An Anti-Dense False Target Jamming Algorithm Based on Agile Frequency Joint Hough Transform
-
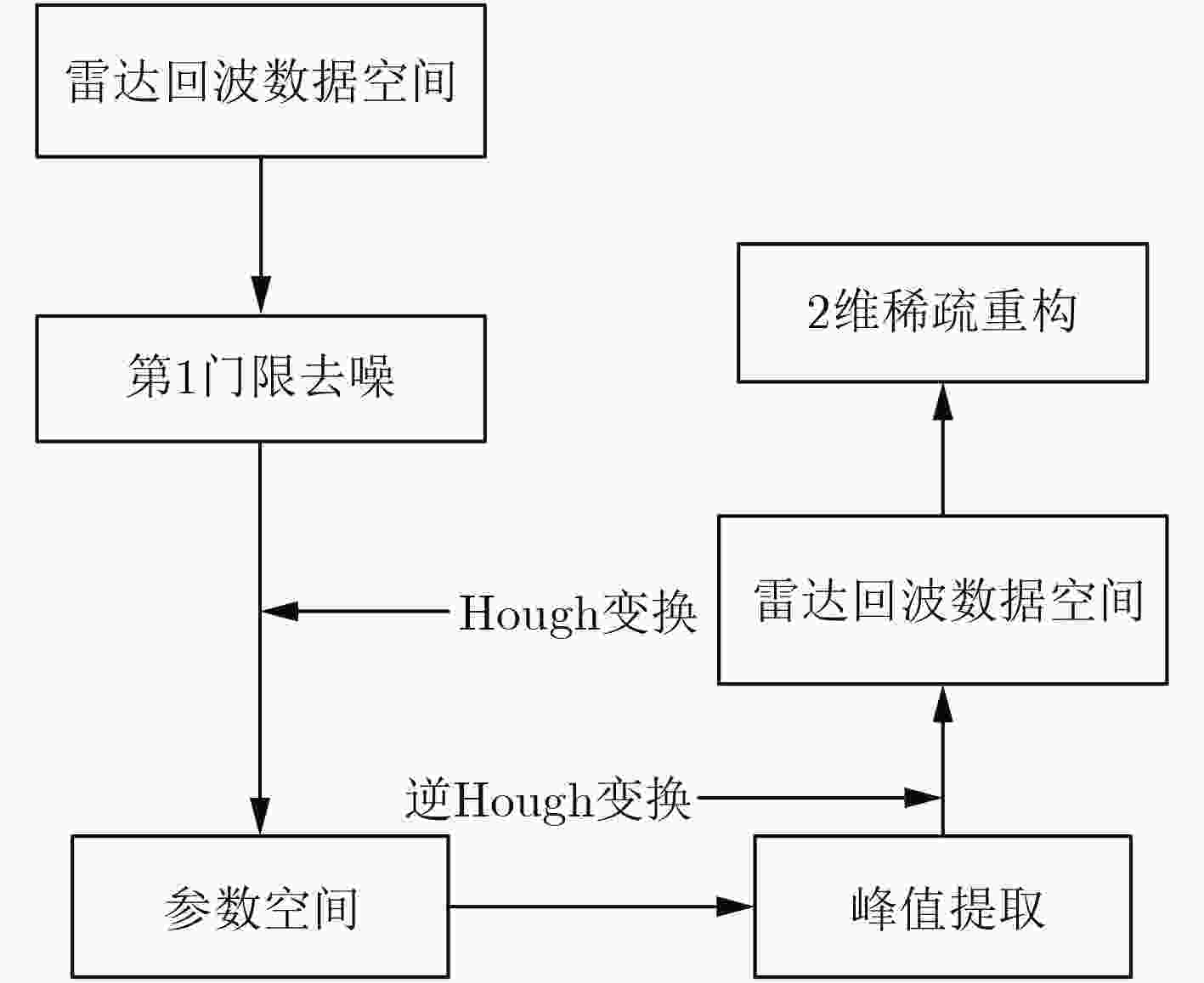
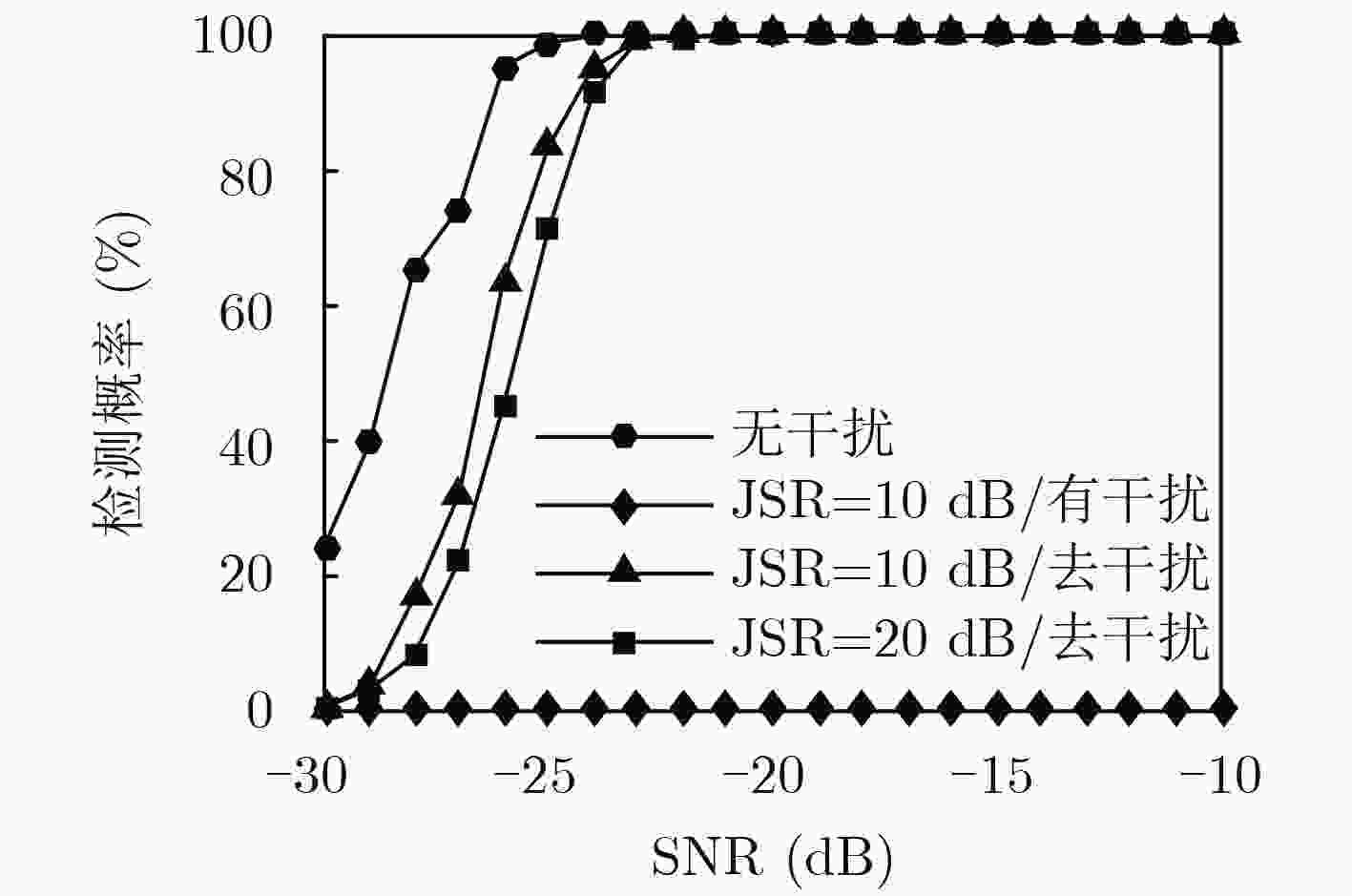
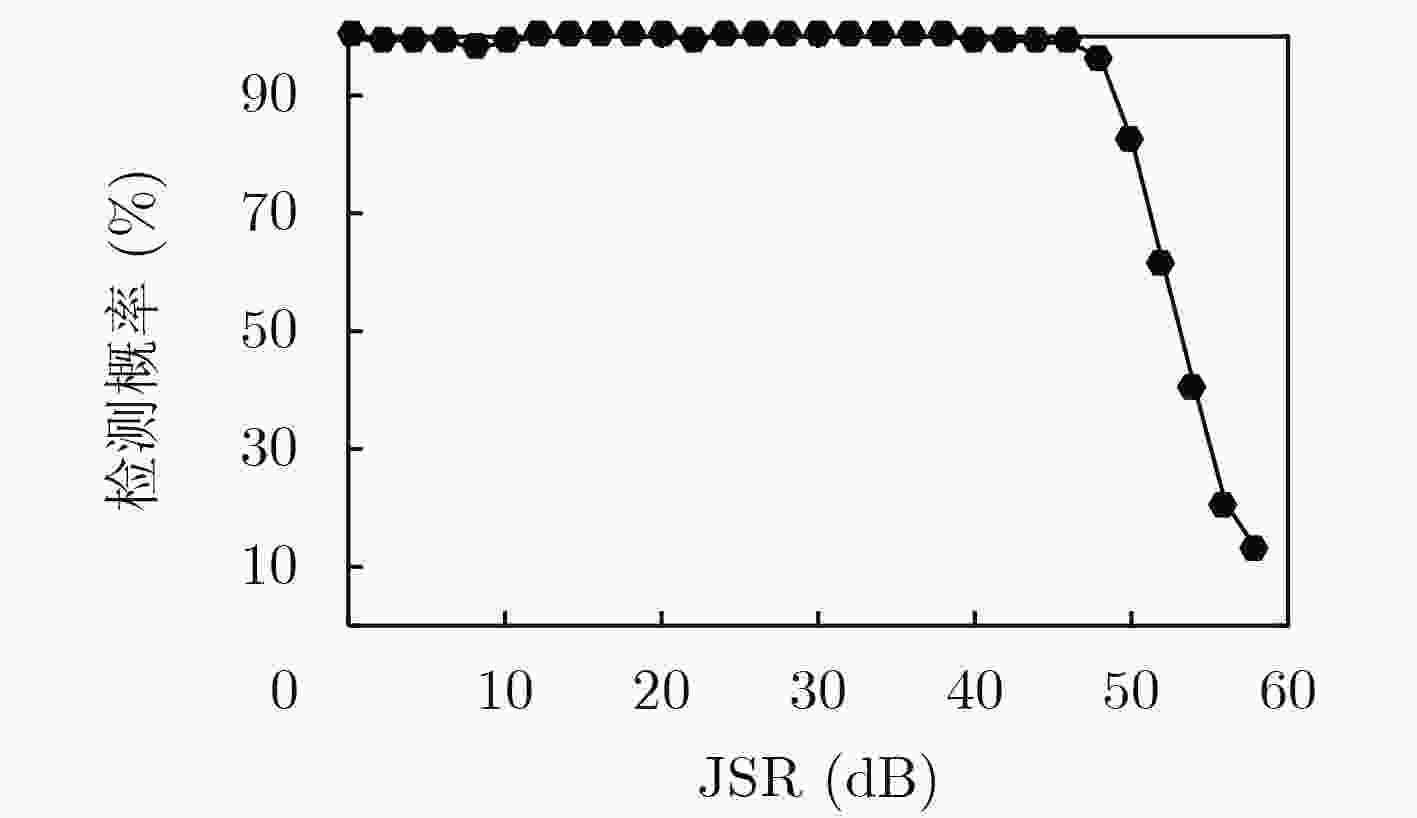
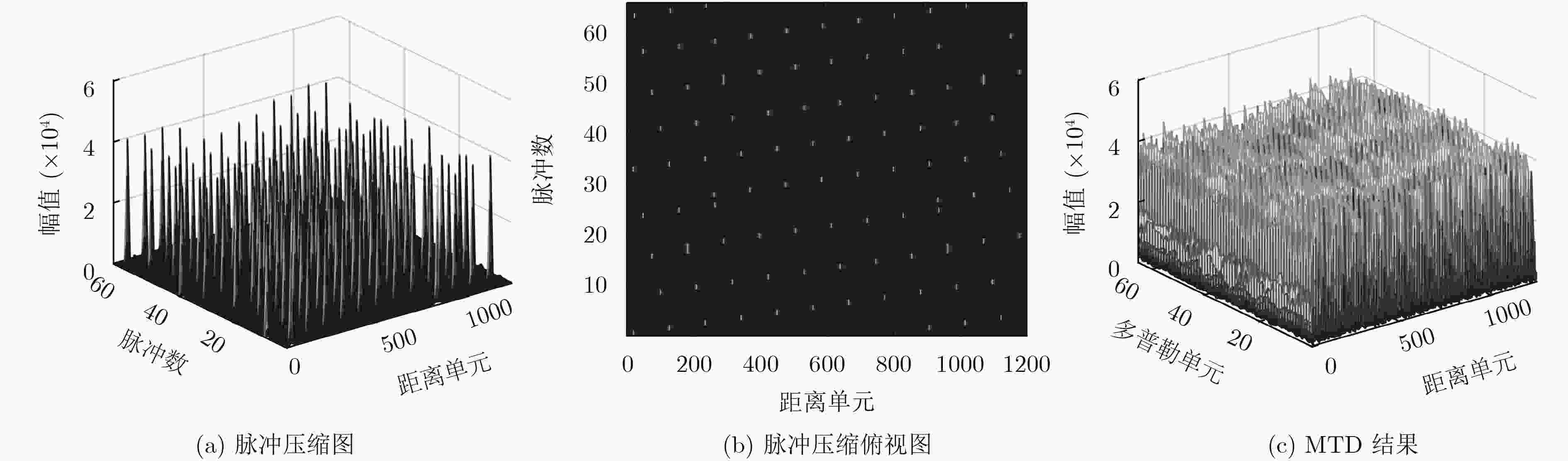
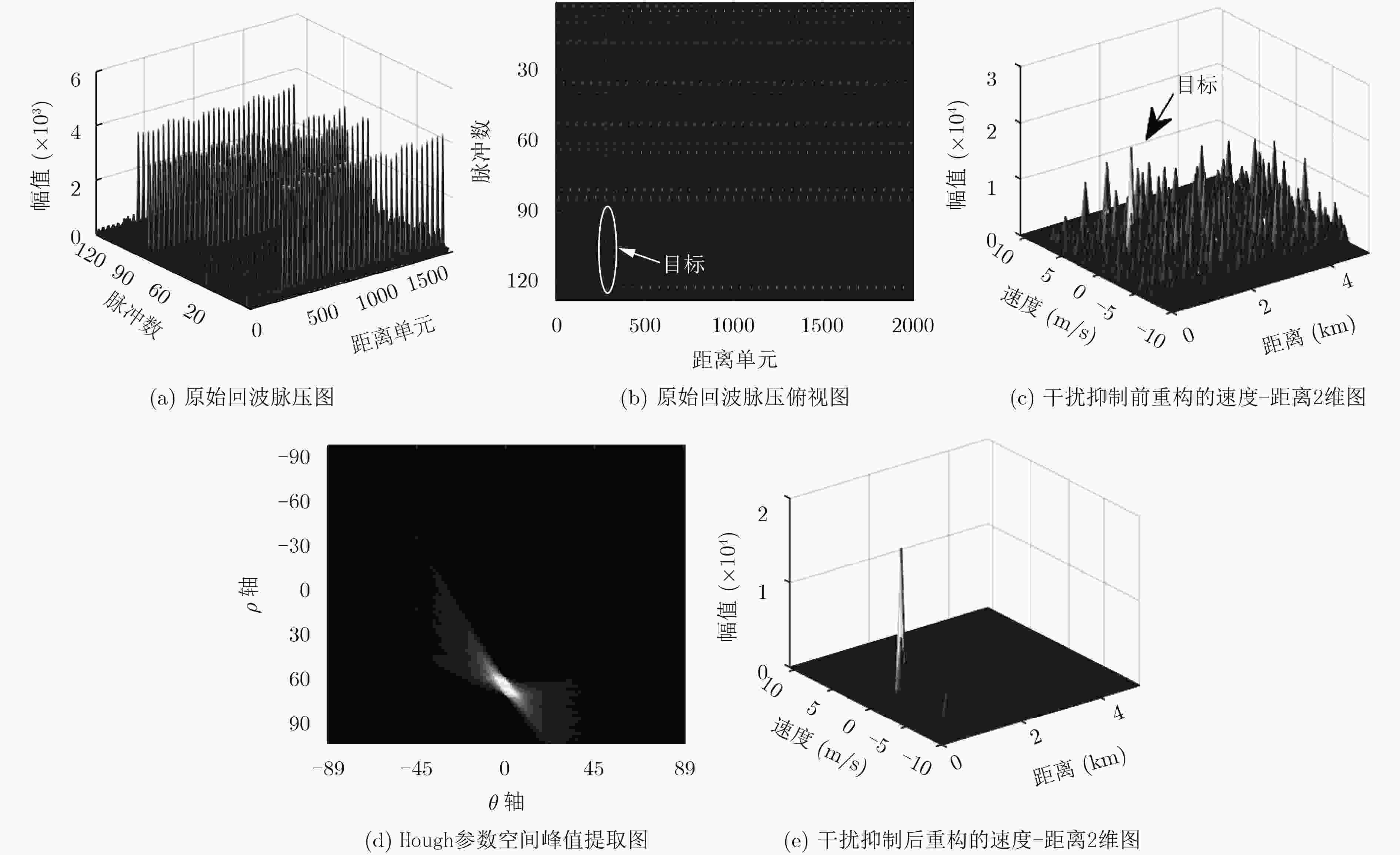
摘要: 转发式密集假目标干扰通过在距离维上产生多个虚假目标,扰乱雷达对真实目标的检测与识别。由于虚假回波信号与真实信号高度相关,雷达很难对其进行有效识别和抑制。而捷变频雷达通过随机改变发射相邻脉冲的载频,大大提高了雷达的低截获和抗干扰能力。但是捷变频雷达不能完全消除干扰,部分目标回波脉冲可能被干扰淹没,无法很好地完成相参积累和目标检测。针对上述问题,该文提出捷变频联合Hough变换的抗干扰方法,首先利用脉间频率捷变技术规避大部分窄带瞄准和欺骗式干扰;然后针对干扰信号时间上的不连续特性,通过Hough变换和峰值提取进行干扰识别与抑制;最终,针对捷变频与传统动目标检测(MTD)不兼容问题,通过稀疏重构完成目标的检测。仿真与实际雷达和干扰机对抗实验表明,该方法可以获得良好的抗干扰性能和目标检测性能。Abstract: Forwarding dense false target jamming disturbs the detection and recognition of real targets by generating multiple false targets in the range dimension. Because the false echo signal is highly correlated with the real signal, it is difficult for radar to recognize and suppress it effectively. Frequency agile radar improves greatly the low interception and anti-jamming ability of radar by randomly changing the carrier frequency of transmitting adjacent pulses. However, agile radar can not completely eliminate the interference, some target echo pulses may be submerged by the interference, agile radar can not complete coherent accumulation and target detection well either. To solve the above problems, an anti-jamming method of frequency agility combined with Hough transform is proposed. Firstly, the inter-pulse frequency agility technology is used to avoid most narrowband aiming and deceptive jamming. Then, according to the time discontinuity of the jamming signal, Hough transform and peak extraction are used to identify and suppress the jamming. Frequency agility is incompatible with the traditional Moving Target Detection(MTD). Target detection is accomplished by sparse reconstruction. The simulation and actual radar and jammer countermeasure experiments show that the proposed method can achieve good anti-jamming performance and target detection performance.
-
表 1 雷达工作及目标参数
指标参数 取值 指标参数 取值 脉冲宽度 4 μs 脉冲重复频率 2.5 kHz 信号带宽 24 MHz 采样频率 48 MHz 脉冲组个数 64 个 初始载频 10 GHz 跳频总数 100 个 步进带宽 20 MHz 目标距离 4 km 目标速度 2 km/s -
SHI Xiaoran, ZHOU Feng, ZHAO Bo, et al. Deception jamming method based on micro-Doppler effect for vehicle target[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(6): 1071–1079. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0371 FENG Dejun, XU Letao, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Jamming wideband radar using interrupted-sampling repeater[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1341–1354. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2670958 ZHOU Chang, TANG Ziyue, DAI Yu, et al. Anti-intermittent sampling repeater jamming method based on convex optimization techniques[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059595. 冯德军, 王俊杰, 王俊卿. 移频导前假目标的特性分析及其鉴别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 325–331. doi: 10.12000/JR17026FENG Dejun, WANG Junjie, and WANG Junqing. Signature analysis and discrimination method of preceded Frequency-shift false target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 325–331. doi: 10.12000/JR17026 SOUMEKH M. SAR-ECCM using phase-perturbed LFM chirp signals and DRFM repeat jammer penalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 191–205. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603414 ZHANG Shuning, XIE Wei, ZHU Hang, et al. Combined eigenvector analysis and independent component analysis for multi-component periodic interferences suppression in PRCPM-PD detection system[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 12552–12562. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2720589 MUSUMECI L, CURRAN J T, and DOVIS F. A comparative analysis of adaptive notch filtering and wavelet mitigation against jammers interference[J]. Navigation, 2016, 63(4): 533–550. doi: 10.1002/navi.167 SHEN Hao and PAPANDREOU-SUPPAPPOLA A. Wideband time-varying interference suppression using matched signal transforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(7): 2607–2612. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.849218 WANG Dinghe, BAO Qinglong, NIU Zhaodong, et al. Long time coherent integration method for frequency agile radar[C]. The 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2014: 553–556. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD.2014.6991330. QUAN Yinghui, WU Yaojun, LI Yachao, et al. Range-Doppler reconstruction for frequency agile and PRF-jittering radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(3): 348–352. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0421 卢刚, 唐斌, 罗双才, 等. LFM雷达中DRFM假目标自适应对消方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2011, 33(8): 1760–1764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.08.16LU Gang, TANG Bin, LUO Shuangcai, et al. Adaptive cancellation of DRFM false targets for LFM radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(8): 1760–1764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.08.16 孙丰荣, 刘积仁. 快速霍夫变换算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2001, 24(10): 1102–1109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2001.10.013SUN Fengrong and LIU Jiren. Fast Hough transform algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2001, 24(10): 1102–1109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2001.10.013 刘向阳, 杨君刚, 孟进, 等. 低信噪比下基于Hough变换的前视阵列SAR稀疏三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 316–323. doi: 10.12000/JR17011LIU Xiangyang, YANG Jungang, MENG Jin, et al. Sparse Three-dimensional imaging based on hough transform for Forward-looking array SAR in low SNR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 316–323. doi: 10.12000/JR17011 STEIN J J and BLACKMAN S S. Generalized correlation of multi-target track data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1975, AES-11(6): 1207–1217. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1975.308178 QUAN Yinghui, LI Yachao, WU Yaojun, et al. Moving target detection for frequency agility radar by sparse reconstruction[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(9): 094703. doi: 10.1063/1.4962700 HUANG Tianyao, LIU Yimin, MENG Huadong, et al. Randomized step frequency radar with adaptive compressed sensing[C]. 2011 IEEE RadarCon, Kansas City, USA, 2011: 411–414. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2011.5960571. 陈小龙, 关键, 何友, 等. 高分辨稀疏表示及其在雷达动目标检测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. doi: 10.12000/JR16110CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HE You, et al. Sparse representation and its applications in radar moving target detection[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 239–251. doi: 10.12000/JR16110 MARQUES E C, MACIEL N, NAVINER L, et al. A review of sparse recovery algorithms[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 1300–1322. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886471 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
