Intelligent Resource Allocation Algorithm for Multi-platform Offloading in Vehicular Networks
-
摘要:
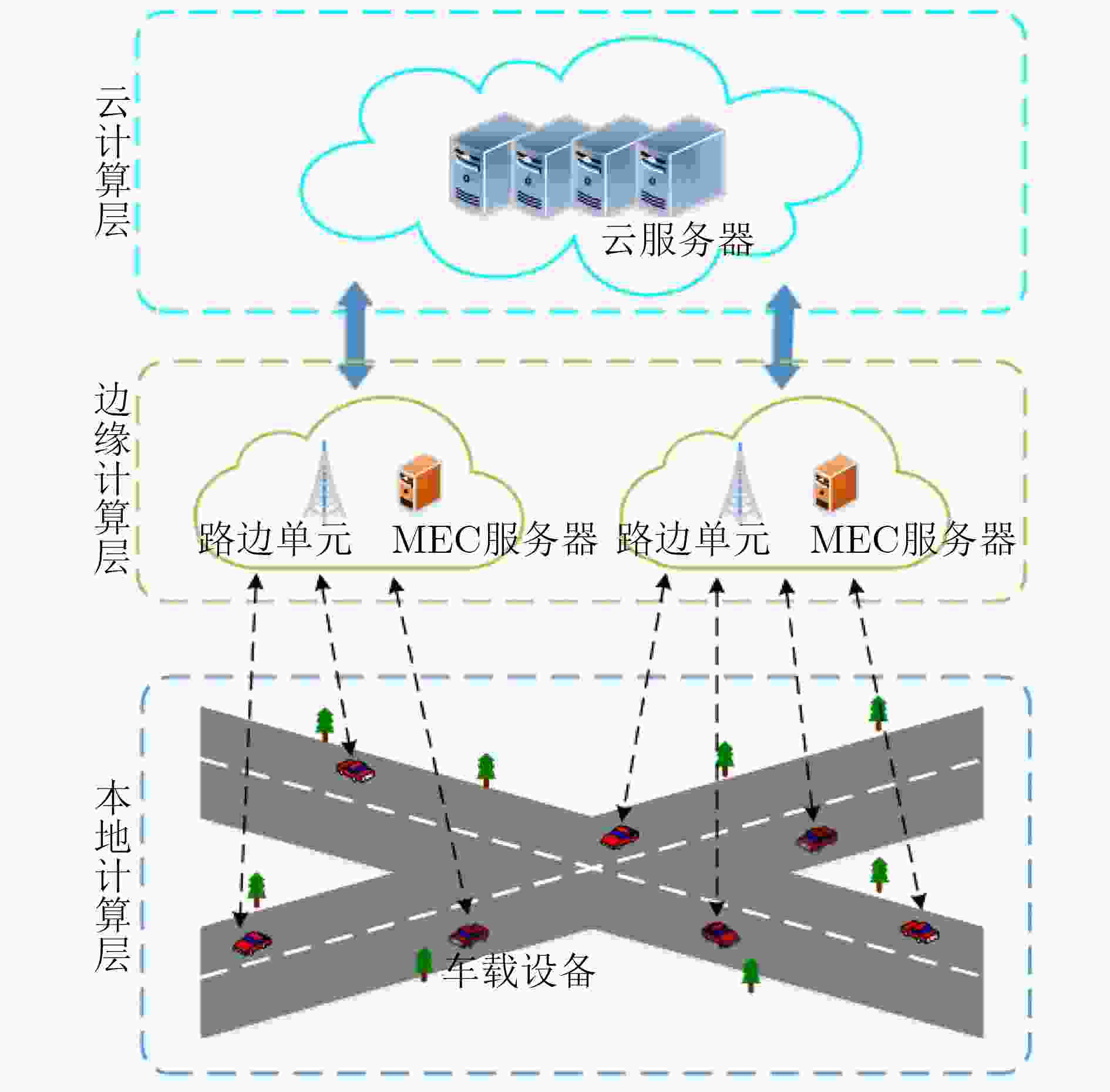
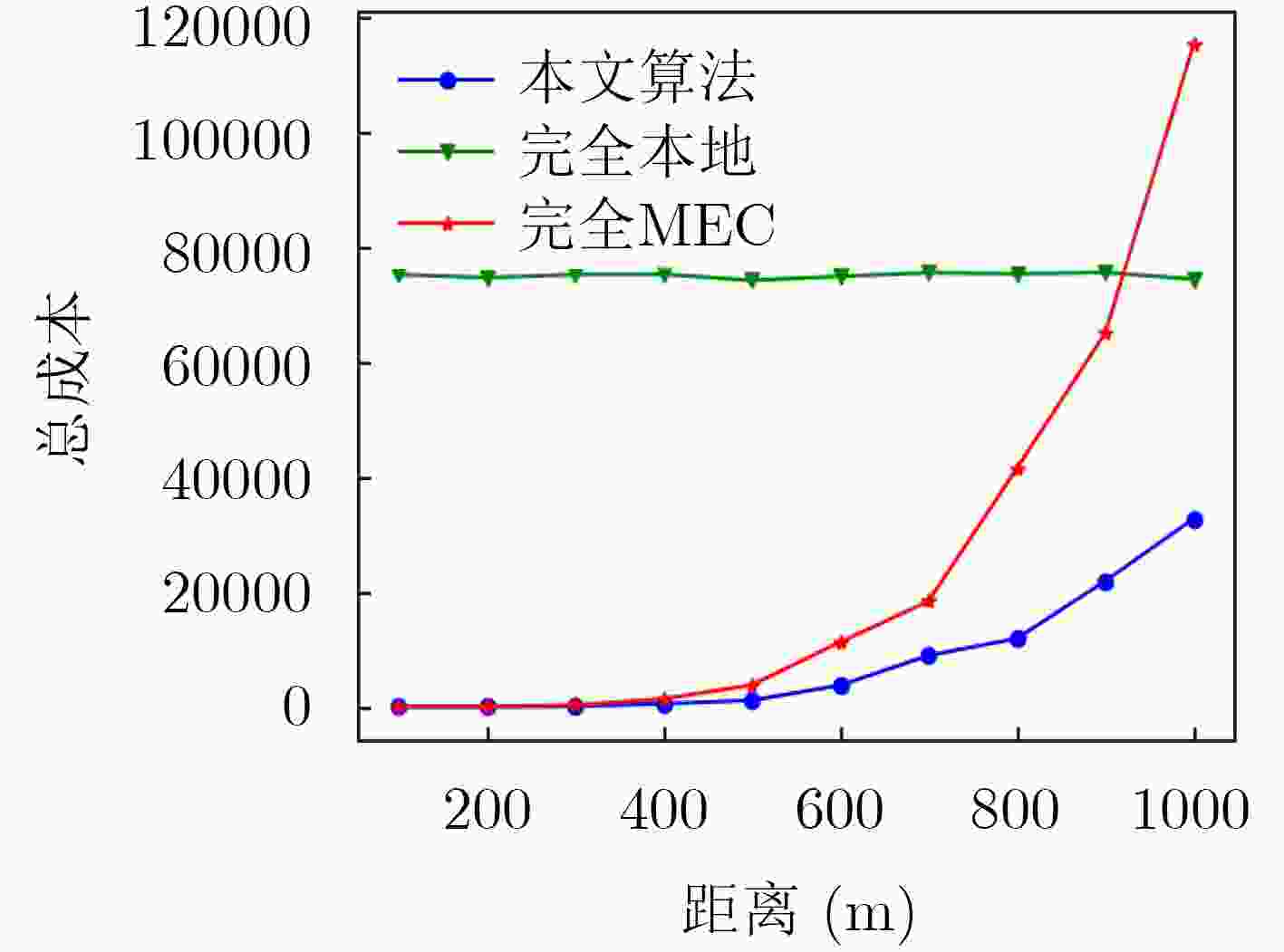
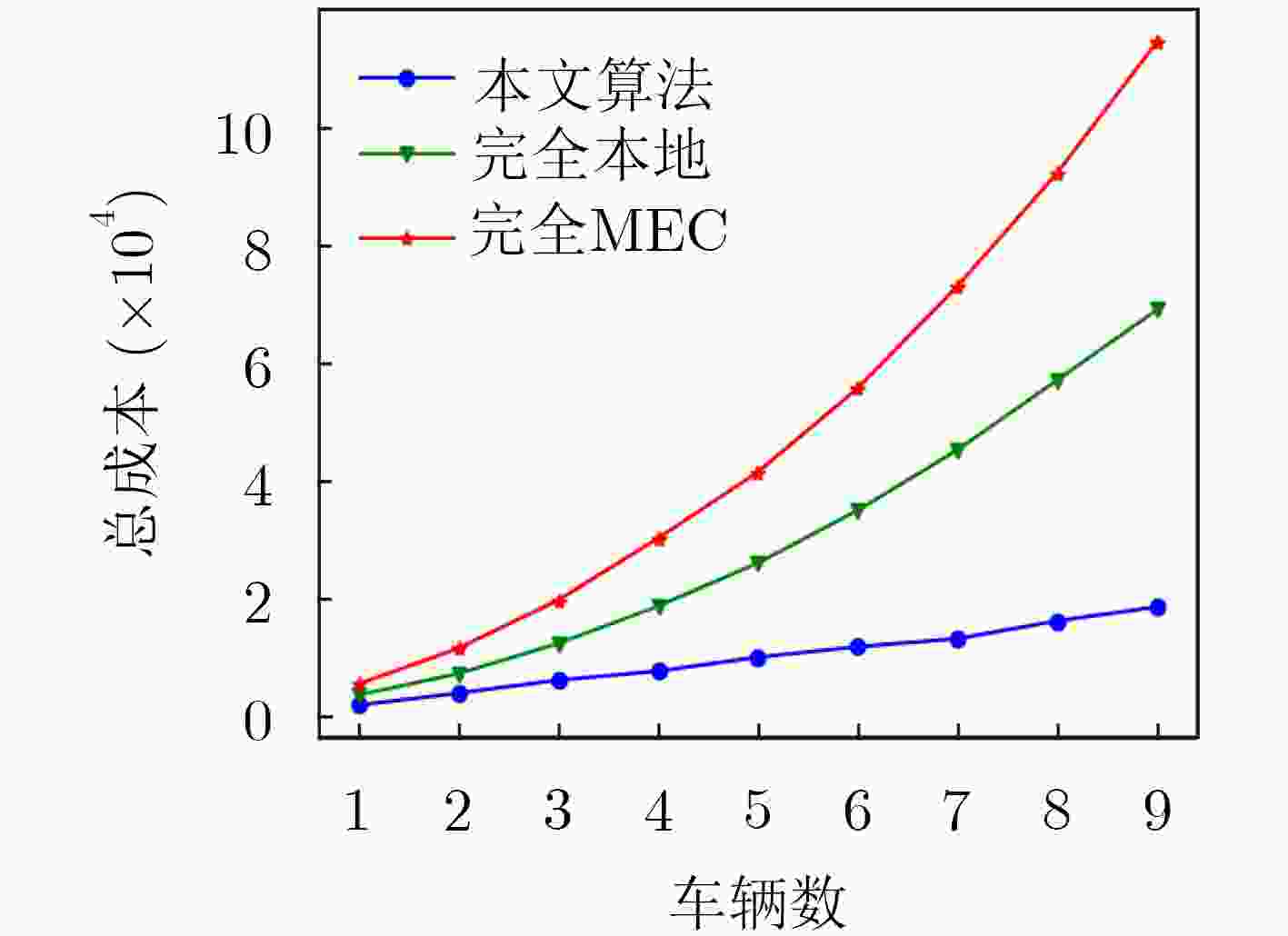
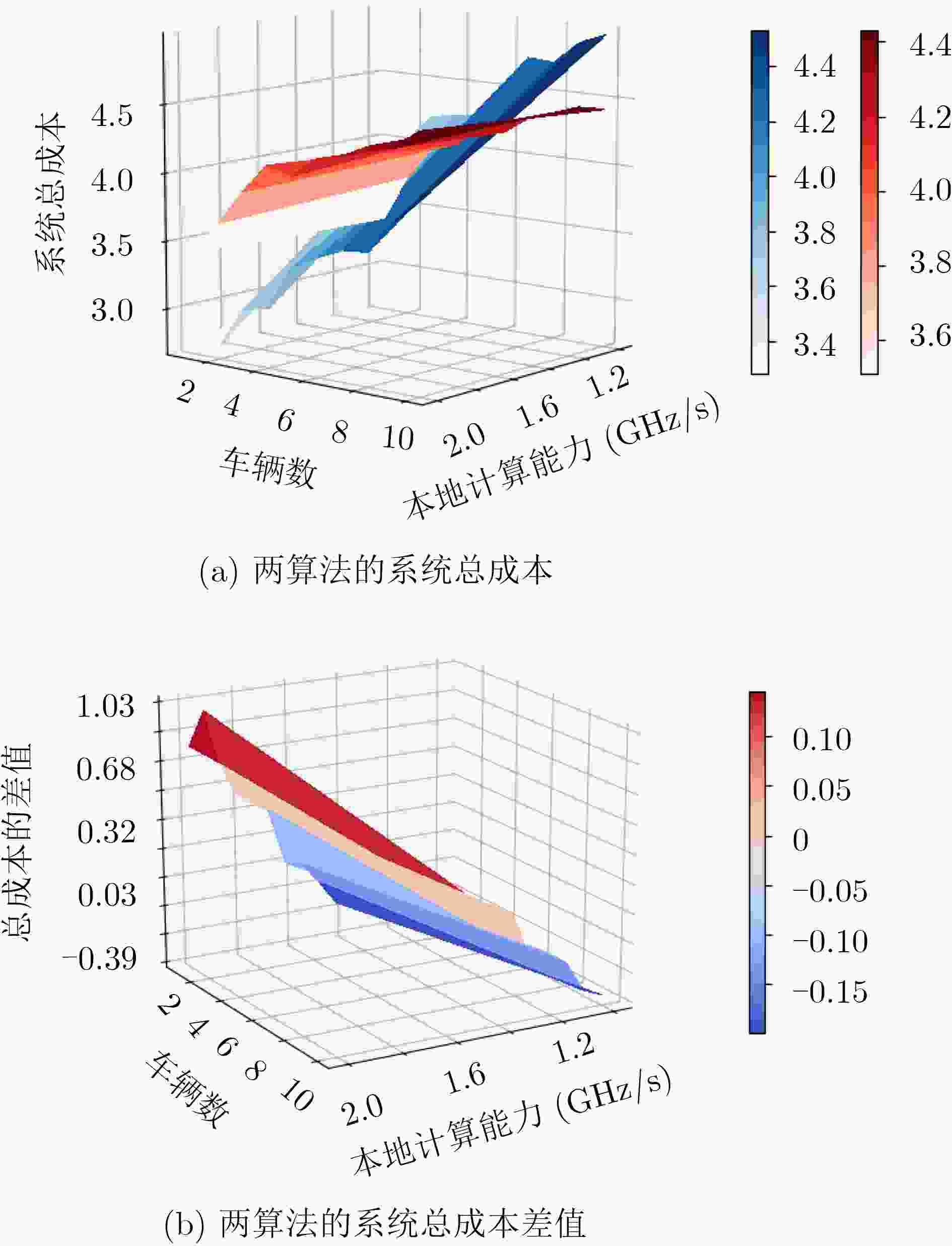
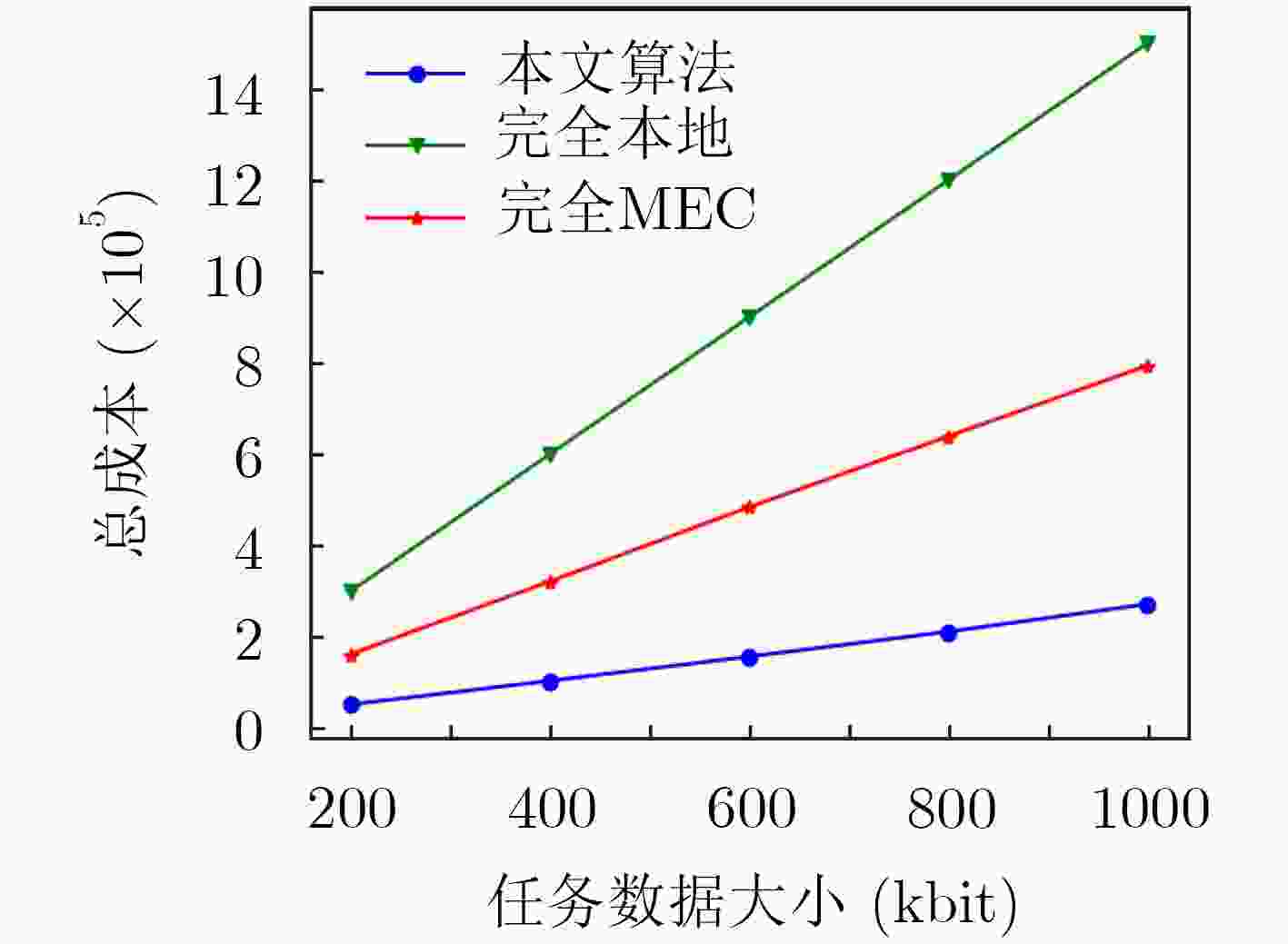
为了降低计算任务的时延和系统的成本,移动边缘计算(MEC)被用于车辆网络,以进一步改善车辆服务。该文在考虑计算资源的情况下对车辆网络时延问题进行研究,提出一种多平台卸载智能资源分配算法,对计算资源进行分配,以提高下一代车辆网络的性能。该算法首先使用K临近(KNN)算法对计算任务的卸载平台(云计算、移动边缘计算、本地计算)进行选择,然后在考虑非本地计算资源分配和系统复杂性的情况下,使用强化学习方法,以有效解决使用移动边缘计算的车辆网络中的资源分配问题。仿真结果表明,与任务全部卸载到本地或MEC服务器等基准算法相比,提出的多平台卸载智能资源分配算法实现了时延成本的显著降低,平均可节省系统总成本达80%。
Abstract:In order to reduce the delay of computing tasks and the total cost of the system, Mobile Eedge Computing (MEC) technology is applied to vehicular networks to improve further the service quality. The delay problem of vehicular networks is studied with the consideration of computing resources. In order to improve the performance of the next generation vehicular networks, a multi-platform offloading intelligent resource allocation algorithm is proposed to allocate the computing resources. In the proposed algorithm, the K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm is used to select the offloading platform (i.e., cloud computing, mobile edge computing, local computing) for computing tasks. For the computing resource allocation problem and system complexity in non-local computing, reinforcement learning is used to solve the optimization problem of resource allocation in vehicular networks using the mobile edge computing technology. Simulation results demonstrate that compared with the baseline algorithms (i.e., all tasks offload to the local or MEC server), the proposed multi-platform offloading intelligent resource allocation algorithm achieves a significant reduction in latency cost, and the average system cost can be saved by 80%.
