An Affine Projection Algorithm with Multi-scale Kernels Learning
-
摘要:
为了提高强非线性信号的噪声消除和信道均衡能力,在核学习自适应滤波方法的基础上,该文提出一种基于惊奇准则的多尺度核学习仿射投影滤波方法(SC-MKAPA)。在核仿射投影滤波算法的基础上,对核组合函数结构进行改进,将多个不同高斯核带宽作为可变参数,与加权系数共同参与滤波器的更新;利用惊奇准则将计算结果稀疏化,根据仿射投影算法的约束条件对惊奇测度进行改进,简化其方差项,降低了计算的复杂度。将该算法应用于噪声消除、信道均衡以及MG时间序列预测中,与多种自适应滤波算法及核学习自适应滤波算法进行仿真结果的对比分析,验证了该算法的优越性。
Abstract:In order to improve the ability of noise elimination and channel equalization of strong non-linear signals, a Multi-scale Kernels learning Affine Projection filtering Algorithm based on Surprise Criterion (SC-MKAPA) is proposed on the basis of kernel learning adaptive filtering method. Based on the kernel affine projection filtering algorithm, the structure of the kernel combination function is improved, and the bandwidths of several different Gaussian kernels are taken as variable parameters to participate in the update of the filter together with the weighted coefficients.The calculation results are sparsed by using the surprise criterion, and the surprise measure is improved according to the constraints of the affine projection algorithm, which simplifies the variance term and reduces the calculation complexity. The algorithm is applied to noise cancellation, channel equalization, and Mackey Glass (MG) time series prediction. The simulation results are compared with the traditional adaptive filtering algorithm and the kernel learning adaptive filtering algorithm, it proves the superiority of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 算法参数
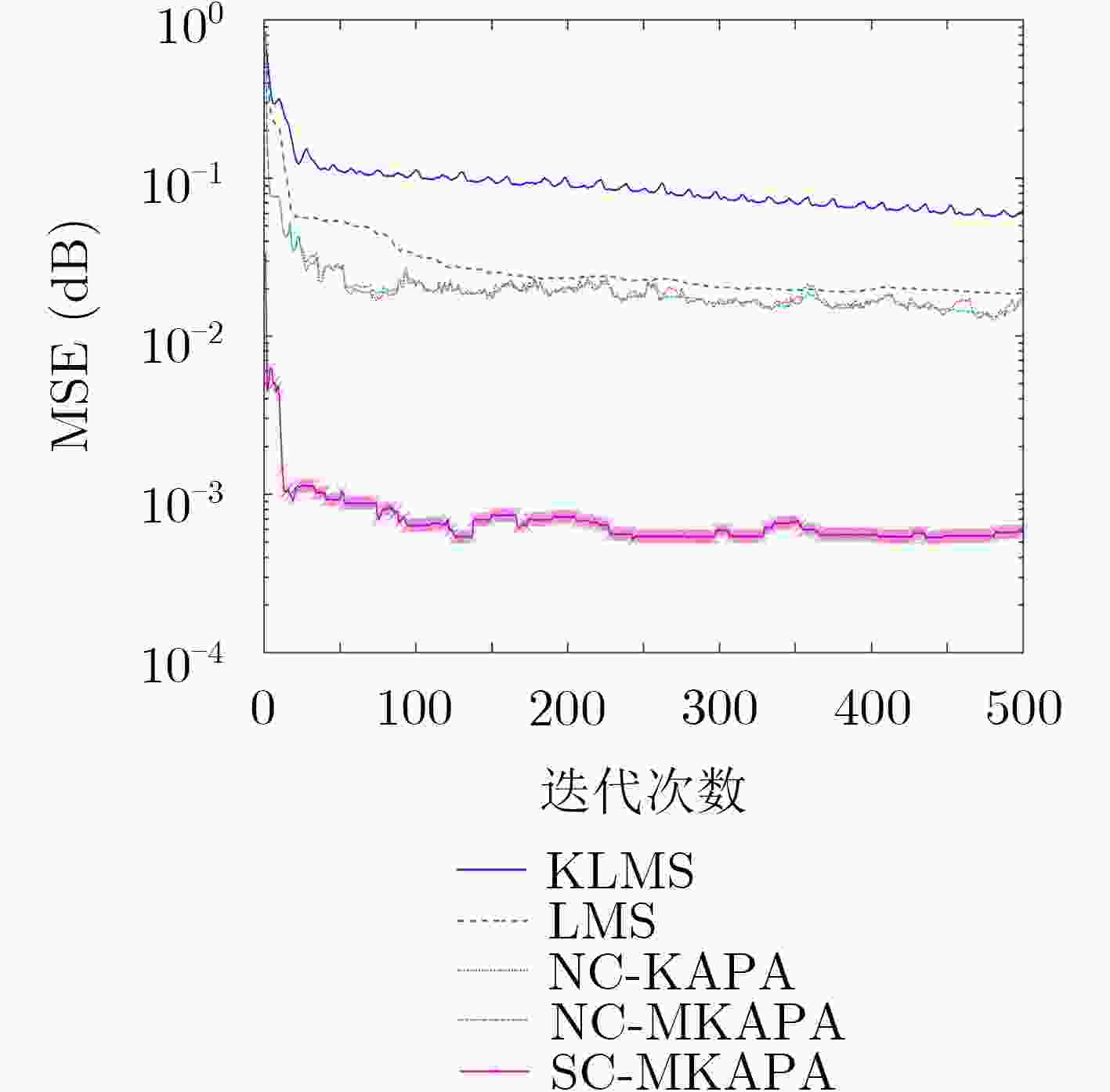
算法 核带宽 收敛因子 正则化参数$\delta $ SC-MKAPA ${\eta _1} = 1.0$, ${\eta _{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{0}}{\rm{.5}}$, ${\eta _{\rm{3}}} = 1{\rm{0}}$ $\mu = 0.2$, $\Delta t = 0.01$ 5.0×10–3 NC-MKAPA ${\eta _1} = 1.0$, ${\eta _{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{0}}{\rm{.5}}$, ${\eta _{\rm{3}}} = 1{\rm{0}}$ $\mu = 0.2$ 5.0×10–3 NC-KAPA ${\eta _1} = 1.0$ $\mu = 0.2$ 5.0×10–3 KLMS ${\eta _1} = 1.0$ $\mu = 0.2$ 5.0×10–3 LMS ${\eta _1} = 1.0$ $\mu = 0.2$ 5.0×10–3 表 2 不同高次项下5种方法MMSE(dB)
高次项$N$ SC-MKAPA NC-MKAPA NC-KAPA KLMS LMS 2 –71.2 –62.8 –67.2 –32.7 –25.6 3 –62.1 –56.9 –60.6 –24.4 –19.3 6 –33.9 –29.3 –30.2 –21.5 –17.8 7 –18.3 –16.3 –15.2 –13.3 –12.9 -
AIZERMAN A, BRAVERMAN E M, and ROZONER L I. Theoretical foundations of the potential function method in pattern recognition learning[J]. Automation and Remote Control, 1964, 25(5): 821–837. FRIEß T and HARRISON R F. A kernel-based adaline for function approximation[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 1999, 3(4): 307–313. doi: 10.3233/IDA-1999-3405 庞业勇, 王少军, 彭宇, 等. 一种在线时间序列预测的核自适应滤波器向量处理器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(1): 53–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150157PANG Yeyong, WANG Shaojun, PENG Yu, et al. A kernel adaptive filter vector processor for online time series prediction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(1): 53–62. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150157 BLANDON J S, VALENCIA C K, ALVAREZ A, et al. Shape classification using Hilbert space embeddings and kernel adaptive filtering[C]. The 15th International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Portugal, 2018: 245–251. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-93000-8_28. GAO Wei, YAN Yi, ZHANG Lingling, et al. Convex combinations of multiple kernel adaptive filters[C]. 2017 IEEE International conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICSPCC.2017.8242551. 孙丹华, 孙亮, 王彬, 等. α稳定分布噪声下基于核方法的非线性信道均衡算法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(3): 223–228. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.02.013SUN Danhua, SUN Liang, WANG Bin, et al. Nonlinear channel equalization algorithm based on kernel method for α-stable noise[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(3): 223–228. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.02.013 SHIN B S, YUKAWA M, CAVALCANTE R L G, et al. Distributed adaptive learning with multiple kernels in diffusion networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5505–5519. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2868040 HAN Yina, YANG Yixin, LI Xuelong, et al. Matrix-regularized multiple kernel learning via (r, p) Norms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(10): 4997–5007. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2785329 LIU Yuqi, SUN Chao, and JIANG Shouda. A reduced gaussian kernel least-mean-square algorithm for nonlinear adaptive signal processing[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(1): 371–394. doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0862-0 SHOAIB B, QURESHI I M, BUTT S A, et al. Adaptive step size kernel least mean square algorithm for Lorenz time series prediction[C]. The 12th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2015: 218–221. doi: 10.1109/IBCAST.2015.7058507. 胡站伟, 焦立国, 徐胜金, 等. 基于多尺度重采样思想的类指数核函数构造[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(7): 1689–1695. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151101HU Zhanwei, JIAO Liguo, XU Shengjin, et al. Design of an exponential-like kernel function based on multi-scale resampling[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(7): 1689–1695. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151101 PUAL T K and OGUNFUNMI T. A kernel adaptive algorithm for quaternion-valued inputs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(10): 2422–2439. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2014.2383912 NISHIKAWA K and NAKAZATO H. Mixture structure of kernel adaptive filters for improving the convergence characteristics[C]. 2012 Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Hollywood, USA, 2012: 1–6. POKHAREL R, SETH S, and PRINCIPE J C. Mixture kernel least mean square[C]. 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Dallas, USA, 2013: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN.2013.6706867. VAN VAERENBERGH S, SCARDAPANE S, and SANTAMARIA I. Recursive multikernel filters exploiting nonlinear temporal structure[C]. The 25th European Signal Processing Conference, Kos, Greece, 2017: 2674–2678. doi: 10.23919/EUSIPCO.2017.8081696. SILVA M T M, CANDIDO R, ARENAS-GARCIA J, et al. Improving multikernel adaptive filtering with selective bias[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018: 4529–4533. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8461290. ISHIDA T and TANAKA T. Multikernel adaptive filters with multiple dictionaries and regularization[C]. 2013 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Kaohsiung, China, 2013: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/APSIPA.2013.6694279. TODA O and YUKAWA M. On kernel design for online model selection by Gaussian multikernel adaptive filtering[C]. Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Siem Reap, Camboya, 2014: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/APSIPA.2014.7041802. LIU Weifeng and PRÍNCIPE J. Kernel affine projection algorithms[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 2008: 784292. doi: 10.1155/2008/784292 RICHARD C, BERMUDEZ J C M, and HONEINE P. Online prediction of time series data with kernels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(3): 1058–1066. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2009895 GAO Wei, CHEN Jie, RICHARD C, et al. Kernel LMS algorithm with forward-backward splitting for dictionary learning[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 5735–5739. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638763. TAKIZAWA M A and YUKAWA M. An efficient sparse kernel adaptive filtering algorithm based on isomorphism between functional subspace and Euclidean space[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 2014: 4508–4512. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2014.6854455. -





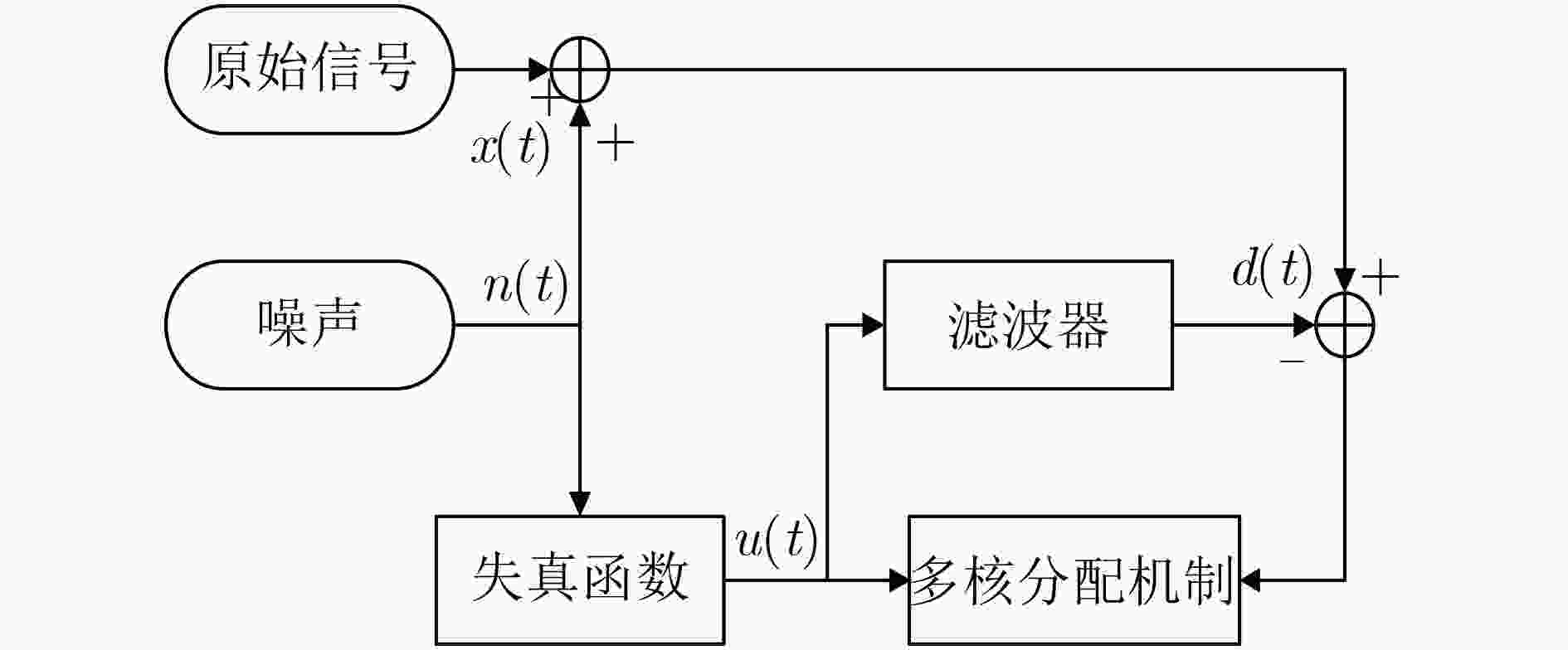
 下载:
下载:
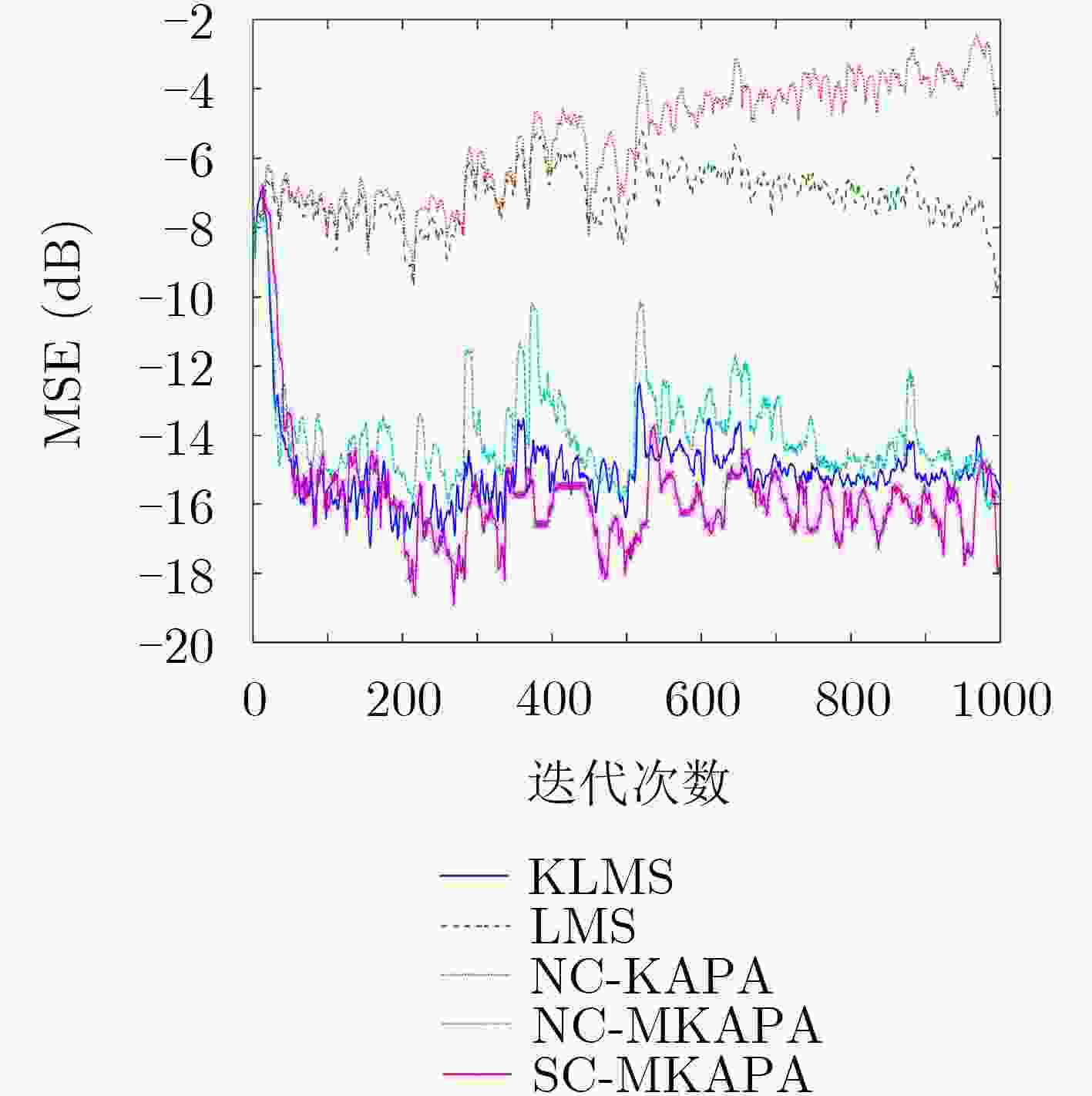
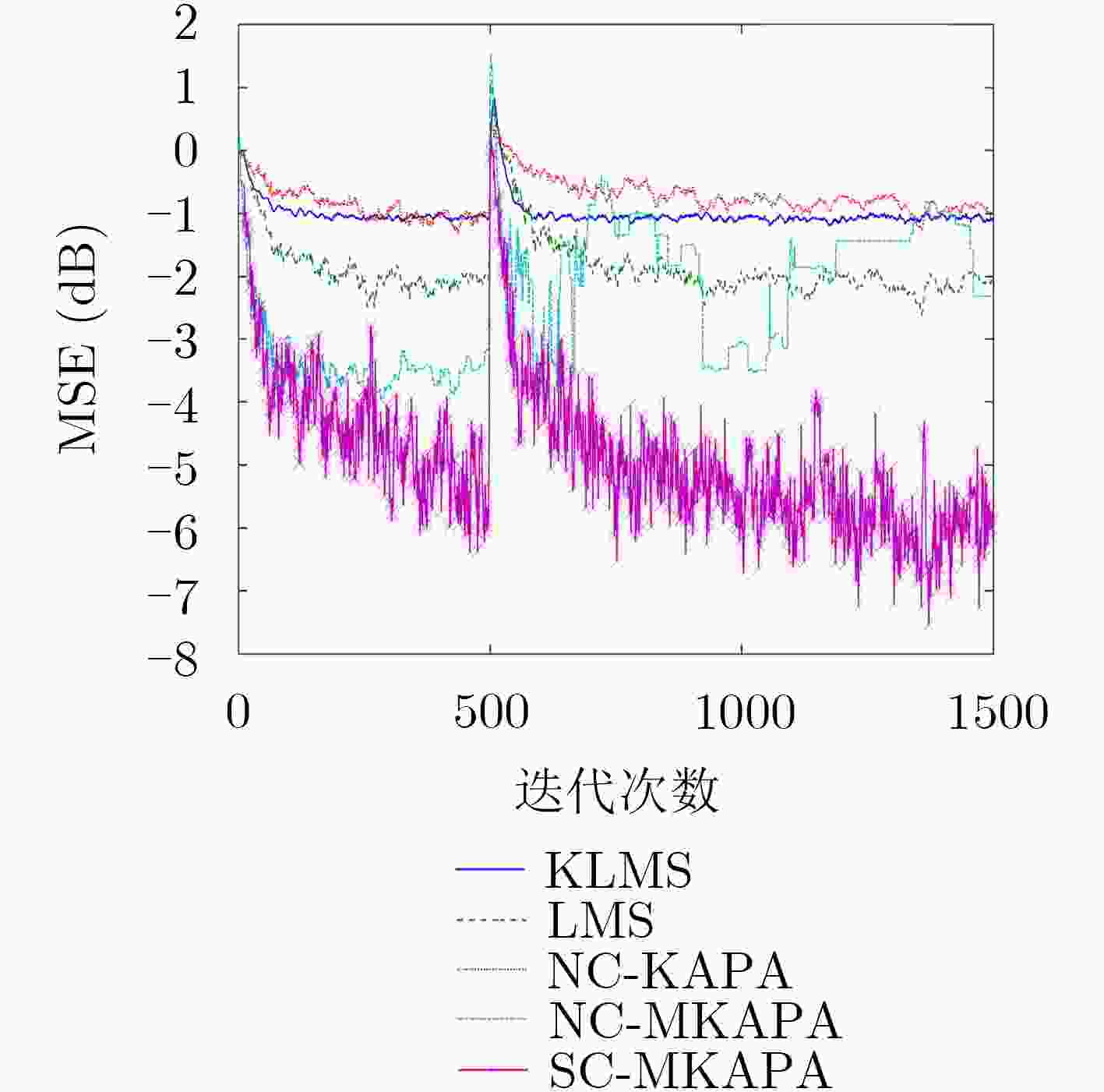


 下载:
下载:
