Multi-feature Map Pyramid Fusion Deep Network for Semantic Segmentation on Remote Sensing Data
-
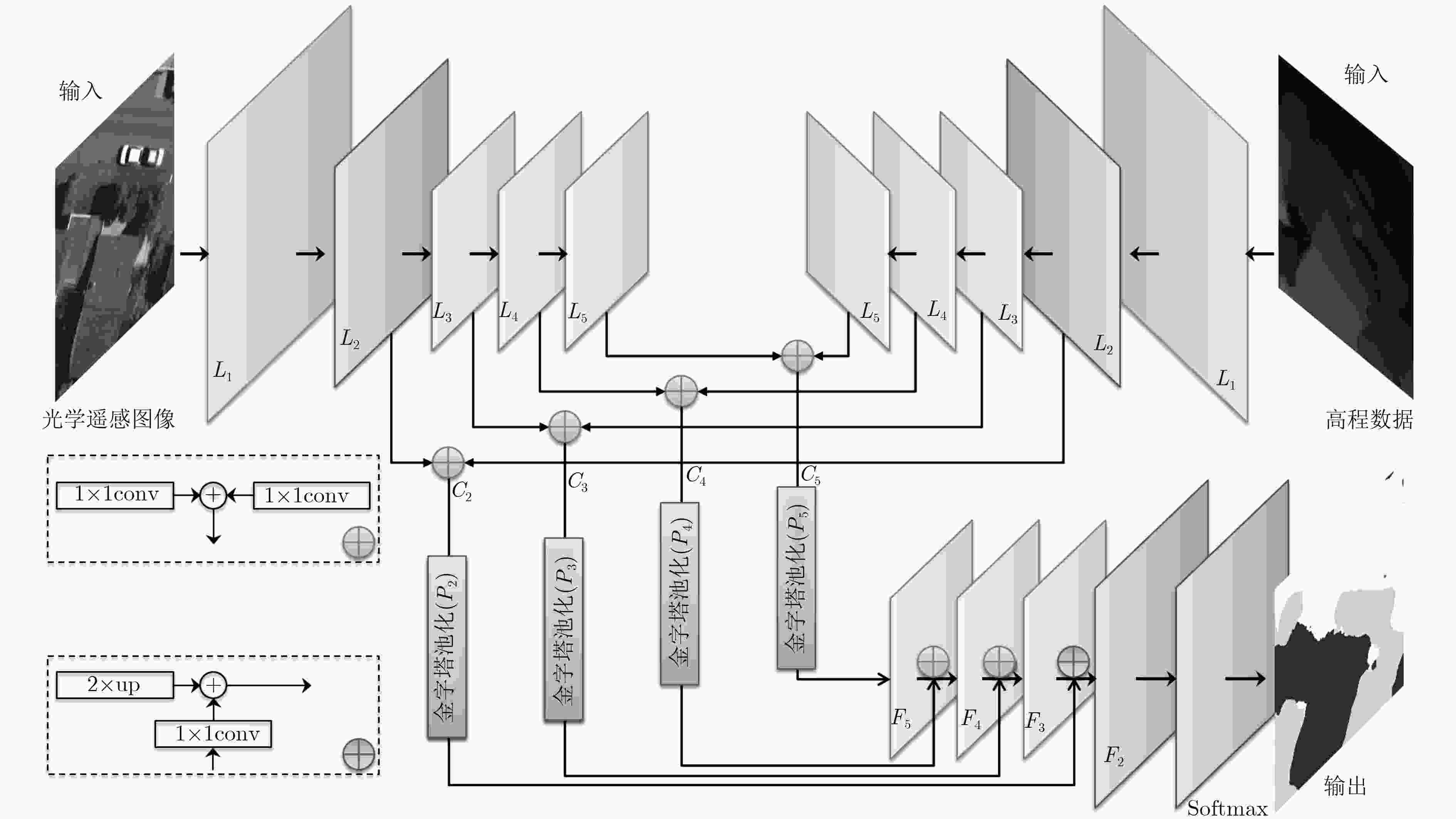
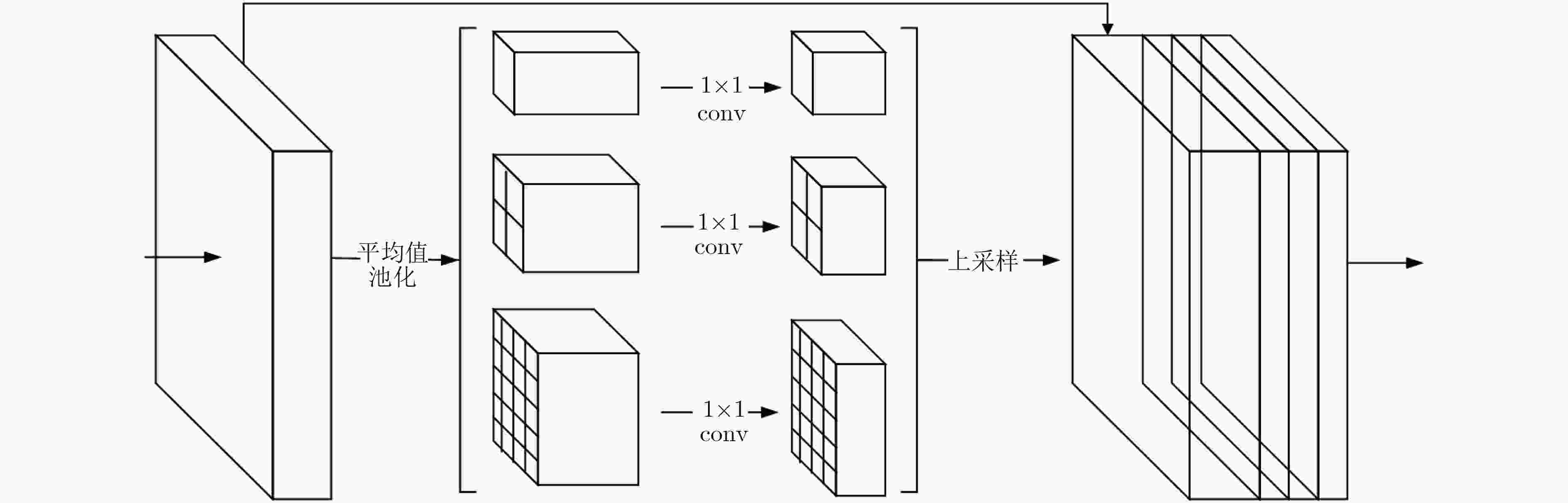
摘要: 在遥感图像语义分割中,利用多元数据(如高程信息)进行辅助是一个研究重点。现有的基于多元数据的分割方法通常直接将多元数据作为模型的多特征输入,未能充分利用多元数据的多层次特征,此外,遥感图像中目标尺寸大小不一,对于一些中小型目标,如车辆、房屋等,难以做到精细化分割。针对以上问题,提出一种多特征图金字塔融合深度网络(MFPNet),该模型利用光学遥感图像和高程数据作为输入,提取图像的多层次特征,然后针对不同层次的特征,分别引入金字塔池化结构,提取图像的多尺度特征,最后,设计了一种多层次、多尺度特征融合策略,综合利用多元数据的特征信息,实现遥感图像的精细化分割。基于Vaihingen数据集设计了相应的对比实验,实验结果证明了所提方法的有效性。Abstract: Utilizing multiple data (elevation information) to assist remote sensing image segmentation is an important research topic in recent years. However, the existing methods usually directly use multivariate data as the input of the model, which fails to make full use of the multi-level features. In addition, the target size varies in remote sensing images, for some small targets, such as vehicles, houses, etc., it is difficult to achieve detailed segmentation. Considering these problems, a Multi-Feature map Pyramid fusion deep Network (MFPNet) is proposed, which utilizes optical remote sensing images and elevation data as input to extract multi-level features from images. Then the pyramid pooling structure is introduced to extract the multi-scale features from different levels. Finally, a multi-level and multi-scale feature fusion strategy is designed, which utilizes comprehensively the feature information of multivariate data to achieve detailed segmentation of remote sensing images. Experiment results on the Vaihingen dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 特征编码网络结构
