Channel Estimation Algorithm of Maritime Sparse Channel Based on Fast Bayesian Matching Pursuit Optimization
-
摘要:
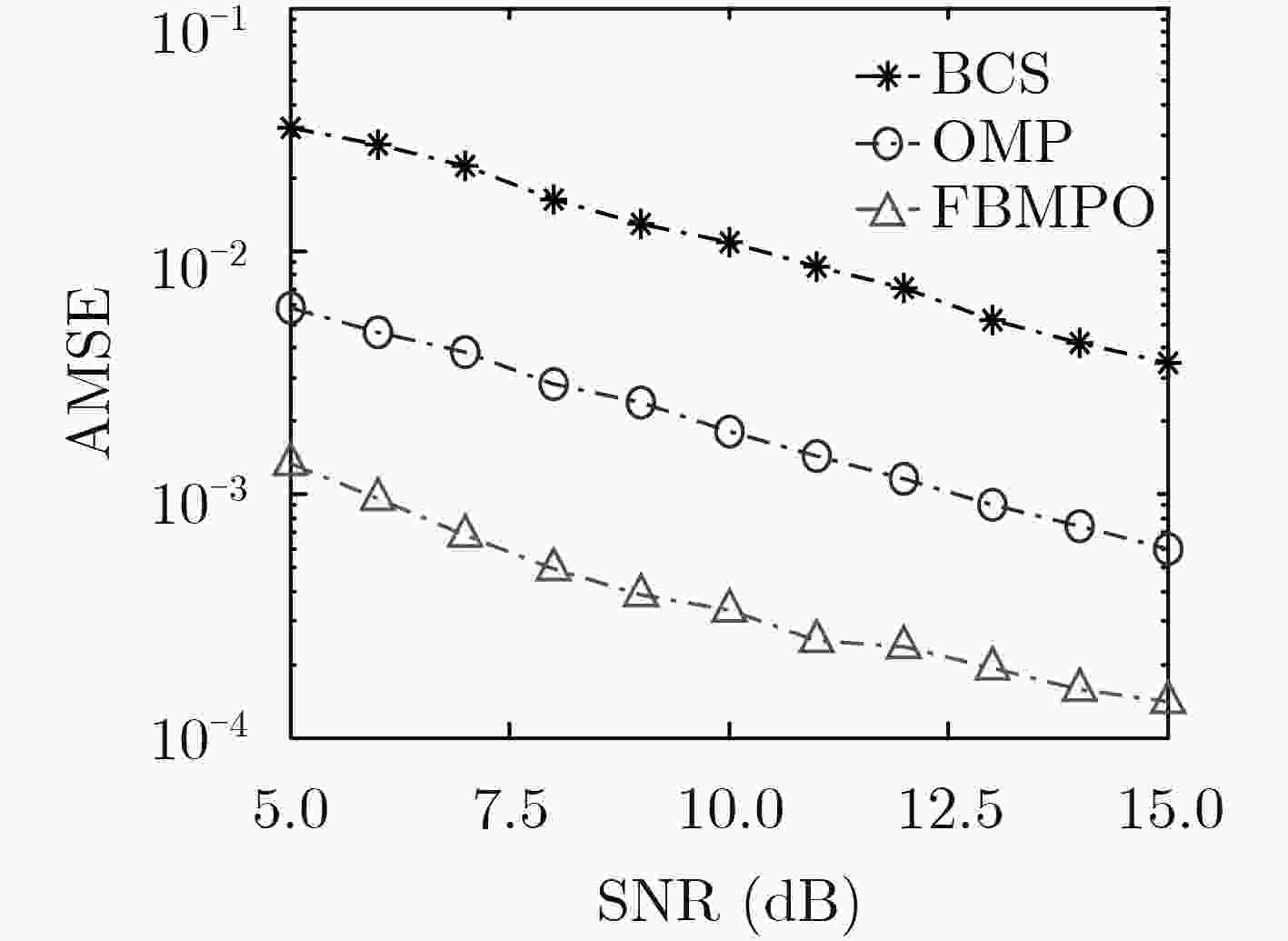
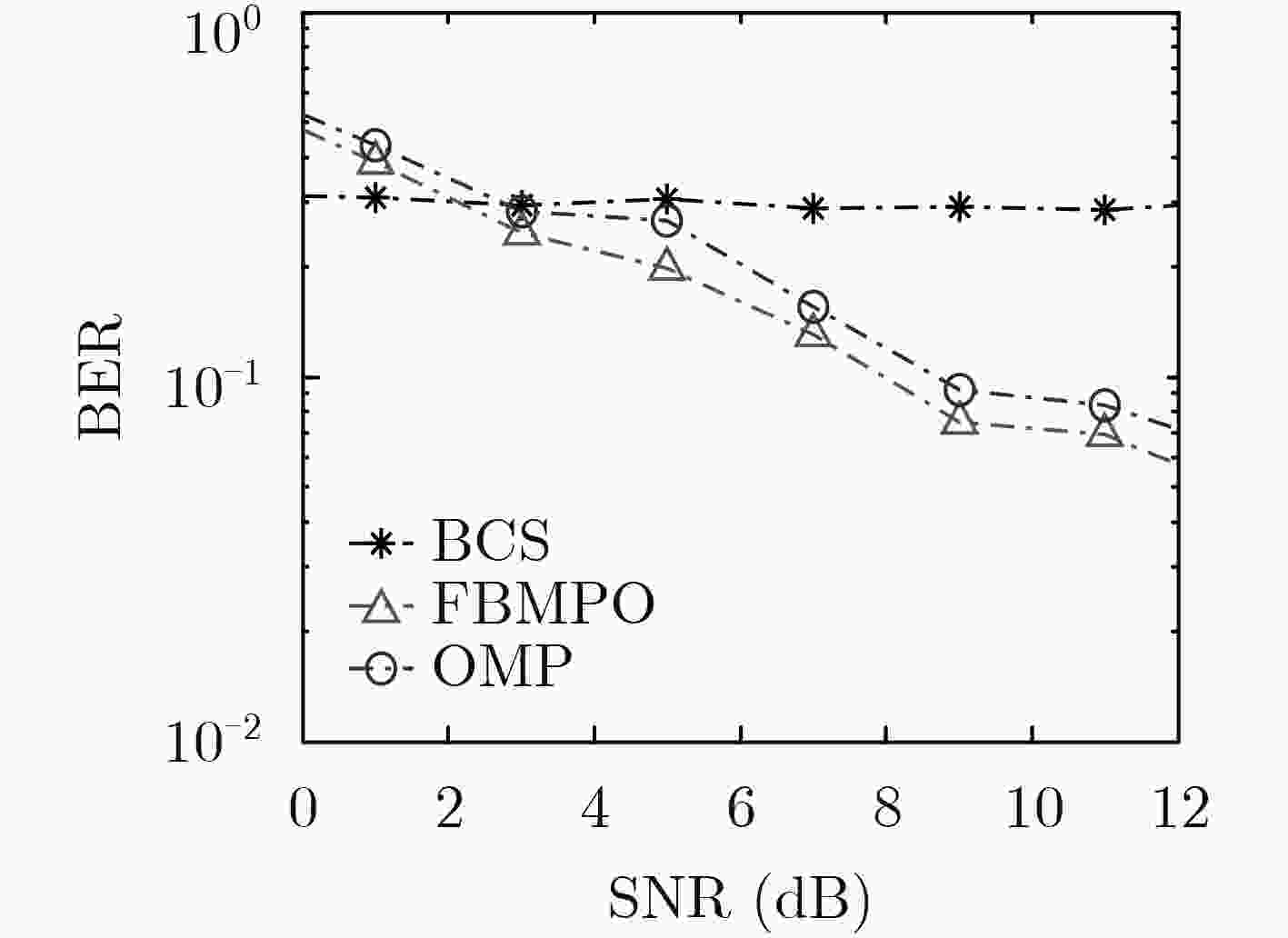
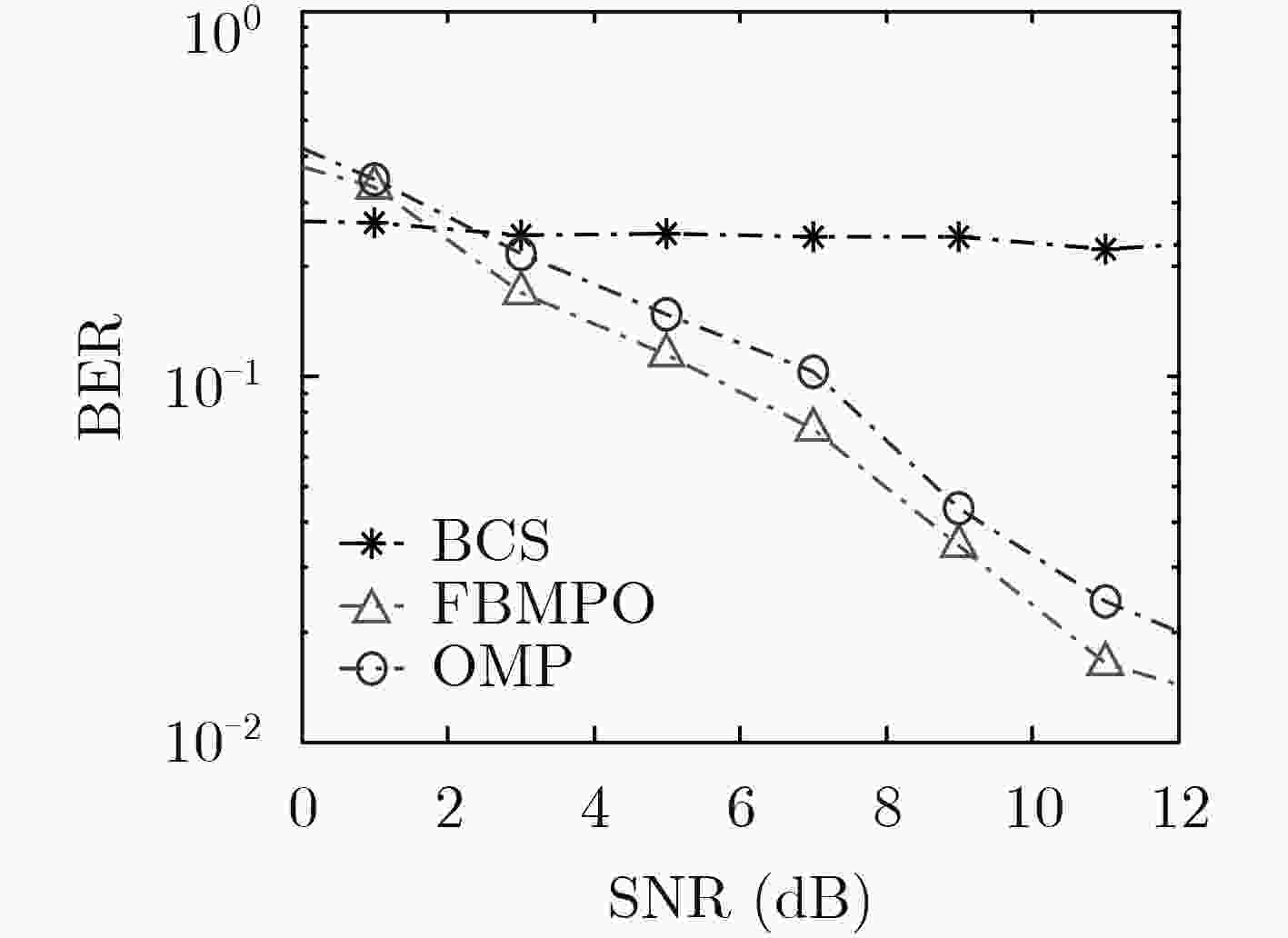
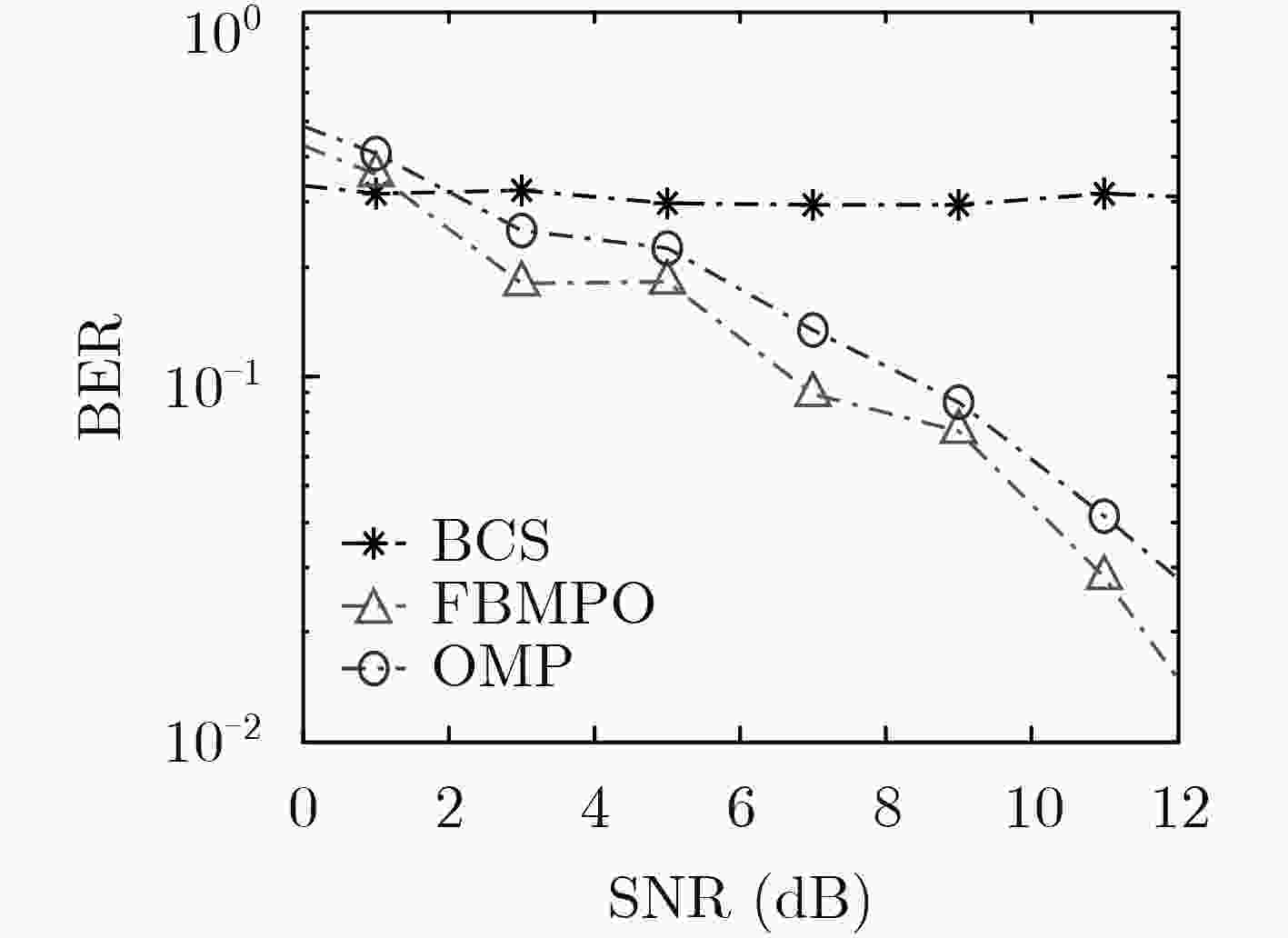
正交频分复用(OFDM)系统中,由于频率发生选择性衰落会导致信道在数据传输中产生符号间干扰,因此接收机往往需要知道信道状态信息。而在海上通信的情况下,信道传输会受到多种外界因素的干扰,往往需要预先进行信道探测估计。为了提高估计性能,该文提出一种基于奇异值分解优化观测矩阵的快速贝叶斯匹配追踪稀疏信道估计优化算法(FBMPO),该算法不仅能够充分考虑海上通信的信道稀疏性,也能够降低信道的不确定性带来的影响。计算机仿真实验表明,与传统的信道估计算法相比,该算法能够提高信道估计的精确度。
Abstract:In the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system, the receiver often needs to know the channel state information, because the frequency selective fading channel will generate inter-symbol interference in the data transmission. In the case of maritime communication, the method of channel estimation is often needed to detect the channel subjected to the interference of various external factors. In order to improve the estimation performance, the Fast Bayesian Matching Pursuit based on singular-value-decomposition for Optimizing observation matrix (FBMPO) is proposed, which fully considers not only the sparse channel of maritime communication, but also reduces the influence of uncertainty of the unpredictable channel. Computer simulation shows, compared with traditional channel estimation algorithms, the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the accuracy of channel estimation.
-
Key words:
- Channel estimation /
- Bayesian criterion /
- Sparse channel /
- Matching pursuit
-
表 1 FBMPO算法的伪代码
FBMPO算法 输入:参数向量s, 观测矩阵${{\varphi } }_i$,迭代阈值K, R and L; 输出:${\tilde h_{ {\rm{MMSE} } } }$; (1) Initialize ${\mu _{0,1}}$ by式(20) (2) for i ← 1 to L: (3) ${{{b}}_i} \leftarrow {{{\varphi}} ^{ - 1}}{{{\phi}} _i};\;{{{\beta }}_i} \leftarrow {\left( {1 + {\sigma _1}^2{{\phi}} _i^{\rm{T}}{{{b}}_i}} \right)^{ - 1}}$; (4) ${\mu _{1,i} }^* \leftarrow {\mu _{0,1} } + \dfrac{1}{2}\lg \left( {\frac{ { { {{\beta} } _i} } }{ { {\sigma _1}^2} } } \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}{ {{\beta} } _i}{\left| { { {{y} }^{\rm{T} } }{ {{b} }_i} } \right|^2}$
$ + {\rm{lg} }\dfrac{ { {p_1} } }{ {1 - {p_1} } }$;(5) end for (6) for q ← 1 to K: (7) ${\mu _{1,q}} \leftarrow {\mu _{1,i}}^*$; ${\rm{}}{b_{1,q}}^{\left( 1 \right)} \leftarrow {\mu _{1,i}}^*$; ${\rm{}}{c_{1,q}}^{\left( 1 \right)} \leftarrow {c_{1,i}}^*$;
${\beta _{1,q}}^{\left( 1 \right)} \leftarrow {\beta _{1,i}}^*$;(8) end for (9) ${{{\phi}}_i} \leftarrow {{{U}}_1} {{W}_2} {{{V}}_1}^{\rm T}$; ${{{\phi}} _i}' \leftarrow {{{U}}_1}{{{W}}_2}'{{{V}}_1}^{\rm{T}}$; (10) for l ← 1 to R: (11) ${{{\beta}} _i} \leftarrow {\left( {1 + {\sigma _1}^2{{{\phi}} _i}{{'}^{\rm{T}}}{{{b}}_i}} \right)^{ - 1}}$; (12) ${{{\mu}} _i} \leftarrow {\mu ^{\left( {l - 1} \right)}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{\rm{lg}}{{{\beta}} _i} + \dfrac{1}{2}{{{\beta}} _i}{\left( {{{{s}}^{\rm{T}}}c_i^{\left( l \right)}} \right)^2} $
$ + {\rm{lg}}\frac{{{p_1}}}{{1 - {p_1}}}$;(13) $i_*^{\left( l \right)} \leftarrow {\rm{argma}}{{\rm{x}}_i}{\mu _i}$; (14) ${G^{\left( l \right)}} \leftarrow {G^{\left( {l - 1} \right)}} \cup ^{\{i_{*}^{(l)}\}} $;
$c_i^{\left( {l + 1} \right)} \leftarrow c_i^{\left( l \right)} - {{i}}_{i_*^{\left( l \right)}}^{\left( l \right)}{{{\beta }}_{i_*^{\left( l \right)}}}{{i}}_{i_*^{\left( l \right)}}^{{{\left( l \right)}^{\rm{T}}}}{{{\phi}} _i}$;(15) end for (16) 计算${\tilde h_{ {\rm{MMSE} } } }$ by式(30) 表 2 系统仿真参数设置
参数仿真 参数值 信道抽头数系统信道带宽 6410 MHz 采样频率循环前缀长度 10 MHz16 调制方式 BPSK 非零抽头概率 p1 {0.04,0.01} FFT/IFFT点数 1024 训练序列长度 {32,48,64} 表 3 不同算法在不同训练序列时的运算时间(s)
N=32 N=48 N=64 OMP 6.4284 8.0413 11.4591 BCS 18.2541 20.8931 24.5212 FBMPO 11.4618 13.7194 15.0951 -
XIAO Liping, LIANG Zhibo, and LIU Kai. A novel compressed sensing-based channel estimation method for OFDM system[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2017, E100.A(1): 322–326. doi: 10.1587/transfun.E100.A.322 DAI Linglong, WANG Zhaocheng, and YANG Zhixing. Compressive sensing based time domain synchronous OFDM transmission for vehicular communications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2013, 31(9): 460–469. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2013.SUP.0513041 DAI Linglong, WANG Zhaocheng, and YANG Zhixing. Next-generation digital television terrestrial broadcasting systems: Key technologies and research trends[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2012, 50(6): 150–158. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2012.6211500 LI Weichang and PREISIG J C. Estimation of rapidly time-varying sparse channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2007, 32(4): 927–939. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2007.906409 GE Lijun, CHENG Yitai, XU Wei, et al. Sparsity adaptive channel estimation based on compressed sensing for OFDM systems[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2017, 40(2): 146–148. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2017.1287597 TAUBOCK G, HLAWATSCH F, EIWEN D, et al. Compressive estimation of doubly selective channels in multicarrier systems: Leakage effects and sparsity-enhancing processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 255–271. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2042410 GUI Guan, WAN Qun, PENG Wei, et al. Sparse multipath channel estimation using compressive sampling matching pursuit algorithm[C]. The 7th IEEE VTS Asia Pacific Wireless Communications Symposium, Kaohsiung, China, 2010: 10–14. GUI Guan, WAN Qun, and PENG Wei. Fast compressed sensing-based sparse multipath channel estimation with smooth L0 algorithm[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing, Qingdao, China, 2011: 242–245. KARABULUT G Z and YONGACOGLU A. Sparse channel estimation using orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm[C]. The 60th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Los Angeles, USA, 2004: 3880–3884. ZHANG Yi, VENKATESAN R, DOBRE O A, et al. Novel compressed sensing-based channel estimation algorithm and near-optimal pilot placement scheme[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(4): 2590–2603. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2505315 CHEN Guorui. Channel estimation with Bayesian framework based on compressed sensing algorithm in multimedia transmission system[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(7): 8813–8825. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6443-1 JOSE R, PAVITHRAN G, and ASWATHI C. Sparse channel estimation in OFDM systems using compressed sensing techniques in a Bayesian framework[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2017, 61: 173–183. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.03.014 BARBU O E, MANCHÓN C N, ROM C, et al. OFDM receiver for fast time-varying channels using block-sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(12): 10053–10057. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2554611 PRASAD R, MURTHY C R, RAO B D. Joint channel estimation and data detection in MIMO-OFDM systems: A sparse Bayesian learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(20): 5369–5382. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2451071 SCHNITER P, POTTER L C, and ZINIEL J. Fast Bayesian matching pursuit[C]. 2008 Information Theory and Applications Workshop, San Diego, USA, 2008: 326–333. WEI Zhuangkun, HU Wenxiu, HAN Dahai, et al. Simultaneous channel estimation and signal detection in wireless ultraviolet communications combating inter-symbol-interference[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(3): 3260–3270. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.003260 HE Chengbing, HUANG Jianguo, ZHANG Qunfei, et al. Single carrier frequency domain equalizer for underwater wireless communication[C]. 2009 WRI International Conference on Communications and Mobile Computing, Kunming, China, 2009: 186–190. QI Chenhao, YUE Guosen, WU Lenan, et al. Pilot design schemes for sparse channel estimation in OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 64(4): 1493–1505. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2331085 胡强, 林云. 基于观测矩阵优化的自适应压缩感知算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2017, 37(12): 3381–3385. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2017.12.3381HU Qiang and LIN Yun. Adaptive compressed sensing algorithm based on observation matrix optimization[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017, 37(12): 3381–3385. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2017.12.3381 CANDÈS E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, 2008, 346(9–10): 589–592. doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014 -





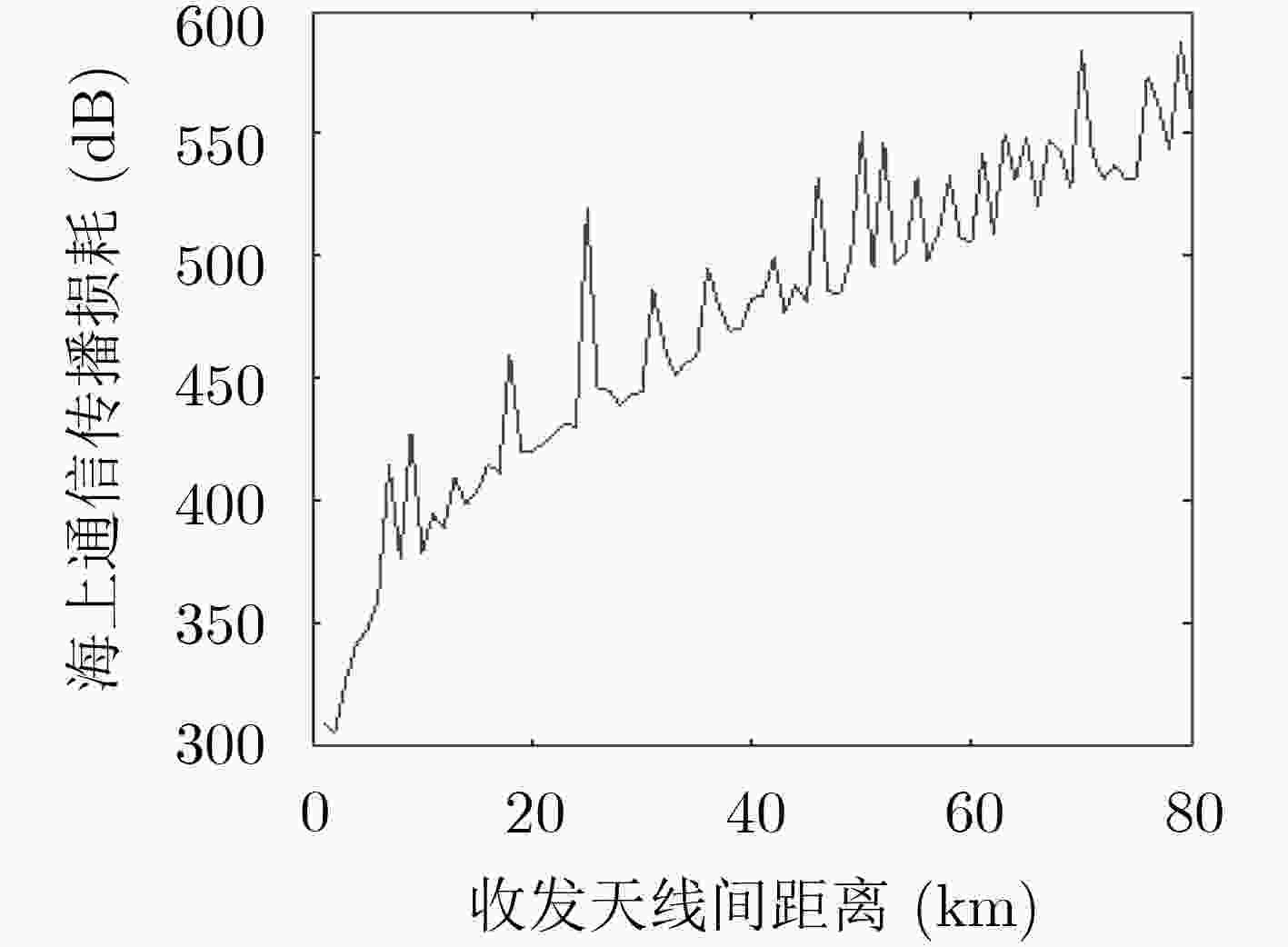
 下载:
下载:
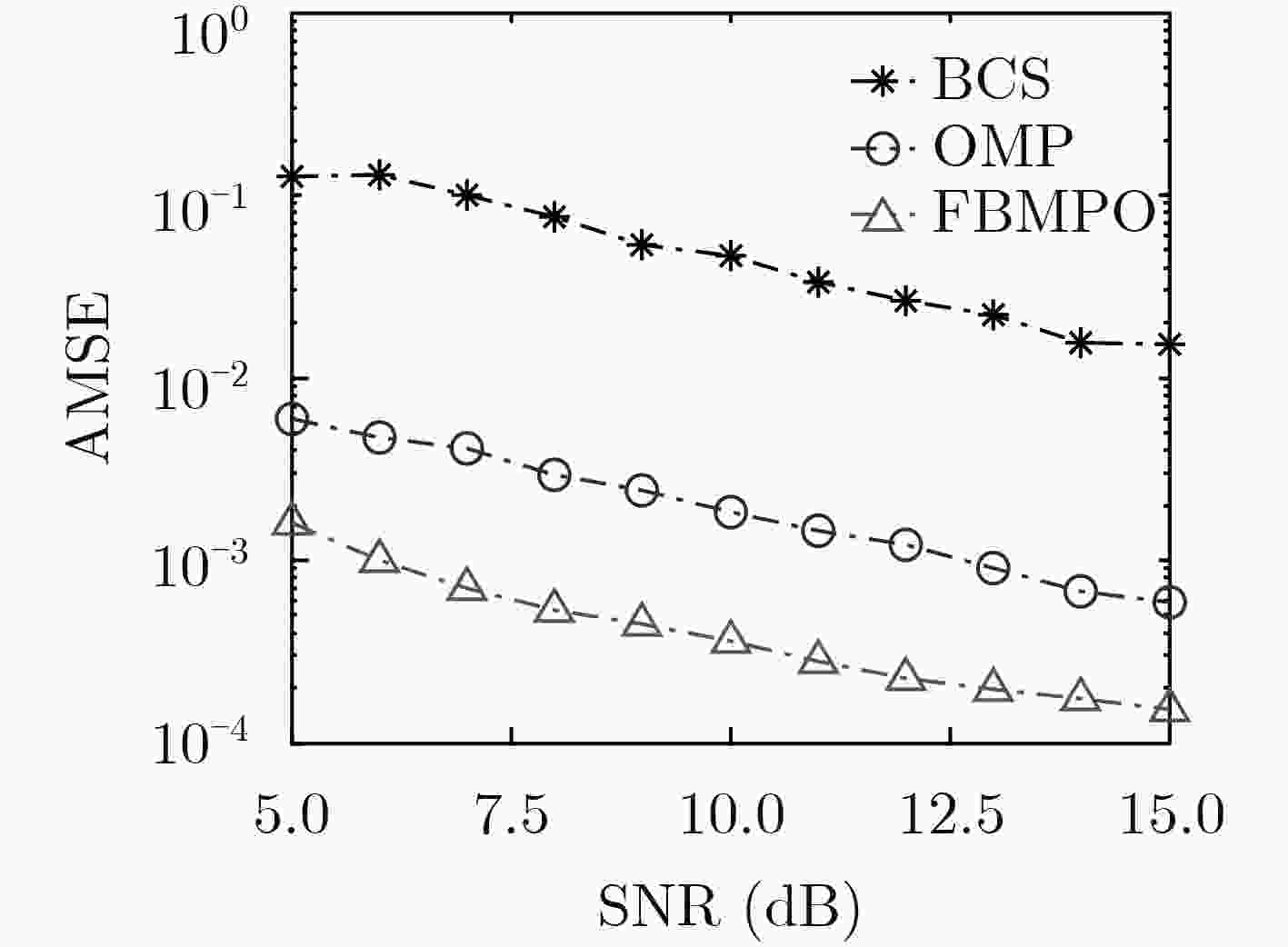
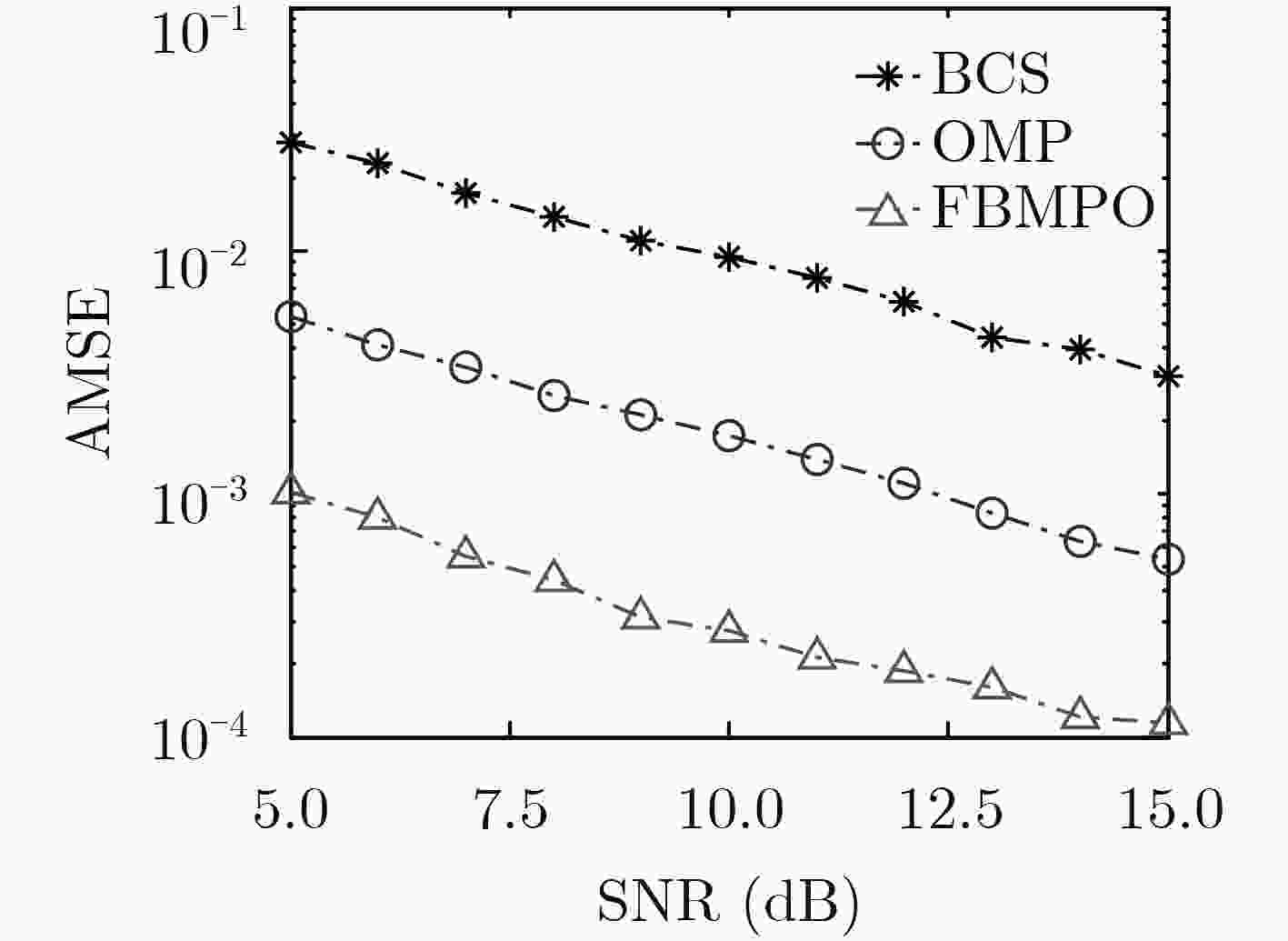
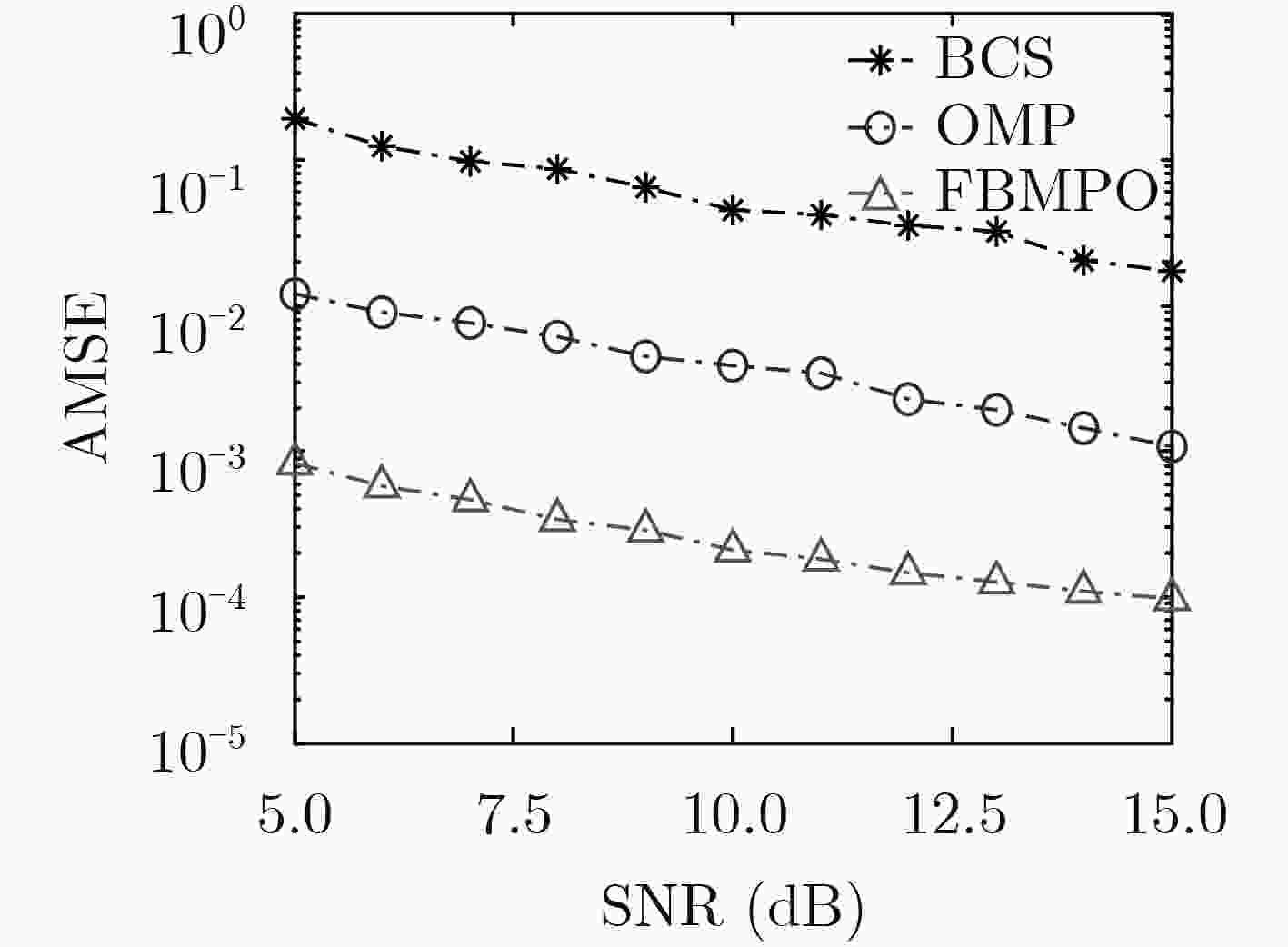



 下载:
下载:
