Security Analysis of 5G Network EAP-AKA′ Protocol Based on Lowe’s Taxonomy
-
摘要: 移动网鉴权认证协议攻击不断涌现,针对5G网络新协议EAP-AKA
$ '$ ,该文提出一种基于Lowe分类法的EAP-AKA$ '$ 安全性分析模型。首先对5G网络协议EAP-AKA$ '$ 、信道及攻击者进行形式化建模。然后对Lowe鉴权性质进行形式化描述,利用TAMARIN证明器分析协议中安全锚点密钥KSEAF的Lowe鉴权性质、完美前向保密性、机密性等安全目标,发现了3GPP隐式鉴权方式下的4条攻击路径。最后针对发现的安全问题提出2种改进方案并验证其有效性,并将5G网络两种鉴权协议EAP-AKA$ '$ 和5G AKA的安全性进行了对比,发现前者在Lowe鉴权性质方面更安全。-
关键词:
- 网络安全 /
- 安全锚点密钥 /
-
EAP-AKA
$ '$ / - Lowe分类法 /
- Dolev-Yao敌手模型 /
- TAMARIN
Abstract: Mobile network authentication protocol attacks continue to emerge. For the new 5G network protocol EAP-AKA', an EAP-AKA' security analysis method based on Lowe’s taxonomy is proposed. Firstly, 5G network, EAP-AKA', communication channel and adversary are formally modeled. Then Lowe authentication property is formally modeled. Using the TAMARIN prover, objectives of the security anchor key KSEAF are analyzed, such as Lowe’s taxonomy, perfect forward secrecy, confidentiality, etc. Four attack paths under 3GPP implicit authentication mode are discovered. Two improved schemes are proposed for the discovered security problems and their security is verified. Finally, the security of the two authentication protocols EAP-AKA’ and 5G AKA of the 5G network is compared, and it is found that the former is safer in terms of Lowe authentication property.-
Key words:
- Network security /
- Security anchor key /
-
EAP-AKA
$ '$ / - Lowe’s taxonomy /
- Dolev-Yao adversary model /
- TAMARIN
-
表 1 符号说明
符号 定义 Create(A, id, R) 对编号为id的角色A创建一个事件 Claim_type(A, t) 角色A在时刻t声明一个事件 Honest(A) 角色A不被攻击者感染 Reveal(A) 角色A被攻击者感染 K(t) 攻击者获取了传递的信息 F@i 在时刻i发生事件F #i<#j 时刻i早于时刻j #i=#j 时刻i与时刻j相同 x=y 消息变量x, y相等 表 2 用spthy语言描述协议状态转移