-
算法1 多平台卸载智能资源分配算法 阶段1:初始化 (1) 任务${R_i}$的最大延迟${\tau _{{R_i}}}$,任务大小${B_{{R_i}}}$; (2) 任务的当前位置$P = 1$; (3) ${{Q}}$矩阵,参数$\gamma $,奖赏矩阵${{R}}$; (4) 本地(l)、移动边缘计算(m)、云计算(c),各平台平 均延迟${\tau _1},{\tau _2},{\tau _3}$,允许最大任务大小${B_1},{B_2},{B_3}$。 阶段2:选择任务卸载位置 计算(${\tau _{{R_i}}},{B_{{R_i}}}$)和(${\tau _1},{B_1}$)的欧式距离$D$ $D = \sqrt {{{({\tau _{{R_i}}} - {\tau _1})}^2} + {{({B_{{R_i}}} - {B_1})}^2}} ,P = 1$ for j=2, 3 do 计算(${\tau _{{R_i}}},{B_{{R_i}}}$)和(${\tau _j},{B_j}$)的欧式距离${d_j}$ if ${d_j} < D$ then $D = {d_j},P = j$ end if end for if P=1 任务卸载到本地 if P=2 or 3 进行阶段3。 阶段3:资源分配 if P=3 then 在云计算服务器中计算任务${R_i}$ end if if P=2 then for 每次迭代 do 随机选择一个状态${s_t}$ for 每一步 do 从状态${s_t}$的可能动作中随机选择动作$a$ 执行动作$a$,计算奖励$r$,进入下一状态$s'$ 计算 $q(s,a) \leftarrow r(s,a) + \gamma \cdot \max [q(s',a')]$ 更新状态$s \leftarrow s'$ until ${{Q}}$矩阵稳定 end for end for end if -
WU Dapeng, ZHANG Feng, WANG Honggang, et al. Security-oriented opportunistic data forwarding in mobile social networks[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 87: 803–815. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.07.028 LUO Changqing, JI Jinlong, WANG Qianlong, et al. Channel state information prediction for 5G wireless communications: A deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2018. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2018.2848960 HUSSAIN R, SON J, EUN H, et al. Rethinking vehicular communications: Merging VANET with cloud computing[C]. The 4th IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science Proceedings, Taipei, China, 2013: 606–609. doi: 10.1109/CloudCom.2012.6427481. LI Chunhai, WANG Siming, HUANG Xumin, et al. Parked vehicular computing for energy-efficient Internet of vehicles: A contract theoretic approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6079–6088. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2869892 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Optimal delay constrained offloading for vehicular edge computing networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2017.7997360. ASHRAF M I, LIU Chenfeng, BENNIS M, et al. Dynamic resource allocation for optimized latency and reliability in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 63843–63858. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2876548 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Contract-theoretic approach for delay constrained offloading in vehicular edge computing networks[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2019, 24(3): 1003–1014. doi: 10.1007/s11036-018-1032-0 DING Qing, SUN Bo, and ZHNAG Xinming. A traffic-light-aware routing protocol based on street connectivity for urban vehicular Ad Hoc networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(8): 1635–1638. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2574708 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: A promising network paradigm with predictive off-loading[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(2): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2668838 HAN Guangjie, LIU Li, CHAN S, et al. HySense: A hybrid mobile Crowdsensing framework for sensing opportunities compensation under dynamic coverage constraint[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2017, 55(3): 93–99. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600658CM SOOKHAK M, YU F R, HE Ying, et al. Fog vehicular computing: Augmentation of fog computing using vehicular cloud computing[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(3): 55–64. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2667499 LI Ji, GAO Hui, LÜ Tiejun, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based computation offloading and resource allocation for MEC[C]. 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2018: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCNC.2018.8377343. HE Ying, ZHAO Nan, and YIN Hongxi. Integrated networking, caching, and computing for connected vehicles: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(1): 44–55. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2760281 LIN Chuncheng, DENG D J, and YAO C C. Resource allocation in vehicular cloud computing systems with heterogeneous vehicles and roadside units[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(5): 3692–3700. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2690961 MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHNAG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 ZHAO Pengtao, TIAN Hui, QIN Cheng, et al. Energy-saving offloading by jointly allocating radio and computational resources for mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 11255–11268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2710056 ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Energy-efficient offloading for mobile edge computing in 5G heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 5896–5907. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2597169 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
