Power Control Algorithm Based on Q-Learning in Femtocell
-
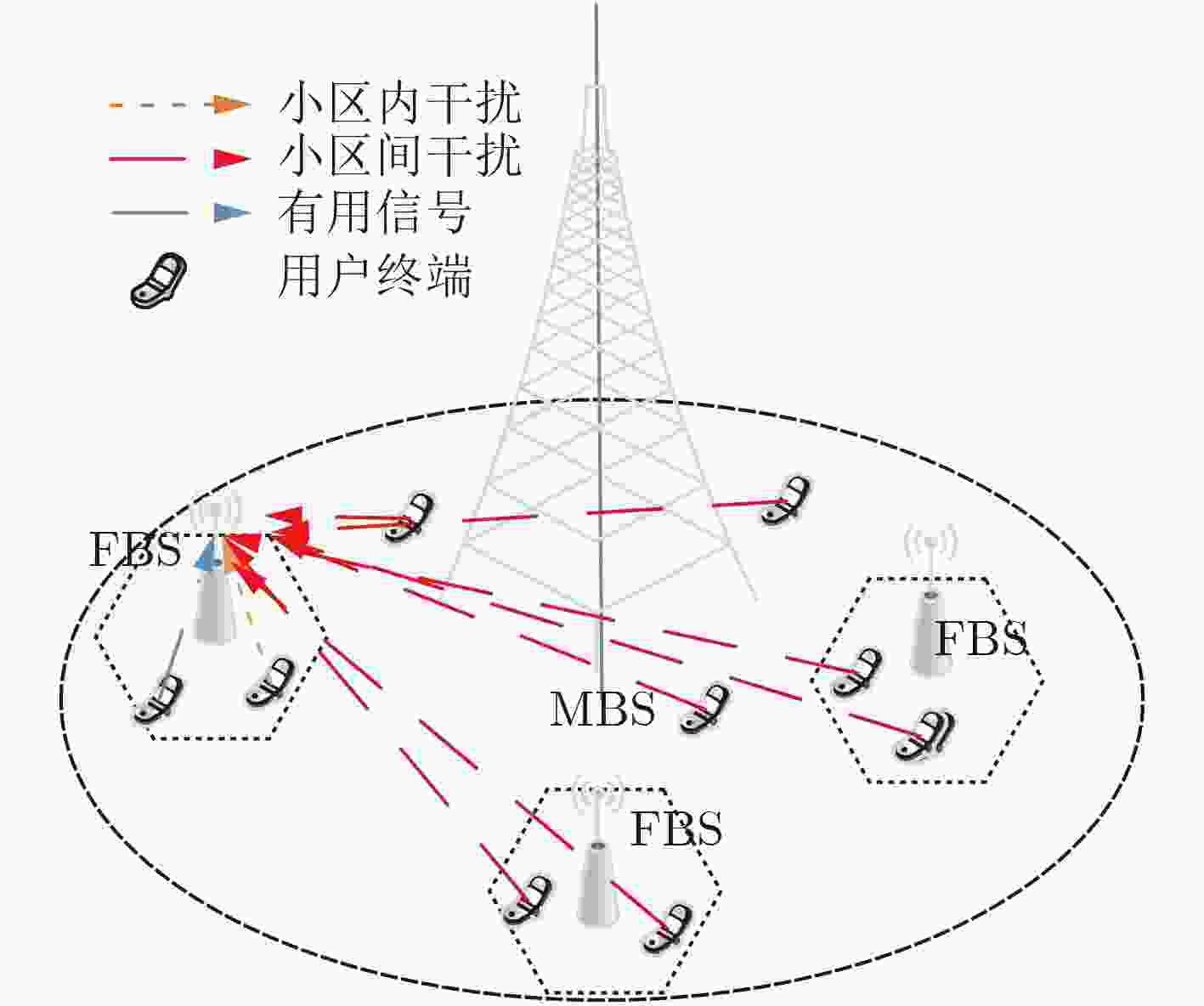
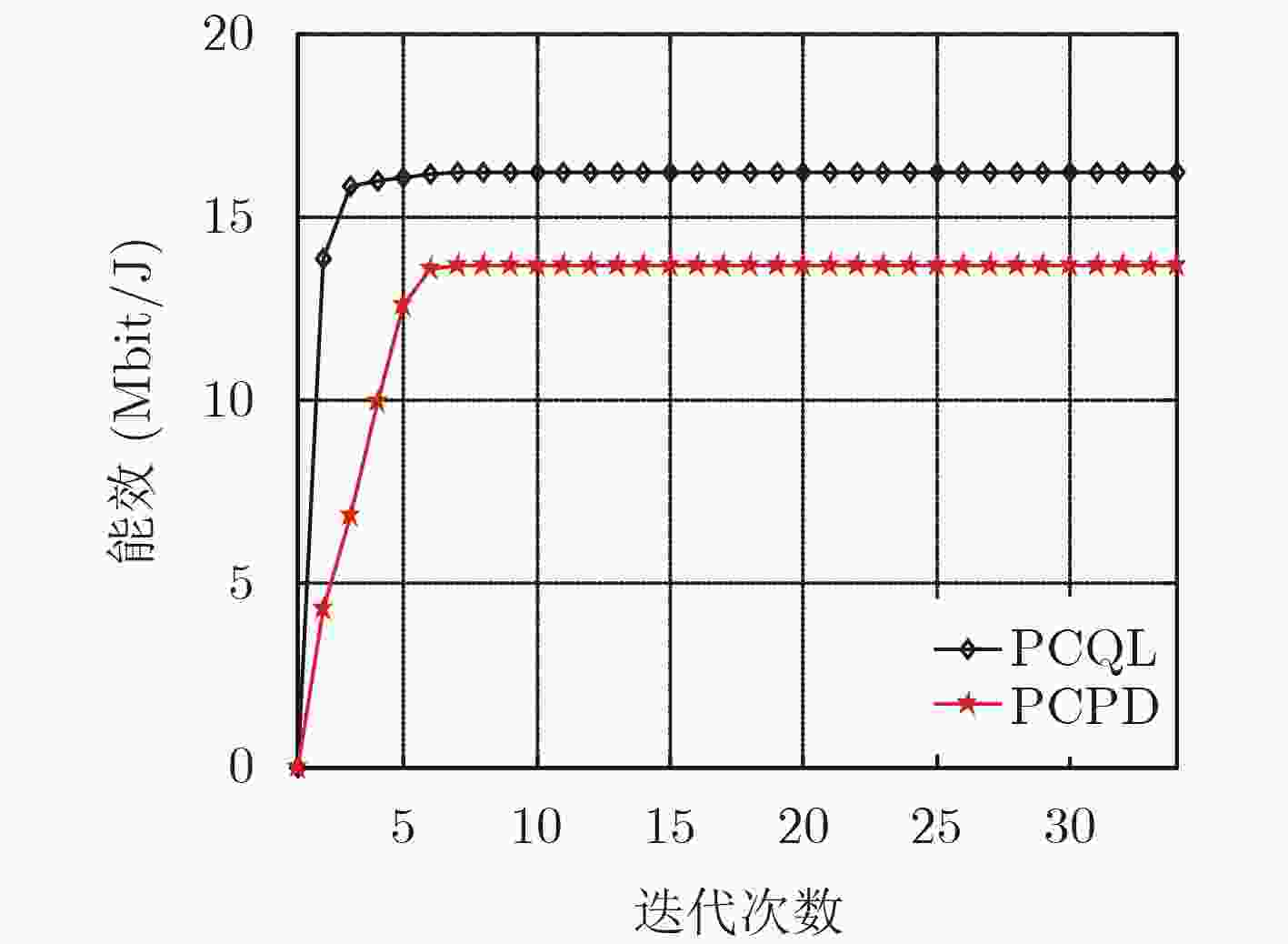
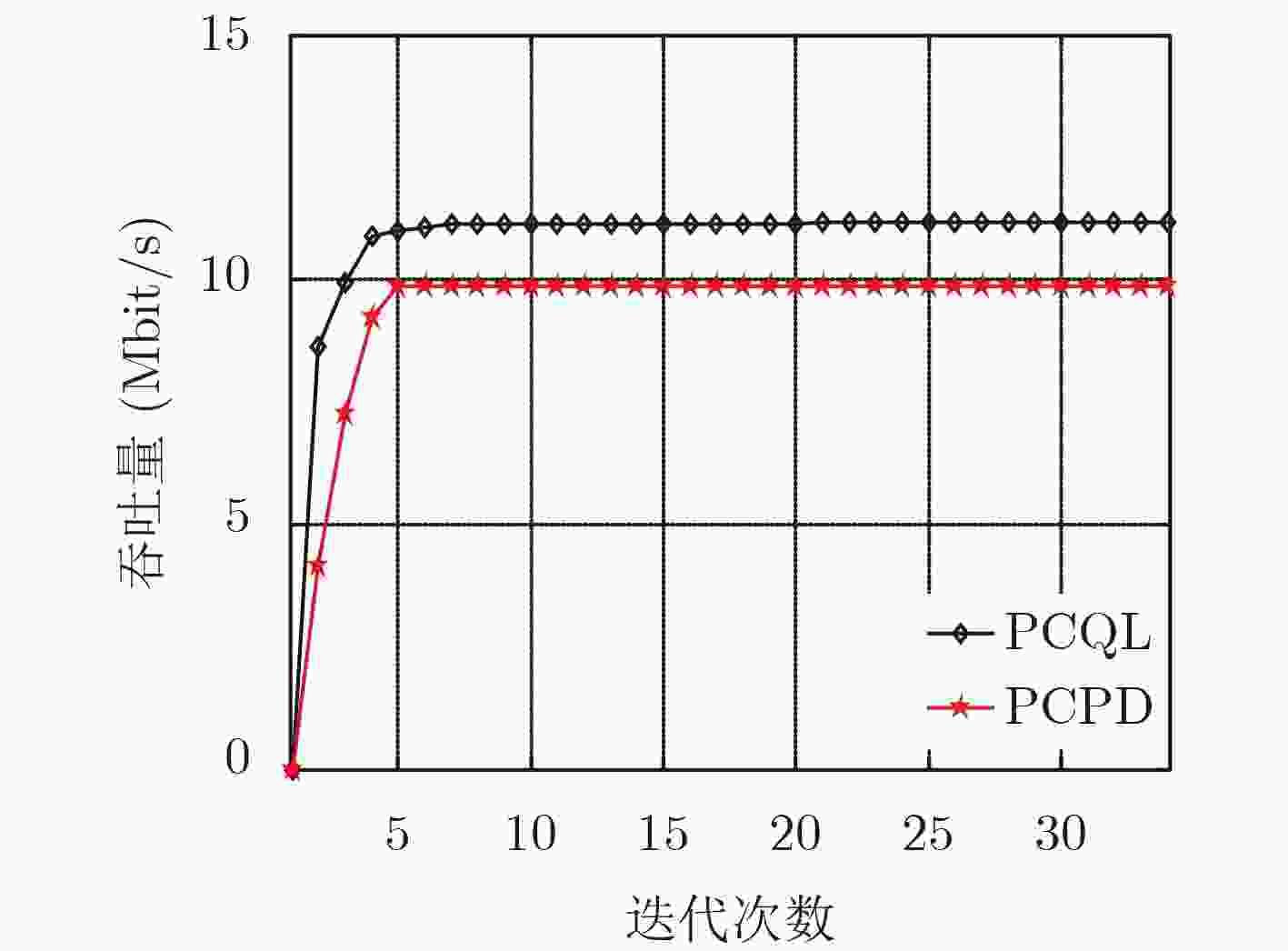
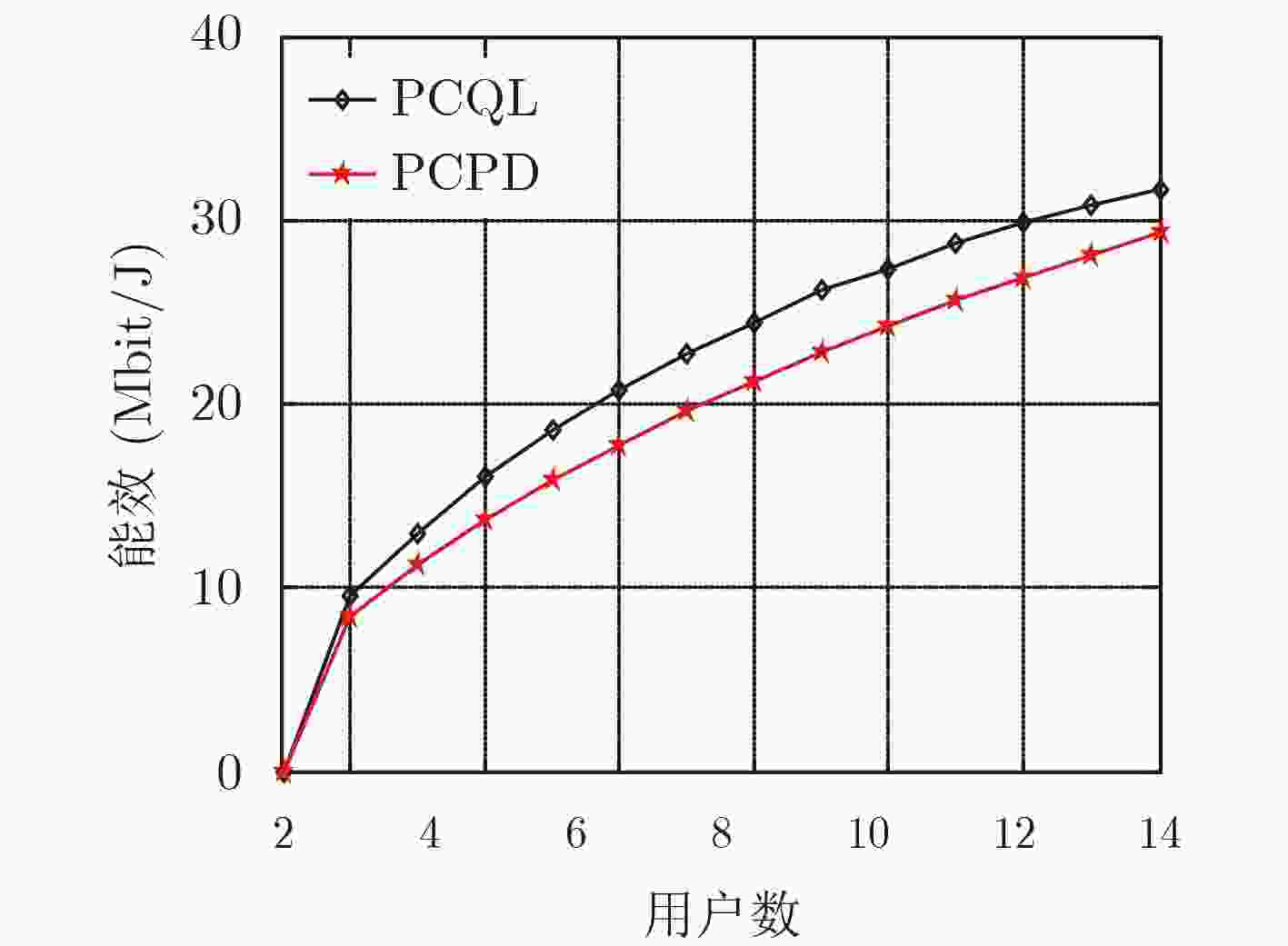
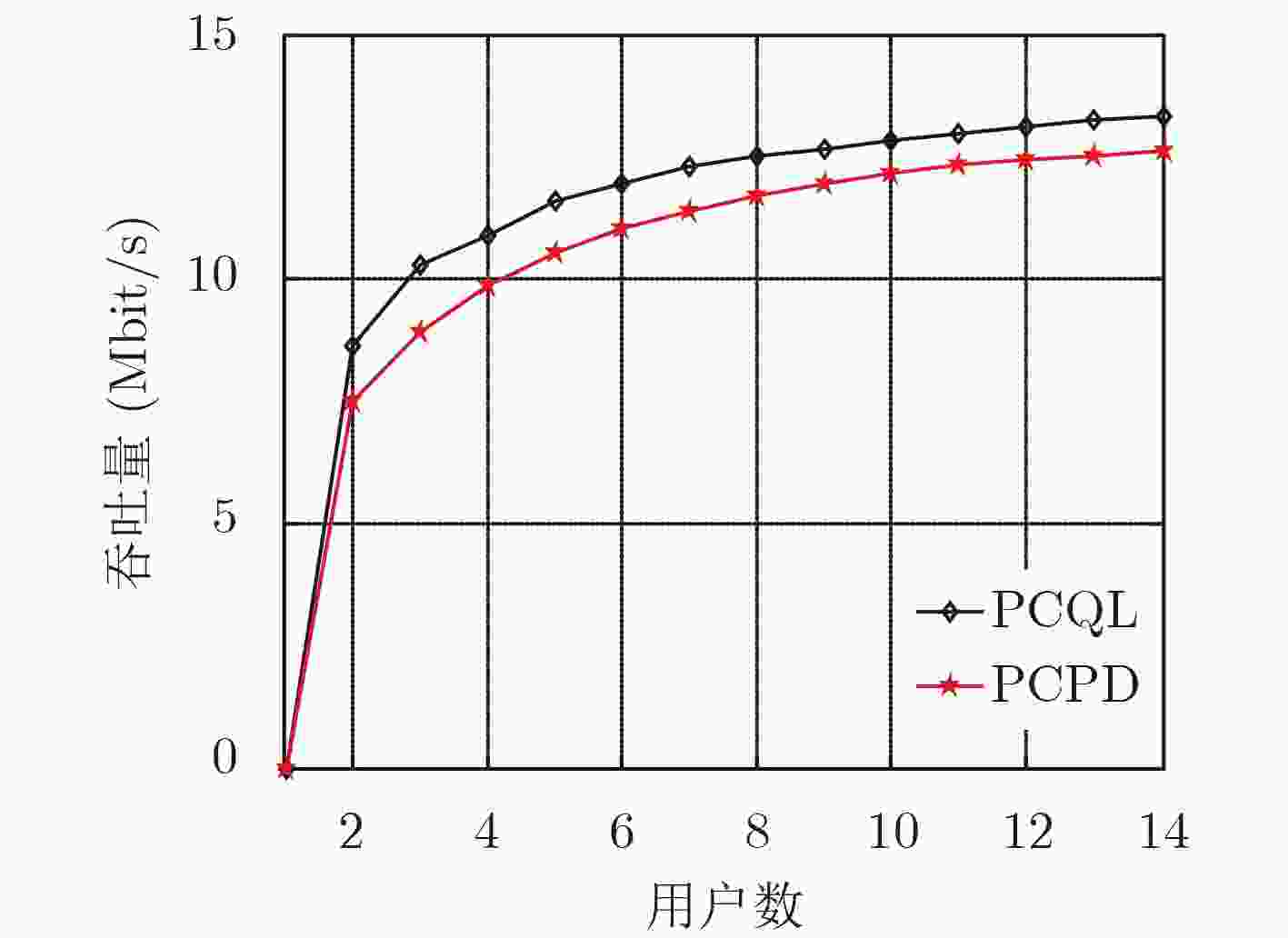
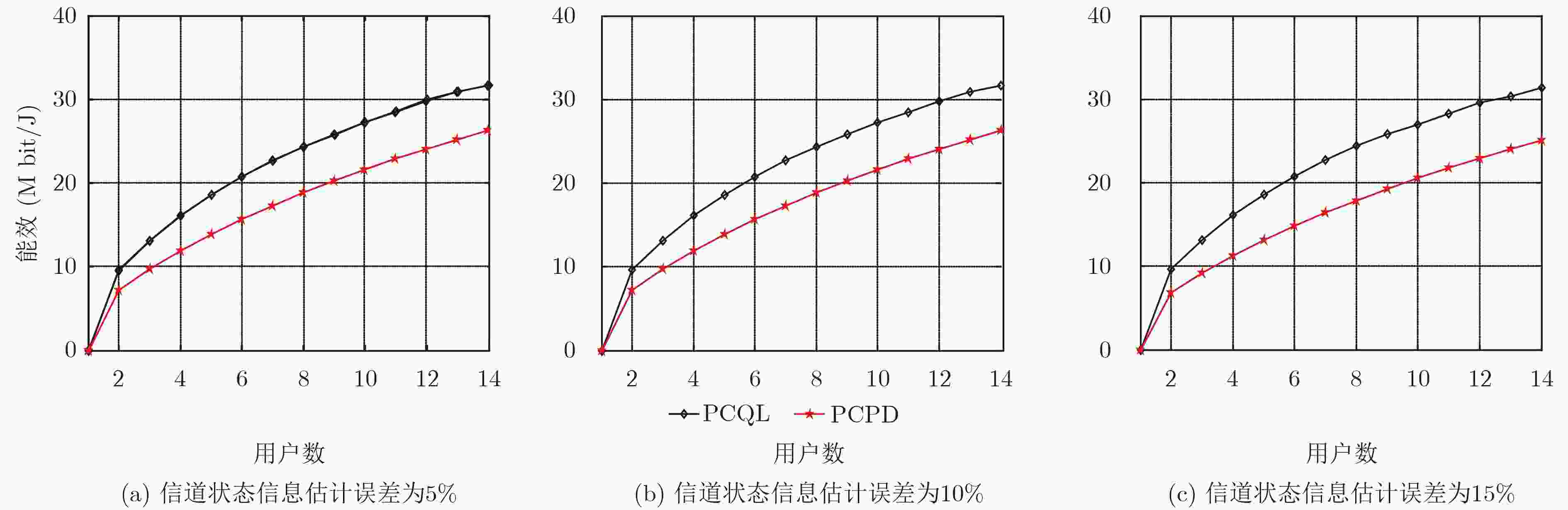
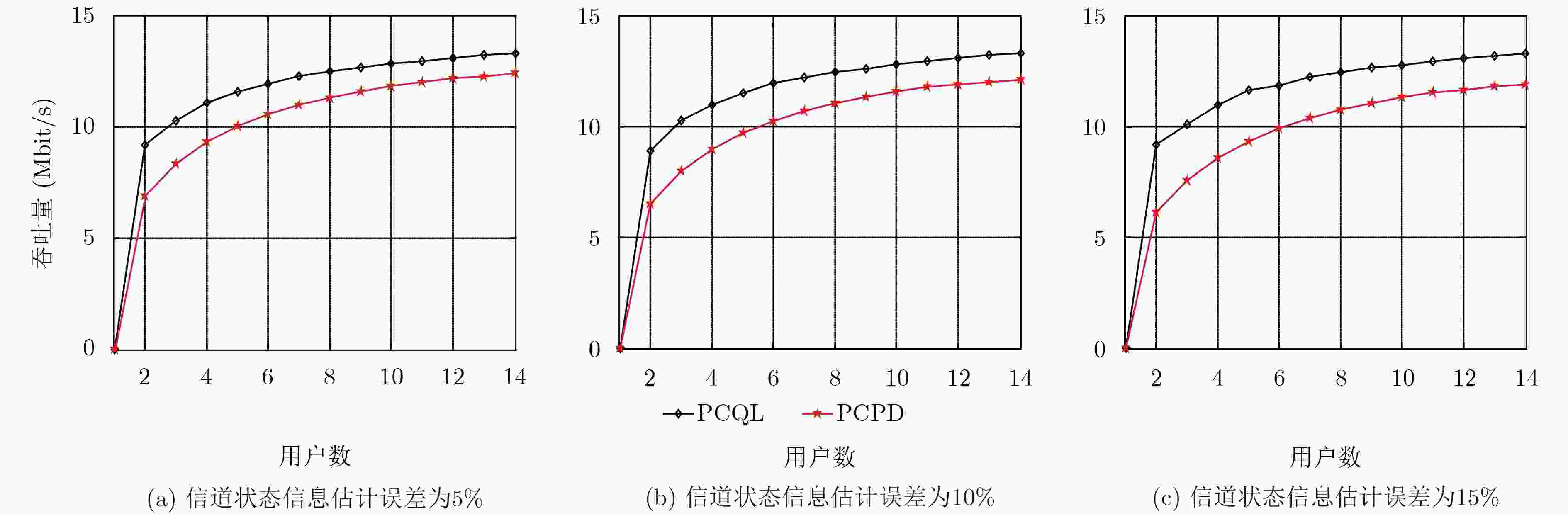
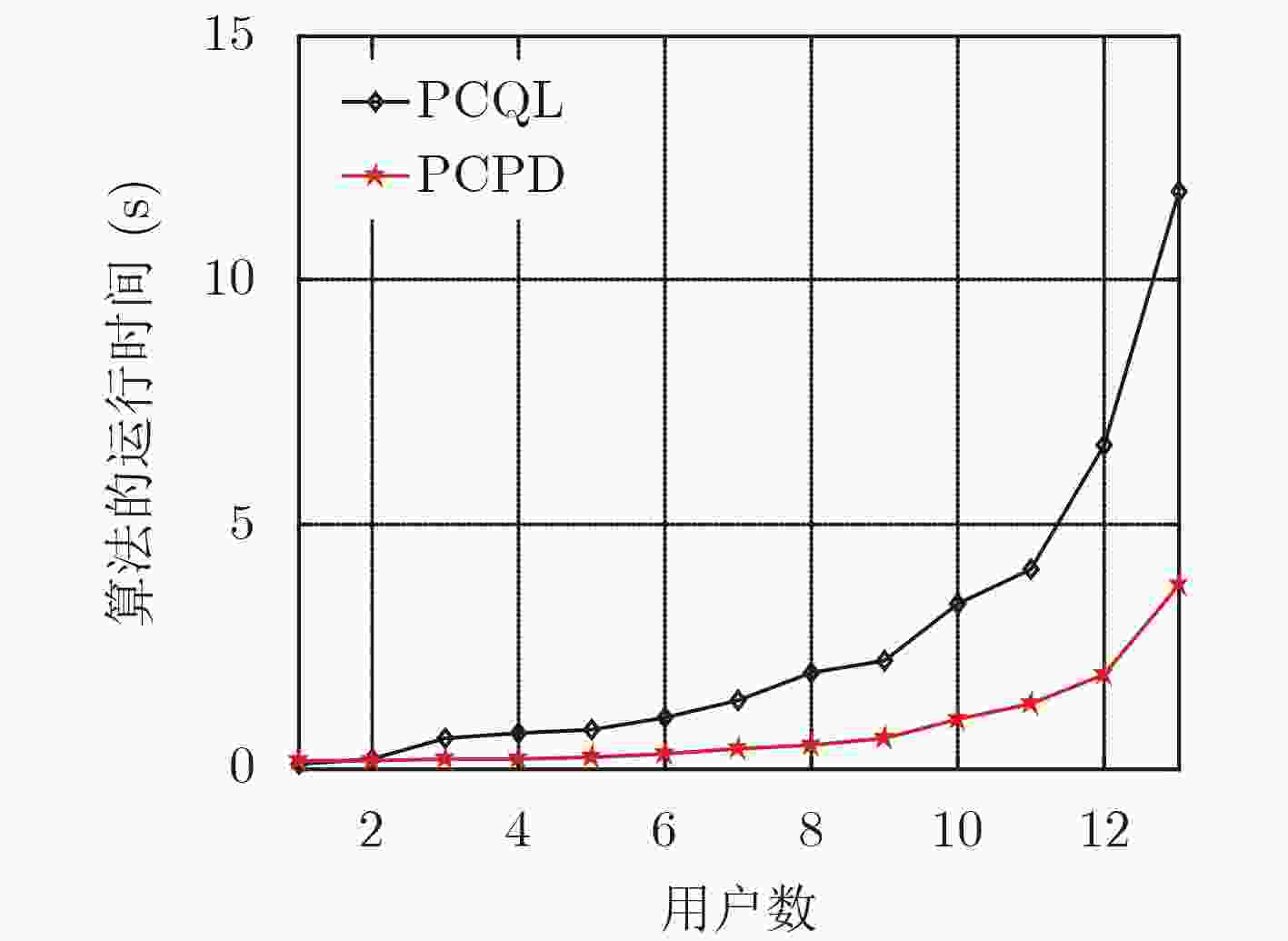
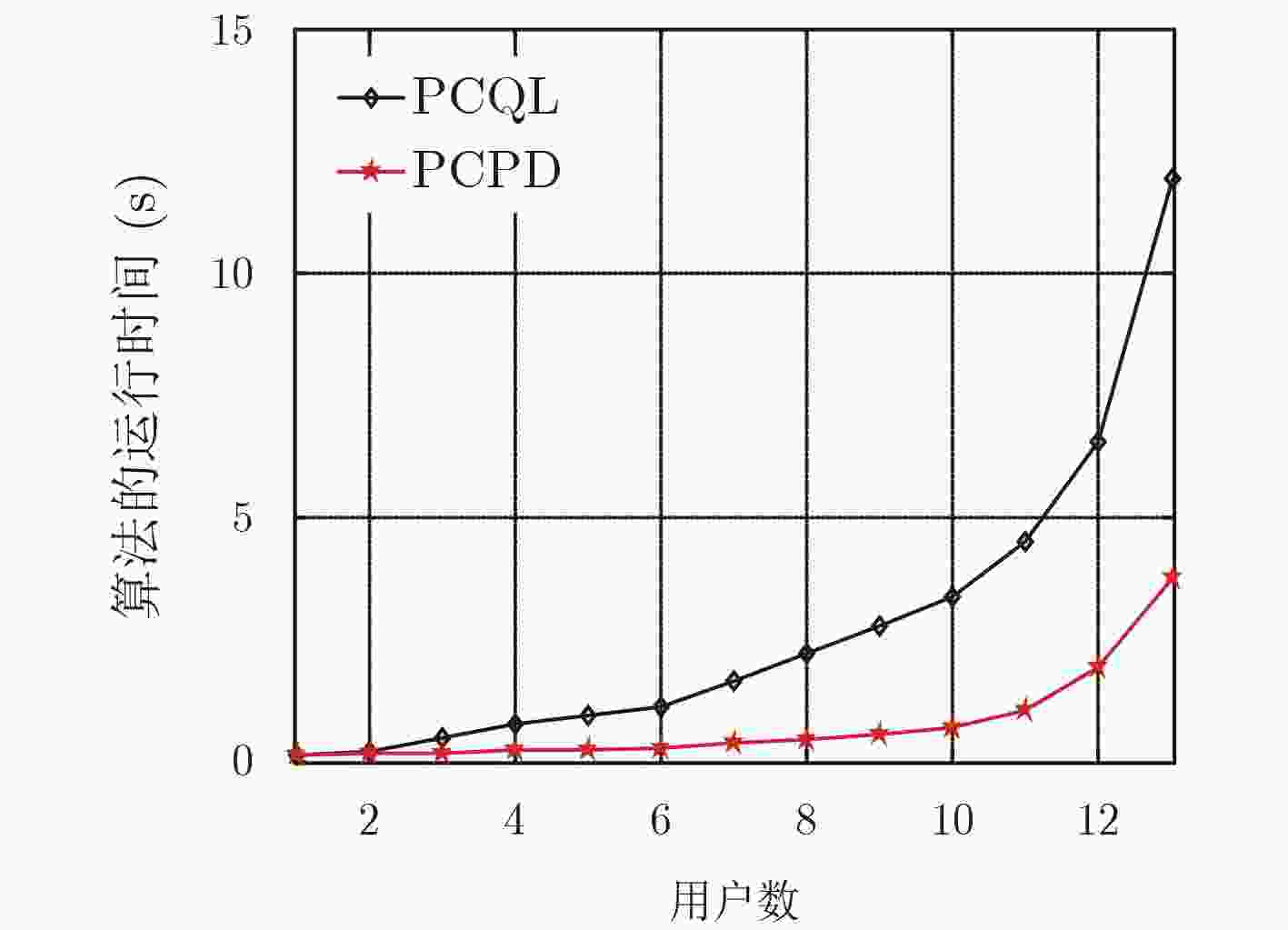
摘要: 该文研究macro-femto异构蜂窝网络中移动用户的功率控制问题,首先建立了以最小接收信号信干噪比为约束条件,最大化毫微微小区的总能效为目标的优化模型;然后提出了基于Q-Learning算法的毫微微小区集中式功率控制(PCQL)算法,该算法基于强化学习,能在没有准确信道状态信息的情况下,实现对小区内所有用户终端的发射功率统一调整。仿真结果表明该算法能实现对用户终端的功率有效控制,提升系统能效。
-
关键词:
- 集中式功率控制 /
- Q-Learning算法 /
- 能效优化
Abstract: The power control problem of mobile users in macro-femto heterogeneous cellular networks is studied. Firstly, an optimization model that maximizes the total energy efficiency of femtocells with the minimum received signal-to-noise ratio as the constraint is established. Then, a femtocell centralized Power Control algorithm based on Q-Learning (PCQL) is proposed. Based on reinforcement learning, the algorithm can adjust the transmit power of the user terminal without accurate channel state information simultaneously. The simulation results show that the algorithm can effectively control the power of the user terminal and improve system energy efficient. -
表 1 基于Q-Learning算法的毫微微小区功率控制算法(PCQL)
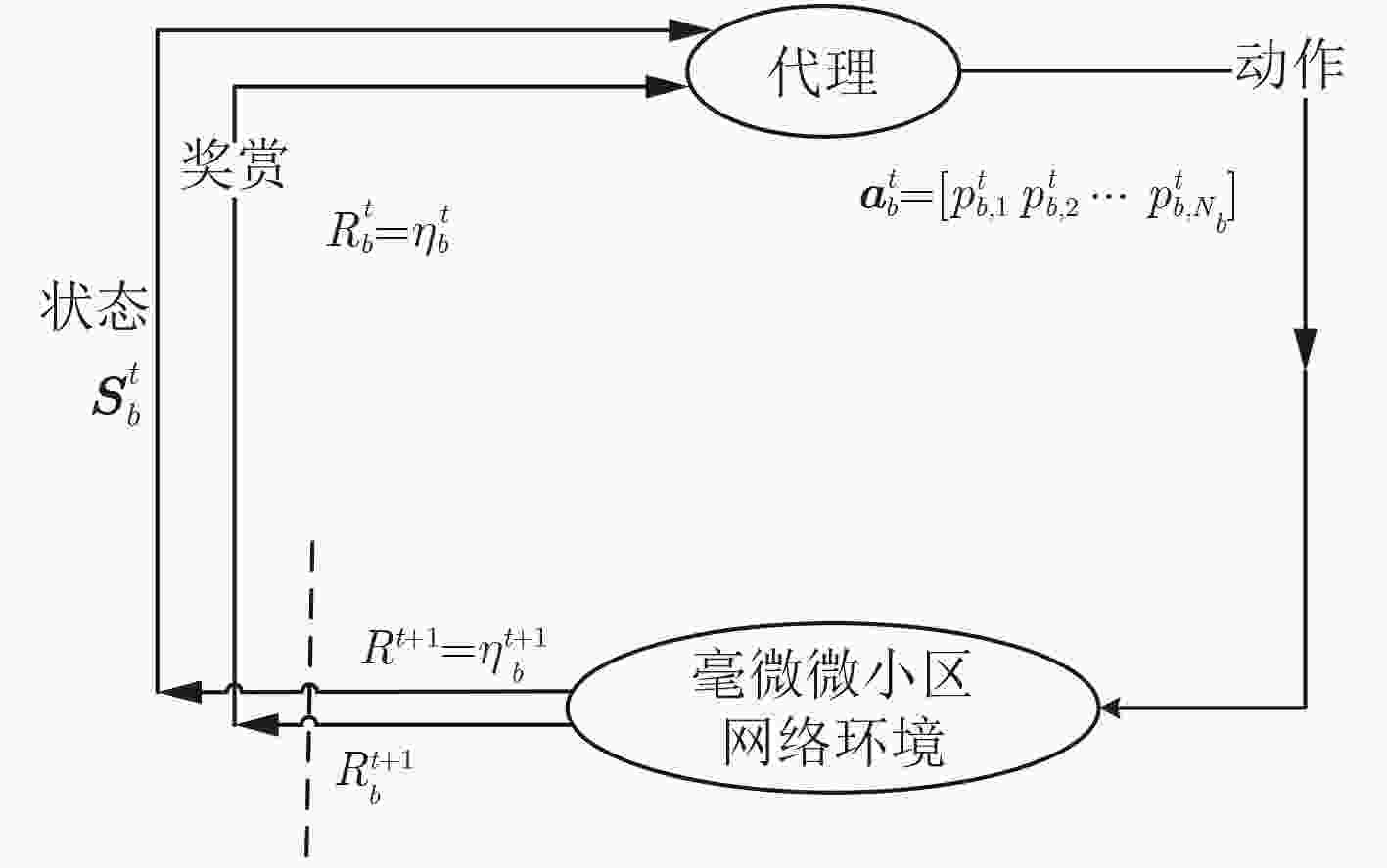
输入:W, ${n_0}$, $P_{b,\mu }^{\rm{c}} $, ${\rm{SINR}}_{b,\mu }^{\min }$, $p_{b,\mu }^{{\rm{max}}}$, $\gamma $, $\alpha $, $T\;$, $\varepsilon $,动作空间${A_b}$; 输出:${{\text{π}}^ * }$, $p_{b,\mu }^*$($\mu \in {U_b}$); 定义:${\text{k}}$表示代理选取的动作;${\rm{SINR}}_{b,\mu }^{{\rm{real}}}$表示${u_{b,\mu }}$与基站$b$通信时 的实际信干噪比; $Q\left( {{{\text{s}}_b},{{\text{a}}_b}} \right) = 0$, ${\text{π}}\left( {{{\text{s}}_b},{{\text{a}}_b}} \right) = \frac{1}{{\left| {{A_b}\left( {{{\text{s}}_b}} \right)} \right|}}$, $\text{s}_b^t = \text{s}_b^0$; for $t = 0,1, ·\!·\!· ,T\;$ do 若rand()<$\varepsilon $,从${A_b}$中随机选动作${\text{k}}$;否则${\text{k}} \!=\! \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{{\text{a}}_b^t} \!Q\left( {{\text{s}}_b^t,{\text{a}}_b^t} \right)$; 根据式(1)确定${\rm{SINR}}_{b,\mu }^{{\rm{real}}}$; for $\mu = 1,2, ·\!·\!· ,{N_b}$ do 若${\rm{SINR}}_{b,\mu }^{{\mathop{\rm real}\nolimits} } \ge {\rm{SINR}}_{b,\mu }^{\min }$,那么${\lambda _{b,\mu }} = 1$;否则${\lambda _{b,\mu }} = 0$; end for; 根据式(7)计算采取动作${\text{a}}_b^t = {\text{k}}$所带来的奖赏值${\Re _b}\left( {{\text{s}}_b^t,{\text{a}}_b^t} \right)$; ${\text{a}}_b^{t + 1} = {\text{π}}\left( {{\text{s}}_b^{t + 1}} \right)$;
${\rm Q}\left( { { {\text{s} } }_b^t,{ {\text{a} } }_b^t} \right) \leftarrow {\rm Q}\left( { { {\text{s} } }_b^t,{ {\text{a} } }_b^t} \right) + \alpha ( {\Re _b}\left( { { {\text{s} } }_b^t,{ {\text{a} } }_b^t} \right) \!+\! \gamma \mathop {\max}\limits_{ {\rm{a} }_b^{t + 1} } \left( { {\rm Q}\left( { { {\text{s} } }_b^{t + 1},{ {\text{a} } }_b^{t + 1} } \right)} \right)$ $\left.- {{\rm Q}\left( {{{\text{s}}}_b^t,{{\text{a}}}_b^t} \right)} \right)$;${\text{s}}_b^t \leftarrow {\text{s}}_b^{t + 1}$; end for; ${{\text{π}}^ * }\left( {{{\text{s}}_b}} \right) = \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{{{\text{a}}_b}} Q\left( {{{\text{s}}_b},{{\text{a}}_b}} \right),\forall {{\text{s}}_b} \in S$. 表 2 主要的仿真参数
参数名称 参数值 MBS/FBS 1个/4个 MUE/FUE最大的发射功率 37 dBm/30 dBm MBS/FBS覆盖范围半径 250 m/50 m ${{\rm{SINR}} _{b,\mu }}^{\min }$ –9 dB 固定的电路功耗 100 mW 信道带宽 10 MHz 高斯白噪声的功率谱密度 ${10^{ - 11}}$ W/Hz -
LÓPEZ-PÉREZ D, DING M, CLAUSSEN H, et al. Towards 1 Gbps/UE in cellular systems: understanding ultra-dense small cell deployments[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 2078–2101. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2439636 YUNAS S F, VALKAMA M, and NIEMELÄ J. Spectral and energy efficiency of ultra-dense networks under different deployment strategies[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2015, 53(1): 90–100. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2015.7010521 MARTOLIA D, SATHYA V, RANGISETTI A K, et al. Enhancing performance of victim macro users via joint ABSF and dynamic power control in LTE HetNets[C]. The Twenty-third National Conference on Communications, Chennai, India, 2017: 1–6. SHIN D and CHOI S. Dynamic power control for balanced data traffic with coverage in femtocell networks[C]. The 8th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference, Limassol, Cyprus, 2012: 648–653. ZHANG Jinzhu, HONG Peilin, XUE Kaiping, et al. A novel power control scheme for femtocell in heterogeneous networks[C]. 2012 IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2012: 802–806. PAN Zhenni, MEGUMI, SAITOU, et al. Neuron control-based power adjustment scheme for sleep two-tier cellular networks[C]. 2014 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 2014: 3201–3206. ZHOU Tianqing, LIU Zunxiong, ZHAO Junhui, et al. Joint user association and power control for load balancing in downlink heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(3): 2582–2593. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2768574 MARTIN-VEGA F J, GOMEZ G, AGUAYO-TORRES M C, et al. Analytical modeling of interference aware power control for the uplink of heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(10): 6742–6757. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2588469 ZHANG Jing, LIAO Yan, and XIN Yili. Uplink power control for heterogeneous small cell networks[C]. 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Nanjing, China, 2016: 1–5. WANG Min, GAO Hui, and LV Tiejun. Energy-efficient user association and power control in the heterogeneous network[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 5059–5068. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2690305 ZHANG Jing, XIANG Lin, NG D W K, et al. Energy efficiency evaluation of multi-tier cellular uplink transmission under maximum power constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(11): 7092–7107. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2739142 PAN Zhenni and SHIMAMOTO S. Cell sizing based energy optimization in joint macro-femto deployments via sleep activation[C]. 2013 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Shanghai, China, 2013: 4765–4770. SHIFAT A S M Z, CHOWDHURY M Z, and JANG Y M. Game-based approach for QoS provisioning and interference management in heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 10208–10220. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2704094 MISHRA S and MURTHY C S R. Increasing energy efficiency via transmit power spreading in dense femto cell networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(1): 971–980. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2016.2573845 GURUACHARYA S, NIYATO D, KIM D I, et al. Hierarchical competition for downlink power allocation in OFDMA femtocell networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(4): 1543–1553. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.022213.120016 WANG Haining, WANG Jiaheng, and DING Zhi. Distributed power control in a two-tier heterogeneous network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(12): 6509–6523. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2456055 MAO Tingli, FENG Gang, LIANG Liang, et al. Energy-efficient power control for macro-femto networks[C]. The 22nd Wireless and Optical Communication Conference, Chongqing, China, 2013: 122–125. MAO Tingli, FENG Gang, LIANG Liang, et al. Distributed energy-efficient power control for macro-femto networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(2): 718–731. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2402618 LAI Weisheng, CHANG T H, and LEE T S. Joint power and admission control for spectral and energy efficiency maximization in heterogeneous OFDMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(5): 3531–3547. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2522958 LOODARICHEH R A, MALLICK S, BHARGAVA V K. Energy-efficient resource allocation for OFDMA cellular networks with user cooperation and QoS provisioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(11): 6132–6146. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2329877 GHADIMI E, CALABRESE F D, PETERS G, et al. A reinforcement learning approach to power control and rate adaptation in cellular networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 2017: 1–7. 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 372–390.ZHOU Zhihua. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 372–390. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