rule SN_1send: let m = ‘Identity Request’ in [ St_SN_0($SN, ~id, $HN, SK) ] --[ Send($SN, m)]-> [ Out(m), St_SN_1($SN, ~id, $HN, SK)] 表 3 隐式鉴权和显式鉴权对比(对KSEAF的机密性、完美前向保密性)
协议参与方 UE SN HN 隐式 显式 隐式 显式 隐式 显式 KSEAF机密性 √ √ √ √ √ √ KSEAF完美前向保密性 × × × × × × 表 4 EAP-AKA
$ '$ 和5G AKA对比(隐式鉴权)协议参与方 UE对SN UE对HN SN对UE HN对UE EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA 存活性 √ × √ √ √ √ √ √ 弱一致性 √ × √ √ √ × √ √ 非单射一致性 × × √ × √ × √ × 单射一致性 × × √ × √ × √ × 表 5 EAP-AKA
$ '$ 和5G AKA对比(显式鉴权)协议参与方 UE对SN UE对HN SN对UE HN对UE EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA EAP-AKA′ 5G AKA 存活性 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 弱一致性 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 非单射一致性 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ × 单射一致性 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ × 表 6 改进MAC计算方式
MAC=f1(K, <SQNHN, R, SNN >) 故AUTN=<CONC, f1(K, MAC)> =< SQNHN⊕AK, f1(K, <SQNHN, R, SNN >)> =< SQNHN⊕f5(K, R), f1(K, <SQNHN, R, SNN >)> =KDFAUTN(SQNHN, K, R, SNN) -
ARAPINIS M, MANCINI L, RITTER E, et al. New privacy issues in mobile telephony: Fix and verification[C]. Proceedings of 2012 ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Raleigh, North Carolina, USA, 2012: 205–216. HUSSAIN S R, CHOWDHURY O, MEHNAZ S, et al. LTEInspector: A systematic approach for adversarial testing of 4G LTE[C]. Network and Distributed Systems Security (NDSS), San Diego, California, USA, 2018. BORGAONKAR R, HIRSHI L, PARK S, et al. New adventures in spying 3G & 4G users: Locate, track, monitor[EB/OL]. https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-17/wednesday/us-17-Borgaonkar-New-Adventures-In-Spying-3G-And-4G-Users-Locate-Track-And-Monitor.pdf, 2017. ZHANG Muxiang and FANG Yuguang. Security analysis and enhancements of 3GPP authentication and key agreement protocol[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2005, 4(2): 734–742. doi: 10.1109/twc.2004.842941 RUPPRECHT D, KOHLS K, HOLZ T, et al. Breaking LTE on layer two[C]. The 40th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2019. SHAIK A, BORGAONKAR R, SEIFERT J P, et al. Practical attacks against privacy and availability in 4G/LTE[C]. The 23nd Annual Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS), San Diego‚ California, USA, 2016. HUSSAIN S R, ECHEVERRIA M, CHOWDHURY O, et al. Privacy attacks to the 4G and 5G cellular paging protocols using side channel information[C]. The 23nd Annual Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS), San Diego‚ California, USA, 2019. RAVISHANKAR B, LUCCA H, SHINJO P, et al. New privacy threat on 3G, 4G, and upcoming 5G AKA protocols[C]. Privacy Enhancing Technologies, Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. BASIN D, DREIER J, HIRSCHI L, et al. A formal analysis of 5G authentication[C]. 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, Canada, 2018: 1383–1396. KOUTSOS A. The 5G-AKA authentication protocol privacy[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1811.06922.pdf, 2019. FERRAG M A, MAGLARAS L, ARGYRIOU A, et al. Security for 4G and 5G cellular networks: A survey of existing authentication and privacy-preserving schemes[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2018, 101: 55–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2017.10.017 RUPPRECHT D, DABROWSKI A, HOLZ T, et al. On security research towards future mobile network generations[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(3): 2518–2542. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2820728 JI Xinsheng, HUANG Kaizhi, JIN Liang, et al. Overview of 5G security technology[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(8): 081301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9426-4 刘彩霞, 李凌书, 汤红波, 等. 基于子图同构的vEPC虚拟网络分层协同映射算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1170–1177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160642LIU Caixia, LI Lingshu, TANG Hongbo, et al. Hierarchical coordination strategy for vEPC virtual network embedding based on subgraph isomorphism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1170–1177. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160642 DOLEV D and YAO A. On the security of public key protocols[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1983, 29(2): 198–208. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1983.1056650 LOWE G. A hierarchy of authentication specifications[C]. The 10th Computer Security Foundations Workshop, Rockport, USA, 1997: 31–43. 3GPP. 3GPP TS 33.501 Security architecture and procedures for 5G system (Release 15)[S].Nice: 3GPP, 2018. -









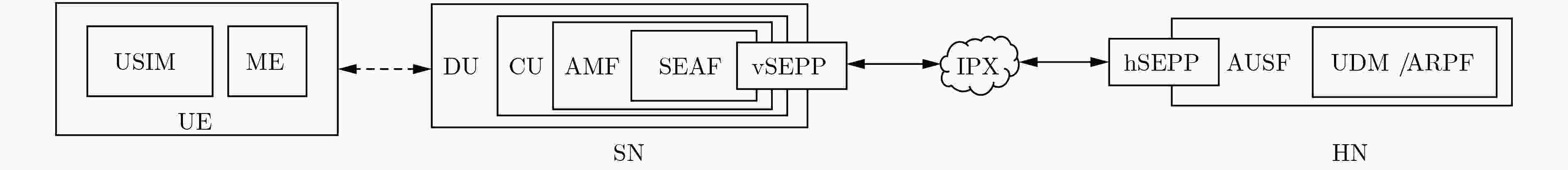
 下载:
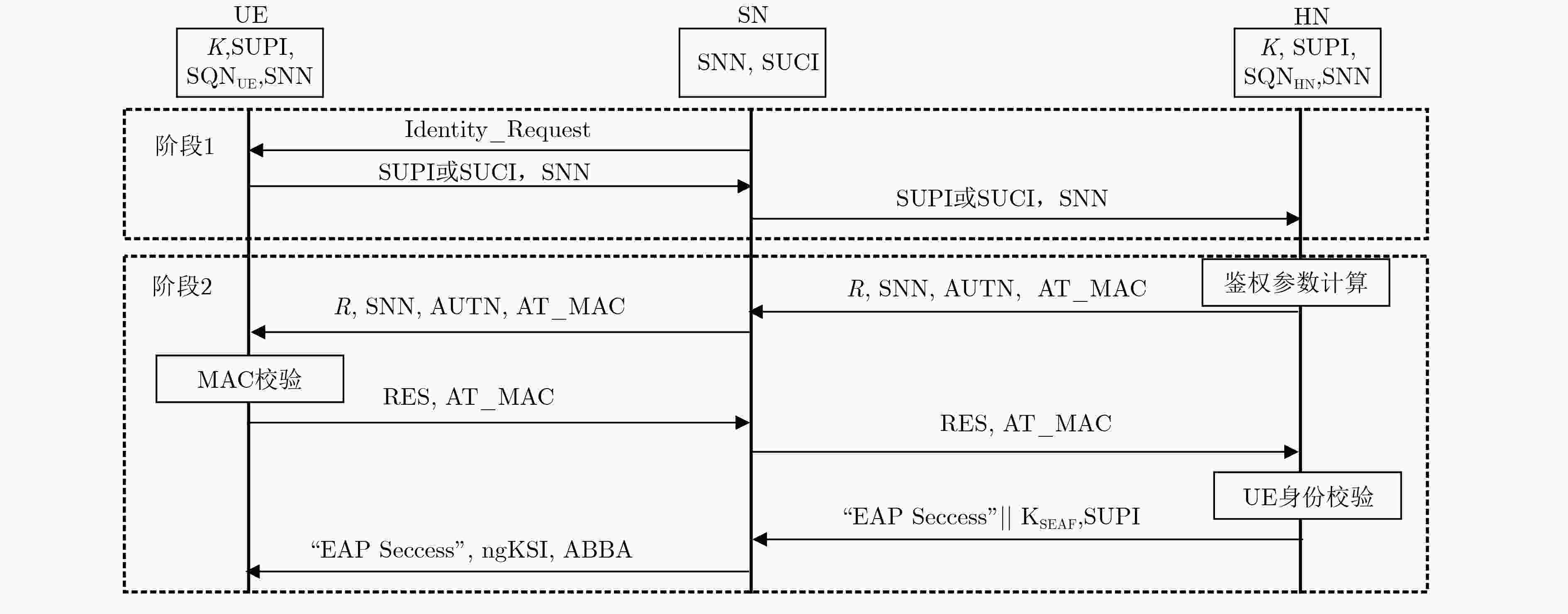
下载:
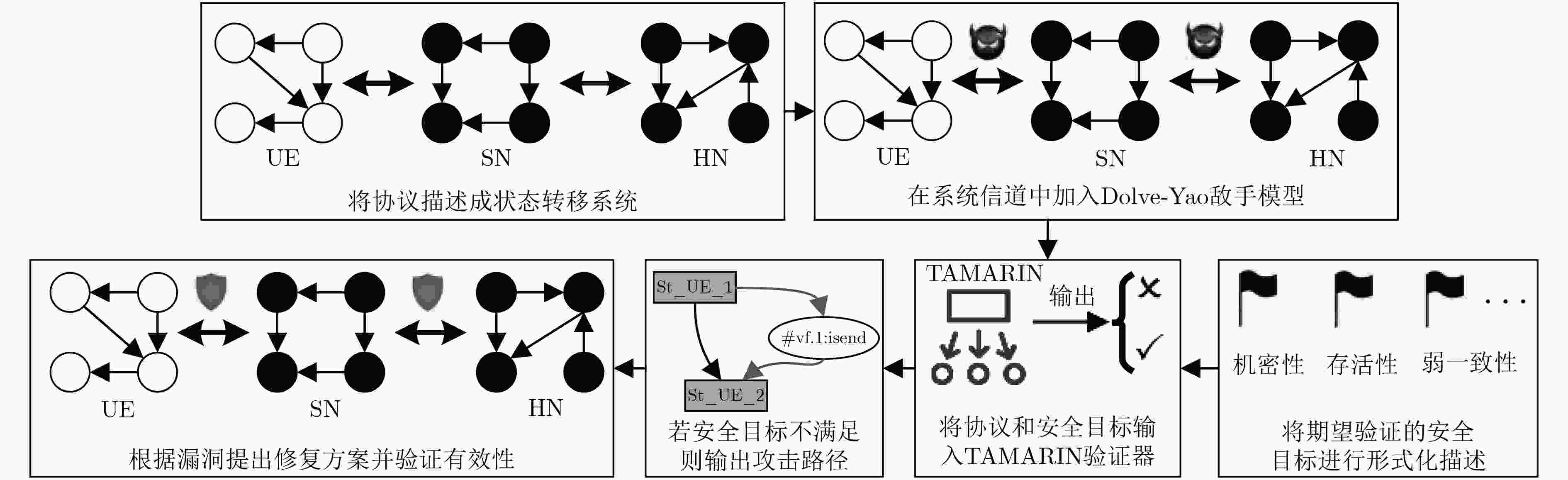







 下载:
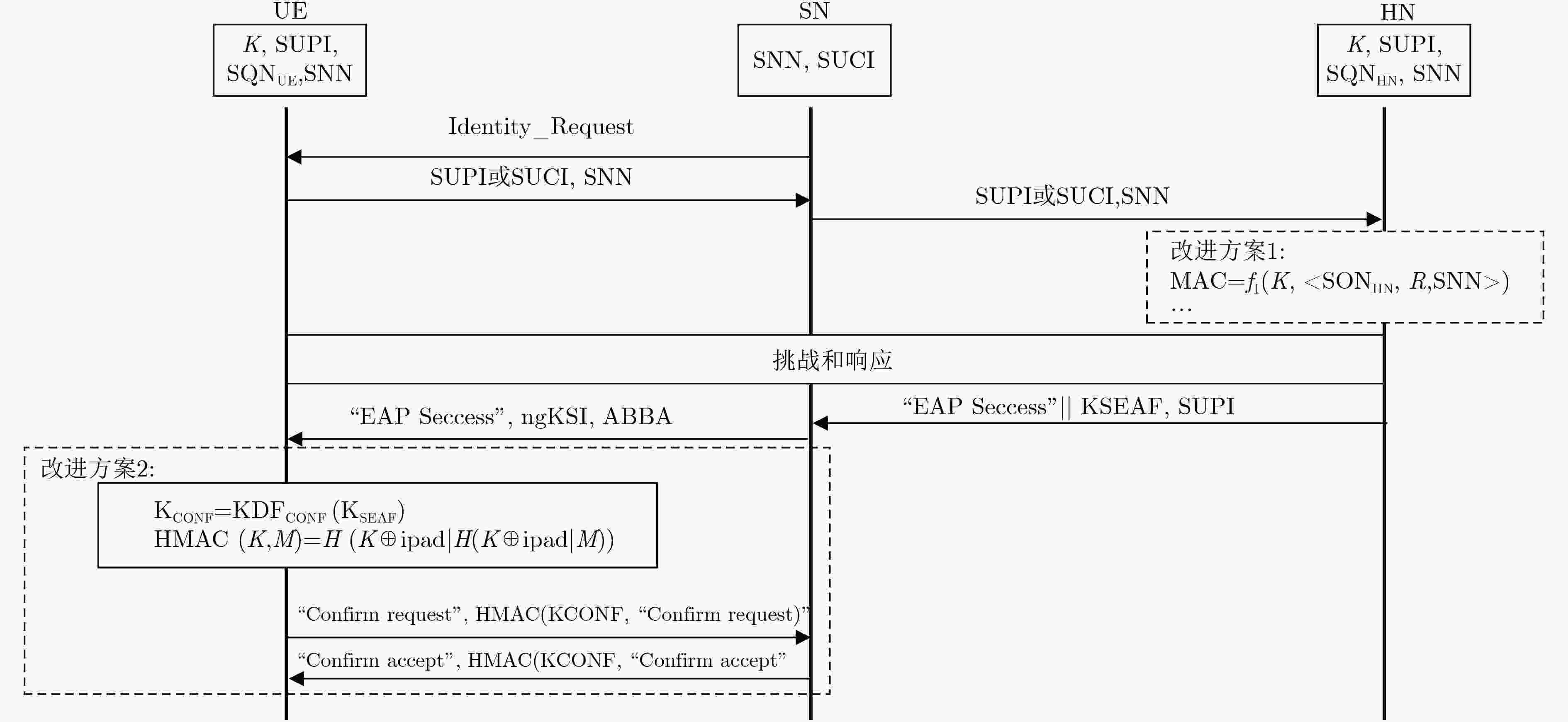
下载:
