Salient Object Detection Using Weighted K-nearest Neighbor Linear Blending
-
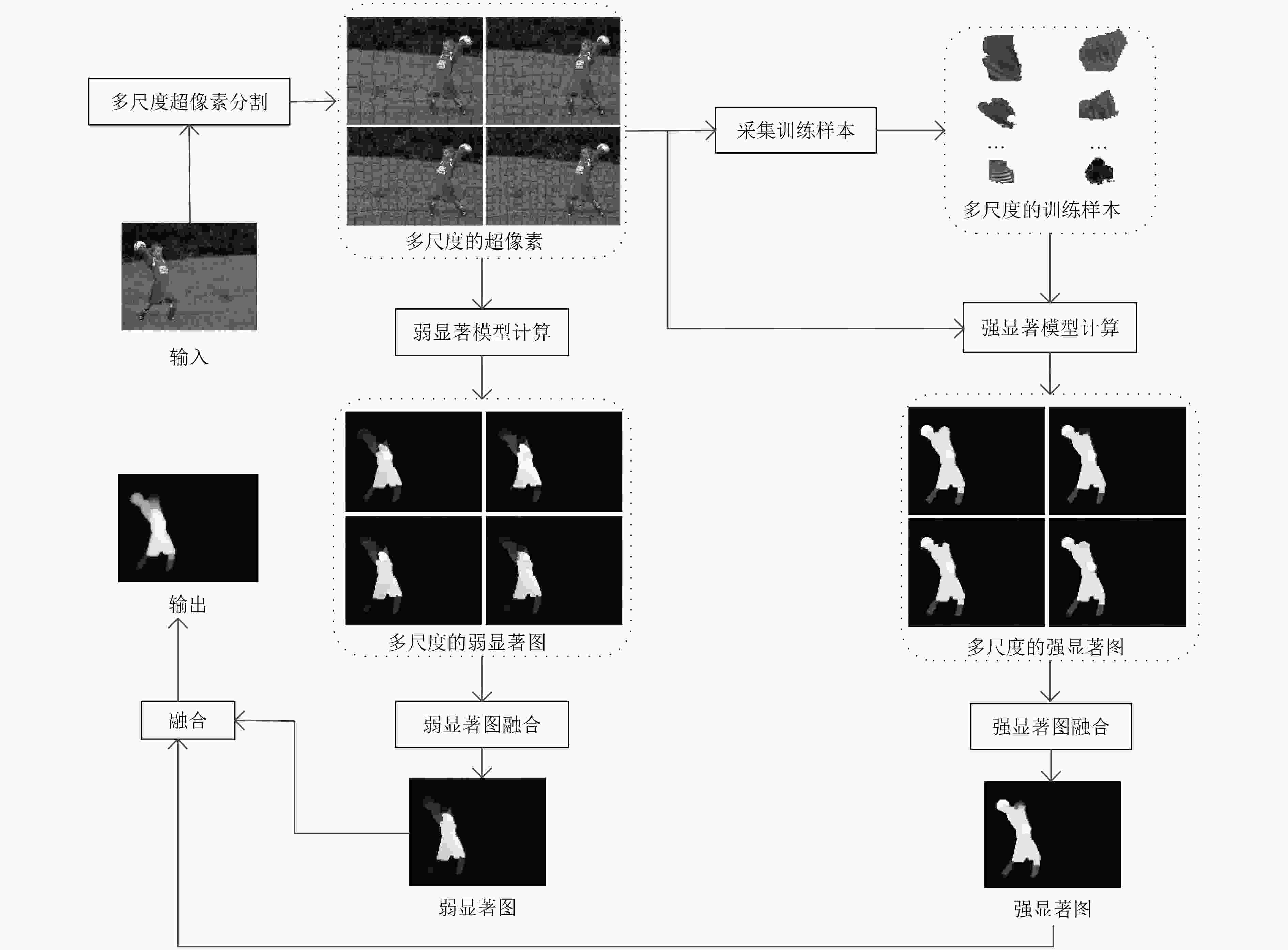
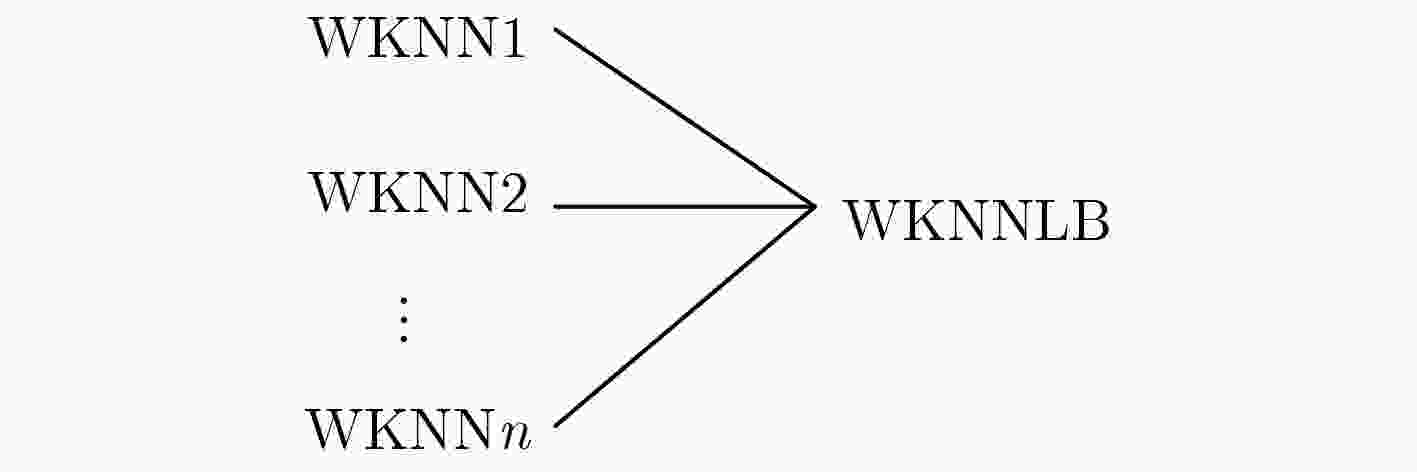
摘要: 显著性目标检测旨在于一个场景中自动检测能够引起人类注意的目标或区域,在自底向上的方法中,基于多核支持向量机(SVM)的集成学习取得了卓越的效果。然而,针对每一张要处理的图像,该方法都要重新训练,每一次训练都非常耗时。因此,该文提出一个基于加权的K近邻线性混合(WKNNLB)显著性目标检测方法:利用现有的方法来产生初始的弱显著图并获得训练样本,引入加权的K近邻(WKNN)模型来预测样本的显著性值,该模型不需要任何训练过程,仅需选择一个最优的K值和计算与测试样本最近的K个训练样本的欧式距离。为了减少选择K值带来的影响,多个加权的K近邻模型通过线性混合的方式融合来产生强的显著图。最后,将多尺度的弱显著图和强显著图融合来进一步提高检测效果。在常用的ASD和复杂的DUT-OMRON数据集上的实验结果表明了该算法在运行时间和性能上的有效性和优越性。当采用较好的弱显著图时,该算法能够取得更好的效果。Abstract: Salient object detection which aims at automatically detecting what attracts human’s attention most in a scene, bootstrap learning based on Support Vector Machine(SVM) has achieved excellent performance in bottom-up methods. However, it is time-consuming for each image to be trained once based on multiple kernel SVM ensemble. So a salient object detection model via Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor Linear Blending (WKNNLB) is proposed. First of all, existing saliency detection methods are employed to generate weak saliency maps and obtain training samples. Then, Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor (WKNN) is introduced to learning salient score of samples. WKNN model needs no pre-training process, only needs selecting K value and computing saliency value by the K-nearest neighbors labels of training sample and the distances between the K-nearest neighbors training samples and the testing sample. In order to reduce the influence of selecting K value, linear blending of multi-WKNNs is applied to generating strong saliency maps. Finally, multi-scale saliency maps of weak and strong model are integrated together to further improve the detection performance. The experimental results on common ASD and complex DUT-OMRON datasets show that the algorithm is effective and superior in running time and performance. It can even perform favorable against the state-of-the-art methods when adopting better weak saliency map.
-
表 1 特征
${\text{f}}_i^j$ 取值(65维)特征维度序号 特征 维度大小 取值范围 0~2 平均RGB值 3 [0,1] 3~5 平均CIELab值 3 [0,1] 6~64 LBP直方图值 59 [0,1] 表 2 5种经典方法及其提高在F-度量值的对比
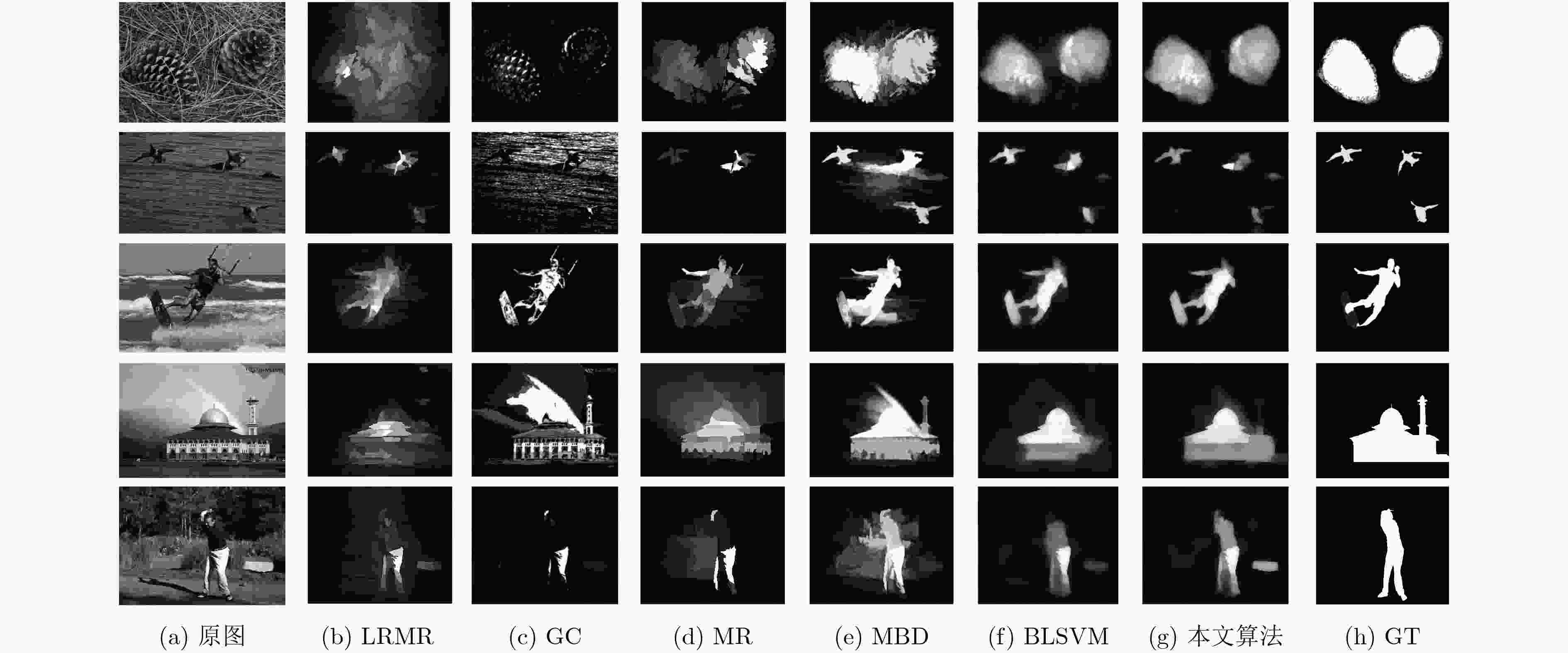
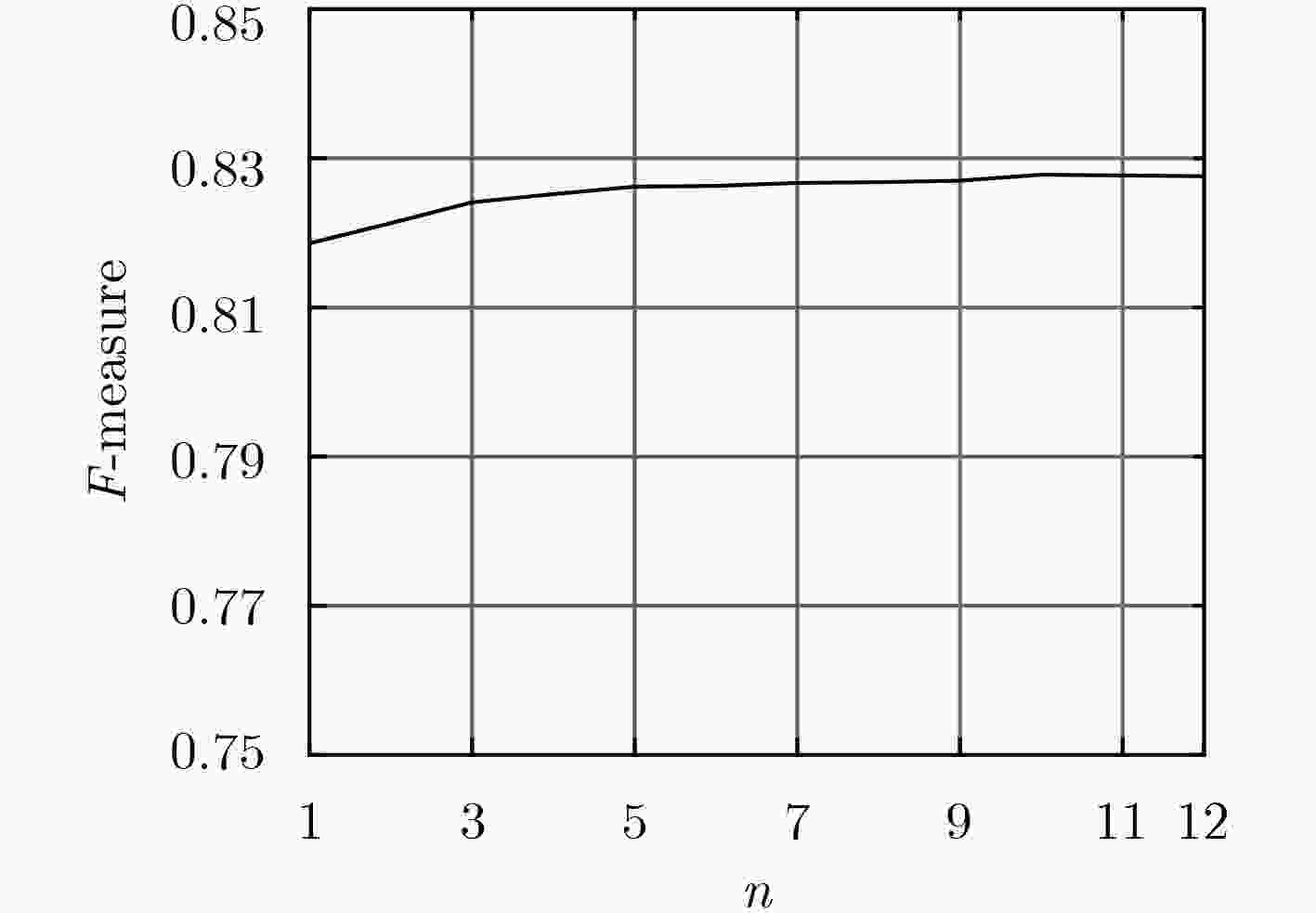
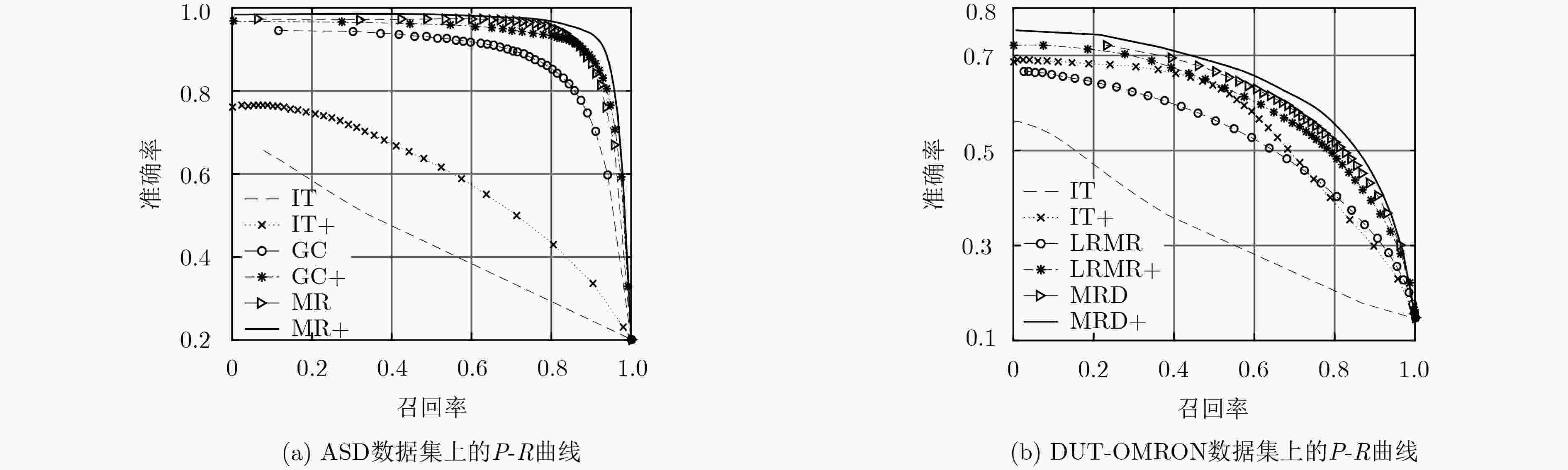
算法 IT IT+ LRMR LRMR+ GC GC+ MR MR+ MBD MBD+ ASD 0.381 0.542 0.727 0.829 0.811 0.848 0.869 0.876 0.855 0.867 DUT-OMRON 0.343 0.541 0.498 0.545 0.520 0.554 0.574 0.576 0.850 0.854 表 3 WKNNLB和BLSVM在4个数据集上F-度量和运行时间(s)对比
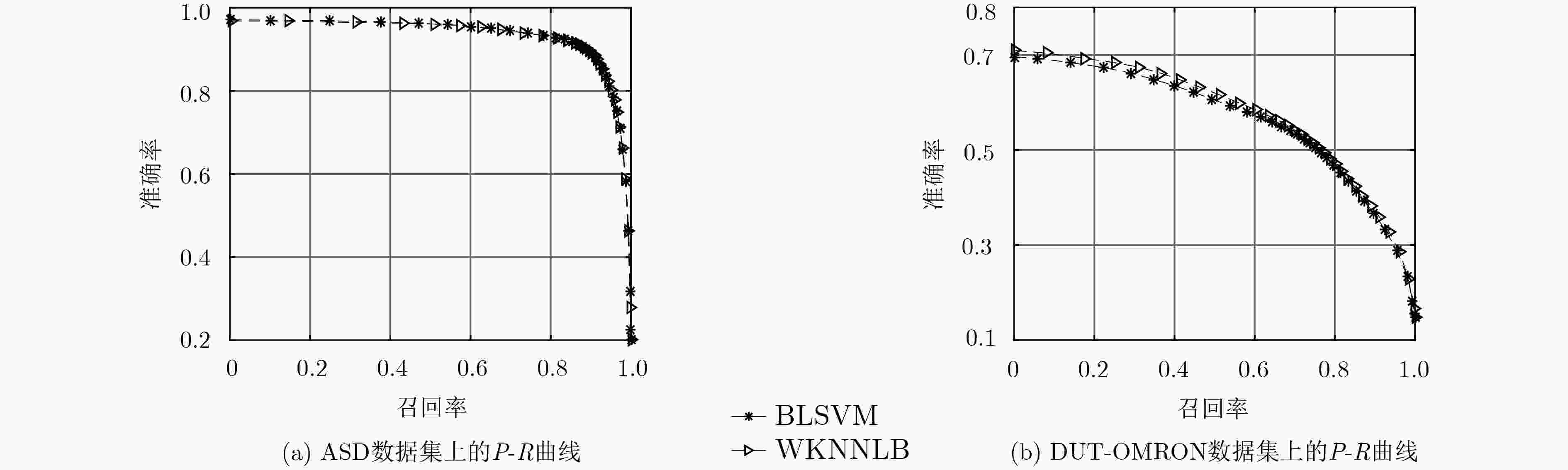
ASD SED2 PASCAL-S DUT-OMRON F-measure Time F-measure Time F-measure Time F-measure Time WKNNLB 0.820 4058 0.758 332 0.655 5000 0.534 30864 BLSVM 0.810 8093 0.740 720 0.651 11184 0.524 65120 -
BORJI A and ITTI L. State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 185–207. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.89 ITTI L. Automatic foveation for video compression using a neurobiological model of visual attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(10): 1304–1318. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.834657 ZHANG Fan, DU Bo, and ZHANG Liangpei. Saliency-guided unsupervised feature learning for scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(4): 2175–2184. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2357078 LU Xiaoqiang, ZHENG Xiangtao, and LI Xuelong. Latent semantic minimal hashing for image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(1): 355–368. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2627801 WEI Yunchao, XIAO Huaxin, SHI Honghui, et al. Revisiting dilated convolution: A simple approach for weakly-and semi-supervised semantic segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7268–7277. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00759. ZHANG Xiaoning, WANG Tiantian, QI Jinqing, et al. Progressive attention guided recurrent network for salient object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 714–722. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00081. CHEN Shuhan, TAN Xiuli, WANG Ben, et al. Reverse attention for salient object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 236–252. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_15. ZHANG Lu, DAI Ju, LU Huchuan, et al. A bi-directional message passing model for salient object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1741–750. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00187. WANG Tiantian, ZHANG Lihe, WANG Shuo, et al. Detect globally, refine locally: A novel approach to saliency detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3127–3135. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00330. HOU Qibin, CHENG Mingming, HU Xiaowei, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(4): 815–828. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2815688 YANG Chuan, ZHANG Lihe, LU Huchuan, et al. Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 3166–3173. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.407. CHENG Mingming, WARRELL J, LIN Wenyan, et al. Efficient salient region detection with soft image abstraction[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 1529–1536. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.193. ZHANG Jianming, SCLAROFF S, LIN Zhe, et al. Minimum barrier salient object detection at 80 FPS[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1404–1412. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.165. BORJI A, CHENG Mingming, JIANG Huaizu, et al. Salient object detection: A benchmark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5706–5722. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2487833 TONG Na, LU Huchuan, RUAN Xiang, et al. Salient object detection via bootstrap learning[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1884–1892. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298798. LU Huchuan, ZHANG Xiaoning, Qi Jinqing, et al. Co-bootstrapping saliency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(1): 414–425. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2627804 SONG Hangke, LIU Zhi, DU Huan, et al. Depth-aware salient object detection and segmentation via multiscale discriminative saliency fusion and bootstrap learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4204–4216. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2711277 WU Lishan, LIU Zhi, SONG Hangke, et al. RGBD co-saliency detection via multiple kernel boosting and fusion[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(16): 21185–21199. doi: 10.1007/s11042-017-5576-y ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 OJALA T, PIETIKAINEN M, and MAENPAA T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(7): 971–987. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2002.1017623 ACHANTA R, HEMAMI S, ESTRADA F, et al. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 1597–1604. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206596. ITTI L, KOCH C, and NIEBUR E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20(11): 1254–1259. doi: 10.1109/34.730558 SHEN Xiaohui and WU Ying. A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 853–860. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247758. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