ResNet卷积层 光学遥感图像分支输出 高程数据分支输出 多元特征融合 融合输出 输出尺寸 7×7,64,步幅2 L1-img L1-ele 1/2 3×3,最大值池化,步幅2
$\left. \begin{aligned}& \ \, 1 \times 1,\;64\\ & \ \, 3 \times 3,\;64\;\;\;\; \times 3\\ & \ \, 1 \times 1,\;256 \end{aligned} \right\}$L2-img L2-ele √ C2 1/4 $\left. \begin{aligned} & 1 \times 1,\;128\\ & 3 \times 3,\;128\;\;\;\; \times 4\\ & 1 \times 1,\;512 \end{aligned} \right\}$ L3-img L3-ele √ C3 1/8 $\left. \begin{aligned} & 1 \times 1,\;128\\ & 3 \times 3,\;128\;\; \times 23\\ & 1 \times 1,\;512 \end{aligned} \right\}\left( {{\text{带孔卷积}} } \right)$ L4-img L4-ele √ C4 1/8 $\left. \begin{aligned}& \ \, 1 \times 1,\;512\\ & \ \, 3 \times 3,\;512\;\; \times 3\\ & \ \, 1 \times 1,\;2048 \end{aligned} \right\}\left( {{\text{带孔卷积}} } \right)$ L5-img L5-ele √ C5 1/8 表 2 MFPNet模型消融实验结果
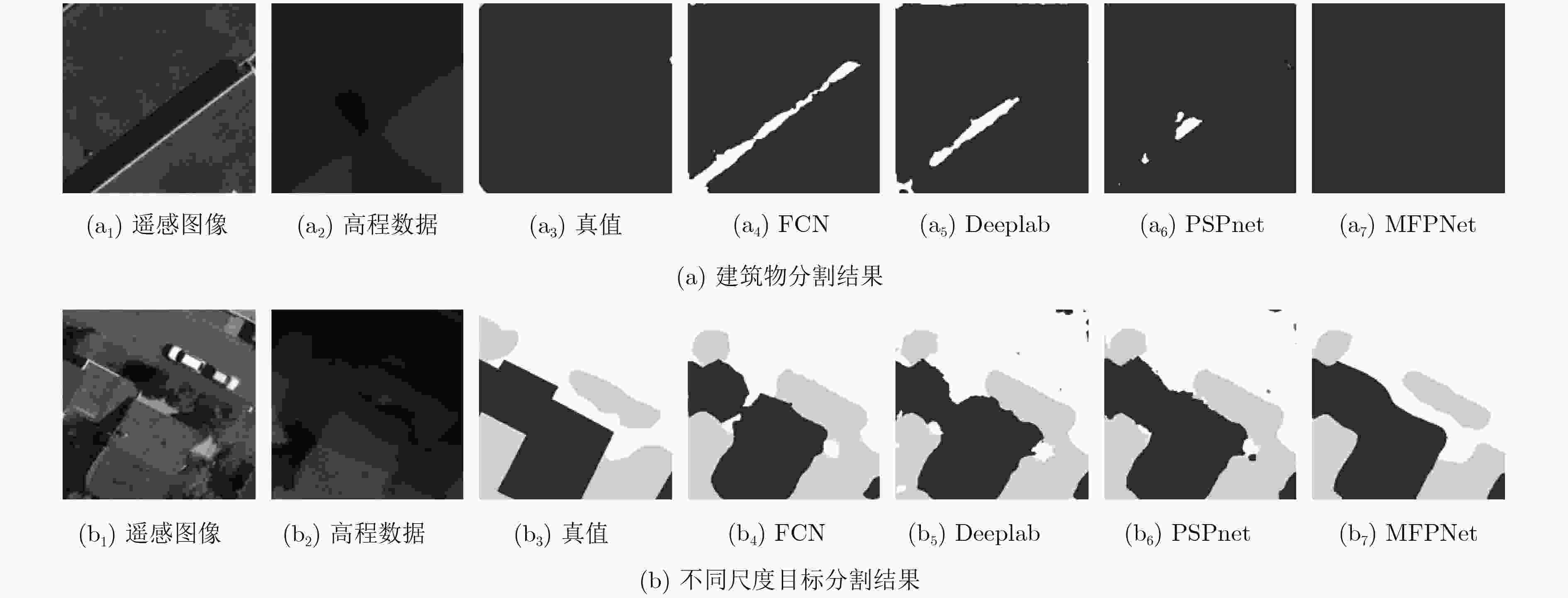
模型 mIOU OA F1 道路 建筑物 草地 树木 车辆 其它 Color-E 68.96 81.77 0.85 0.88 0.72 0.83 0.50 0.59 MFFNet 75.81 84.75 0.89 0.91 0.79 0.87 0.62 0.68 MFPNet 77.10 85.95 0.91 0.96 0.82 0.88 0.76 0.75 表 3 MFPNet与其他方法的对比结果
方法 mIoU OA F1 道路 建筑物 草地 树木 车辆 其它 FCN 59.65 79.67 0.82 0.86 0.69 0.81 0.56 0.59 Deeplab 70.85 82.75 0.86 0.89 0.72 0.82 0.60 0.61 PSPNet 74.96 83.92 0.90 0.93 0.74 0.81 0.65 0.63 MFPNet 77.10 85.95 0.91 0.96 0.82 0.88 0.76 0.75 -
DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 SHOTTON J, JOHNSON M, and CIPOLLA R. Semantic texton forests for image categorization and segmentation[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, Nevada, 2012: 1097–1105. LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. KAMPFFMEYER M, SALBERG A B, and JENSSEN R. Semantic segmentation of small objects and modeling of uncertainty in urban remote sensing images using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1–9. MAGGIORI E, TARABALKA Y, CHARPIAT G, et al. Convolutional neural networks for large-scale remote-sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(2): 645–657. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2612821 SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 MARMANIS D, WEGNER J D, GALLIANI S, et al. Semantic Segmentation of Aerial Images with an Ensemble of CNNS[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2016, III-3: 473–480. doi: 10.5194/isprsannals-III-3-473-2016 SHERRAH J. Fully convolutional networks for dense semantic labelling of high-resolution aerial imagery[J]. arXiv: 1606.02585, 2016. ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2016: 6230–6239. HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. HAZIRBAS C, MA L N, DOMOKOS C, et al. FuseNet: Incorporating depth into semantic segmentation via fusion-based CNN architecture[C]. The 13th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, China, 2016. ISPRS 2D semantic labeling contest[EB/OL]. http://www2.isprs.org/commissions/comm3/wg4/semantic-labeling.html, 2019. ABADI M, BARHAM P, CHEN Jianmin, et al. TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning[C]. The 12th USENIX Conference on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, Savannah, USA, 2016. CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
