An Improved Four-component Decomposition Method Based on the Characteristic of Polarization and the Optimal Parameters of PolInSAR
-
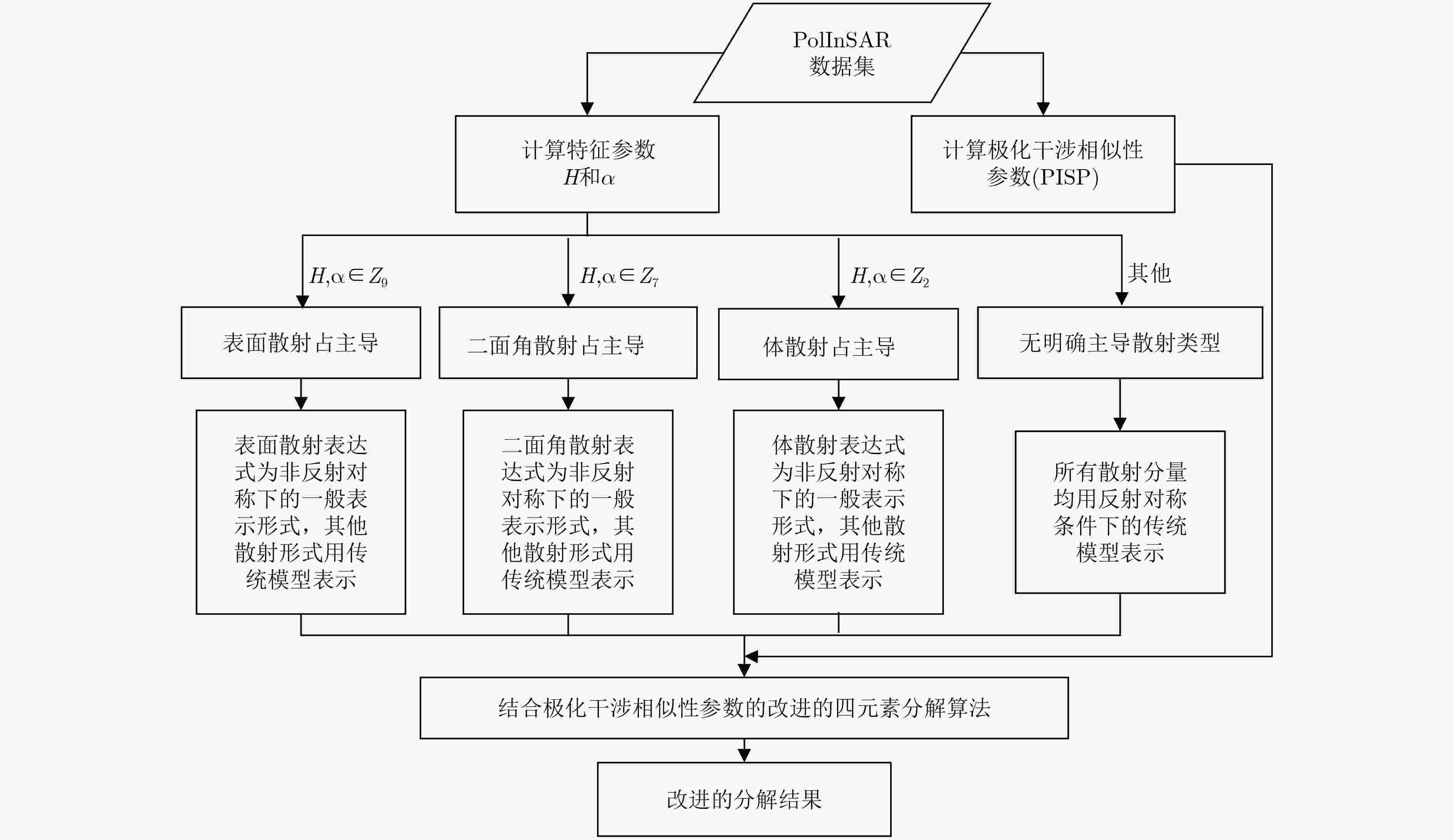
摘要: 雷达目标的后向散射对目标姿态与雷达视线的相对几何关系十分敏感,同一目标相对于雷达视线的姿态不同时,散射特性十分不同。倾斜地表和倾斜建筑物等目标可能扭转后向散射回波的极化基,进而导致交叉极化分量过高,图像体散射成分过估计。该文针对图像体散射成分过估计的现象,提出一种基于极化特征参数(
$ H/{\alpha} $ )和极化干涉相似性参数(PISP)的极化干涉分解方法。该方法充分考虑了散射体在雷达视线方向上的散射多样性,对不同取向的倾斜地表和倾斜建筑物等目标产生的交叉极化分量进行更好的适配,得到更好的分解结果。最后,利用由中国科学院电子学研究所获取的机载C波段全极化干涉数据验证该方法在极化干涉分解中的有效性。实验结果表明,该改进算法可以有效、正确地区分地物散射特性。-
关键词:
- 极化干涉合成孔径雷达 /
- H/a分解 /
- 极化干涉相似性参数 /
- 四元素分解 /
- 极化干涉最优相干参数
Abstract: The backscattering of the radar targets is sensitive to the relative geometry between orientations of the targets and the radar line of sight. When the orientations of the same target are different from the radar line of sight, the scattering characteristics are quite different. Targets such as inclined ground and inclined buildings may reverse the polarization base of the backscattered echo, which causes the cross-polarization component to be too high and the volume scattering component of the image is overestimated. In this paper, a polarimetric interferometric decomposition method based on polarimetric parameters ($ H/{\alpha} $ ) and Polarimetric Interferometric Similarity Parameters (PISP) is proposed to solve the overestimation problem. The method makes full use of the scattering diversity of the scatterer in the radar line of sight. The cross-polarization components generated by targets such as inclined grounds and inclined buildings with different orientations are better adapted to obtain better decomposition results. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method in polarimetric interferometric decomposition is verified by the airborne C-band PolInSAR data obtained by the Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The experimental results show that the proposed improved algorithm can distinguish the scattering characteristics of terrain types effectively and correctly. -
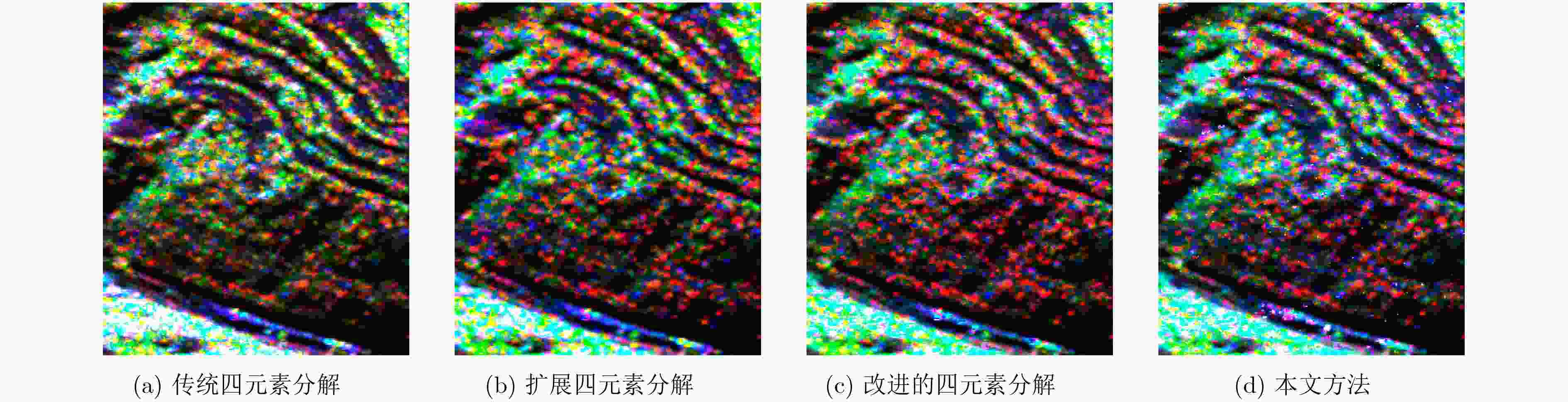
表 1 散射功率量化统计
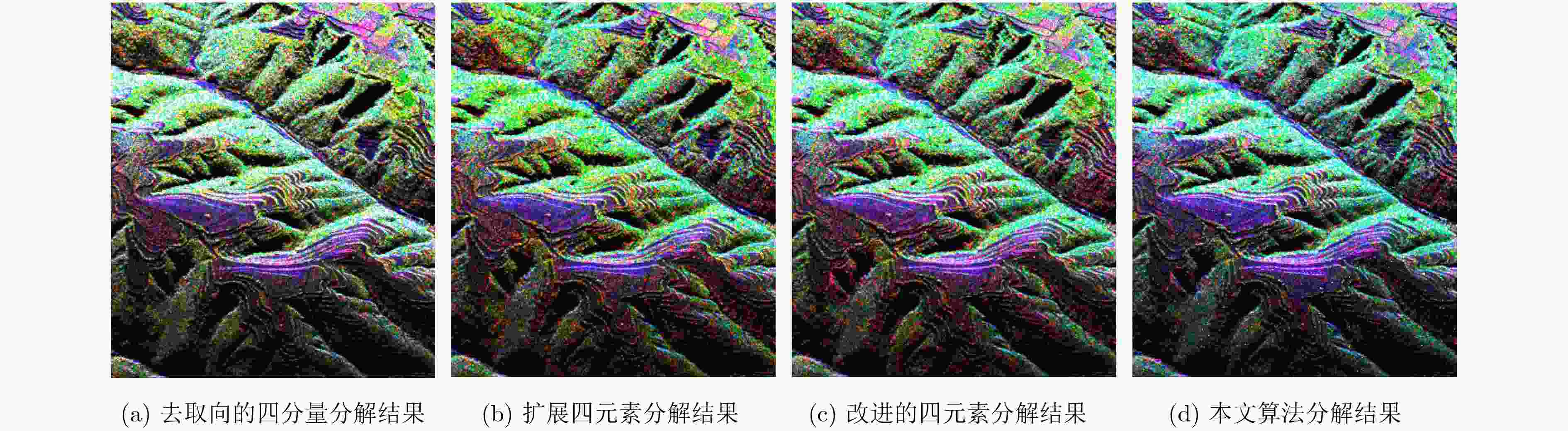
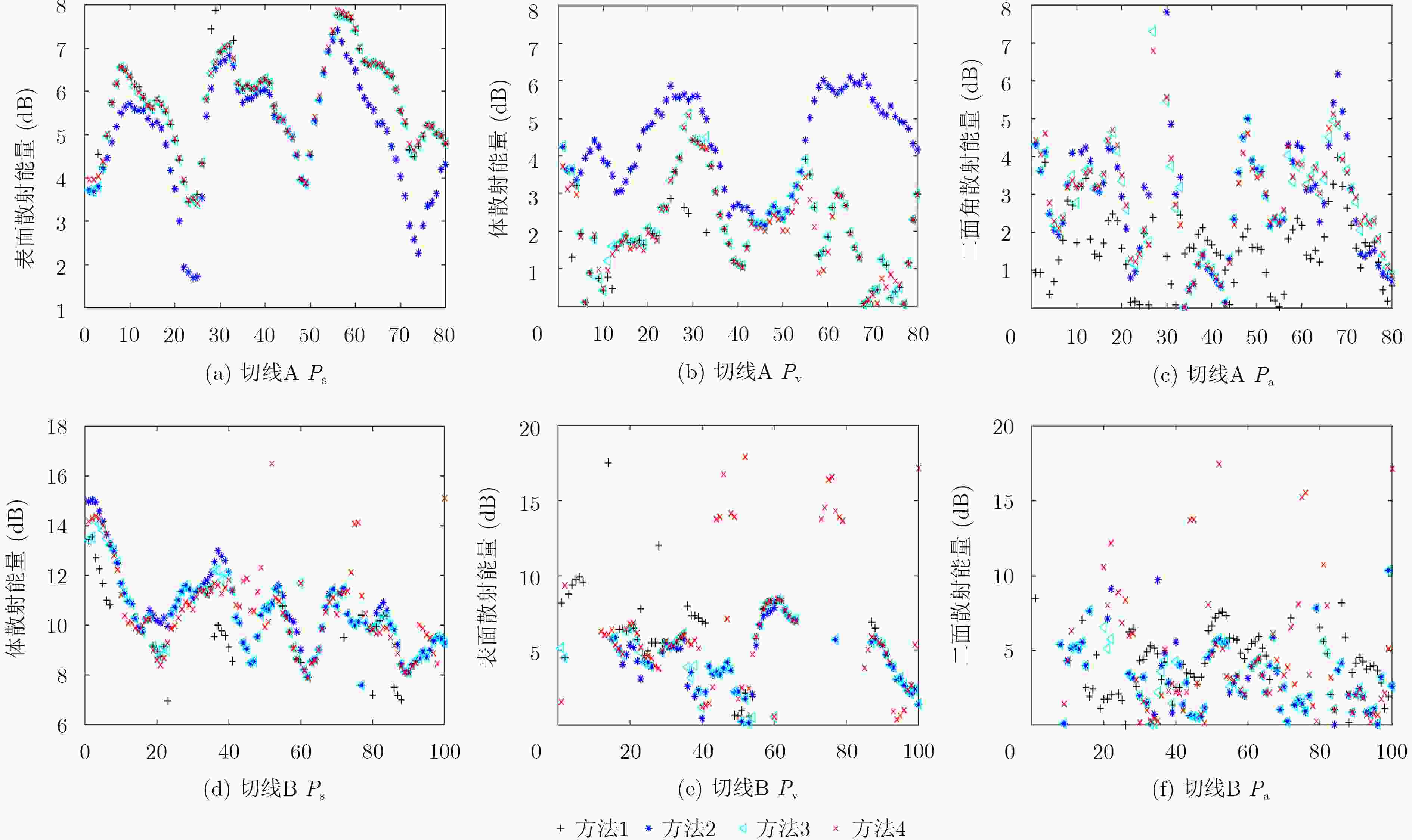
分解方法 ${P_{\rm{v}}}$ ${P_{\rm{s}}}$ ${P_{\rm{d}}}$ ${P_{\rm{c}}}$ 传统的四元素分解算法 0.8664 0.0227 0.1038 0.0071 扩展的四元素分解算法 0.8338 0.0258 0.1309 0.0095 改进的四元素分解算法 0.7563 0.0267 0.2087 0.0083 本文方法 0.7304 0.0326 0.2283 0.0087 表 2 典型区域1散射功率量化统计
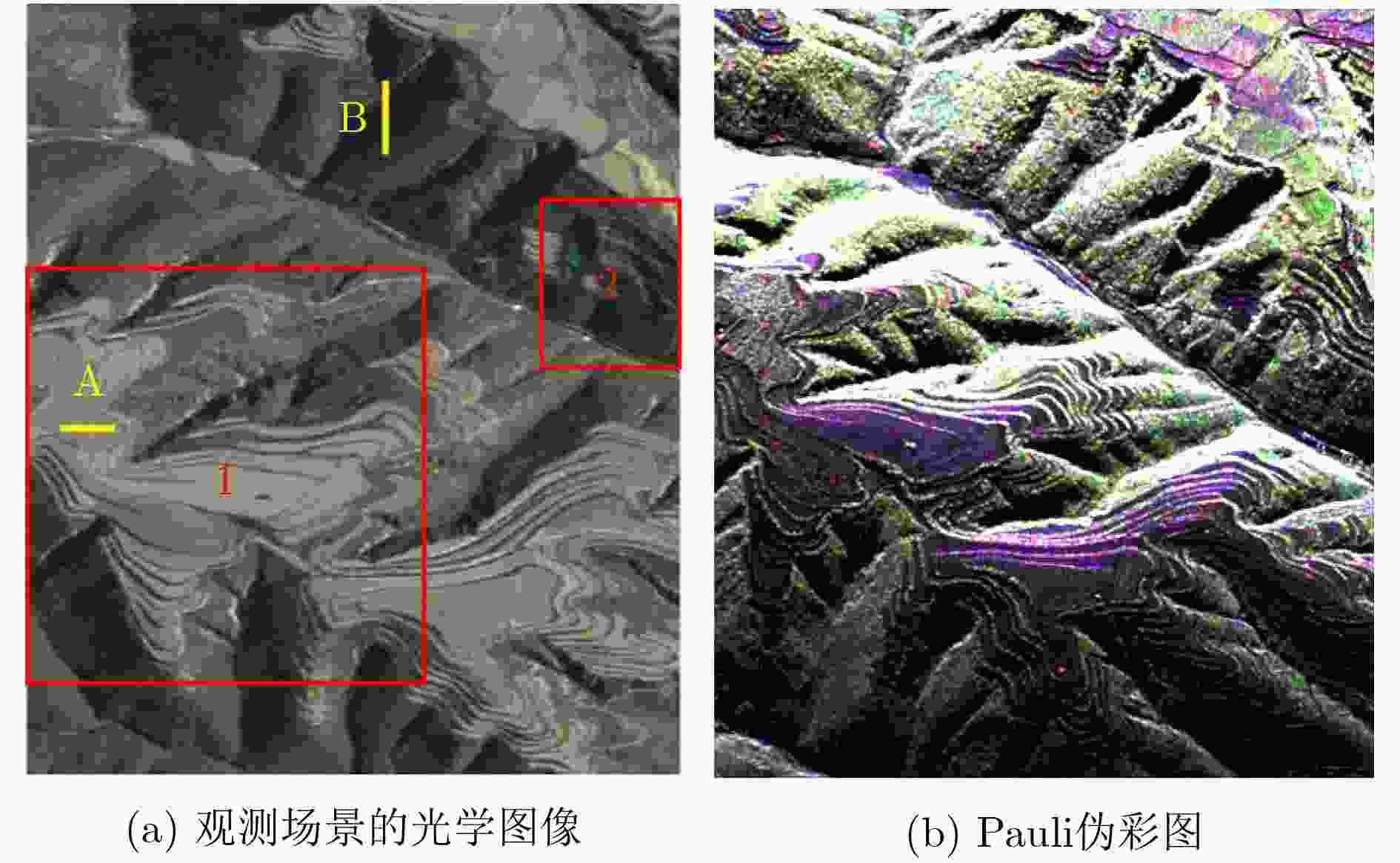
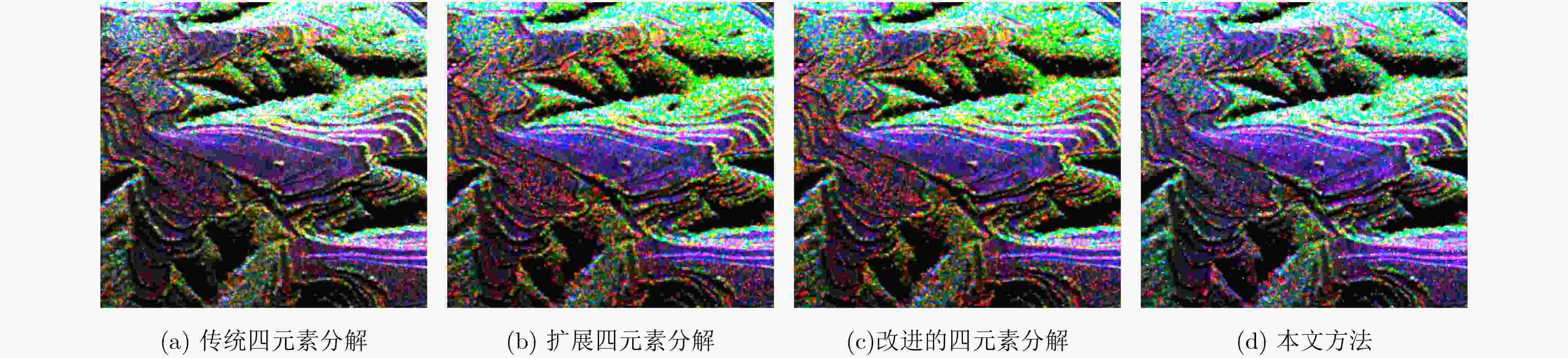
分解方法 ${P_{\rm{v}}}$ ${P_{\rm{s}}}$ ${P_{\rm{d}}}$ ${P_{\rm{c}}}$ 传统的四元素分解算法 0.8664 0.0227 0.1028 0.0081 扩展的四元素分解算法 0.7338 0.0258 0.2289 0.0115 改进的四元素分解算法 0.7563 0.0267 0.2077 0.0093 本文方法 0.7304 0.0326 0.2264 0.0106 表 3 典型区域2散射功率量化统计
分解方法 ${P_{\rm{v}}}$ ${P_{\rm{s}}}$ ${P_{\rm{d}}}$ ${P_{\rm{c}}}$ 传统的四元素分解算法 0.7737 0.0330 0.1847 0.0086 扩展的四元素分解算法 0.7909 0.0397 0.1615 0.0079 改进的四元素分解算法 0.7283 0.0508 0.2105 0.0104 本文方法 0.7148 0.0525 0.2216 0.0111 表 4 典型区域2分解算法准确性统计结果
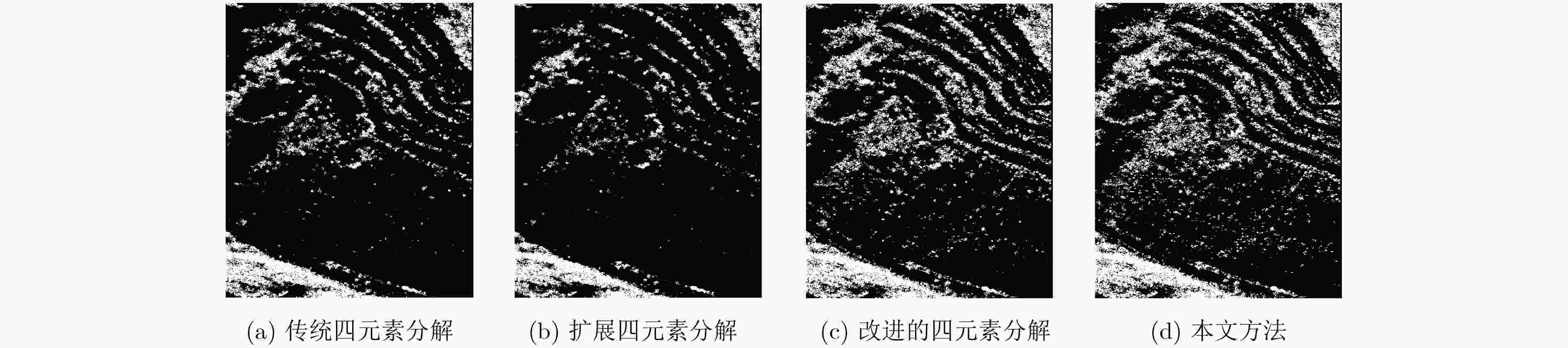
分解方法 传统的四元素分解算法 扩展的四元素分解算法 改进的四元素分解算法 本文方法 二面角散射像素点个数 提取得到的二面角散射像素点个数 47986 41571 52612 55462 63625 提取准确性(%) 75.42 66.91 82.69 87.17 -
CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 SALEHI M, MAGHSOUDI Y, and MOHAMMADZADEH A. Assessment of the potential of H/A/Alpha decomposition for polarimetric interferometric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(4): 2440–2451. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2780195 YAMAGUCHI Y, MORIYAMA T, ISHIDO M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(8): 1699–1706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084 FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 QUAN Sinong, XIANG Deliang, XIONG Boli, et al. A hierarchical extension of general four-component scattering power decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 856. doi: 10.3390/rs9080856 SUN Xiang, SONG Hongjun, WANG R, et al. High-resolution polarimetric SAR image decomposition of urban areas based on a POA correction method[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 9(4): 363–372. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2017.1418989 KUMAR A, PANIGRAHI R K, and DAS A. Three-component decomposition technique for hybrid-pol SAR data[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(9): 1569–1574. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0298 XIANG Deliang, WANG Wei, TANG Tao, et al. Multiple-component polarimetric decomposition with new volume scattering models for PolSAR urban areas[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(3): 410–419. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0105 CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. doi: 10.1109/36.718859 CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, LI Yongzhen, et al. Adaptive model-based polarimetric decomposition using PolInSAR coherence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1705–1718. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2253780 CHEN Siwei, OHKI M, SHIMADA M, et al. Deorientation effect investigation for model-based decomposition over oriented built-up areas[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 273–277. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2203577 CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Uniform polarimetric matrix rotation theory and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4756–4770. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2284359 陈思伟, 李永祯, 王雪松, 等. 极化SAR目标散射旋转域解译理论与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. doi: 10.12000/JR17033CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, et al. Polarimetric SAR target scattering interpretation in rotation domain: Theory and application[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. doi: 10.12000/JR17033 MAURYA H and PANIGRAHI R K. Non-negative scattering power decomposition for PolSAR data interpretation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(6): 593–602. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0581 王春乐, 李光廷, 禹卫东. 改进的极化SAR图像三分量分解方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(7): 980–986. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.06.013WANG Chunle, LI Guangting, and YU Weidong. Improved three-component scattering power decomposition for polarimetric SAR image[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(7): 980–986. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2013.06.013 XIE Qinghua, ZHU Jianjun, LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M, et al. A modified general polarimetric model-based decomposition method with the simplified Neumann volume scattering model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(8): 1229–1233. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2830503 CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. General polarimetric model-based decomposition for coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1843–1855. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2255615 ARII M, VAN ZYL J J, and KIM Y. A general characterization for polarimetric scattering from vegetation canopies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(9): 3349–3357. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2010.2046331 SATO A, YAMAGUCHI Y, SINGH G, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with extended volume scattering model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(2): 166–170. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2011.2162935 许丽颖, 李世强, 邓云凯, 等. 基于极化干涉相似性参数的四元素分解[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(4): 908–914. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01095XU Liying, LI Shiqiang, DENG Yunkai, et al. Four-component decomposition based on polarimetric interferometric similarity parameter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(4): 908–914. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01095 LATRACHE H, OUARZEDDINE M, and SOUISSI B. Improved model-based polarimetric decomposition using the POLINSAR similarity parameter[J]. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2016, XLI-B7: 847–850. doi: 10.5194/isprs-archives-XLI-B7-847-2016 -







 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
