Robust Discriminative Feature Subspace Learning Based on Low Rank Representation
-
摘要:
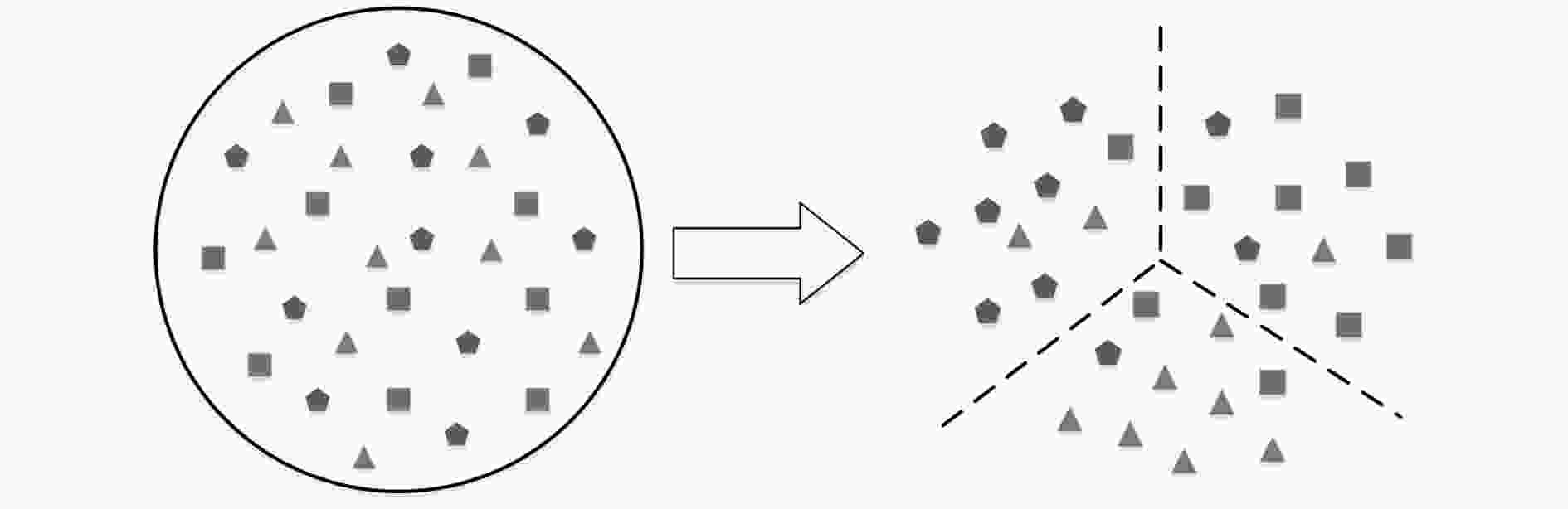
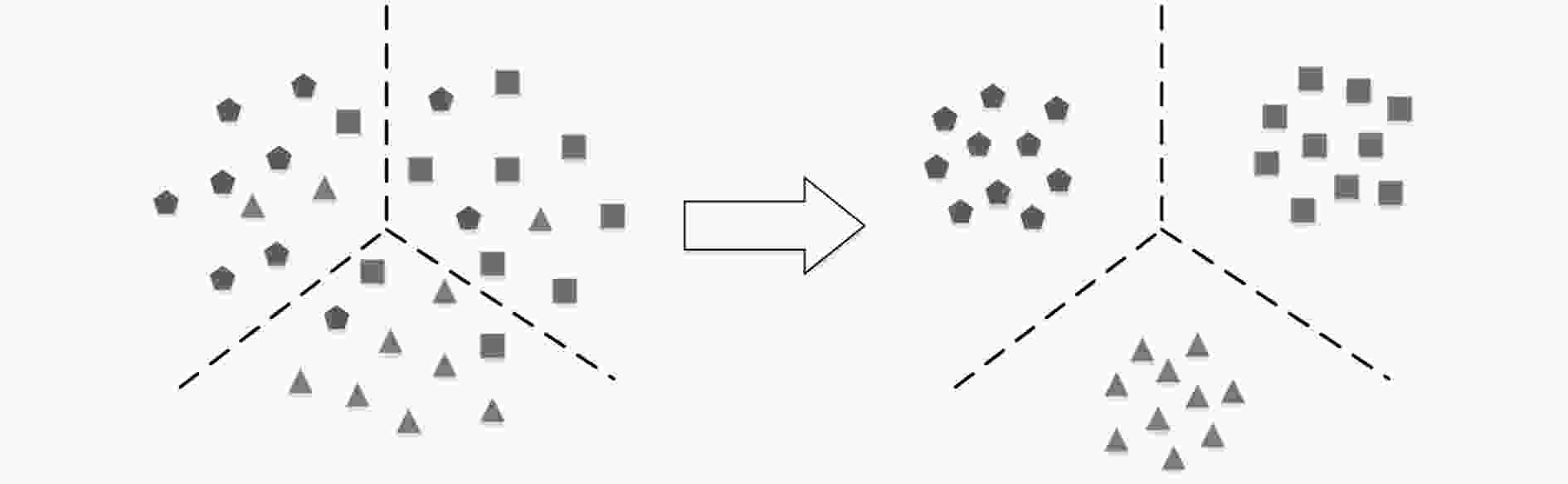
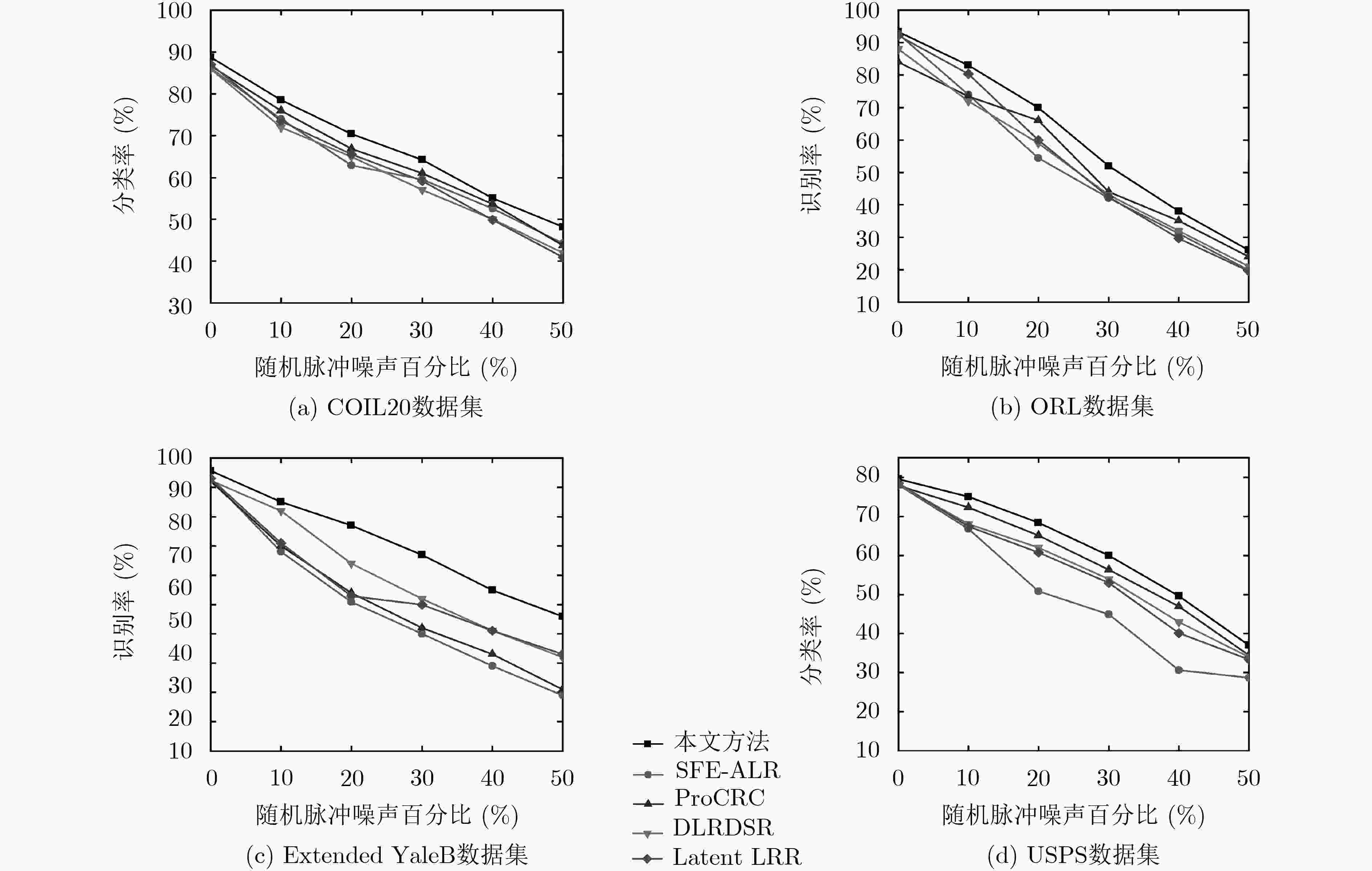
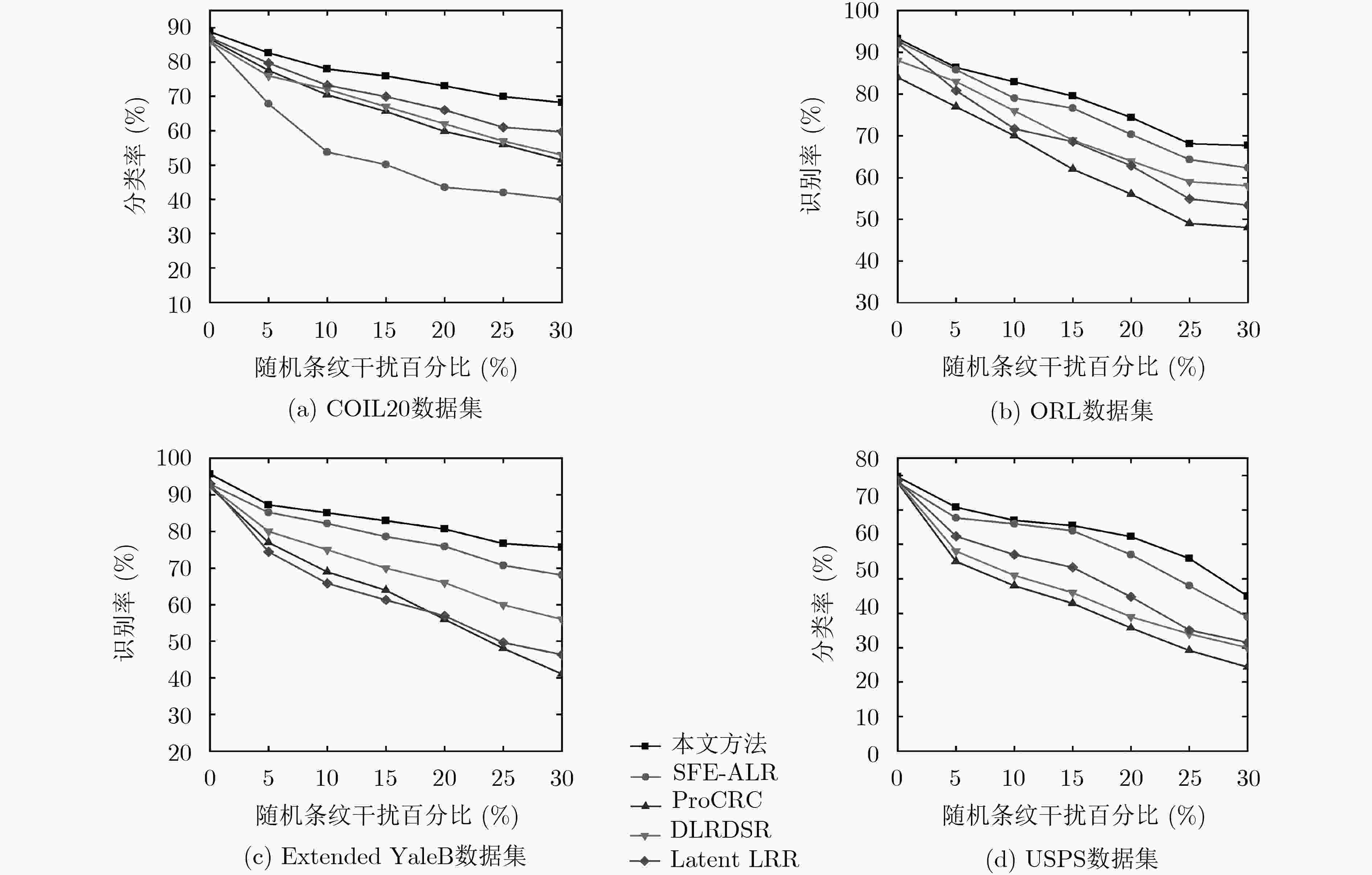
特征子空间学习是图像识别及分类任务的关键技术之一,传统的特征子空间学习模型面临两个主要的问题。一方面是如何使样本在投影到特征空间后有效地保持其局部结构和判别性。另一方面是当样本含噪时传统学习模型所发生的失效问题。针对上述两个问题,该文提出一种基于低秩表示(LRR)的判别特征子空间学习模型,该模型的主要贡献包括:通过低秩表示探究样本的局部结构,并利用表示系数作为样本在投影空间的相似性约束,使投影子空间能够更好地保持样本的局部近邻关系;为提高模型的抗噪能力,构造了一种利用低秩重构样本的判别特征学习约束项,同时增强模型的判别性和鲁棒性;设计了一种基于交替优化技术的迭代数值求解方案来保证算法的收敛性。该文在多个视觉数据集上进行分类任务的对比实验,实验结果表明所提算法在分类准确度和鲁棒性方面均优于传统特征学习方法。
Abstract:Feature subspace learning is a critical technique in image recognition and classification tasks. Conventional feature subspace learning methods include two main problems. One is how to preserve the local structures and discrimination when the samples are projected into the learned subspace. The other hand when the data are corrupted with noise, the conventional learning models usually do not work well. To solve the two problems, a discriminative feature learning method is proposed based on Low Rank Representation (LRR). The novel method includes three main contributions. It explores the local structures among samples via low rank representation, and the representation coefficients are used as the similarity measurement to preserve the local neighborhood existed in the samples; To improve the anti-noise performance, a discriminative learning item is constructed from the recovered samples via low rank representation, which can enhance the discrimination and robustness simultaneously; An iterative numerical scheme is developed with alternating optimization, and the convergence can be guaranteed effectively. Extensive experimental results on several visual datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms conventional feature learning methods on both of accuracy and robustness.
-
算法1:综合目标函数的数值求解方案 输入: 训练集X,类别标签Y, ${\lambda _1}$, ${\lambda _2}$, $\eta $, ${{Z}} = {{G}} = {{R}} = 0$,
${{E}} = 0$, ${{{Y}}_{\rm{1}}} = {{{Y}}_{\rm{2}}} = {{{Y}}_{\rm{3}}} = 0$, $\mu = 0.6$, ${\mu _{\max }} = {10^{10}}$, $\rho = 1.1$。输出: ${{P}}$ While not convergence do 1. 使用式(5)—(9)进行更新${{{P}}^{k + 1}}$, ${{{G}}^{k + 1}}$, ${{{R}}^{k + 1}}$, ${{{Z}}^{k + 1}}$, ${{{E}}^{k + 1}}$; 2. 更新拉格朗日乘子及参数$\mu $: ${{{Y}}_1}^{k + 1} = {{{Y}}_1}^k + \mu \left( {{{X}} - {{X}}{{{Z}}^{k + 1}} - {{{E}}^{k + 1}}} \right)$; ${{{Y}}_2}^{k + 1} = {{{Y}}_2}^k + \mu \left( {{{{Z}}^{k + 1}} - {{{G}}^{k + 1}}} \right)$; ${{{Y}}_3}^{k + 1} = {{{Y}}_3}^k + \mu \left( {{{{Z}}^{k + 1}} - {{{R}}^{k + 1}}} \right)$; $\mu = \min \left( {{\mu _{\max }},\rho \mu } \right)$; end while -
张涛, 唐振民. 一种基于非负低秩稀疏图的半监督学习改进算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(4): 915–921. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160559ZHANG Tao and TANG Zhenmin. Improved algorithm based on non-negative low rank and sparse graph for semi-supervised learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(4): 915–921. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160559 成宝芝, 赵春晖, 张丽丽. 子空间稀疏表示高光谱异常检测新算法[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2017, 38(4): 640–645. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201604006CHENG Baozhi, ZHAO Chunhui, and ZHANG Lili. An anomaly detection algorithm for hyperspectral images using subspace sparse representation[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2017, 38(4): 640–645. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201604006 BELHUMEUR P N, HESPANHA J P, and KRIEGMAN D J. Eigenfaces vs. fisherfaces: Recognition using class specific linear projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1997, 19(7): 711–720. doi: 10.1109/34.598228 CAI Deng, HE Xiaofei, ZHOU Kun, et al. Locality sensitive discriminant analysis[C]. The 20th International Joint Conference on Artifical Intelligence, Hyderabad, India, 2007: 708–713. CAI Sijia, ZHANG Lei, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. A probabilistic collaborative representation based approach for pattern classification[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2950–2959. REN Jiahuan, ZHANG Zhao, LI Sheng, et al. Robust projective low-rank and sparse representation by robust dictionary learning[C]. The 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2018: 1851–1856. RAZZAGHI P, RAZZAGHI P, and ABBASI K. Transfer subspace learning via low-rank and discriminative reconstruction matrix[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 163: 174–185. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.026 KANG Zhao, PENG Chong, and CHENG Qiang. Kernel-driven similarity learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 267: 210–219. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.06.005 LI Sheng, SHAO Ming, and FU Yun. Multi-view low-rank analysis with applications to outlier detection[J]. ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data, 2018, 12(3): 32–53. doi: 10.1145/3168363 LIU Guangcan and YAN Shuicheng. Latent low-rank representation for subspace segmentation and feature extraction[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1615–1622. FANG Xiaozhao, HAN Na, WU Jigang, et al. Approximate low-rank projection learning for feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(11): 5228–5241. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2796133 MA Long, WANG Chunheng, XIAO Baihua, et al. Sparse representation for face recognition based on discriminative low-rank dictionary learning[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 2586–2593. LI Ao, LIU Xin, WANG Yanbing, et al. Subspace structural constraint-based discriminative feature learning via nonnegative low rank representation[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(5): e0215450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215450 PENG Chong, KANG Zhao, and CHENG Qiang. Subspace clustering via variance regularized ridge regression[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 21–26. ZHANG He and PATEL V M. Convolutional sparse and low-rank coding-based image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(5): 2121–2133. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2786469 LIN Zhouchen, CHEN Minming, and MA Yi. The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices[J]. 2010, arXiv: 1009.5055. WEN Zaiwen and YIN Wotao. A feasible method for optimization with orthogonality constraints[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2013, 142(1/2): 397–434. doi: 10.1007/s10107-012-0584-1 CANDÈS E J, LI Xiaodong, MA Yi, et al. Robust principal component analysis?[J]. Journal of the ACM (JACM) , 2011, 58(3): 11–49. doi: 10.1145/1970392.1970395 YANG Junfeng and ZHANG Yin. Alternating direction algorithms for $\ell_1$ -problems in compressive sensing[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2011, 33(1): 250–278. doi: 10.1137/090777761YANG Junfeng, YIN Wotao, ZHANG Yin, et al. A fast algorithm for edge-preserving variational multichannel image restoration[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 569–592. doi: 10.1137/080730421 -





 下载:
下载:
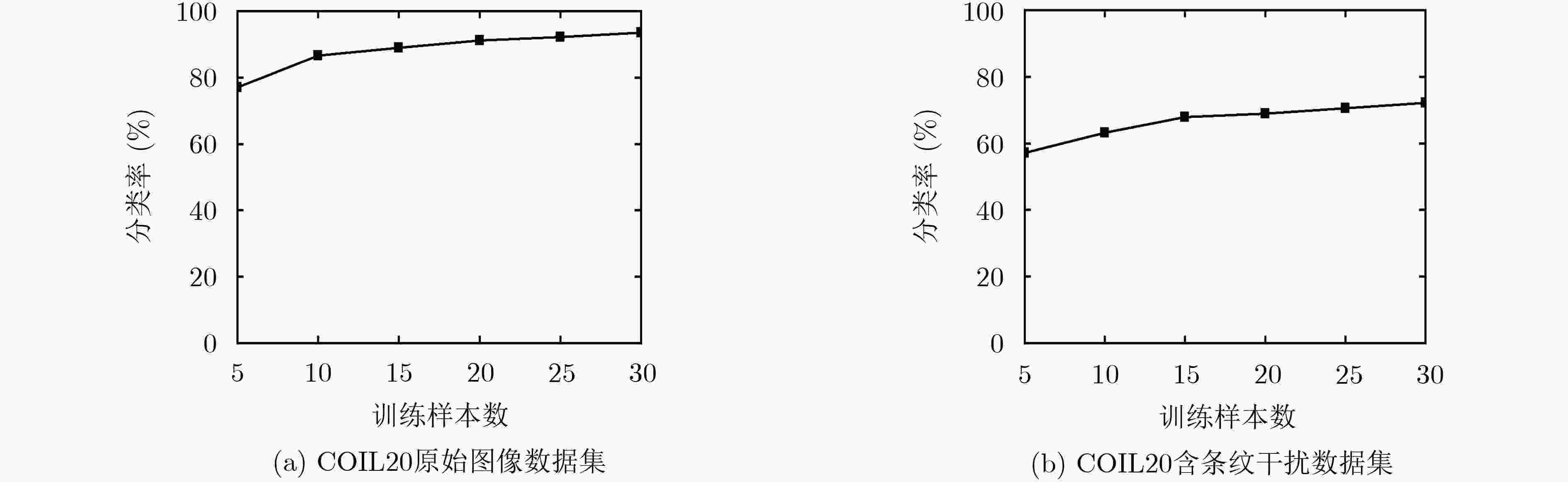
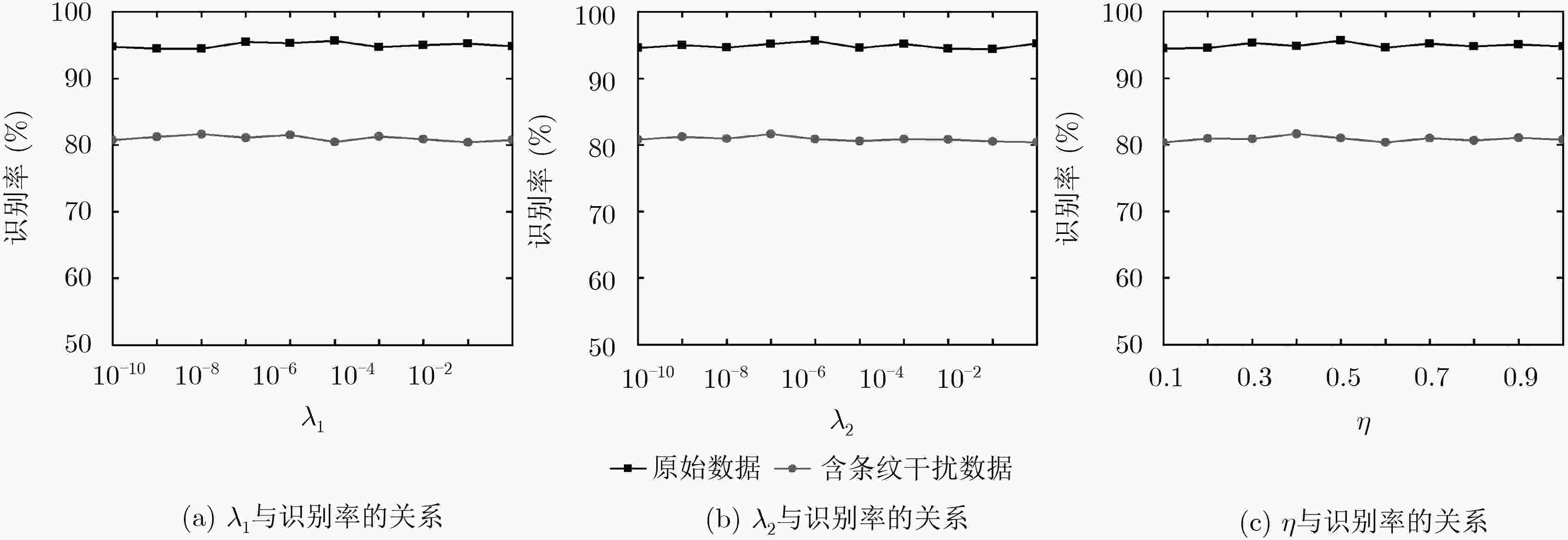
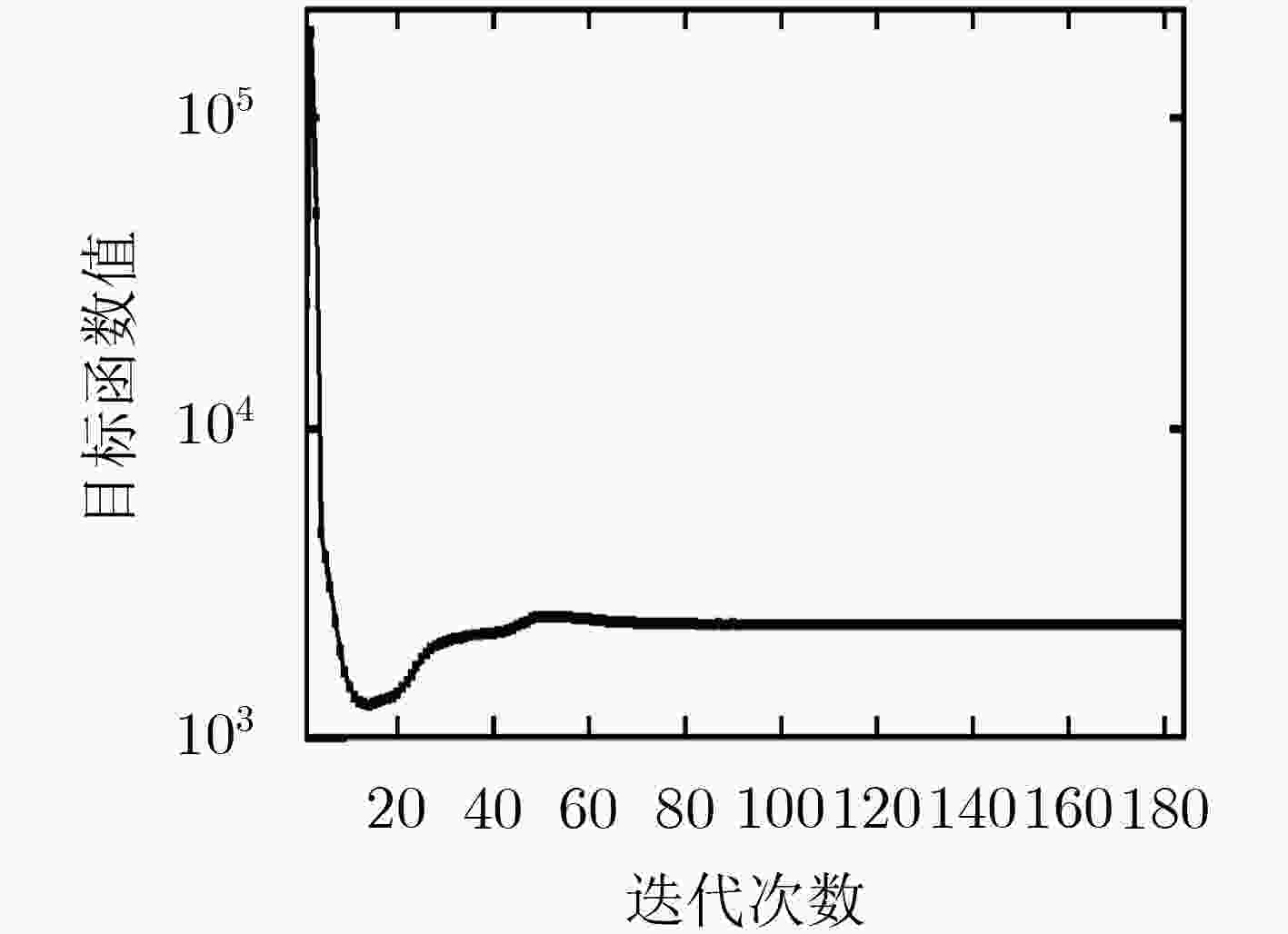



 下载:
下载:
