Research on Channel Selection and Power Control Strategy for D2D Networks
-
摘要: 针对D2D通信的资源分配问题,该文研究了D2D信道选择与功率控制策略。在保证蜂窝用户服务质量(QoS)的前提下,提出一种基于启发式的D2D信道选择算法,为系统内的D2D用户找到合适的信道复用资源。同时,利用拉格朗日对偶方法求解得到D2D用户最优传输功率。仿真结果表明当蜂窝用户与多对D2D用户共享信道资源时能够大幅度提升系统平均吞吐量。在相同条件下,该算法的性能要明显优于现有算法。Abstract: Considering the resource allocation problem for Device-to-Device (D2D) communications, a channel selection and power control strategy for D2D communications is investigated. On the premise of guaranteeing the Quality of Service (QoS) of cellular users, a heuristic based D2D channel selection algorithm is proposed to find the suitable channel reusing resources for D2D users in the system. At the same time, the optimal transmission power of D2D users is obtained by using the Lagrange dual method. Simulation results demonstrate that when the cellular user shares channel resources with multiple pairs of D2D users, the system throughput can be dramatically improved. The performance of this algorithm outperforms the exiting algorithms under the same conditions.
-
Key words:
- D2D communications /
- Channel selection /
- Power control /
- Lagrange dual
-
表 1 基于启发式思想的DUEs信道选择算法
(1)初始化:${D_i} = \varnothing ,\forall i \in C$; ${M_i} = D,\forall i \in C$; $\xi _i^j = 0,\forall i \in C,\forall j \in D$;利用式(11)得到所有DUEs 最优的发射功率$P_{j,i}^{{\rm{d}} {\rm{opt}}}$,并求解出与之相对 应的$T(P_{j,i}^{{\rm{d}} {\rm{opt}}})$值; (2) repeat (3) $({i^ * },{j^*}) = \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{(i,j):i \in C,j \in {M_i}} T\;(P_{j,i}^{{\rm{d}} {\rm{opt}}})$ // 求解得到吞吐量最大值所对应的CUE${i^ * }$与DUE${j^*}$;
(4) if $\left[ {{{{P^{\rm{c}}}g_{{i^*}}^{\rm{c}}} \Biggr/ {\left( {\sigma _0^2 + \sum\limits_{q \in \left\{ {{D_{{i^*}}} \cup {j^*}} \right\}} {P_{q,{i^*}}^{{\rm{d}} {\rm{opt}}}g_{q,{i^*}}^{\rm{d}}} } \right)}}} \right] \ge {\gamma _{{\rm{th}}}}$ then // 判断DUE${j^*}$复用CUE${i^ * }$信道资源时,CUE${i^ * }$的SINR是否满足系统限制条件, 当满足限制条件时:(5) set $\xi _{{i^*}}^{{j^*}} = 1$; // 将复用指示因子$\xi _{{i^*}}^{{j^*}}$的值设置为1; (6) ${M_i} = {M_i}\backslash \left\{ {{j^*}} \right\},\forall i \in C$;${D_{{i^*}}} = {D_{{i^*}}} \cup \left\{ {{j^*}} \right\}$; // 将DUE${j^*}$从集合${M_i}$中删除, 同时将DUE${j^*}$加入到复用CUE${i^ * }$ 信道资源的DUEs集合 ${D_{{i^*}}}$中; (7) else // 当不满足限制条件时: (8) ${M_{{i^*}}} = {M_{{i^*}}}\backslash \left\{ {{j^*}} \right\}$; // 将DUE${j^*}$从集合${M_{{i^*}}}$中删除; (9) end if (10) until ${M_i} = \varnothing ,\forall i \in C$ // 当集合${M_i}$为空集时停止运行; (11) return ${D_i},\forall i \in C$; $\xi _i^j,\forall i \in C,\forall j \in D$. // 输出集合${D_i}$及复用指示因子$\xi _i^j$的值。 表 2 DUEs功率控制算法
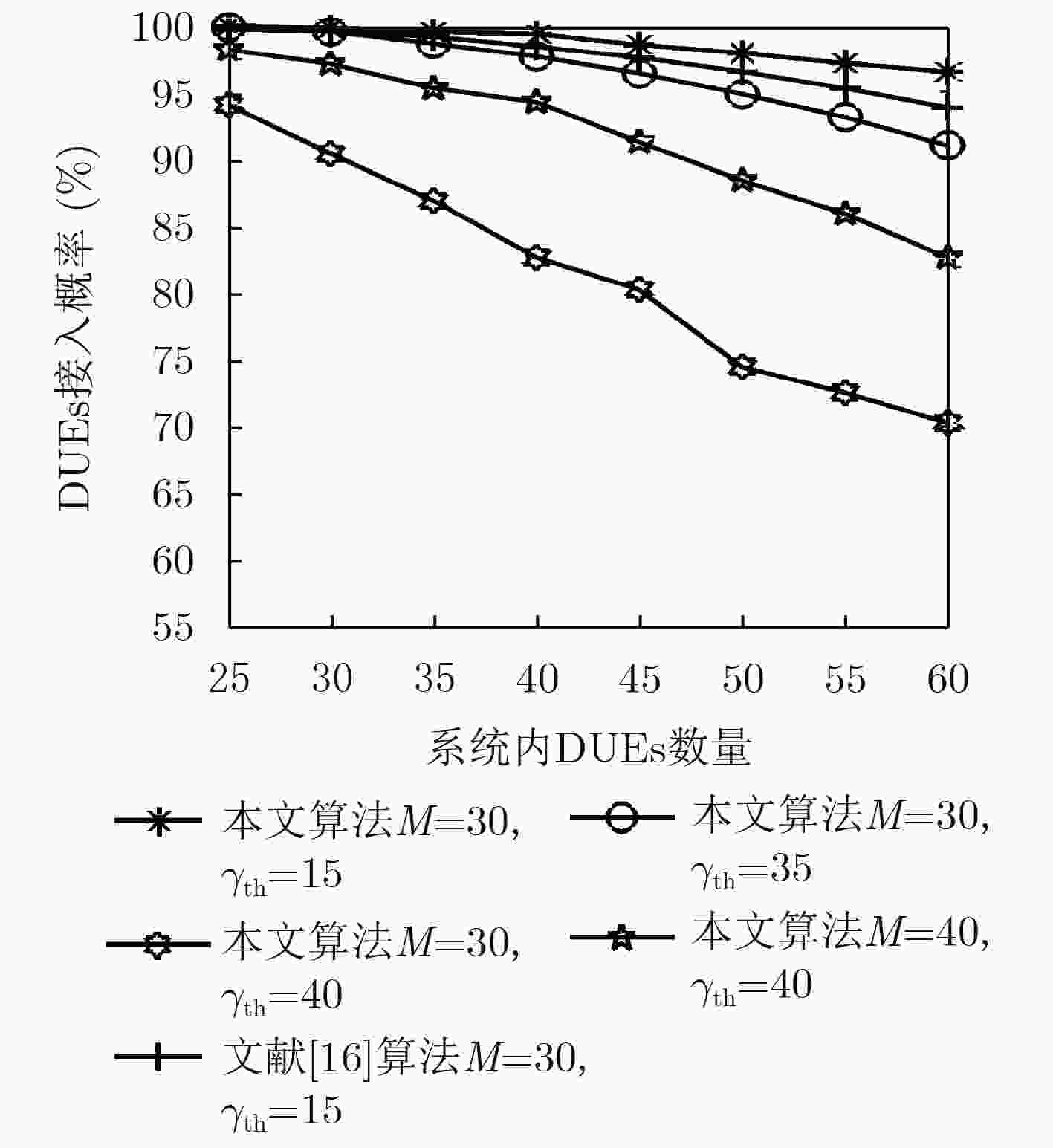
(1) 根据表1对集合${D_i},\forall i \in C$进行初始化; (2) for all $i \in C$ do (3) for all $j \in {D_i}$ do (4) 根据式(21)—式(23)计算DUE j传输功率$P_{j,i}^{\rm{d}}$。 (5) end for (6) end for (7) return $P_{j,i}^d,\forall i \in C,\forall j \in D$. // 输出DUEs最优传输功率。 表 3 仿真参数
参数 数值 CUEs数量 30, 40 DUEs数量 25~60 DUEs间通信距离 30~100 (m) CUEs通信路径损耗 128.1+37.6lg(d(km)) DUEs通信路径损耗 148+40lg(d(km)) 噪声谱密度 –114 dBm/Hz DUEs最小吞吐量限制 1.5 Mbps CUEs传输功率 24 dBm -
BENNIS M, DEBBAH M, and POOR H V. Ultrareliable and low-latency wireless communication: Tail, risk, and scale[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(10): 1834–1853. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2867029 钱志鸿, 阎双叶, 田春生, 等. LTE-A网络中D2D通信的资源分配算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180043QIAN Zhihong, YAN Shuangye, TIAN Chunsheng, et al. Research on resource allocation algorithm for D2D communications underlaying LTE-A networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2287–2293. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180043 王练, 王萌, 任治豪, 等. D2D网络中基于立即可解网络编码的时延最小化重传方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1691–1698. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170976WANG Lian, WANG Meng, REN Zhihao, et al. Delay minimization retransmission scheme based on instantly decodable network coding for D2D communications[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1691–1698. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170976 钱志鸿, 王雪. 面向5G通信网的D2D技术综述[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37(7): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016129QIAN Zhihong and WANG Xue. Reviews of D2D technology for 5G communication networks[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37(7): 1–14. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2016129 XIANG Shangwen, PENG Tao, LIU Ziyang, et al. A distance-dependent mode selection algorithm in heterogeneous D2D and IMT-advanced network[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Anaheim, USA, 2012: 416–420. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOMW.2012.6477608. WEN Si, ZHU Xiaoyue, LIN Zhesheng, et al. Distributed resource management for device-to-device (D2D) communication underlay cellular networks[C]. The 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 2013: 1624–1628. doi: 10.1109/PIMRC.2013.6666402. LEE D H, CHOI K W, JEON W S, et al. Two-stage semi-distributed resource management for device-to-device communication in cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(4): 1908–1920. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.022014.130480 ZHANG Wei, HE Wanbing, WU Dan, et al. Joint mode selection, link allocation and power control in underlaying D2D communication[J]. KSⅡ Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2016, 10(11): 5209–5228. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2016.11.001 WANG Xianxian, LÜ Shaobo, WANG Xing, et al. Greedy heuristic resource allocation algorithm for device-to-device aided cellular systems with system level simulations[J]. KSⅡ Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2018, 12(4): 1415–1435. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2018.04.002 AHMAD M, NAEEM M, IQBAL M, et al. Joint user selection, mode assignment, and power allocation in cognitive radio-assisted D2D networks[J]. IET Communications, 2018, 12(10): 1207–1214. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2017.1206 XU Jun, GUO Chengcheng, and ZHANG Hao. Joint channel allocation and power control based on PSO for cellular networks with D2D communications[J]. Computer Networks, 2018, 133: 104–119. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.01.017 GJENDEMSJO A, GESBERT D, OIEN G E, et al. Optimal power allocation and scheduling for two-cell capacity maximization[C]. The 4th International Symposium on Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc and Wireless Networks, Boston, USA, 2006: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WIOPT.2006.1666517. ESMAT H H, ELMESALAWY M M, and IBRAHIM I I. Joint channel selection and optimal power allocation for multi-cell D2D communications underlaying cellular networks[J]. IET Communications, 2017, 11(5): 746–755. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2016.0955 UL HASSAN N, YUEN C, SAEED S, et al. Power control for sum-rate maximization on interference channels under sum power constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(2): 593–609. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2324289 ITU-R. Guidelines for evaluation of radio interface technologies for IMT-advanced[R]. Report ITU-R M.2135, 2009. DINH-VAN S, SHIN Y, and SHIN O S. Resource allocation and power control based on user grouping for underlay device-to-device communications in cellular networks[J]. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 2017, 28(1): e2920. doi: 10.1002/ett.2920 -





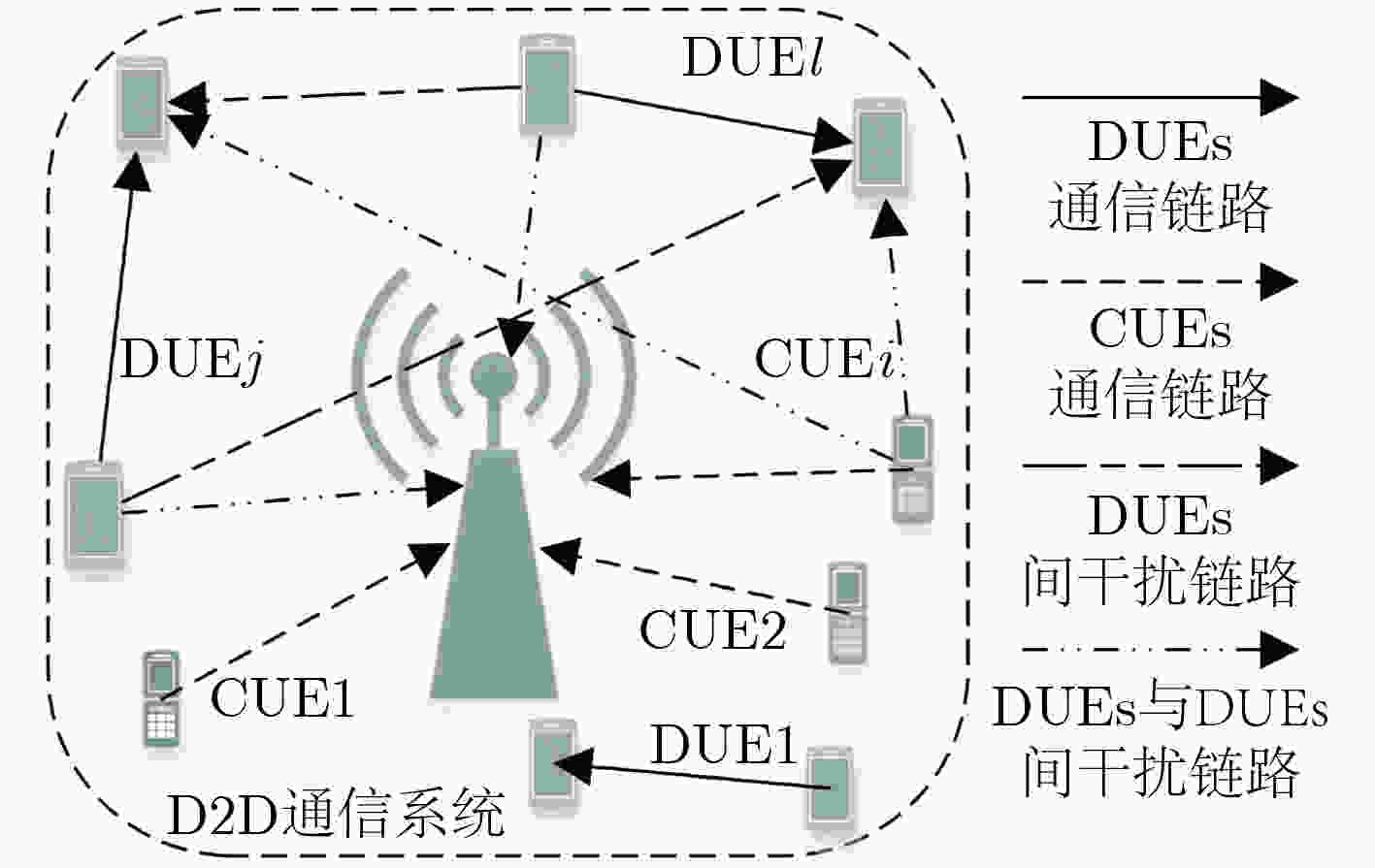
 下载:
下载:
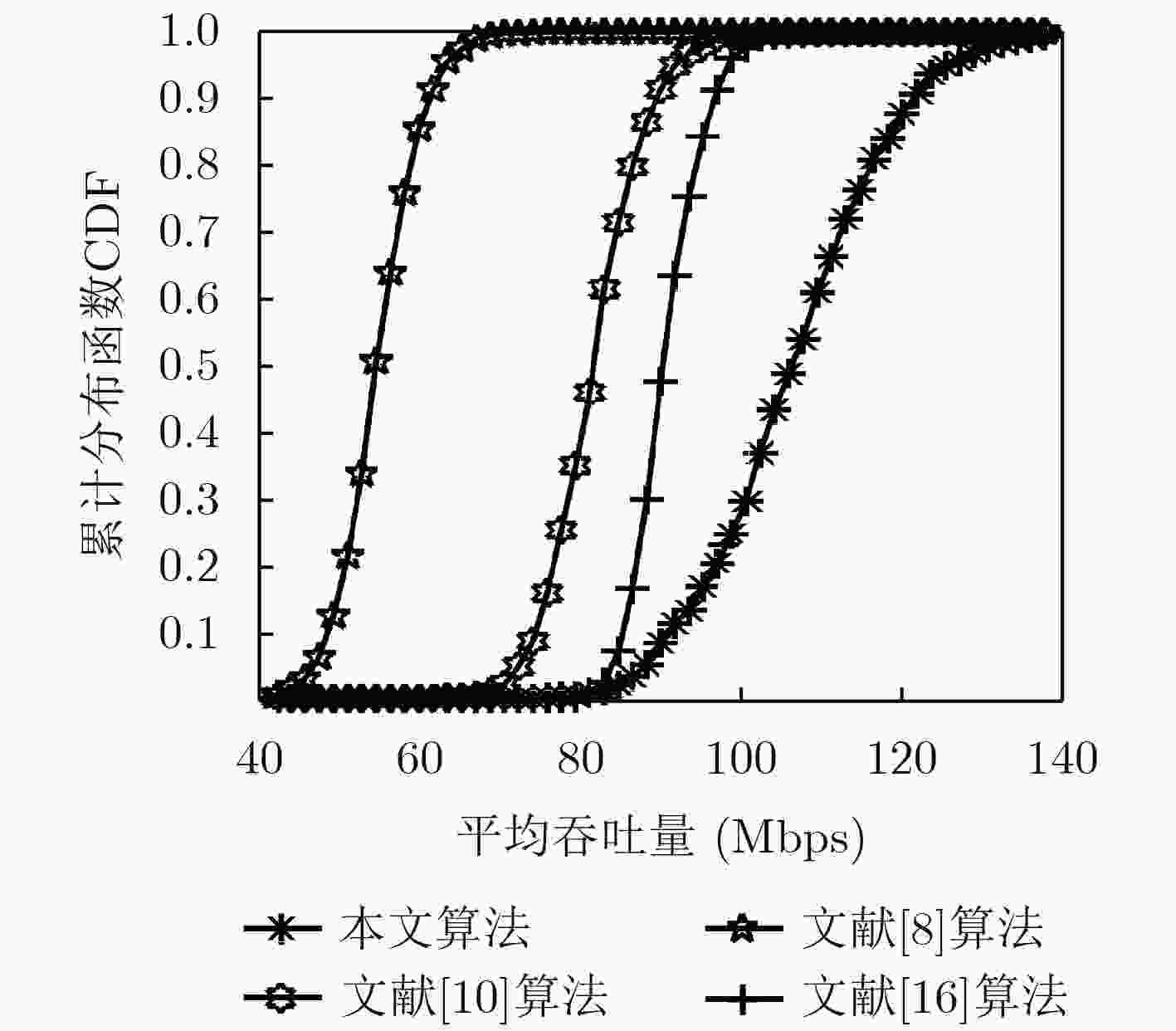
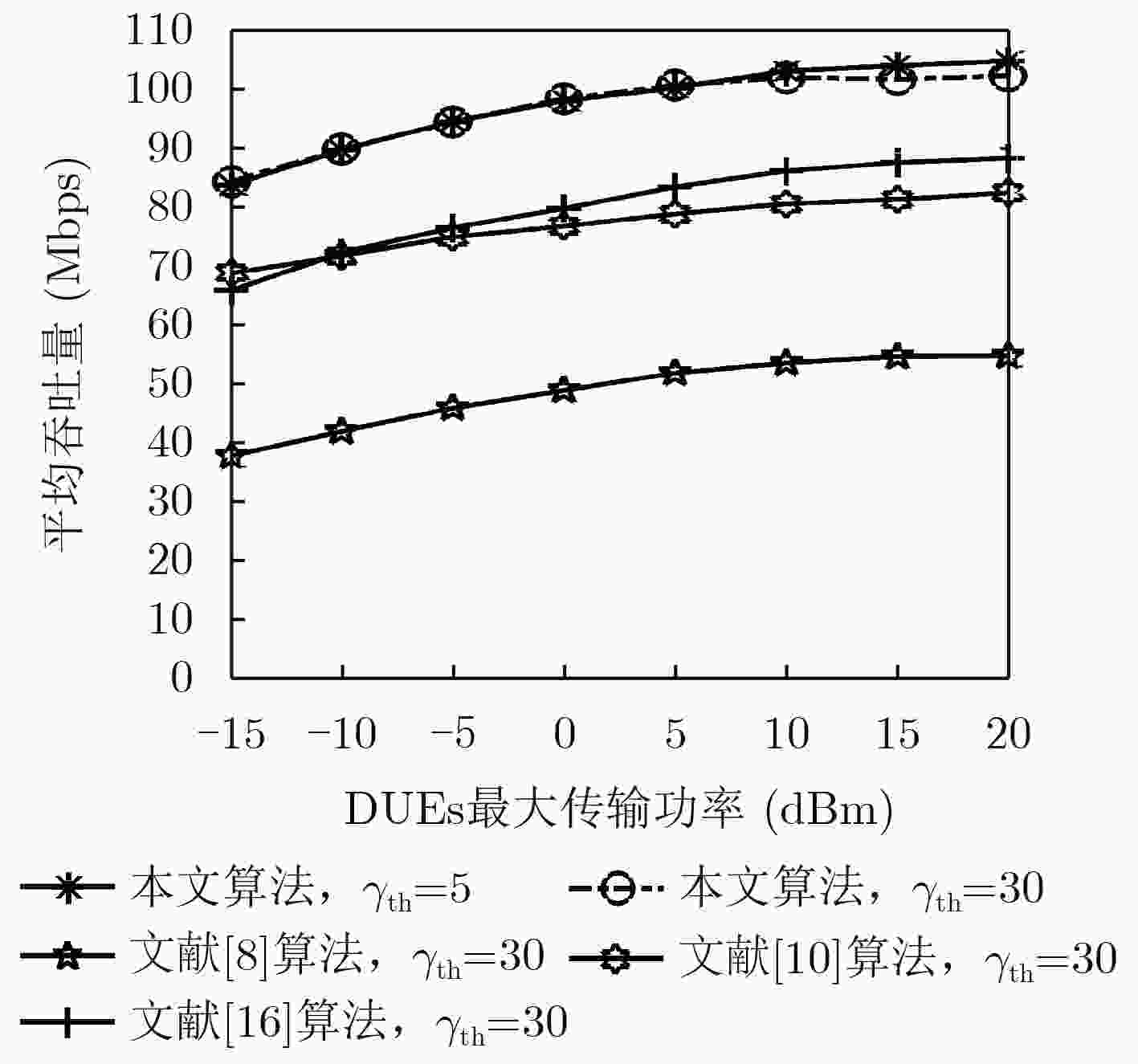
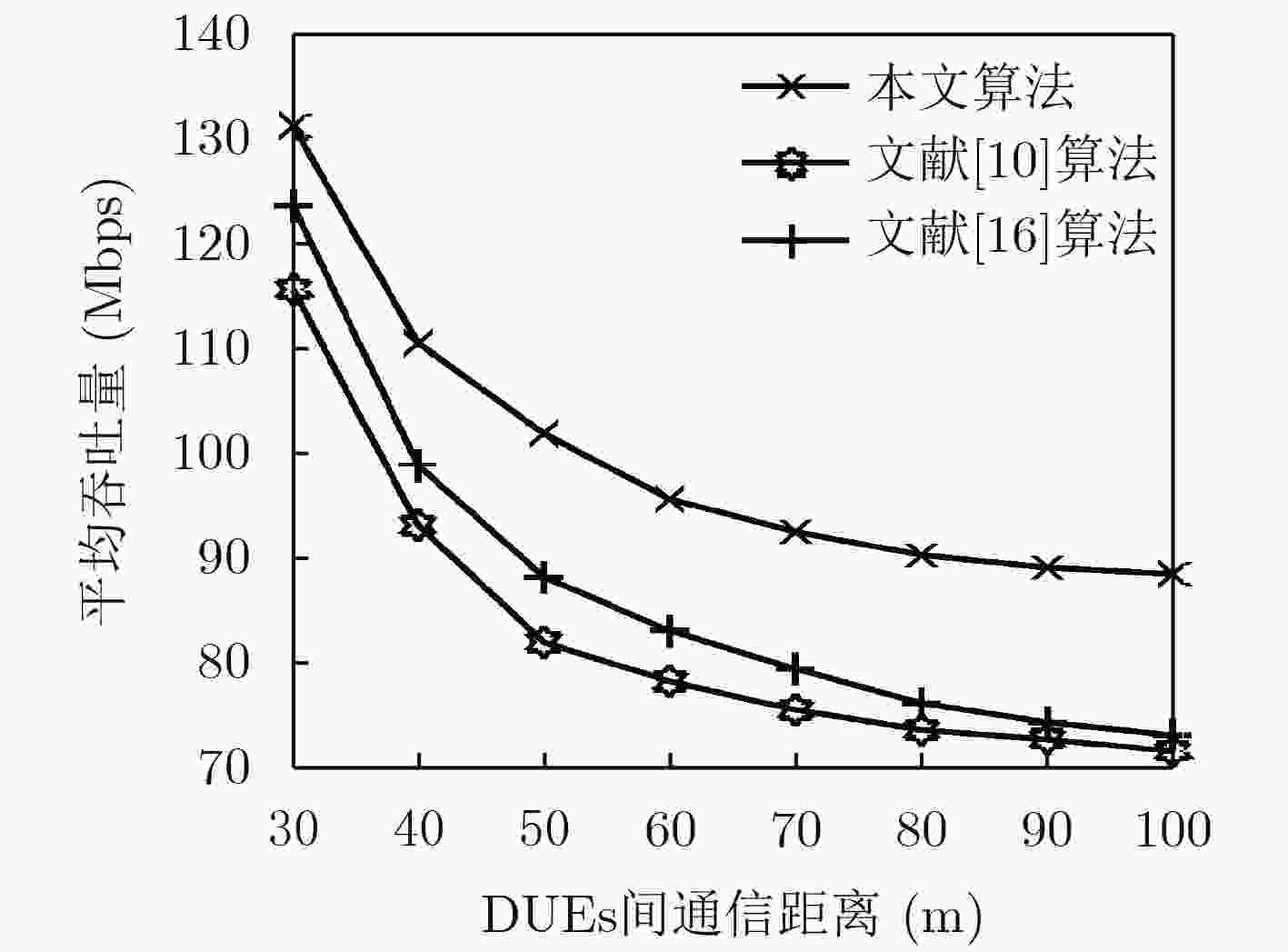


 下载:
下载:
