Optimization Algorithm of Dual-port Memory Mapping on FPGA
-
摘要: FPGA存储器映射算法负责将用户的逻辑存储需求映射到芯片中的分布式存储资源上实现。前人对双端口存储器的映射算法研究相对较少,成熟的商业EDA工具的映射结果仍有不少改进空间。该文分别针对面积、延时、功耗这3个常用指标,提出一种双端口存储器映射的优化算法,并给出了具体配置方案。实验表明,在面向简单存储需求时,与商用工具Vivado的映射结果一致;在面向复杂存储需求时,面积优化和功耗优化的映射结果对比商用工具改善了至少50%。Abstract: FPGA memory mapping algorithm utilizes distributed storage resources on chip and cooperates with some auxiliary circuits to realize the different needs of users in designing logical storage functions. Previous studies on dual-port memory mapping algorithm are relatively few. There is still much space for improvement in the mapping results by mature commercial EDA tools. An optimization algorithm of dual-port memory mapping is proposed for area, delay and power consumption, and a specific configuration scheme is given. Experiments show that when facing simple storage requirements, the mapping results are consistent with those of commercial tools; when facing complex storage requirements, the mapping results of area optimization and power optimization are improved by at least 50% compared with commercial tools Vivado.
-
Key words:
- FPGA /
- Dual-port memory mapping /
- Delay optimization /
- Area optimization /
- Power optimization
-
表 1 Virtex-4存储器块配置方式
i 索引 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 地址深度 d[i] 256 512 1k 2k 4k 8k 16k 地址位宽 b[i] 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 数据位宽 w[i] 72 36 18 9 4 2 1 表 2 AlgoPower映射策略方案
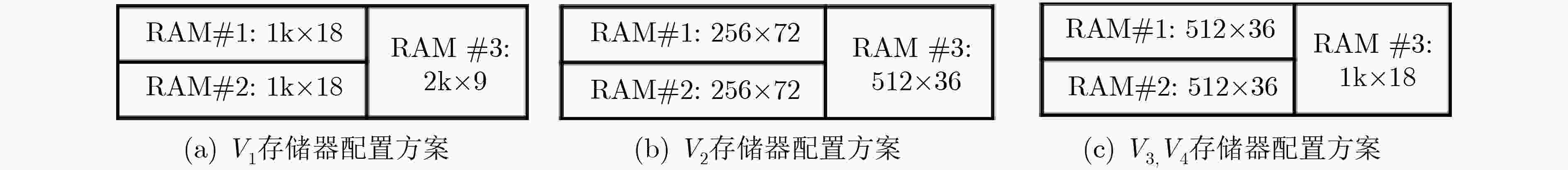
序号 视图 配置 地址端口连接 数据端口连接 译码/选通 #1 V1 1k×18 a9 a8 ··· a1 a0 d33 d32 ··· d17 d16 – V2 1k×18 a10 a9 ··· a2 a1 d25 d24 ··· d9 d8 (a0) = 0 V3 V4 1k×18 a11 a10 ··· a3 a2 d21 d20 ··· d5 d4 (a1 a0) = 00 #2 V1 1k×18 a9 a8 ··· a1 a0 d51 d50 ··· d35 d34 – V2 1k×18 a10 a9 ··· a2 a1 d43 d42 ··· d27 d26 (a0) = 0 V3 V4 1k×18 a11 a10 ··· a3 a2 d21 d20 ··· d5 d4 (a1 a0) = 01 #3 V1 1k×18 a9 a8 ··· a1 a0 d69 d68 ··· d53 d52 – V2 1k×18 a10 a9 ··· a2 a1 d25 d24 ··· d9 d8 (a0) = 1 V3 V4 1k×18 a11 a10 ··· a3 a2 d21 d20 ··· d5 d4 (a1 a0) = 10 #4 V1 1k×18 a9 a8 ··· a1 a0 d87 d86 ··· d71 d70 – V2 1k×18 a10 a9 ··· a2 a1 d43 d42 ··· d27 d26 (a0) = 1 V3 V4 1k×18 a11 a10 ··· a3 a2 d21 d20 ··· d5 d4 (a1 a0) = 11 #5 V1 1k×18 a9 a8 ··· a1 a0 d15 d14 ··· d1 d0 – V2 2k×9 a10 a9 ··· a1 a0 d7 d6 ··· d1 d0 – V3 V4 4k×4 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d3 d2 d1 d0 – 表 3 AlgoDelay映射策略方案
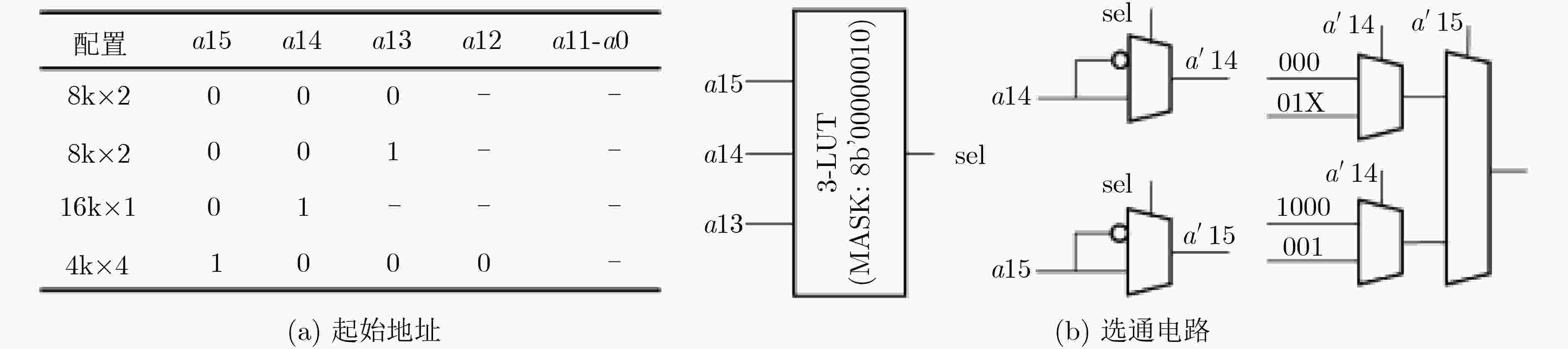
序号 视图 配置 地址端口连接 数据端口连接 译码/选通 #1 V1 8k×2 a12 a11 ··· a1 a0 d1 d0 (a′15 a′14) = 00 V2 4k×4 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′14 a′13) = 00 V3 V4 2k×8 a10 a9 ··· a1 a0 d7 d6 d5 d4 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′13 a′12) = 00 #2 V1 8k×2 a12 a11 ··· a1 a0 d1 d0 (a′15 a′14) = 11 V2 4k×4 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′14 a′13) = 11 V3 V4 2k×8 a10 a9 ··· a1 a0 d7 d6 d5 d4 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′13 a′12) = 11 #3 V1 16k×1 a12 a11 ··· a1 a0 d1 (a′15 a′14) = 01 V2 8k×2 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d3 d1 (a′14 a′13) = 01 V3 V4 4k×4 a10 a9 ··· a1 a0 d7 d5 d3 d1 (a′13 a′12) = 01 #4 V1 16k×1 a12 a11 ··· a1 a0 d0 (a′15 a′14) = 01 V2 8k×2 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d2 d0 (a′14 a′13) = 01 V3 V4 4k×4 a10 a9 ··· a1 a0 d6 d4 d2 d0 (a′13 a′12) = 01 #5 V1 4k×4 a13 a12 ··· a1 a0 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′15 a′14) = 10 V2 2k×8 a12 a11 ··· a1 a0 d7 d6 d5 d4 d3 d2 d1 d0 (a′14 a′13) = 10 V3 V4 1k×16 a11 a10 ··· a1 a0 d15 d14 ··· d1 d0 (a′13 a′12) = 10 表 4 功耗优化实验结果
序号 地址1 读1 写1 地址2 读2 写2 Vivado平均触发数 AlgoPower平均触发数 优化比例(%) 1 10 32 32 10 32 32 1 1.00 0 2 10 32 64 10 32 256 8 1.14 85.7 3 11 16 32 10 32 256 8 1.09 86.4 4 11 16 32 10 32 128 4 1.06 73.5 5 11 16 256 10 32 128 8 1.33 83.4 6 11 32 32 10 64 64 2 1.00 50.0 7 11 32 64 10 64 128 4 1.11 72.2 8 11 16 32 11 16 128 4 1.05 73.8 表 5 延时优化实验结果
序号 V1(rd) V2(rd) V3(wr) V4(wr) AlgoDelay选通级数 1 36k×4 72k×2 18k×8 9k×16 V1: 2 V2: 3 2 81k×16 324k×4 162k×8 162k×8 V1: 3 V2: 5 3 18k×4 9k×8 36k×2 18k×4 V1: 2 V2: 1 4 4k×25 2k×50 1k×100 4k×25 V1: 1 V2: 1 5 16k×4 32k×2 8k×8 4k×16 V1: 1 V2: 2 表 6 面积优化实验结果
序号 地址1 读1 写1 地址2 读2 写2 Vivado使用资源 AlgoArea使用资源 优化比例(%) 1 10 32 32 10 32 32 2 2 0 2 10 32 64 10 32 256 8 4 50 3 11 16 32 10 32 256 8 4 50 4 11 16 32 10 32 128 4 2 50 5 11 16 256 10 32 128 4 4 0 6 11 32 32 10 64 64 4 4 0 7 11 32 64 10 64 128 4 4 0 8 11 16 32 11 16 128 4 2 50 -
TRIMBERGER S M. Three ages of FPGAs: A retrospective on the first thirty years of FPGA technology[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2015, 103(3): 318–331. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2015.2392104 KUON I and ROSE J. Measuring the gap between FPGAs and ASICs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2007, 26(2): 203–215. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2006.884574 WILTON S J E. Architectures and algorithms for Field-Programmable Gate Arrays with embedded memory[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Toronto, 1997. TESSIER R, BETZ V, NETO D, et al. Power-efficient RAM mapping algorithms for FPGA embedded memory blocks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2007, 26(2): 278–290. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2006.887924 HSU T Y and WANG Tingchi. A generalized network flow based algorithm for power-aware FPGA memory mapping[C]. The 45th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, Anaheim, USA, 2008: 30–33. DU Fangqing, LIN C Y, CUI Xiuhai, et al. Timing-constrained minimum area/power FPGA memory mapping[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Field programmable Logic and Applications, Porto, Portugal, 2013: 1–4. HO W K C and WILTON S J E. Logical-to-physical memory mapping for FPGAs with dual-port embedded arrays[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Glasgow, UK, 1999: 111–123. CONG J and YAN K. Synthesis for FPGAs with embedded memory blocks[C]. 2000 ACM/SIGDA Eighth International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, USA, 2000: 75–82. MA Yufei, CAO Yu, VRUDHULA S, et al. An automatic RTL compiler for high-throughput FPGA implementation of diverse deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 27th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Ghent, Belgium, 2017: 1–8. GUAN Yijin, LIANG Hao, XU Ningyi, et al. FP-DNN: An automated framework for mapping deep neural networks onto FPGAs with RTL-HLS hybrid templates[C]. The 25th IEEE Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines (FCCM), Napa, USA, 2017: 152–159. LIANG Shuang, YIN Shouyi, LIU Leibo, et al. FP-BNN: Binarized neural network on FPGA[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 1072–1086. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.046 GUO Kaiyuan, SUI Lingzhi, QIU Jiantao, et al. Angel-eye: A complete design flow for mapping CNN onto embedded FPGA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(1): 35–47. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2705069 MA Yufei, SUDA N, CAO Yu, et al. ALAMO: FPGA acceleration of deep learning algorithms with a modularized RTL compiler[J]. Integration, 2018, 62: 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.vlsi.2017.12.009 Xilinx. Virtex-4 FPGA user guide[EB/OL]. https://china.xilinx.com/support/documentation/user_guides/ug070.pdf, 2008. Xilinx. LogiCORE IP product guide block memory generator v8.4[EB/OL]. https://china.xilinx.com/support/documentation/ip_documentation/blk_mem_gen/v8_4/pg058-blk-mem-gen.pdf, 2019. -







 下载:
下载:
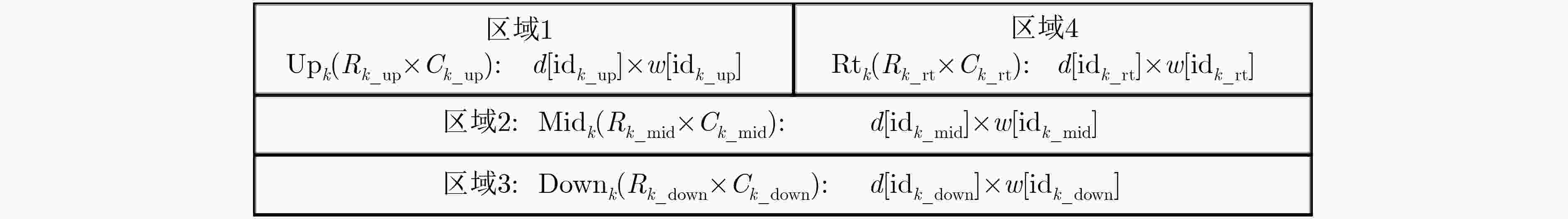




 下载:
下载:
