Research on Efficient FPGA Bitstream Generation System Based on Mode Matching and Hierarchical Mapping
-
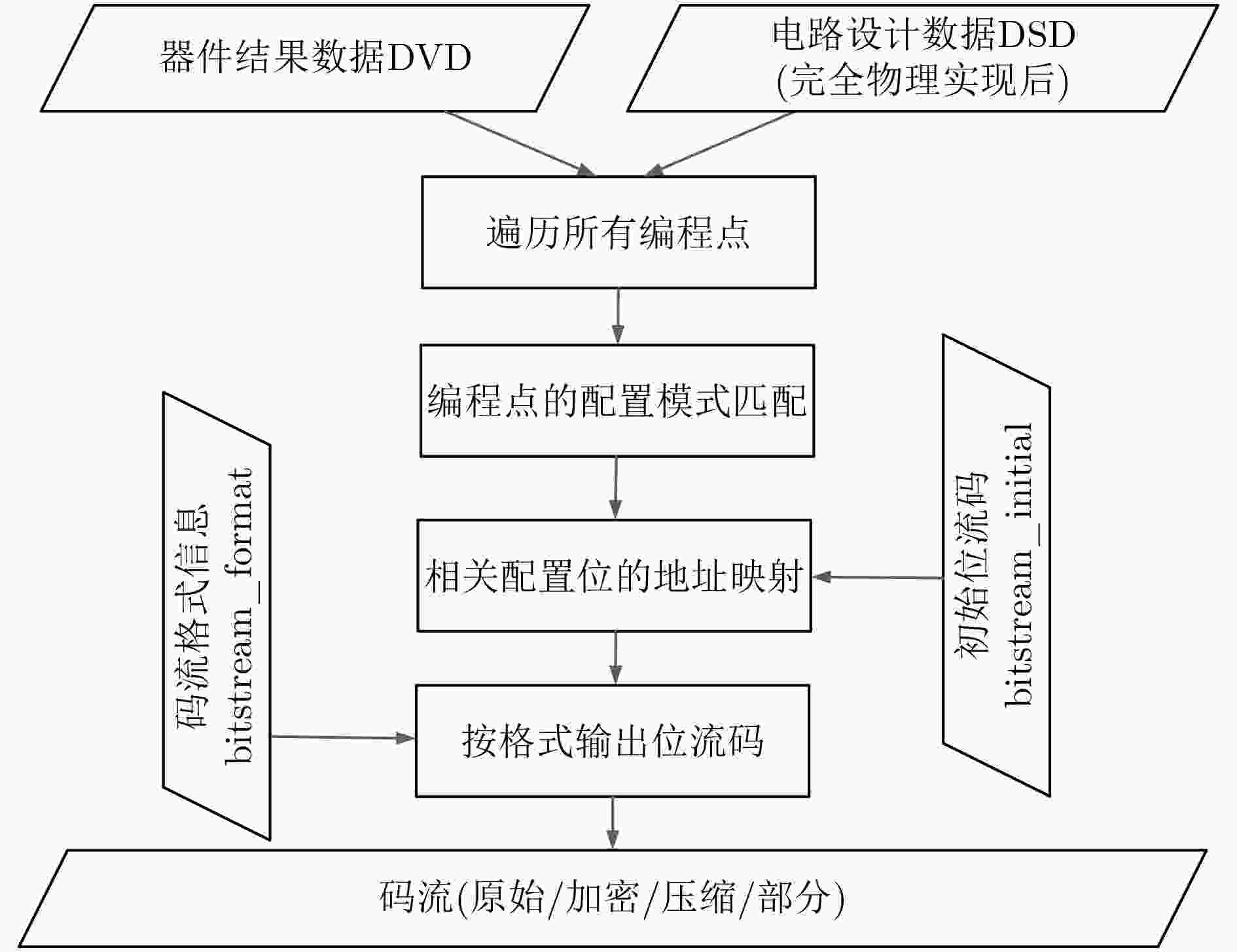
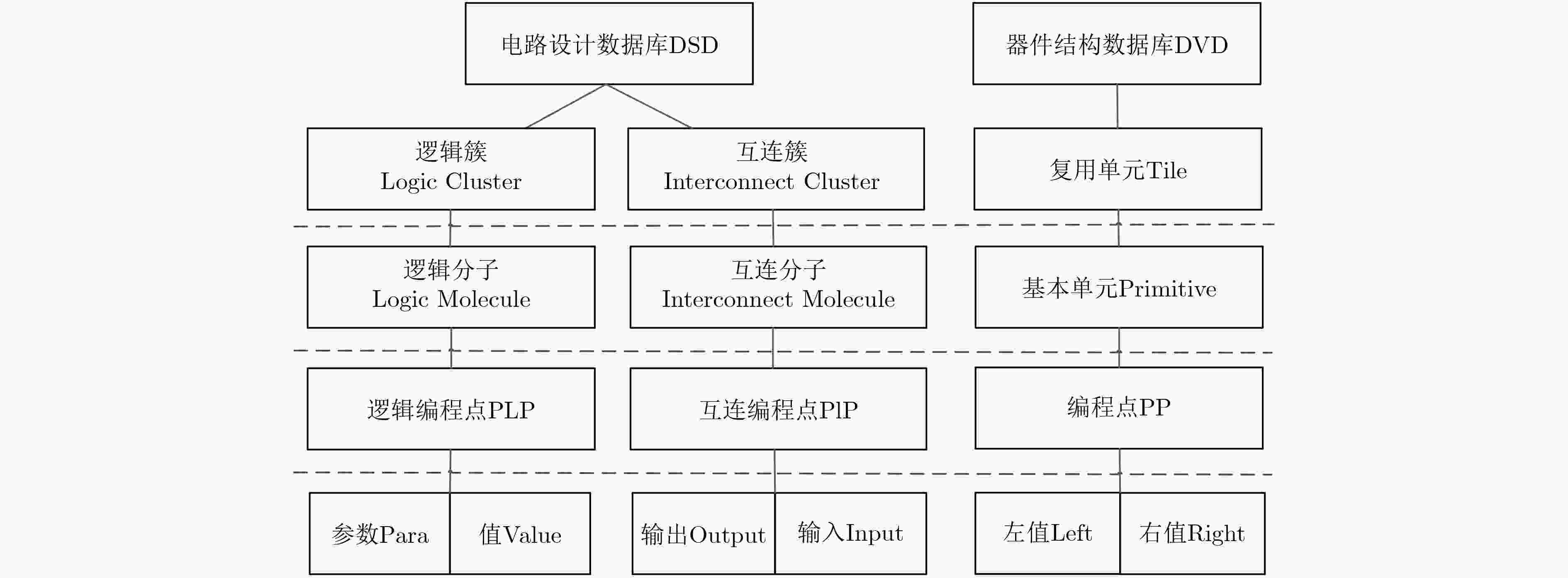
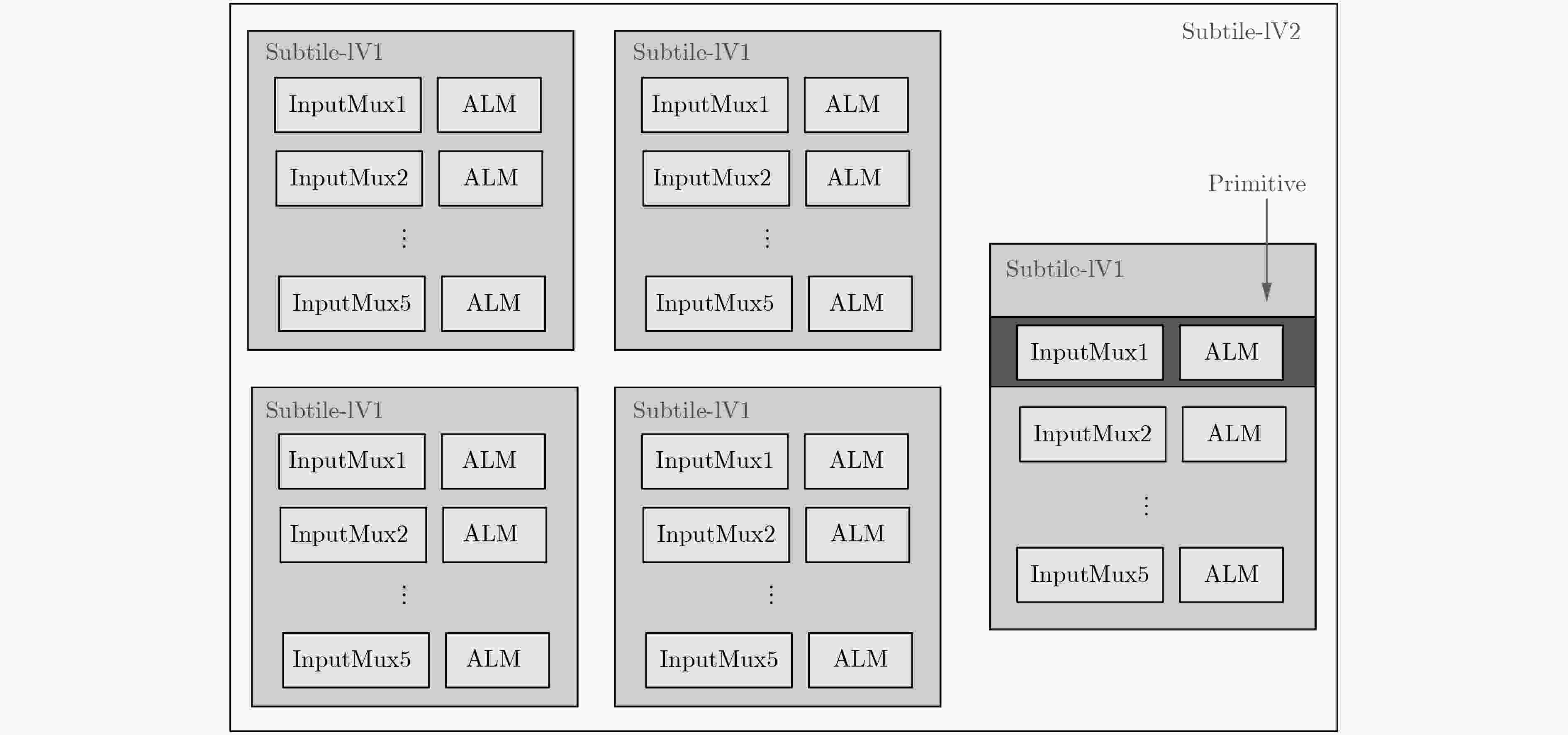
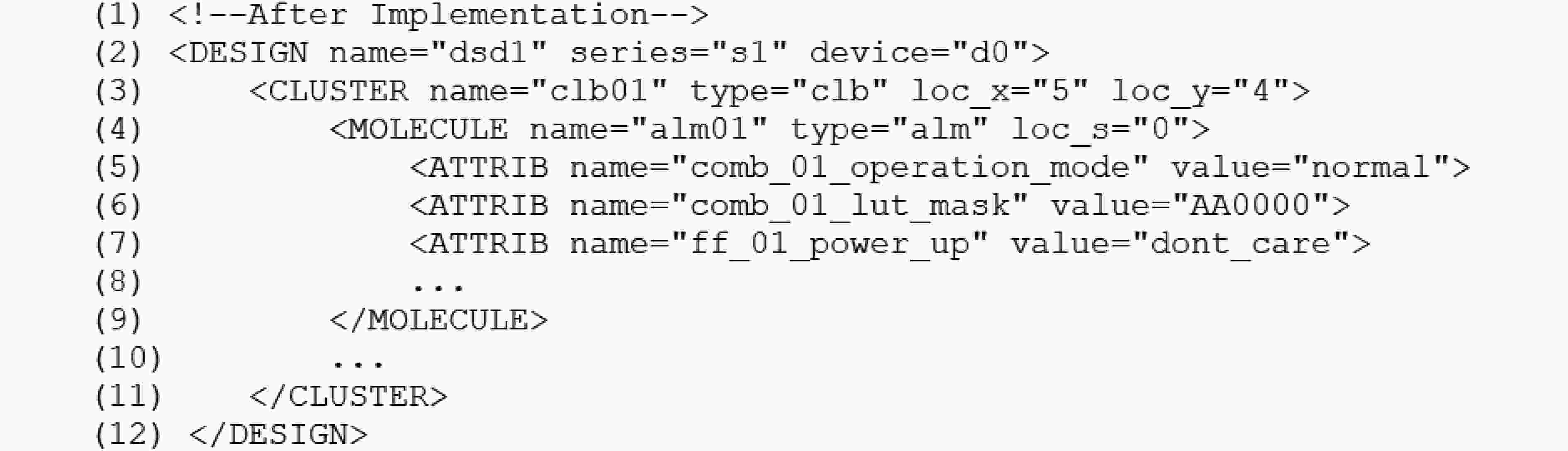
摘要: 码流生成在FPGA电子设计自动化(EDA)流程中,提供应用电路在芯片上物理实现所需的精准配置信息。现代FPGA的发展一方面呈现出器件规模及码流容量越来越大的趋势,另一方面越来越多可变阵列大小的嵌入式应用(例如eFPGA)又要求码流生成器具备更高的配置效率以及更精简的可重构数据库。针对码流生成时间增加的问题和阵列规模任意缩放的需求,该文提出一种模式匹配和层次映射的码流生成方法,即对编程单元按配置模式进行分类建模,在配置时按模型进行调用匹配,并采用了层次化的码流映射策略,使得数据库可随阵列排布调整动态生成。该方法可有效应对FPGA嵌入式应用中码流容量的增大以及阵列规模可变所带来的挑战,同时相比平面化的建模及映射方法,码流配置的时间复杂度由O(n)降低为O(lgn)。Abstract: Bitstream generator in FPGA Electronic Design Automation(EDA) offers precise configuration information, which enables the application circuits to be implemented on the target device. On one hand, modern FPGAs tend to have larger device scale and more configuration bits, on the other hand, embedded applications (e.g. eFPGAs) require better configuration efficiency and smaller, more adaptive database. In order to meet these new requirements, a bit-stream generation method is proposed which firstly models the configurable resources by configuration modes and matches the netlist with these models, then hierarchical mapping strategy is used to search every bit on a dynamically generated database determined by the array floorplan. This method well meets the challenges that embedded applications may bring-the surge of configuration bit count and the changeable size of the array. Compared to flattened modelling and mapping method, its time complexity is reduced from O(n) to O(lgn).
-
Key words:
- FPGA /
- Bitstream generation /
- Embedded /
- Configuration mode /
- Hierarchy
-
表 1 芯片相关数据库大小(kB)
器件模型* config_modes tile/primitive_first_addresses initial_bitstream bitstream_format_info 数据库总大小(kB) 器件a(3 M Gates) 512 10/15 226 2 765 器件b(10 M Gates) 512 32/15 226 2 787 器件c(30 M Gates) 512 99/15 226 2 854 器件d(50 M Gates) 512 158/15 226 2 913 器件e(70 M Gates) 512 210/15 226 2 965 器件f(90 M Gates) 512 268/15 226 2 1023 *注:器件模型均属一个系列,该系列包含10种复用单元 表 2 不同电路设计、相同芯片规模(同系列)下的码流配置时间
电路设计 需要配置的
码位总数(bit)码流配置
时间(s)电路1(用满25 k Gates器件资源) 5.8 k 0.016 电路2(用满1 M Gates器件资源) 250.4 k 0.682 电路3(用满10 M Gates器件资源) 2.3 M 6.360 电路4(用满30 M Gates器件资源) 7.0 M 19.419 电路5(用满50 M Gates器件资源) 11.5 M 30.334 电路6(用满80 M Gates器件资源) 18.4 M 50.886 表 3 相同电路设计、不同芯片规模(同系列)下的码流配置时间
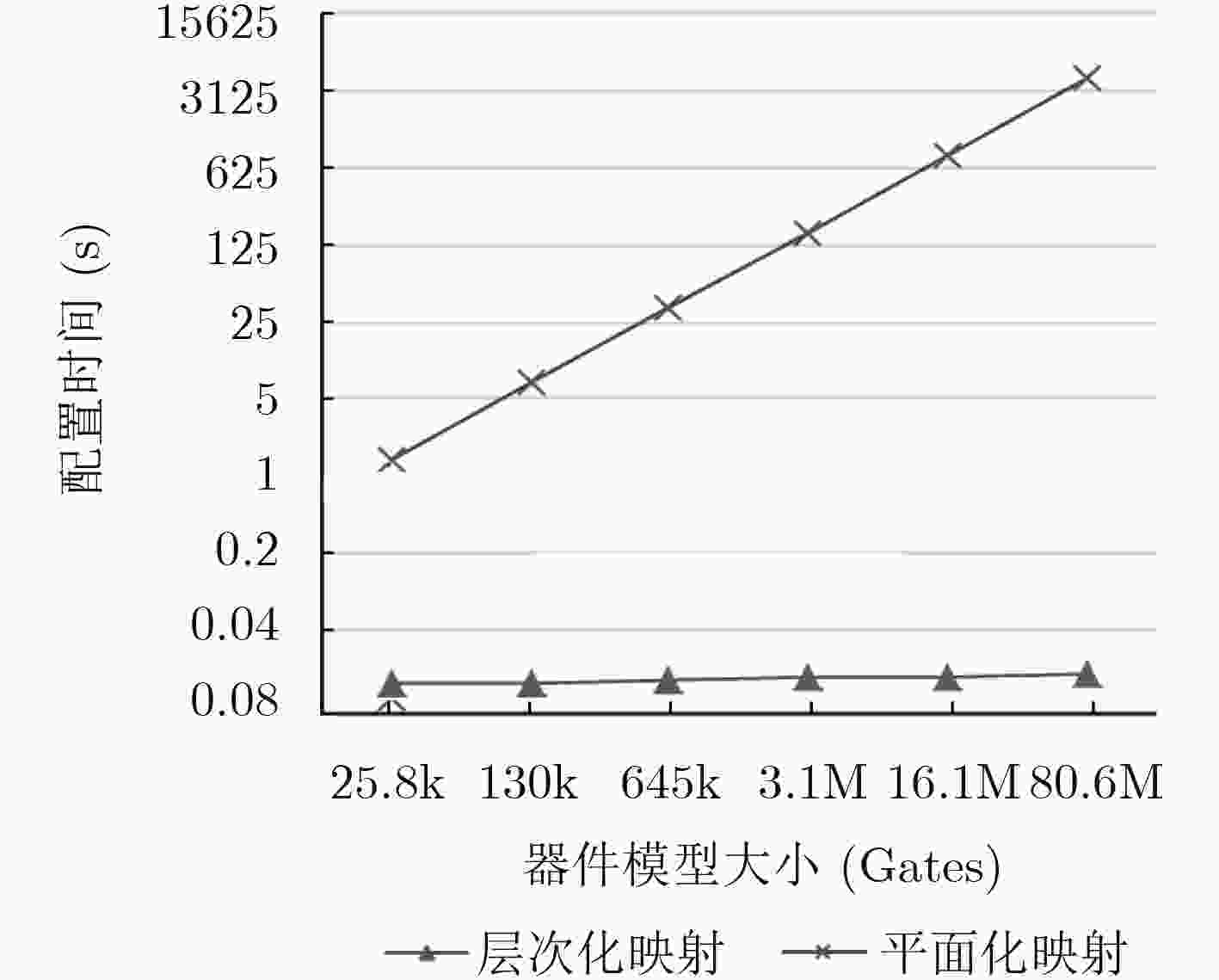
器件模型 映射层数l 全器件的码位总数n(bit) 平面化映射码流(传统方法)
配置时间t1(s)层次化映射码流(本文方法)
配置时间t2(s)器件1(25.8 k Gates) 3 12.5 k 1.4 0.013 器件2(130 k Gates) 4 62.5 k 7.0 0.013 器件3(645 k Gates) 5 312.5 k 34.1 0.014 器件4(3.1 M Gates) 6 1.5 M 155.2 0.015 器件5(16.1 M Gates) 7 7.8 M 820.2 0.015 器件6(80.6 M Gates) 8 39 M 4066.0 0.016 -
王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040 IŠA R and MATOUŠEK J. A novel architecture for LZSS compression of configuration bitstreams within FPGA[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Symposium on Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits & Systems, Dresden, Germany, 2017: 171–176. Intel Inc. UGS10CONFIG-Intel stratix 10 configuration user guide[EB/OL]. https://www.intel.com/content/dam/altera-www/global/en_US/pdfs/literature/hb/stratix-10/ug-s10-config.pdf, 2018. ABDELLATIF K M, CHOTIN-AVOT R, and MEHREZ H. Protecting FPGA bitstreams using authenticated encryption[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International New Circuits and Systems Conference, Paris, France, 2013: 1–4. Xilinx Inc. UG909-Vivado design suite user guide partial reconfiguration[OL]. https://www.xilinx.com/support/documentation/sw_manuals/xilinx2016_1/ug909-vivado-partial-reconfiguration.pdf, 2018. PATTERSON C and GUCCIONE S A. JBits TM design abstractions[C]. Proceedings of the 9th Annual IEEE Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, Rohnert Park, USA, 2001: 251–252. POETTER A, HUNTER J, PATTERSON C, et al. JHDLBits: The merging of two worlds[C]. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference Field Programmable Logic and Application, Leuven, Belgium, 2004: 414–423. PHAM K D, HORTA E, and KOCH D. BITMAN: A tool and API for FPGA bitstream manipulations[C]. Proceedings of 2017 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2017: 894–897. STEINER N, WOOD A, SHOJAEI H, et al. Torc: Towards an open-source tool flow[C]. Proceedings of the 19th ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, USA, 2011: 41–44. TOWNSEND T and NELSON B. Vivado design interface: An export/import capability for vivado FPGA designs[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Ghent, Belgium, 2017: 1–7. NOTE J B and RANNAUD É. From the bitstream to the netlist[C]. Proceedings of the 16th International ACM/SIGDA Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, USA, 2008: 264. BENZ F, SEFFRIN A, and HUSS S A. Bil: A tool-chain for bitstream reverse-engineering[C]. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Oslo, Norway, 2012: 735–738. DING Zheng, WU Qiang, ZHANG Yizhong, et al. Deriving an NCD file from an FPGA bitstream: Methodology, architecture and evaluation[J]. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2013, 37(3): 299–312. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2012.12.003 ROSE J, LUU J, YU Chiwai, et al. The VTR project: Architecture and CAD for FPGAs from verilog to routing[C]. Proceedings of the ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, USA, 2012: 77–86. HUNG E, ESLAMI F, and WILTON S J E. Escaping the academic sandbox: Realizing VPR circuits on Xilinx devices[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 21st Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, Seattle, USA, 2013: 45–52. HUNG E. Mind the (synthesis) gap: Examining where academic FPGA tools lag behind industry[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, London, UK, 2015: 1–4. SONI R K, STEINER N, and FRENCH M. Open-source bitstream generation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE 21st Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, Seattle, USA, 2013: 105–112. 李智华, 黄娟, 李威, 等. 一种SRAM型FPGA互连资源的位流码配置方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2016, 14(1): 136–142. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201601.0136LI Zhihua, HUANG Juan, LI Wei, et al. An automatic approach for bitstream configuration of routing resource in SRAM FPGA[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2016, 14(1): 136–142. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201601.0136 -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
