Research on D2D Multi-multiplex Communication Resource Blocks Allocation Algorithm Based on Unbalanced Solution
-
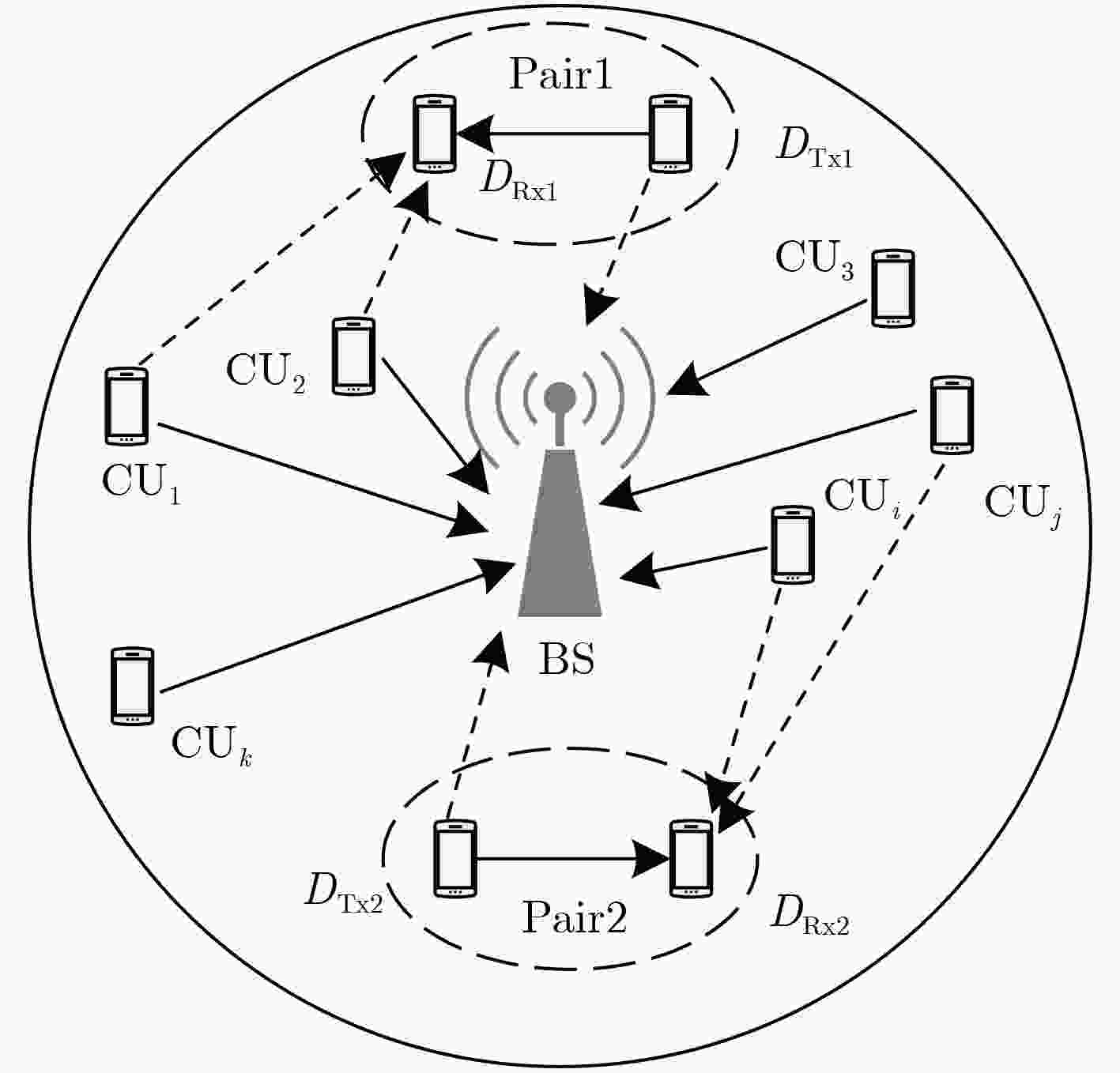
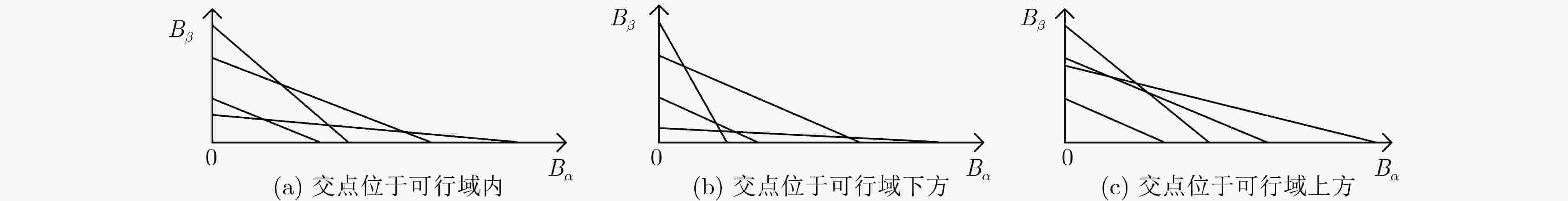
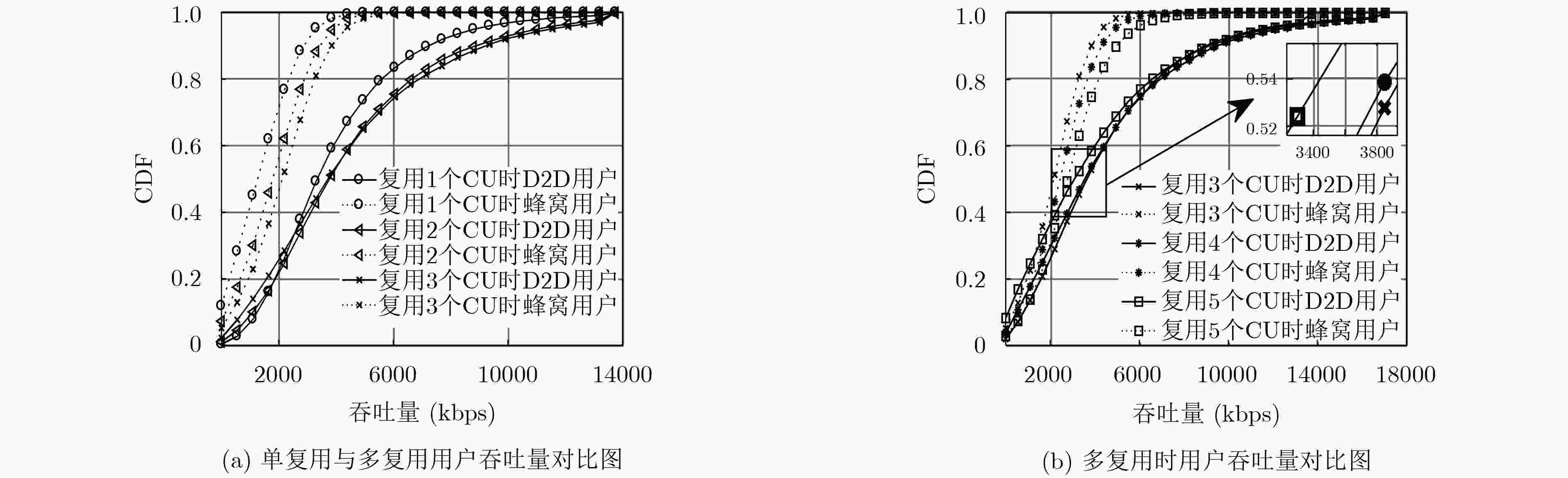
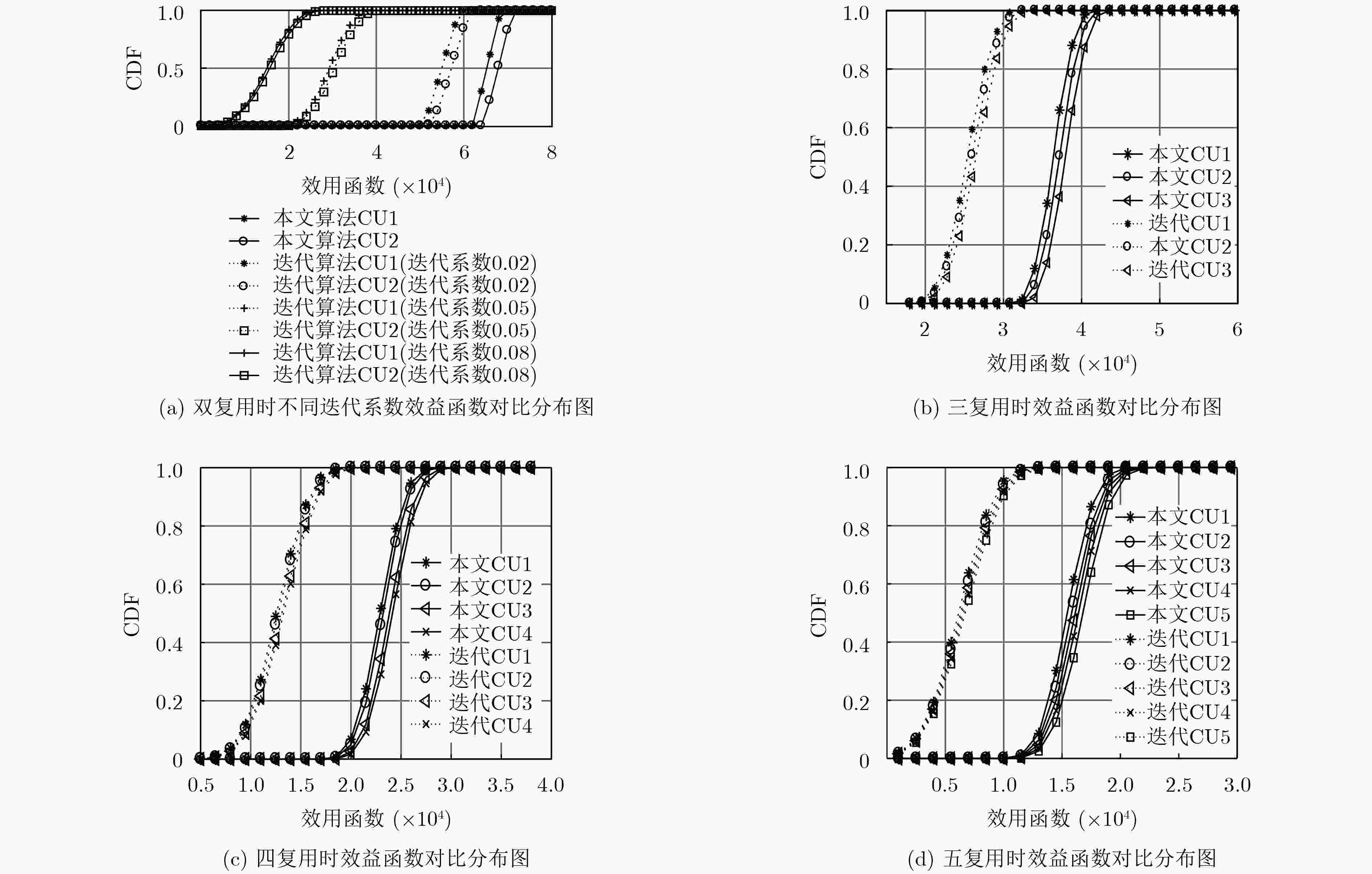
摘要: 针对小区内D2D多复用的通信资源块分配问题,该文以一个D2D用户分别复用2个和3个蜂窝为基础,提出基于非均衡求解的D2D多复用模式下的资源块分配方案。利用博弈论将资源块划分问题转化为求解被复用蜂窝用户收益联合最大问题。当纳什均衡解不存在时,分析目标函数特性,在可行域内求解“最优解”,保证对不均衡解处理的最优性;对于均衡解存在的情况,将其取整后作为资源分配方案依据,保持其最优性。通过理论分析及仿真实验表明该算法可以提升系统吞吐率,提高小区通信性能。Abstract: In order to solve the problem of the Device to Device (D2D) multi-multiplex communication resource blocks allocation in a cell, the resource blocks allocation scheme about D2D multi-multiplex mode based on non-equilibrium solution is proposed after analyzing a D2D user to multiplex two and three cells respectively. The problem of resource blocks partitioning is transformed into the problem of solving the joint revenue maximum value of the multiplexed cellular user by using game theory. When the Nash equilibrium solution does not exist, the objective function is analyzed, the "optimal solution" is solved in the feasible domain and the optimality of unbalanced solution processing is guaranteed. When the equilibrium solution exists, it is rounded up and used as the basis of the resource allocation scheme to maintain its optimality. The theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the proposed algorithm enhances significantly the system performance and sum rate.
