Transfer Weight Based Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation
-
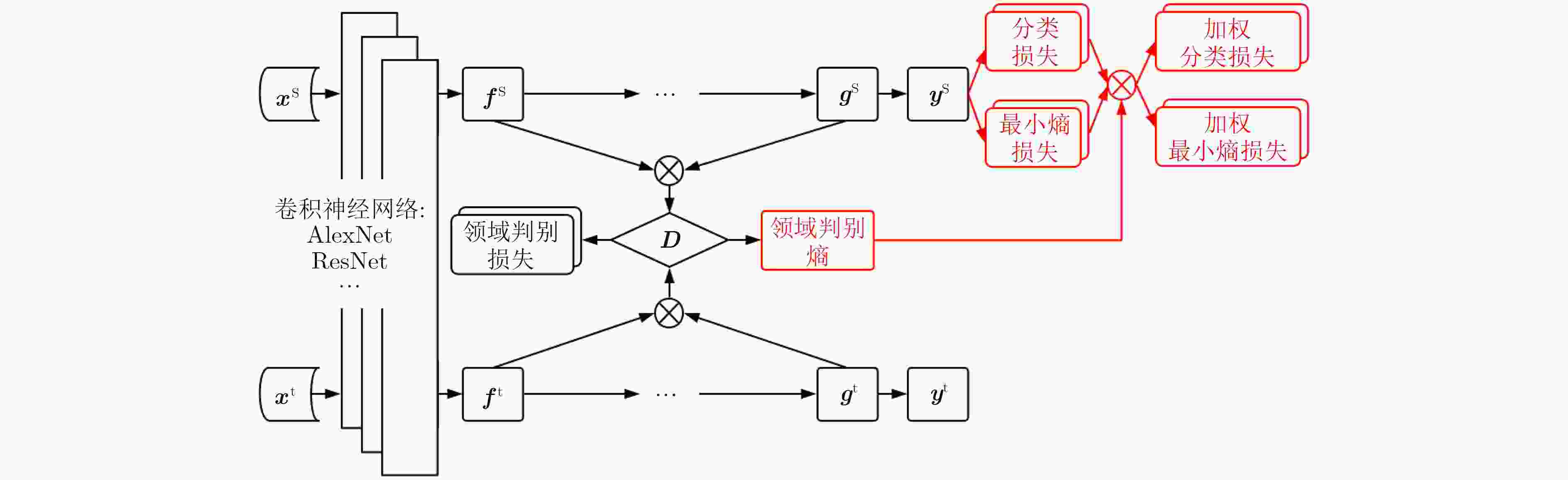
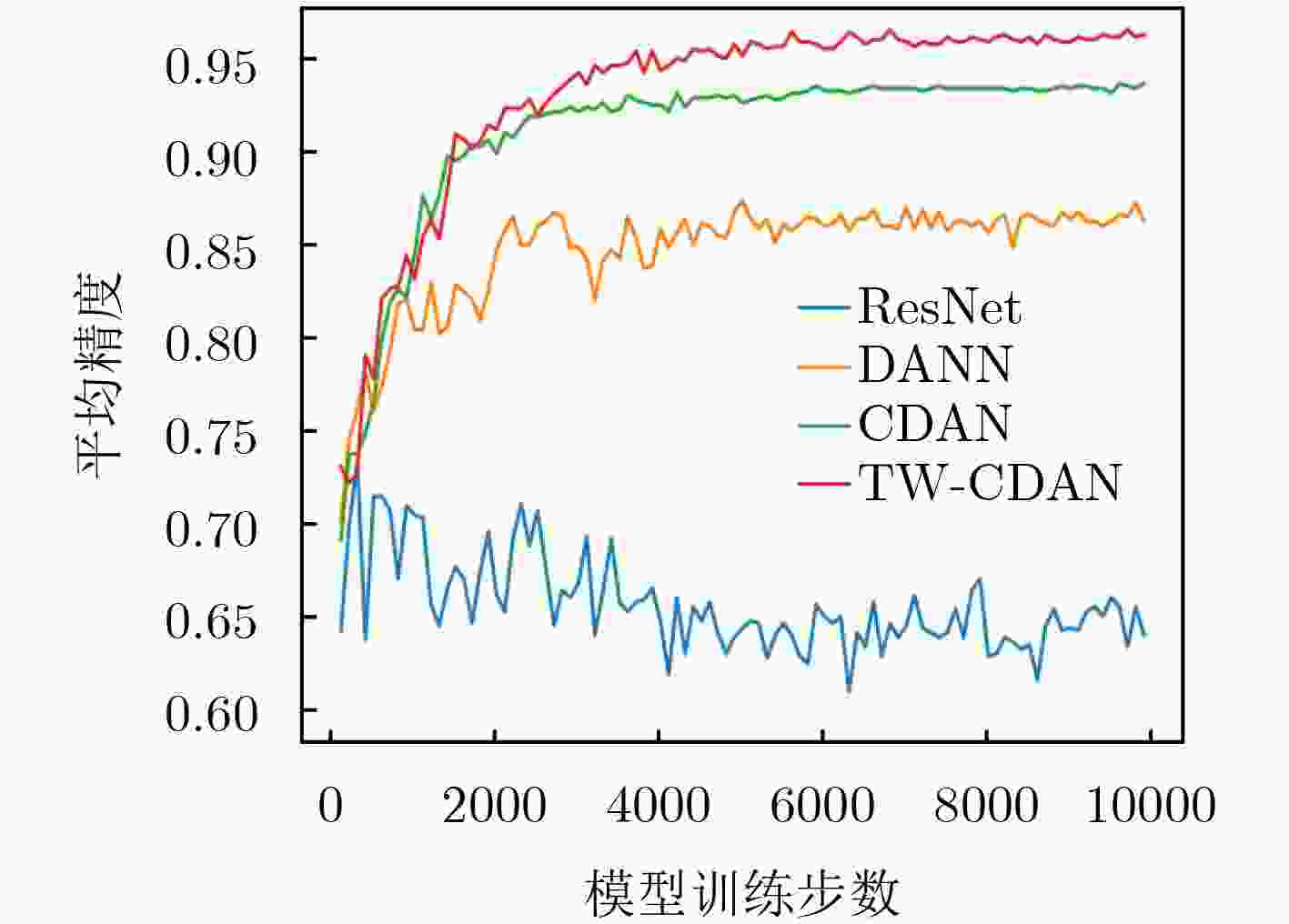
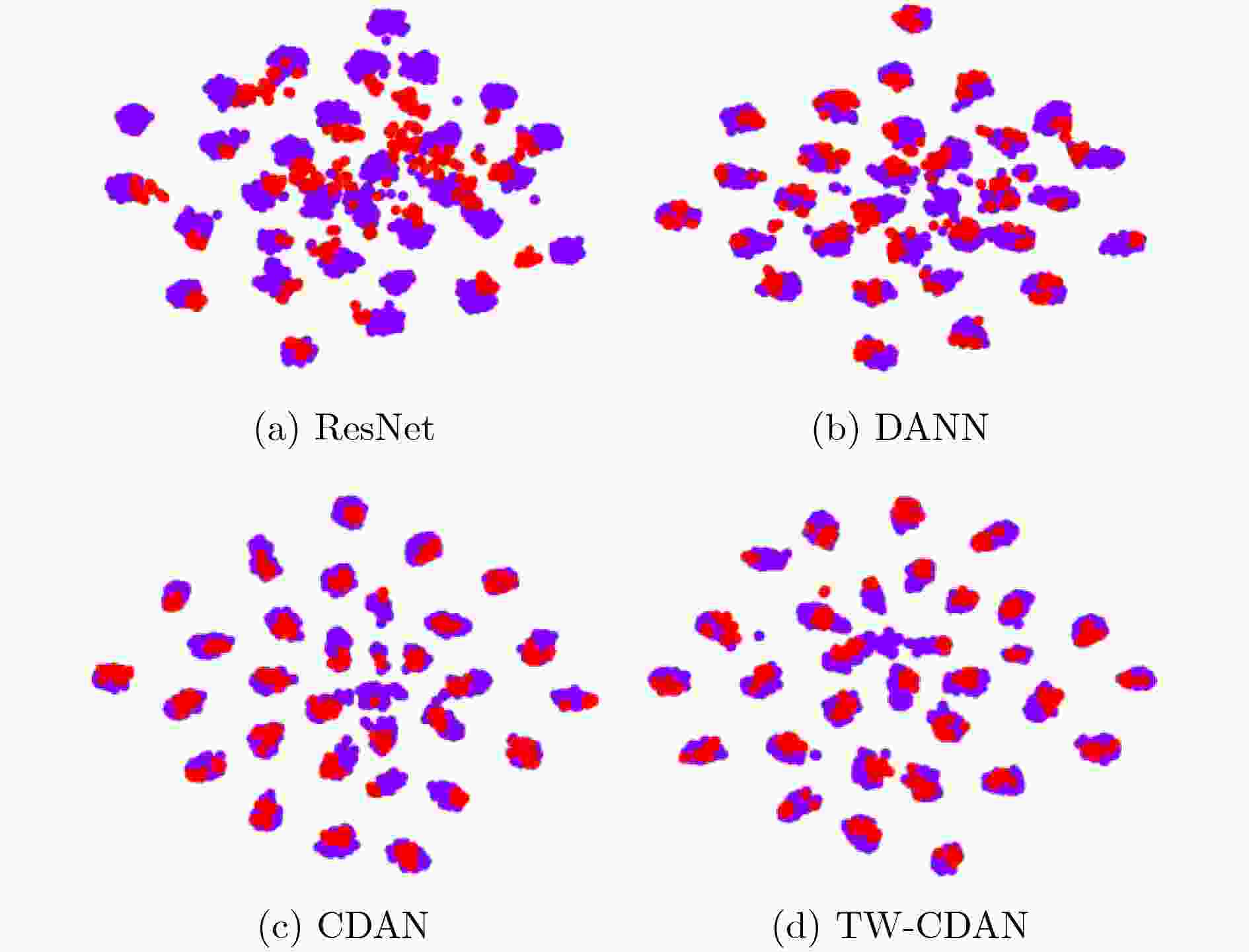
摘要: 针对条件对抗领域适应(CDAN)方法未能充分挖掘样本的可迁移性,仍然存在部分难以迁移的源域样本扰乱目标域数据分布的问题,该文提出一种基于迁移权重的条件对抗领域适应(TW-CDAN)方法。首先利用领域判别模型的判别结果作为衡量样本迁移性能的主要度量指标,使不同的样本具有不同的迁移性能;其次将样本的可迁移性作为权重应用在分类损失和最小熵损失上,旨在消除条件对抗领域适应中难以迁移样本对模型造成的影响;最后使用Office-31数据集的6个迁移任务和Office-Home数据集的12个迁移任务进行了实验,该方法在14个迁移任务上取得了提升,在平均精度上分别提升1.4%和3.1%。Abstract: Considering the failure of the Conditional adversarial Domain AdaptatioN(CDAN) to fully utilize the sample transferability, which still struggle with some hard-to-transfer source samples disturbed the distribution of the target domain samples, a Transfer Weight based Conditional adversarial Domain AdaptatioN(TW-CDAN) is proposed. Firstly, the discriminant results in the domain discriminant model as the main factor are employed to measure the transfer performance. Then the weight is applied to class loss and minimum entropy loss. It is for eliminating the influence of hard-to-transfer samples of the model. Finally, experiments are carried out using the six domain adaptation tasks of the Office-31 dataset and the 12 domain adaptation tasks of the Office-Home dataset. The proposed method improves the 14 domain adaptation tasks and increases the average accuracy by 1.4% and 3.1% respectively.
-
Key words:
- Transfer learning /
- Domain adaptation /
- Adversarial learning /
- Transfer Weight(TW)
-
表 1 Office-31数据集结果(使用平均精度进行评价)
方法 A→W D→W W→D A→D D→A W→A 平均 ResNet-50[17] 68.4 96.7 99.3 68.9 62.5 60.7 76.1 DAN[7] 80.5 97.1 99.6 78.6 63.6 62.8 80.4 RTN[8] 84.5 96.8 99.4 77.5 66.2 64.8 81.6 DANN[10] 82.0 96.9 99.1 79.7 68.2 67.4 82.2 ADDA[11] 86.2 96.2 98.4 77.8 69.5 68.9 82.9 JAN[18] 85.4 97.4 99.8 84.7 68.6 70.0 84.3 GTA[19] 89.5 97.9 99.8 87.7 72.8 71.4 86.5 CDAN[13] 93.1 98.6 100.0 92.9 71.0 69.3 87.5 TW-CDAN 94.9 99.2 100.0 94.0 72.7 72.5 88.9 表 2 Office-Home数据集结果(使用平均精度进行评价)
方法 Ar→Cl Ar→Pr Ar→Rw Cl→Ar Cl→Pr Cl→Rw Pr→Ar Pr→Cl Pr→Rw Rw→Ar Rw→Cl Rw→Pr 平均 ResNet-50[17] 34.9 50.0 58.0 37.4 41.9 46.2 38.5 31.2 60.4 53.9 41.2 59.9 46.1 DAN[7] 43.6 57.0 67.9 45.8 56.5 60.4 44.0 43.6 67.7 63.1 51.5 74.3 56.3 DANN[10] 45.6 59.3 70.1 47.0 58.5 60.9 46.1 43.7 68.5 63.2 51.8 76.8 57.6 JAN[18] 45.9 61.2 68.9 50.4 59.7 61.0 45.8 43.4 70.3 63.9 52.4 76.8 58.3 CDAN[13] 50.6 65.9 73.4 55.7 62.7 64.2 51.8 49.1 74.5 68.2 56.9 80.7 62.8 TW-CDAN 48.8 71.1 76.7 61.6 68.9 70.2 60.4 46.6 77.9 71.3 55.4 81.9 65.9 表 3 不同迁移权重设置在Office-31数据集结果(使用平均精度进行评价)
方法 A→W D→W W→D A→D D→A W→A 平均 CDAN[13] 93.1 98.6 100.0 92.9 71.0 69.3 87.5 CDAN(S) 93.0 98.7 100.0 92.7 71.0 69.1 87.4 TW-CDAN(E) 93.7 98.8 100.0 93.4 71.5 71.3 88.1 TW-CDAN(C) 94.2 98.9 100.0 93.1 72.1 71.8 88.4 TW-CDAN 94.9 99.2 100.0 94.0 72.7 72.5 88.9 -
YOSINSKI J, CLUNE J, BENGIO Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks?[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 3320-3328. PAN S J and YANG Qiang. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345–1359. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 GEBRU T, HOFFMAN J, LI Feifei, et al. Fine-grained recognition in the wild: A multi-task domain adaptation approach[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1358–1367. GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Domain adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification: A deep learning approach[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, Bellevue, USA, 2011: 513–520. WANG Mei and DENG Weihong. Deep visual domain adaptation: A survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 312: 135–153. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.083 GRETTON A, BORGWARDT K, RASCH M, et al. A kernel method for the two-sample-problem[C]. Proceedings of the 19th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2007: 513–520. LONG Mingsheng, CAO Yue, WANG Jianmin, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 97–105. LONG Mingsheng, ZHU Han, WANG Jianmin, et al. Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks[C]. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 2208–2217. GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. GANIN Y, USTINOVA E, AJAKAN H, et al. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17(1): 2096–2030. TZENG E, HOFFMAN J, SAENKO K, et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2962–2971. MIRZA M and OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.1784, 2014. LONG Mingsheng, CAO Zhangjie, WANG Jianmin, et al. Conditional adversarial domain adaptation[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 1647–1657. GRANDVALET Y and BENGIO Y. Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2004: 529–536. SAENKO K, KULIS B, FRITZ M, et al. Adapting visual category models to new domains[C]. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 2010: 213–226. VENKATESWARA H, EUSEBIO J, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Deep hashing network for unsupervised domain adaptation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5385–5394. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. LONG Mingsheng, ZHU Han, WANG Jianmin, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation with residual transfer networks[C]. Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 136–144. SANKARANARAYANAN S, BALAJI Y, CASTILLO C D, et al. Generate to adapt: Aligning domains using generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8503–8512. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
