Online Blind Equalization Algorithm for Satellite Channel Based on Echo State Network
-
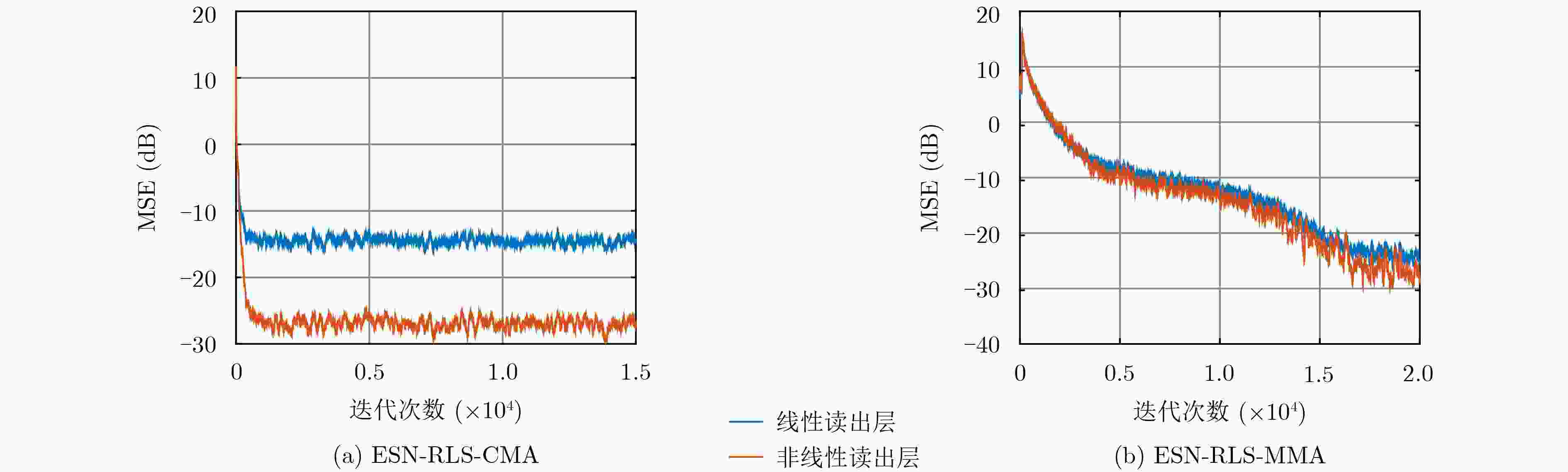
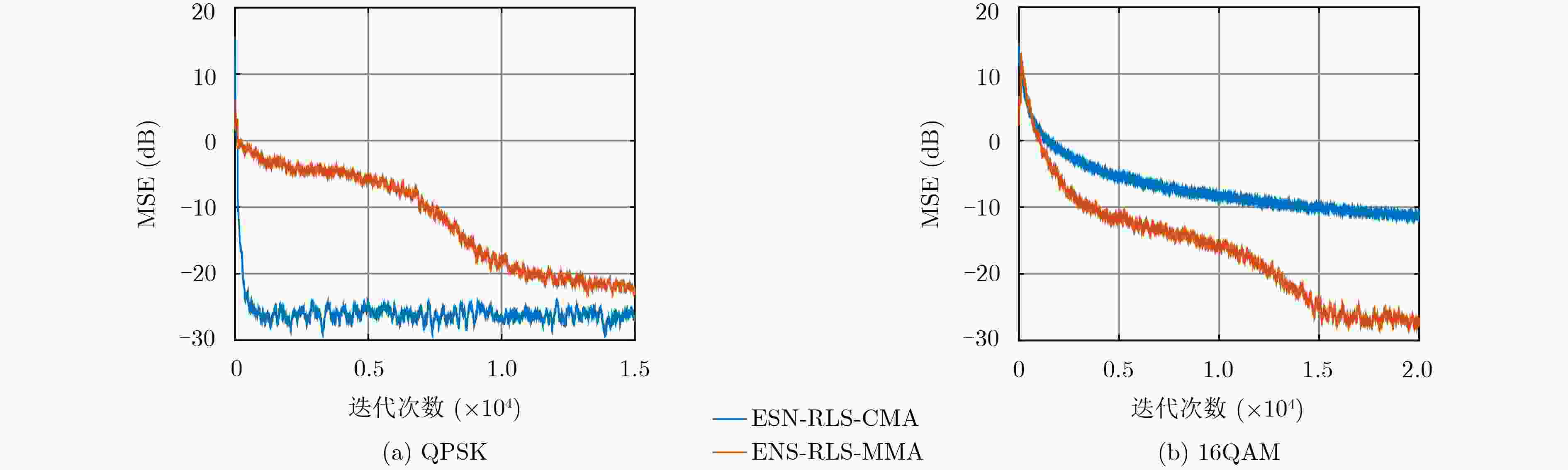
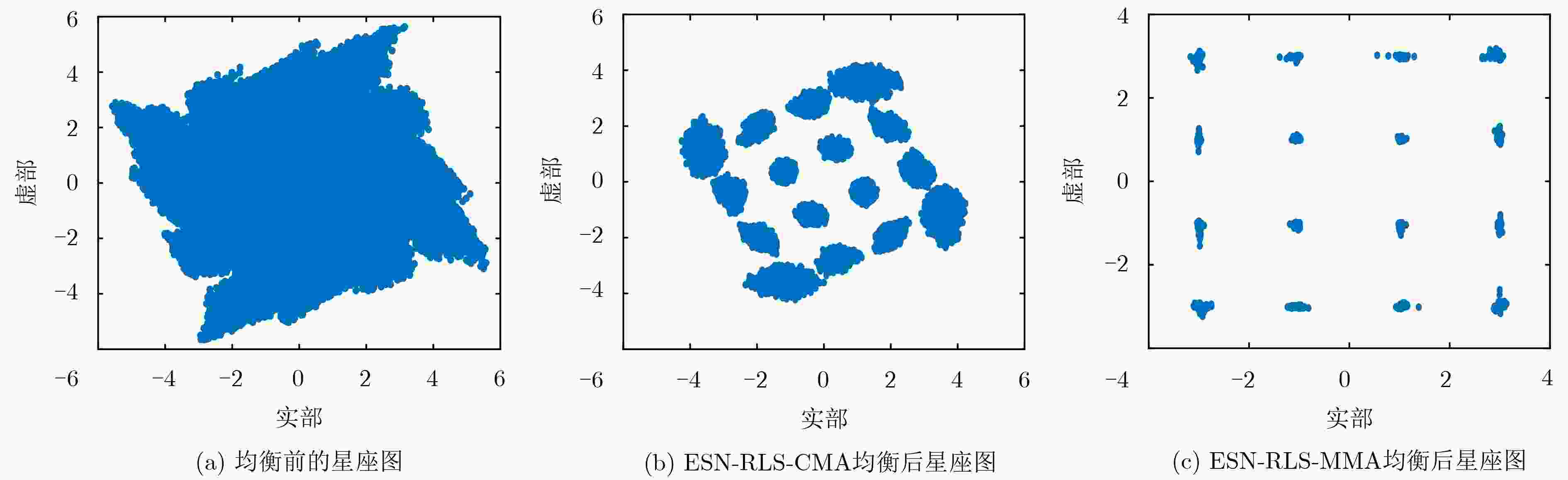
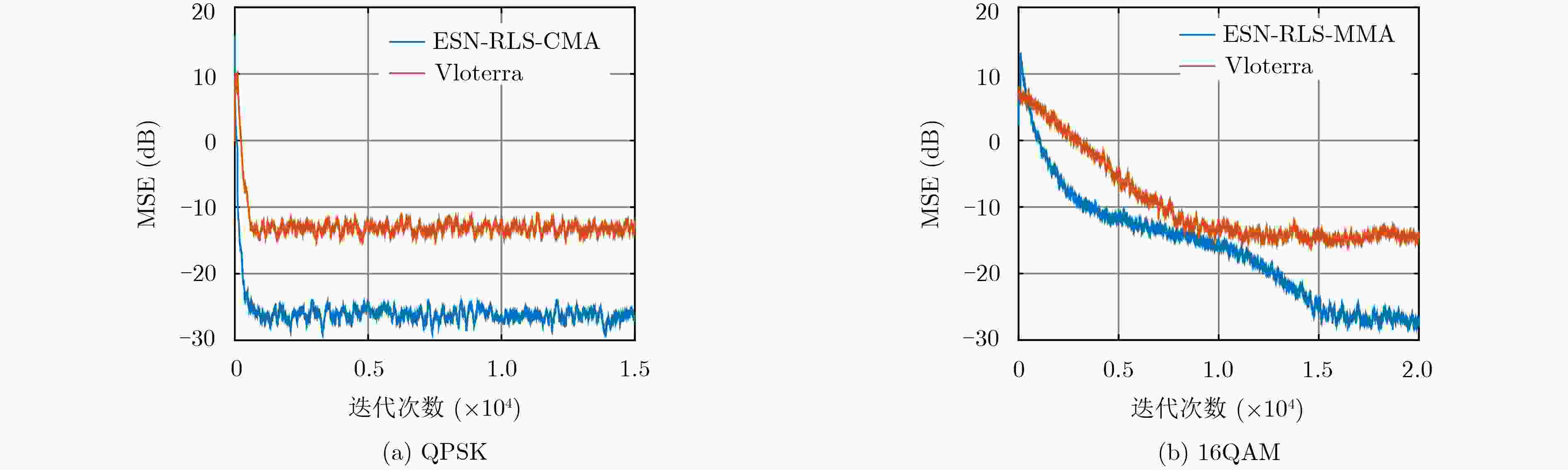
摘要: 针对非线性卫星信道,该文提出了两种基于回声状态网络(ESN)的在线盲均衡算法。利用ESN良好的非线性逼近能力,将发送信号的高阶统计量(HOS)代入ESN,结合常模算法(CMA)和多模算法(MMA)构造盲均衡的代价函数,并采用递归最小二乘(RLS)算法对ESN输出权值进行迭代寻优,实现了Volterra卫星信道下常模和多模信号的在线盲均衡。实验表明,该文算法可以有效降低非线性信道对发送信号产生的畸变,相较于传统的Volterra滤波方法,有更快的收敛速度和更低的均方误差值。
-
关键词:
- Volterra卫星信道 /
- 回声状态网络 /
- 常模算法 /
- 多模算法 /
- 递归最小二乘算法
Abstract: Two online blind equalization algorithms based on Echo State Network (ESN) in this paper are proposed for the nonlinear satellite channel. These two algorithms take advantage of the good nonlinear approximation of ESN to bring the High-Order Statistics (HOS) of the transmitted signal into the ESN, and constructing cost function of blind equalization by combining Constant Modulus Algorithm (CMA) and Multi-Modulus Algorithm (MMA). Then, the Recursive Least Squares (RLS) algorithm is used to iteratively optimize the network output weights, and the online blind equalization of the constant modulus signals and the multi-modulus signals over the channel of Volterra satellite are realized. Experiments show that the proposed algorithms can effectively reduce the distortion of the transmitted signal by the nonlinear channel. Compared with the traditional Volterra filtering method, they have faster convergence speed and lower mean square error. -
表 1 ESN-RLS-CMA算法
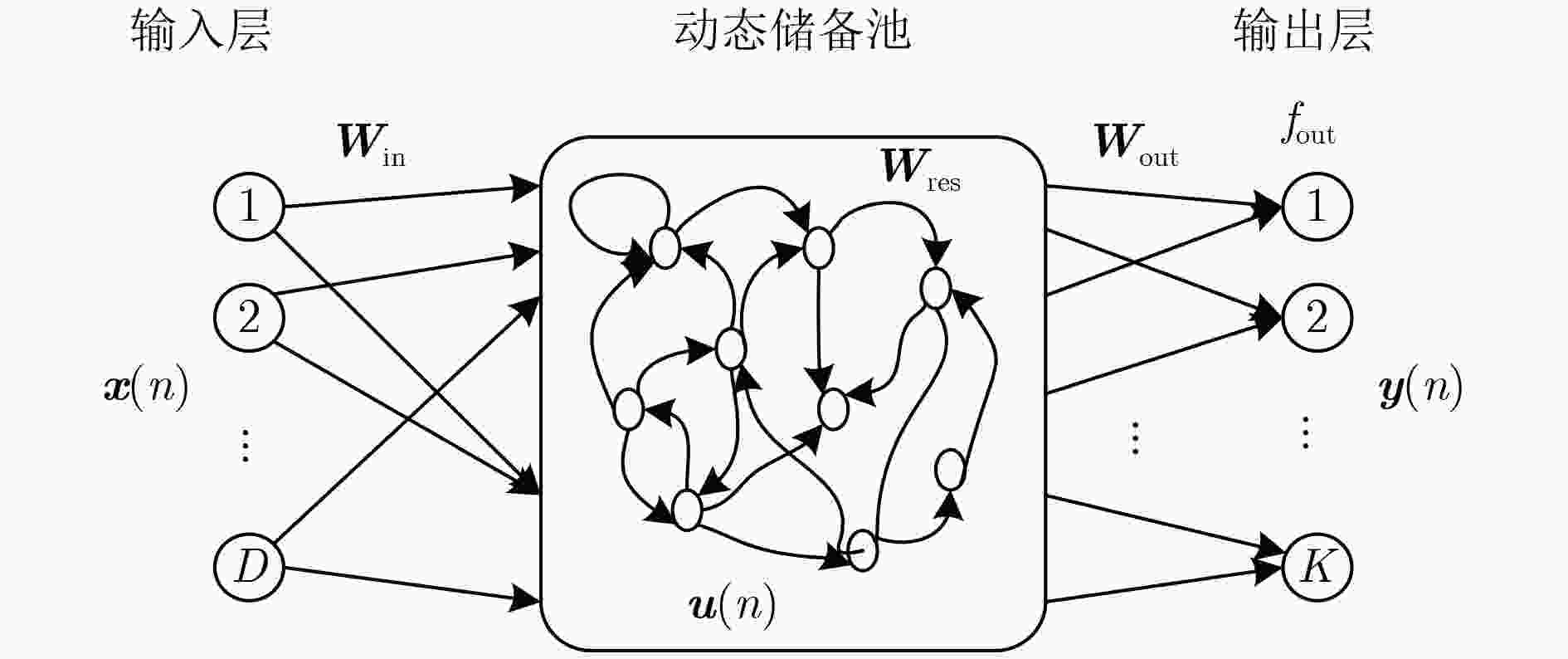
步骤 1 均衡器初始化:随机生成(${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{res}}}},{{\text{W}}_{{\rm{in}}}}$),初始化
${\text{u}}(0)$,${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}$和$\lambda $; ${\text{P}}(0) = {\delta ^{ - 1}}{\text{I}}$($\delta $是一个很小的正数);步骤 2 For:n=1, 2,···, N; (1) 更新储备池状态:${\text{u}}(n) = f({{\text{W}}_{{\rm{res}}}}{\text{u}}(n - 1) + {{\text{W}}_{{\rm{in}}}}x(n))$; (2) 计算$y\left( n \right) = {{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}\left( {n - 1} \right){\text{u}}\left( n \right)$; (3) 由式(7)得到${\tilde{\text U}}(n,n)$,通过式(11)计算自相关矩阵${\text{P}}(n)$; (4) 按照式(12)更新ESN的输出权值${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}(n)$; (5) 根据文献[14]的方法调整$\lambda $值。 End; 步骤 3 迭代直到网络收敛为止。 表 2 ESN-RLS-MMA算法
步骤 1 均衡器初始化:随机生成(${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{res}}}},{{\text{W}}_{{\rm{in}}}}$);初始化
${\text{u}}(0)$,${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}$,$\lambda $($0 \ll \lambda < 1$),${{\hat{\text R}}^{ - 1}}(0){\rm{ = }}\delta {\text{I}}$($\delta $是一个很小的正
数);设置$\gamma {\rm{ \!=\! }}3{\rm{E}} \{ s_{\rm{R}}^2(n)\} \!-\! {R_{{\rm{MMA}}}}$,门限值T=$3{\rm{E}}\{ {\left|\! {s(n)}\! \right|^2}\} $;步骤 2 For:n=1,2,···,N; (1) 更新储备池状态:${\text{u}}(n) = f({{\text{W}}_{{\rm{res}}}}{\text{u}}(n - 1) + {{\text{W}}_{{\rm{in}}}}x(n))$; (2) 计算$y(n) = {{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}(n - 1){\text{u}}(n)$; (3) 通过式(30)计算${{\hat{\text R}}^{ - 1}}(n)$; (4) 计算:${d_{\rm{R}}}(n) = \left[ {\gamma + {R_{{\rm{MMA}}}} - y_{\rm{R}}^2(n)} \right]{y_{\rm{R}}}(n)$,
${d_{\rm{I}}}(n) = \left[ {\gamma + {R_{{\rm{MMA}}}} - y_{\rm{I}}^2(n)} \right]{y_{\rm{I}}}(n)$$d(n) = {\gamma ^{{\rm{ - }}1}}\left[ {{d_{\rm{R}}}(n) + j{d_{\rm{I}}}(n)} \right]$; (5) If ${\left| {y(n)} \right|^2}$>T; $d(n) = 0$ End; (6) 根据式(32)更新${{\text{W}}_{{\rm{out}}}}(n)$。 End; 步骤 3 迭代直到网络收敛为止。 表 3 取不同储备池规模N时两种算法的MSE值(dB)
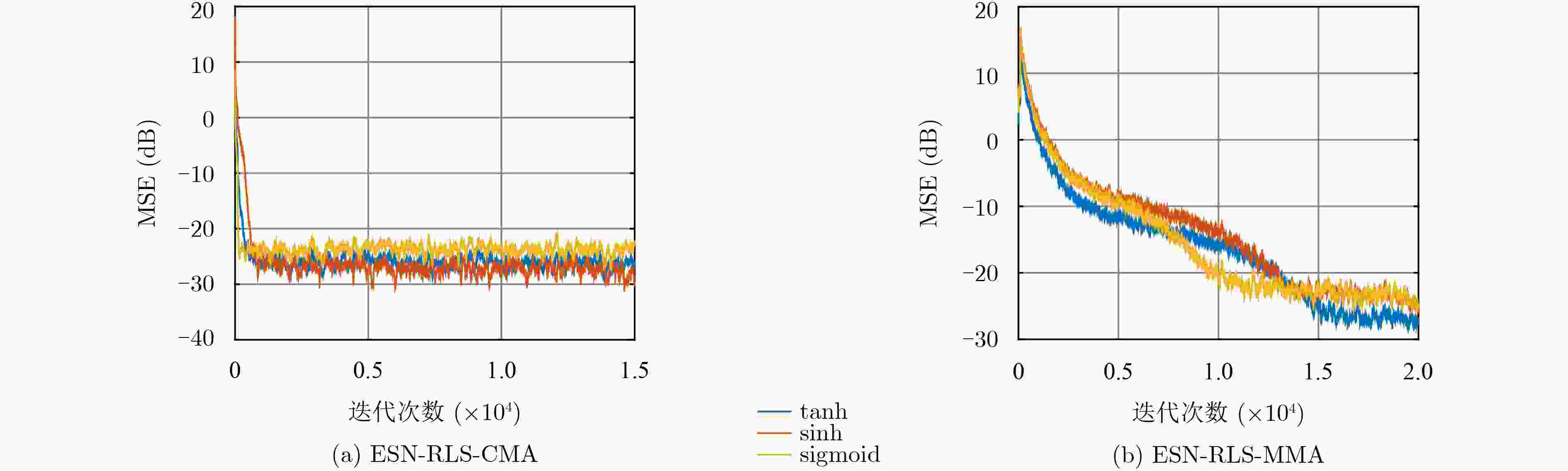
算法 N=20 N=50 N=100 N=200 N=300 ESN-RLS-CMA –22.56 –28.12 –29.06 –28.41 –28.72 ESN-RLS-MMA –18.12 –29.58 –30.62 –29.10 –29.29 表 4 本文算法与5阶Volterra滤波算法的运算复杂度对比
算法 运算复杂度 Volterra O(24M5+16M3+8M) ESN-RLS-CMA O(4N3+18N2+10N) ESN-RLS-MMA O(4N3+19N2+10N) -
MELONI A and MURRONI M. On the genetic optimization of APSK constellations for satellite broadcasting[C]. 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting, Beijing, China, 2014: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BMSB.2014.6873465. MOUSSA A, POULIQUEN M, FRIKEL M, et al. Blind equalisation in the presence of bounded noise[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2018, 12(8): 957–965. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2017.0445 孙海飞, 江桦. 非线性卫星信道下的粒子滤波盲均衡方法[J]. 信号处理, 2015, 31(5): 587–593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.05.011SUN Haifei and JIANG Hua. Particle filtering blind equalization method in nonlinear satellite channel[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(5): 587–593. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.05.011 SÉNÉCAL S, AMBLARD P O, and CAVAZZANA L. Particle filtering equalization method for a satellite communication channel[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2004, 2004: 591429. doi: 10.1155/S1110865704404090 MALONE J and WICKERT M A. Practical volterra equalizers for wideband satellite communications with TWTA nonlinearities[C]. 2011 Digital Signal Processing and Signal Processing Education Meeting, Sedona, USA, 2011: 481–53. doi: 10.1109/DSP-SPE.2011.5739185. 郭业才, 费赛男, 王惠. 基于多小波双变换的非线性卫星信道盲均衡算法[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44(10): 2384–2390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.10.015GUO Yecai, FEI Sainan, and WANG Hui. Nonlinear satellite channel blind equalization algorithm based on multi-wavelet double transformation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44(10): 2384–2390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.10.015 BENVENUTO N, MARCHESI M, PIAZZA F, et al. Non linear satellite radio links equalized using blind neural networks[C]. 1991 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Toronto, Canada, 1991: 1521–1524. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1991.150526. LI Yanqin, GUO Chunsheng, ZHANG Zhen, et al. A novel feed-forward neural network blind equalization algorithm[C]. 2010 International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing, Dalian, China, 2010: 404–408. doi: 10.1109/ICICIP.2010.5564245. 王贵银. 复数Hopfield神经网络盲均衡QAM信号[J]. 电子测试, 2011(5): 57–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2011.05.014WANG Guiyin. Blind equalization of QAM with a complex Hopfield neural network[J]. Electronic Test, 2011(5): 57–60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2011.05.014 RUAN Xiukai, LI Chang, YANG Weibo, et al. Blind sequence detection using reservoir computing[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 62: 81–90. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.10.012 ZORN S, EHM H J, and WEIGEL R. A novel technique for determining kernels of volterra based behavioral models for RF amplifiers[C]. The 38th European Microwave Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2008: 246–249. doi: 10.1109/EUMC.2008.4751434. 唐成凯, 张玲玲, 廉保旺. 卫星高阶调制信号通信下非线性误差修正均衡方法[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(1): 117–125. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017014TANG Chengkai, ZHANG Lingling, and LIAN Baowang. Nonlinear error modified equalization algorithm in high-order modulation of satellite communication[J]. Journal of Communications, 2017, 38(1): 117–125. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017014 ZHOU Haowen, HUANG Jinquan, LU Feng, et al. Echo state kernel recursive least squares algorithm for machine condition prediction[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 111: 68–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.03.047 PARK D J, JUN B E, and KIM J H. Fast tracking RLS algorithm using novel variable forgetting factor with unity zone[J]. Electronics Letters, 1991, 27(23): 2150–2151. doi: 10.1049/el:19911331 李进, 冯大政, 刘文娟. 快速QAM信号多模盲均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00609LI Jin, FENG Dazheng, and LIU Wenjuan. A fast multimodulus blind equalization algorithm for QAM signal[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(2): 273–279. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00609 PAVAN F R M, SILVA M T M, and MIRANDA M D. A numerically robust blind equalization scheme applied to MIMO communication systems[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(1): 596–624. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2017.10.036 MBOUP M and REGALIA P A. A gradient search interpretation of the super-exponential algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2000, 46(7): 2731–2734. doi: 10.1109/18.887889 MIRANDA M D, SILVA M T M, and NASCIMENTO V H. Avoiding divergence in the shalvi-weinstein algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(11): 5403–5413. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.928505 -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
