Combined Bipercentile Parameter Estimation of Generalized Pareto Distributed Sea Clutter Model
-
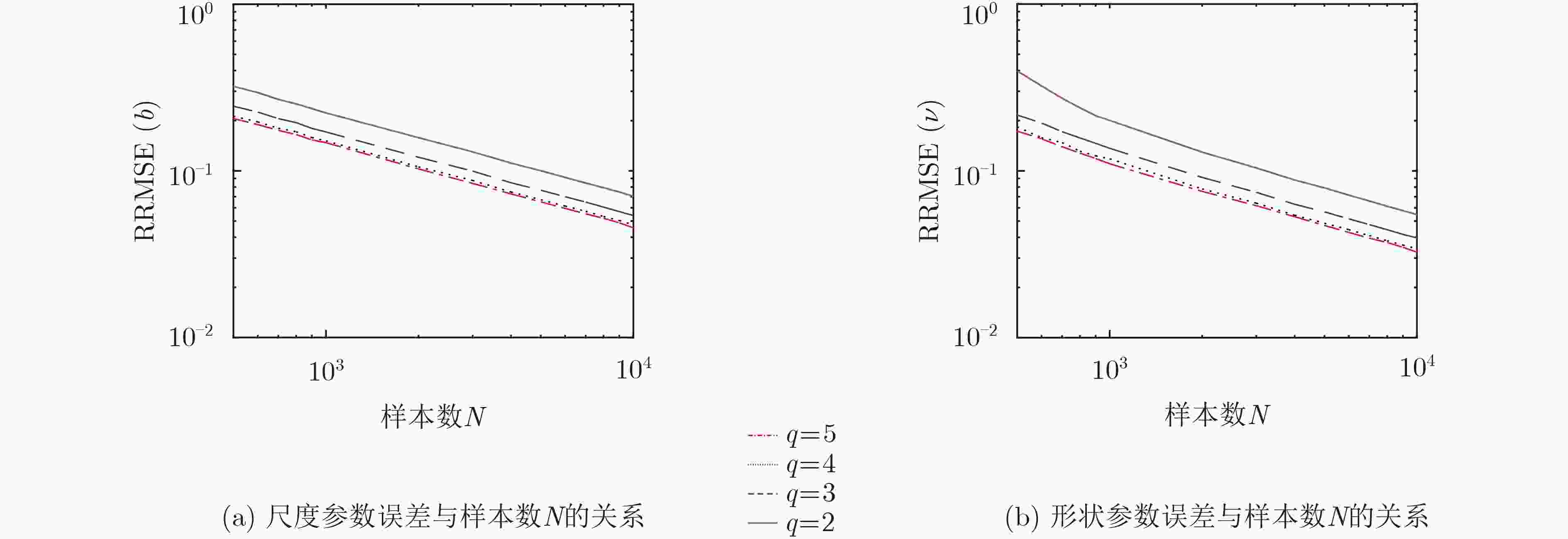
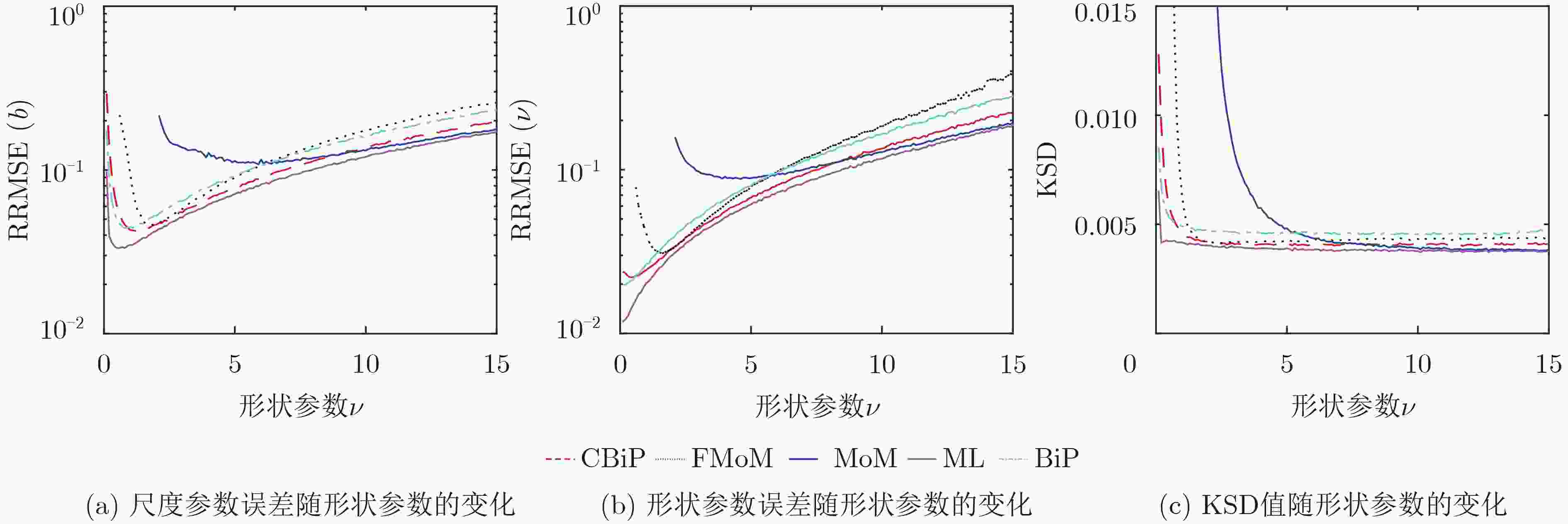
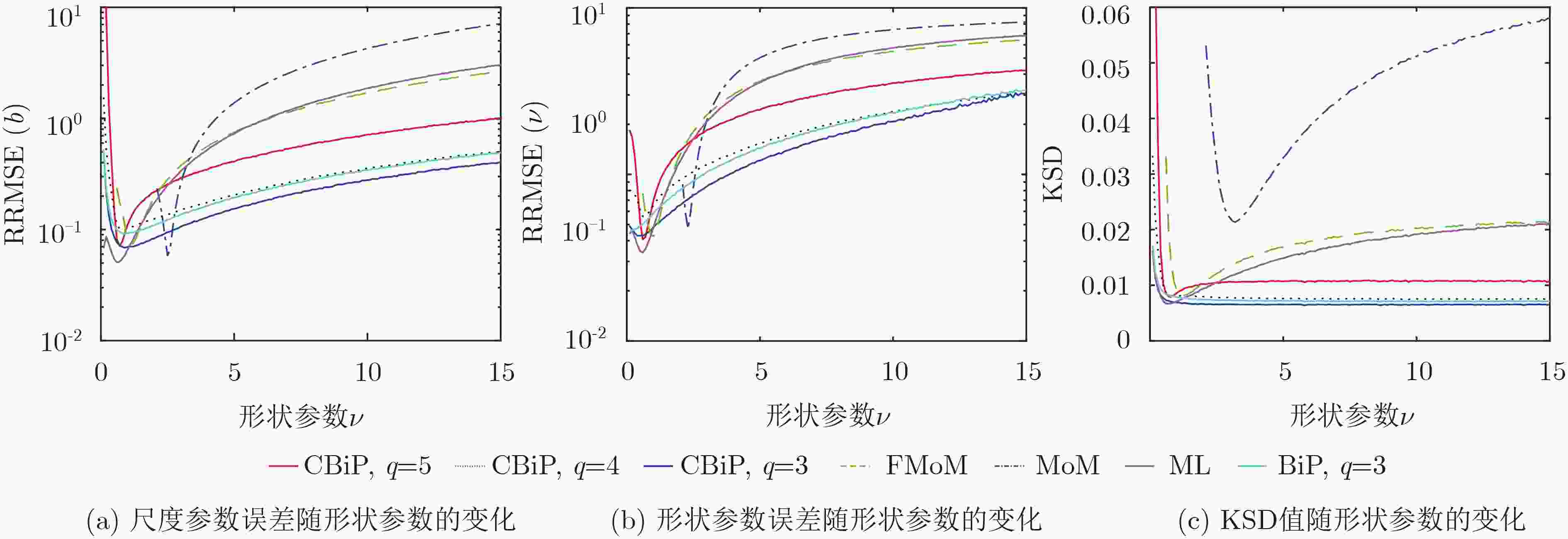
摘要: 广义Pareto分布的复合高斯模型可以很好地描述高分辨低擦地角对海探测场景中海杂波的重拖尾特性,实现该杂波模型下双参数的有效估计对雷达检测性能具有重要意义。对此,该文提出一种双参数的组合双分位点(CBiP)估计方法。该估计方法基于低阶多项式方程的显式求根表达式,充分组合利用回波中的样本信息,旨在实现高精度的双参数估计过程。此外,考虑到实际雷达工作中存在岛礁、渔船等造成的功率异常大的野点样本时,不同于传统的矩估计、最大似然(ML)估计等方法,组合双分位点估计方法仍可保持估计性能的鲁棒性。仿真及实测数据实验表明,在纯杂波环境中,组合双分位点估计方法可以实现与最大似然估计方法近似的估计精度,若存在异常样本,组合双分位点估计方法的估计性能优于上述几种传统估计方法。
-
关键词:
- 参数估计 /
- 广义Pareto分布模型 /
- 最大似然估计 /
- 组合双分位点估计 /
- 野点鲁棒性
Abstract: The generalized Pareto distributed sea clutter model, known as one of the compound-Gaussian models, is able to describe heavy-tailed characteristic of sea clutter under high-resolution and low grazing angle detection scene efficiently, and the accuracy of parameter estimation under this condition heavily impacts radar’s detection property. In this paper, Combined BiPercentile (CBiP) estimator is proposed to estimate the parameters. The CBiP estimator is realized based on the explicit roots of low-order polynomial equations and full application of sample information in returns, which provides a highly-accurate parameter estimation process. Besides, the CBiP estimator can maintain the robustness of estimation performance when outliers with extremely large power are existing in samples, while other estimators, including moment-based and Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimators, degrade extremely in estimation accuracy. Without outliers in samples, the combined bipercentile estimator shows similar accuracy with the ML estimator. With outliers, the combined percentile estimator is the only method with robustness in performance, compared with other estimators aforementioned. Moreover, the ability of the new estimator is verified by measured clutter data. -
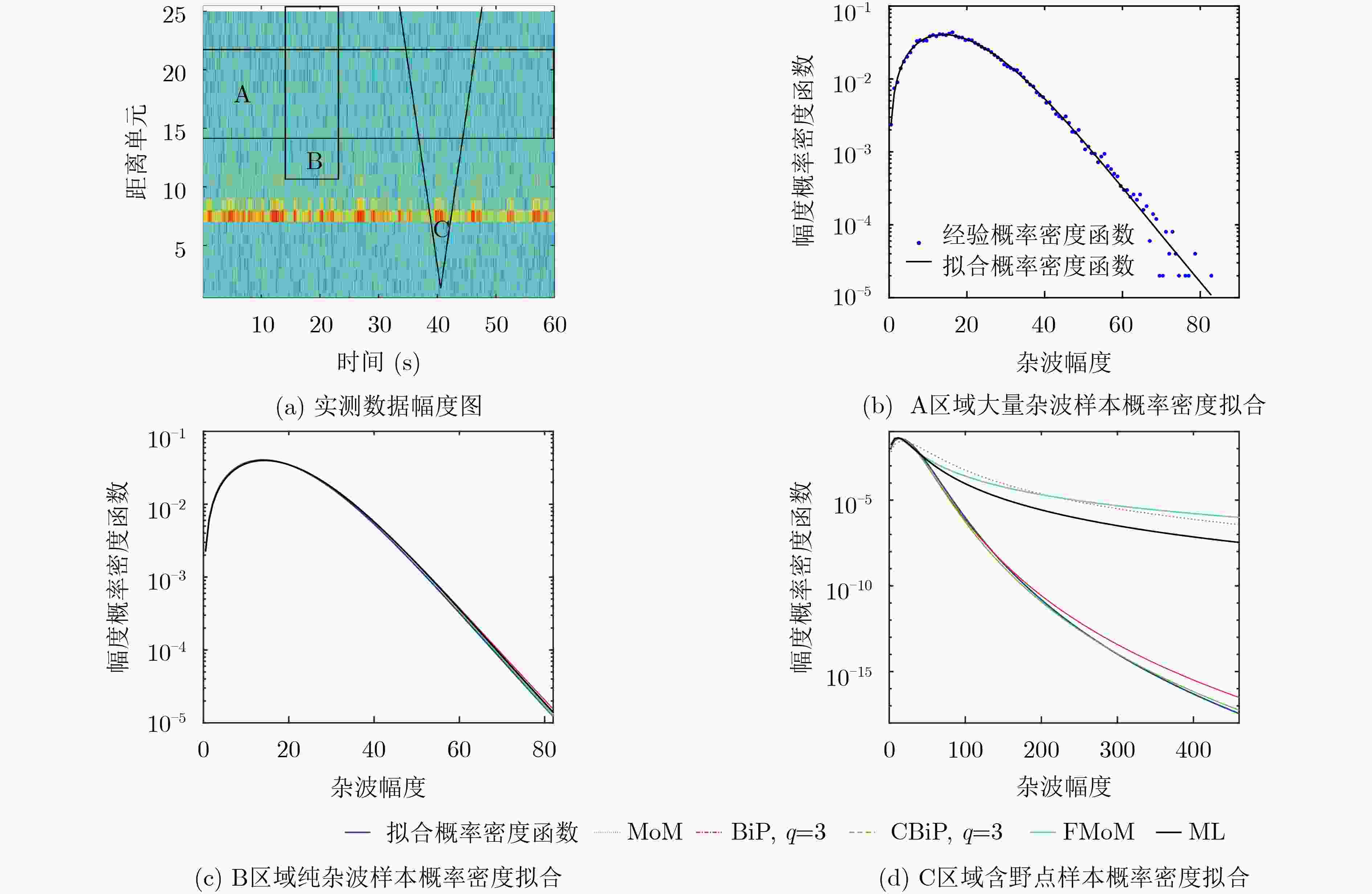
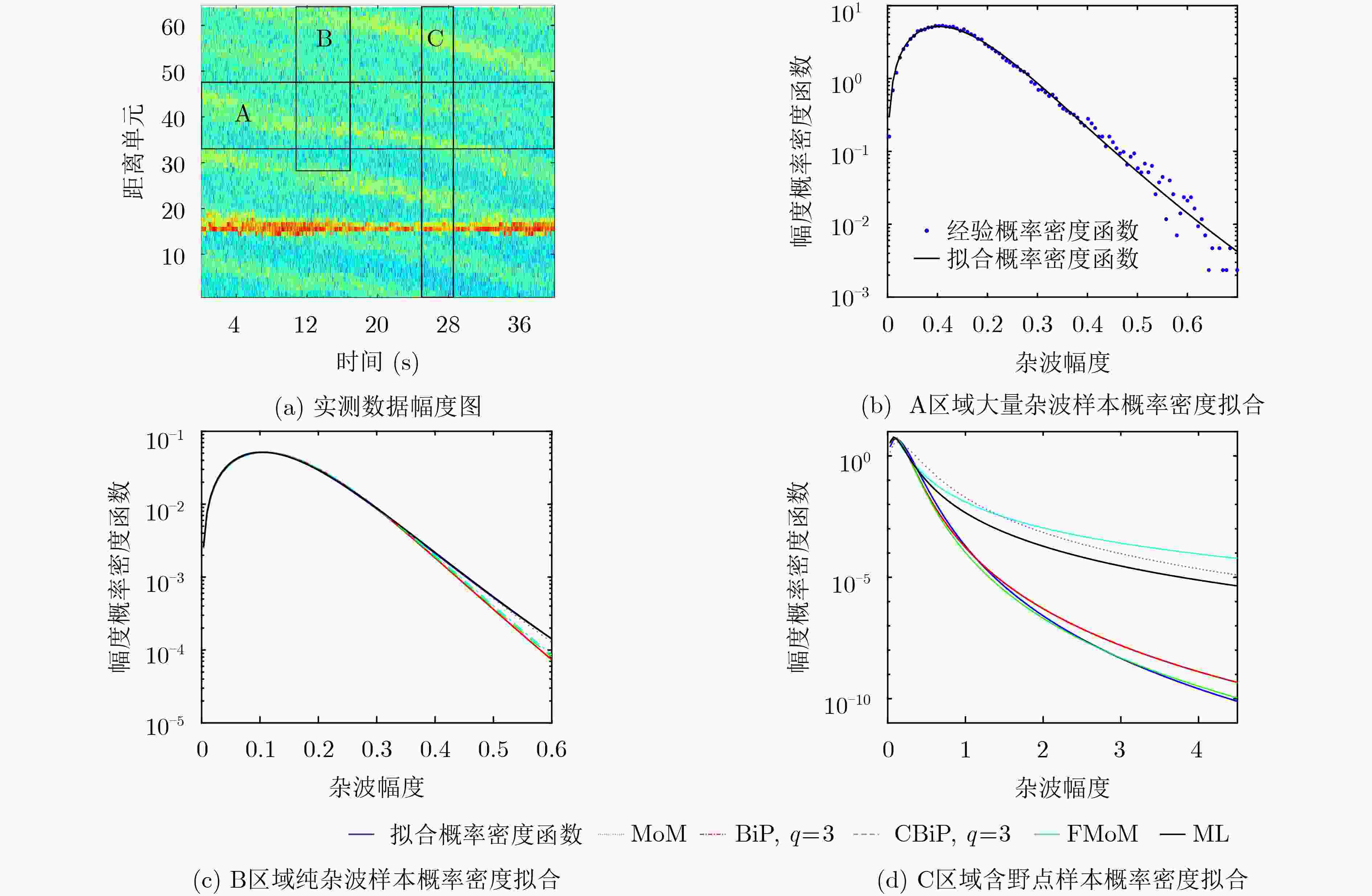
表 1 IPIX实测数据(19980206_195948_ANTSTEP)中5种估计方法的估计结果比较
估计区域 区域A 纯杂波区域B 含野点区域C 估计方法 ML CBiP FMoM MoM ML BiP CBiP FMoM MoM ML BiP 形状参数 9.1209 8.9967 9.6100 9.7443 9.4106 9.8734 8.4874 1.3400 2.0260 2.1385 8.0111 尺度参数(×10–4) 2.6649 2.6062 2.4252 2.3880 2.4824 2.3601 3.3050 31.0000 6.7579 16.0000 3.5223 K-S距离 2.6131×10–6 0.0134 0.0138 0.0141 0.0133 0.0165 0.0135 0.0999 0.2462 0.0756 0.0485 表 2 CSIR实测数据(TFA10_004.02)中5种估计方法的估计结果比较
估计区域 区域A 纯杂波区域B 含野点区域C 估计方法 ML CBiP FMoM MoM ML BiP CBiP FMoM MoM ML BiP 形状参数 4.5746 6.2565 6.2900 5.0549 4.7048 6.4637 4.2017 1.2900 2.0223 1.8314 3.8543 尺度参数(×10–4) 9.2877 6.4383 6.2729 8.0752 8.8359 6.2430 13.4301 60.0855 12.4512 36.9231 14.9068 K-S距离 3.6008×10–6 0.0111 0.0174 0.0105 0.0064 0.0126 0.0907 0.1213 0.2060 0.1060 0.0144 -
ANGELLIAUME S, ROSENBERG L, and RITCHIE M. Modeling the amplitude distribution of radar sea clutter[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(3): 319. doi: 10.3390/rs11030319 WARD K, TOUGH R J A, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. United Kingdom: Institute of Engineering Technology, 2013: 101-134. BALLERI A, NEHORAI A, and WANG Jian. Maximum likelihood estimation for compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gamma texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2007, 43(2): 775–779. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2007.4285370 尹志盈, 张玉石. 雷达海杂波统计特性建模研究[J]. 装备环境工程, 2017, 14(7): 29–34. doi: 10.7643/issn.1672-9242.2017.07.006YIN Zhiying and ZHANG Yushi. Radar sea clutter modeling of statistical characteristic[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2017, 14(7): 29–34. doi: 10.7643/issn.1672-9242.2017.07.006 SHUI Penglang, SHI Lixiang, YU Han, et al. Iterative maximum likelihood and outlier-robust bipercentile estimation of parameters of compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gaussian texture[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(11): 1572–1576. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2605129 于涵, 水鹏朗, 施赛楠, 等. 复合高斯海杂波模型下最优相干检测进展[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 109–118. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.012YU Han, SHUI Penglang, SHI Sainan, et al. Development of optimum coherent detection under compound- Gaussian clutter model[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 109–118. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.012 赵文静, 刘畅, 刘文龙, 等. K分布海杂波背景下基于最大特征值的雷达信号检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Chang, LIU Wenlong, et al. Maximum eigenvalue based radar signal detection method for K distribution sea clutter environment[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2235–2241. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171092 丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006 SHUI Penglang and LIU Ming. Subband adaptive GLRT-LTD for weak moving targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(1): 423–437. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140783 SHUI Penglang, YU Han, SHI Lixiang, et al. Explicit bipercentile parameter estimation of compound-Gaussian clutter with inverse Gamma distributed texture[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(2): 202–208. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0174 YU Han, SHUI Penglang, ZENG Weiliang, et al. Multiscan recursive bayesian method for parameter estimation of spatially-varying sea clutter models[C]. 2018 International Conference on Radar, Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8557270. 夏晓云, 黎鑫, 张玉石, 等. 基于相位的岸基雷达地海杂波分割方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(3): 552–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.10XIA Xiaoyun, LI Xin, ZHANG Yushi, et al. Sea-land clutter segmentation method of shore-based radar based on phase information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 552–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.10 BALAKRISHNAN N and COHEN A C. Order Statistics and Inference[M]. Boston: Academic Press, 1991: 7–17. WARD K D, BAKER C J, and WATTS S. Maritime surveillance radar. I. Radar scattering from the ocean surface[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1990, 137(2): 51–62. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1990.0009 孙娜, 刘继文, 肖东亮. 基于BFGS拟牛顿法的压缩感知SL0重构算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2408–2414. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170813SUN Na, LIU Jiwen, and XIAO Dongliang. SL0 reconstruction algorithm for compressive sensing based on BFGS quasi newton method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2408–2414. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170813 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
