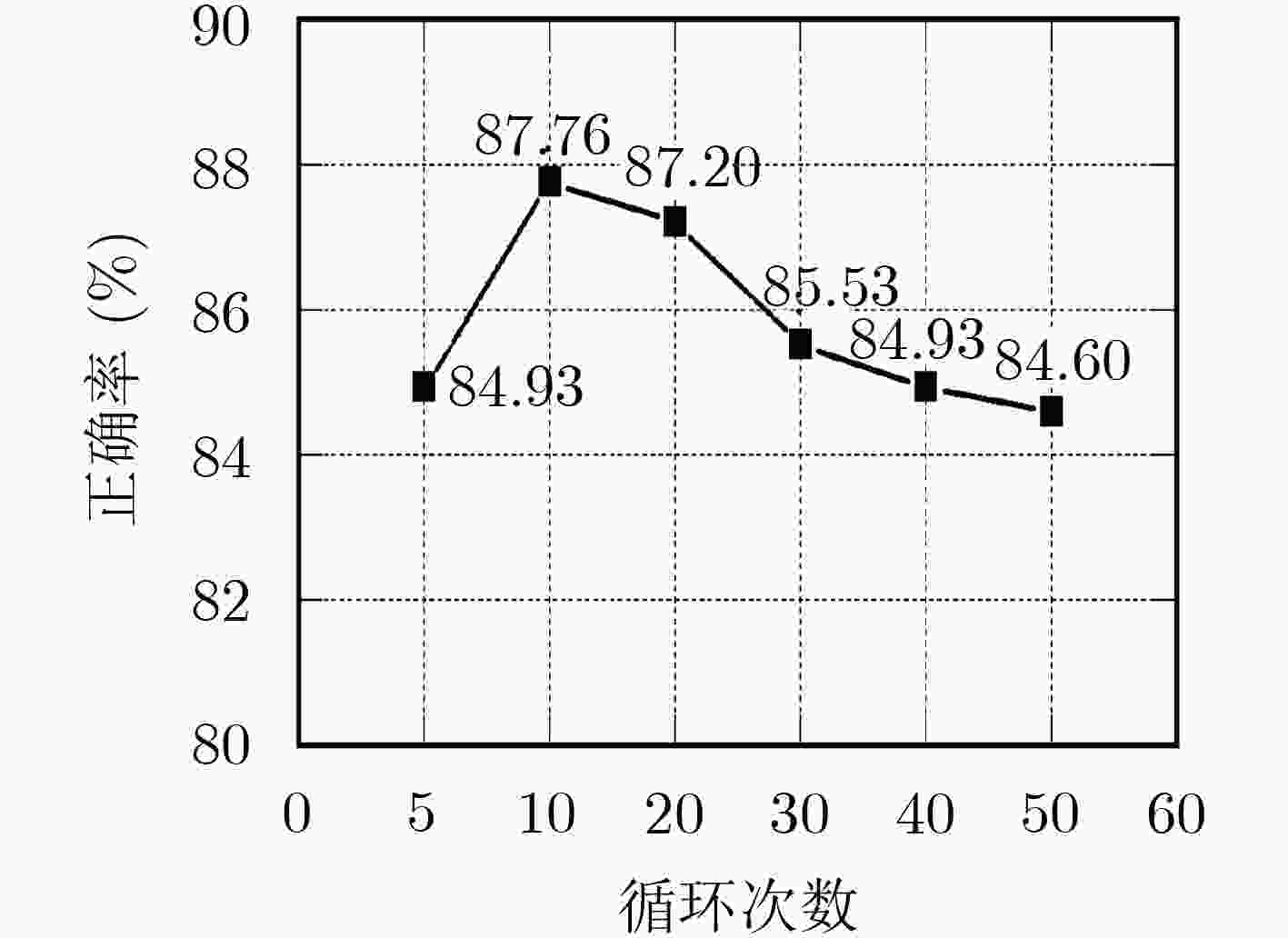
表 3 15 Scene的正确率与训练时间
组合方法 SVM KELM F-ELM CF-ELM 组合1 组合2 组合4 组合1 组合2 组合4 组合1 组合2 组合4 组合1 组合2 组合4 15 Scene(%) 74.34 77.92 86.46 72.00 80.73 83.53 77.20 82.06 84.33 79.00 83.06 87.76 训练时间(s) 347.44 106.25 106.25 347.12 106.11 106.11 347.37 106.41 106.41 367.50 120.10 120.10 -
HUANG Guangbin, ZHU Qinyu, and SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2006, 70(1/3): 489–501. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126 HUANG Guangbin, ZHOU Hongming, DING Xiaojian, et al. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B, 2012, 42(2): 513–529. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2168604 KASUN L L C, ZHOU Hongming, HUANG Guangbin, et al. Representational learning with extreme learning machine for big data[J]. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2013, 28(6): 31–34. XING Hongjie and WANG Xinmei. Training extreme learning machine via regularized correntropy criterion[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2013, 23(7/8): 1977–1986. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-1184-y CHEN Liangjun, HONEINE P, QU Hua, et al. Correntropy-based robust multilayer extreme learning machines[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 84: 357–370. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.07.011 LUO Xiong, SUN Jiankun, WANG Long, et al. Short-term wind speed forecasting via stacked extreme learning machine with generalized correntropy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(11): 4963–4971. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2854549 HAN Honggui, WANG Lidan, and QIAO Junfei. Hierarchical extreme learning machine for feedforward neural network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 128: 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.01.057 LI Qing, PENG Qiang, CHEN Junzhou, et al. Improving image classification accuracy with ELM and CSIFT[J]. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2019, 21(5): 26–34. doi: 10.1109/MCSE.2018.108164708 LAZEBNIK S, SCHMID C, and PONCE J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories[C]. 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2006: 2169–2178. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2006.68. JÉGOU H, DOUZE M, SCHMID C, et al. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 3304–3311. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540039. SÁNCHEZ J, PERRONNIN F, MENSINK T, et al. Image classification with the fisher vector: Theory and practice[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 105(3): 222–245. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0636-x 李雅倩, 吴超, 李海滨, 等. 局部位置特征与全局轮廓特征相结合的图像分类方法[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(7): 1726–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.026LI Yaqian, WU Chao, LI Haibin, et al. Image classification method combining local position feature with global contour feature[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(7): 1726–1731. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.07.026 AHMED K T, IRTAZA A, and IQBAL M A. Fusion of local and global features for effective image extraction[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2017, 47(2): 526–543. doi: 10.1007/s10489-017-0916-1 MANSOURIAN L, ABDULLAH M T, ABDULLAH L N, et al. An effective fusion model for image retrieval[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(13): 16131–16154. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-5192-x ZOU Jinyi, LI Wei, CHEN Chen, et al. Scene classification using local and global features with collaborative representation fusion[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 348: 209–226. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.02.021 KONIUSZ P, YAN Fei, GOSSELIN P H, et al. Higher-order occurrence pooling for bags-of-words: Visual concept detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 313–326. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2545667 WANG Jinjun, YANG Jianchao, YU Kai, et al. Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 3360–3367. ZHU Qihai, WANG Zhezheng, MAO Xiaojiao, et al. Spatial locality-preserving feature coding for image classification[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2017, 47(1): 148–157. doi: 10.1007/s10489-016-0887-7 XIONG Wei, ZHANG Lefei, DU Bo, et al. Combining local and global: Rich and robust feature pooling for visual recognition[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 62: 225–235. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.08.006 GUI Jie, LIU Tongliang, TAO Dacheng, et al. Representative vector machines: A unified framework for classical classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(8): 1877–1888. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2457234 GOH H, THOME N, CORD M, et al. Learning deep hierarchical visual feature coding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(12): 2212–2225. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2307532 肖文华, 包卫东, 陈立栋, 等. 一种用于图像分类的语义增强线性编码方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 791–797. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140743XIAO Wenhua, BAO Weidong, CHEN Lidong, et al. A semantic enhanced linear coding for image classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 791–797. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140743 LI Lijia, SU Hao, LIM Y, et al. Object bank: An object-level image representation for high-level visual recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 107(1): 20–39. doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0660-x SONG Xinhang, JIANG Shuqiang, and HERRANZ L. Multi-scale multi-feature context modeling for scene recognition in the semantic manifold[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2721–2735. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2686017 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