-
表 1 多复用资源分配策略
算法1 资源分配策略 (1)输入:
${N_0},{G_{i,j}},x,y,{z_1},{z_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{z_n},t,a,b,$${B_1},{B_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{B_n},{B_{\min }},{B_{\max }}$;(2)开始:计算${R_1},{R_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{R_n}$, ${U_1},{U_2}, ·\!·\!· ,{U_n}$,
${B_{10}},{B_{20}}, ·\!·\!· ,{B_{n0}}$;(3)资源分配 if ${\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n{B_{i0}}} < {B_{\min}}$ for $i=1$ to $i = n$
${B_i}_1 = \left\lceil {({B_{\min} } + (n - 1){B_i}_0 - {\sum\nolimits_{j = 1 \atop j \ne i }^n{B_{j0} } } /n} \right\rceil $;end for if $ {\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n{B_{i0}}} > {B_{\max}}$
for $i=1$ to $i = n$${B_i}_1 = \left\lfloor {({B_{\max} } + (n - 1){B_i}_0 - {\sum\nolimits_{j = 1 \atop j \ne i }^n{B_{j0} } } /n} \right\rfloor$ end for else for $i=1$ to $i = n$ ${B_i}_1 = \left[ { {B_{i0}} + 0.5} \right] $; end for end (4)输出:${B_{i1}},{B_{i2}}, ·\!·\!· ,{B_{in}}$ 表 2 仿真参数表
参数 取值 小区半径 1000 m D2D对最大通信范围 50 m 小区基站带宽 20 MHz CU的发射功率 25 dBm D2D用户的发射功率 0~25 dBm D2D对数量 10 CU数量 50 ${B_{\min}}$ 0.06 MHz ${B_{\max}}$ 0.8 MHz ${N_0}$ –117 dBm/Hz $\tau ,y,{z_1},{z_2}, ·\!·\!·,{z_n}$ 1 x 0.02 a,b 0.8 用户间路径损耗 $140 + 40\lg({d_{ij}}[{\rm{km}}])$ 基站与用户间路径损耗 $128 + 37.6\lg({d_{ij}}[{\rm{km}}])$ 阴影衰落 标准差为8的对数正态分布 多径衰落 均值为1的指数分布 用户噪声系数 9 dB 基站噪声系数 5 dB -
钱志鸿, 王雪. 面向5G通信网的D2D技术综述[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(7): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016129QIAN Zhihong and WANG Xue. Reviews of D2D technology for 5G communication networks[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(7): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016129 DOPPLER K, RINNE M, WIJTING C, et al. Device-to-Device communication as an underlay to LTE-advanced networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2009, 47(12): 42–49. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2009.5350367 KAUFMAN B and AAZHANG B. Cellular networks with an overlaid device to device network[C]. The 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2008: 1537–1541. IMRAN A, ZOHA A, and ABU-DAYYA A. Challenges in 5G: How to empower SON with big data for enabling 5G[J]. IEEE Network, 2014, 28(6): 27–33. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2014.6963801 IMT-2020(5G) Promotion Group. 5G vision and requirements, white paper[EB/OL]. http://www.IMT-2020.cn, 2014. YANG Lianxin, WU Dan, SHI Hongkui, et al. Social-aware joint mode selection and link allocation for Device-to-Device communication underlaying cellular networks[J]. China Communications, 2018, 15(8): 92–107. doi: 10.1109/CC.2018.8438276 HUANG Hongcheng, XIANG Wei, TAO Yang, et al. Relay-assisted D2D transmission for mobile health applications[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4417. doi: 10.3390/s18124417 冯大权. D2D通信无线资源分配研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2015.FENG Daquan. Resource allocation for D2D communicatios in cellular networks[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015. 代海波, 陆忞, 黄永明, 等. D2D通信系统中节能功率控制算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(4): 997–1001. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160553DAI Haibo, LU Wen, HUANG Yongming, et al. Energy-efficient power control algorithm for D2D communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(4): 997–1001. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160553 DOMINIC S and JACOB L. Distributed resource allocation for D2D communications underlaying cellular networks in time-varying environment[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(2): 388–391. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2771778 HUANG Jun, YIN Ying, ZHAO Yanxiao, et al. A game-theoretic resource allocation approach for intercell Device-to-Device communications in cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2016, 4(4): 475–486. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2014.2384372 JIANG Yanxiang, LIU Qiang, ZHENG Fuchun, et al. Energy-efficient joint resource allocation and power control for D2D communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(8): 6119–6127. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2472995 YANG Kai, STEVEN M, XING Chengwen, et al. Energy-efficient power control for device-to-device communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3208–3220. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.26240785 NIYATO D and HOSSAIN E. A game-theoretic approach to competitive spectrum sharing in cognitive radio networks[C]. 2007 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Hong Kong, China, 2007: 16–20. 钱志鸿, 阎双叶, 田春生, 等. LTE-A网络中D2D通信的资源分配算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180043QIAN Zhihong, YAN Shuangye, TIAN Chunsheng, et al. Research on resource allocation algorithm for D2D communications underlaying LTE-A networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180043 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
