Traceable Lightweight and Fine-grained Access Control in Named Data Networking
-
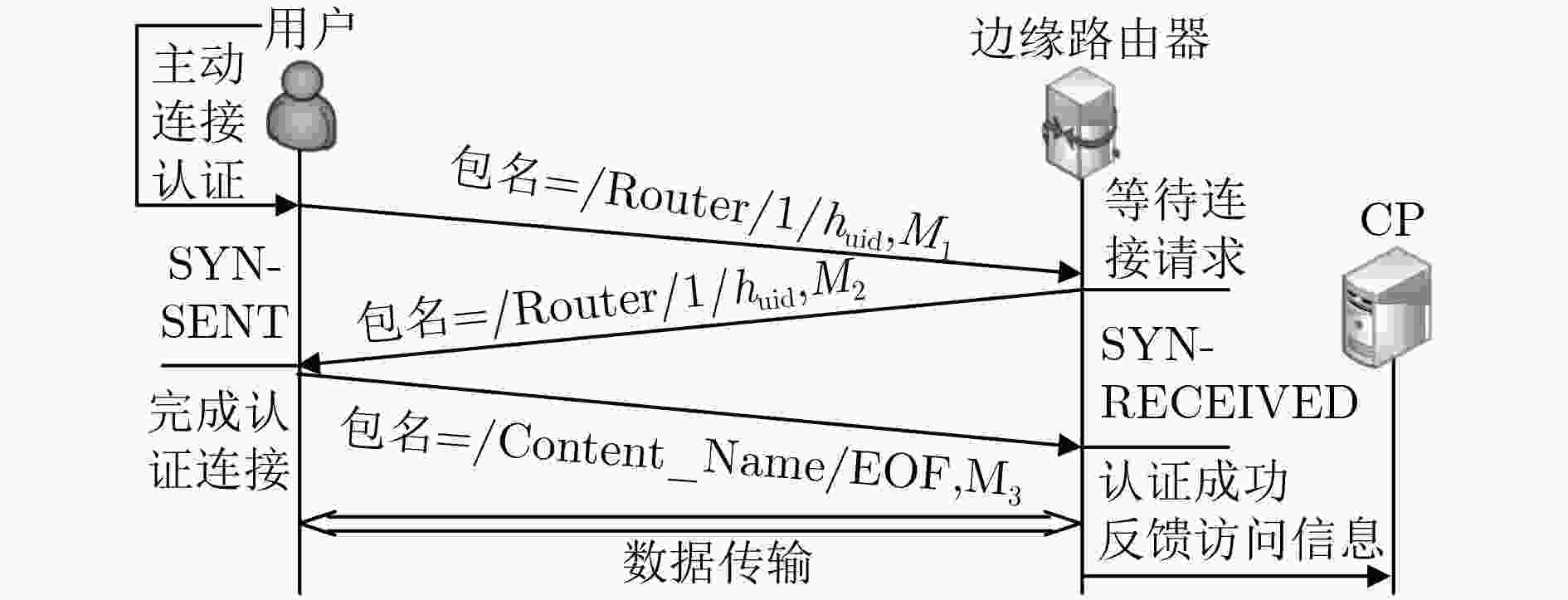
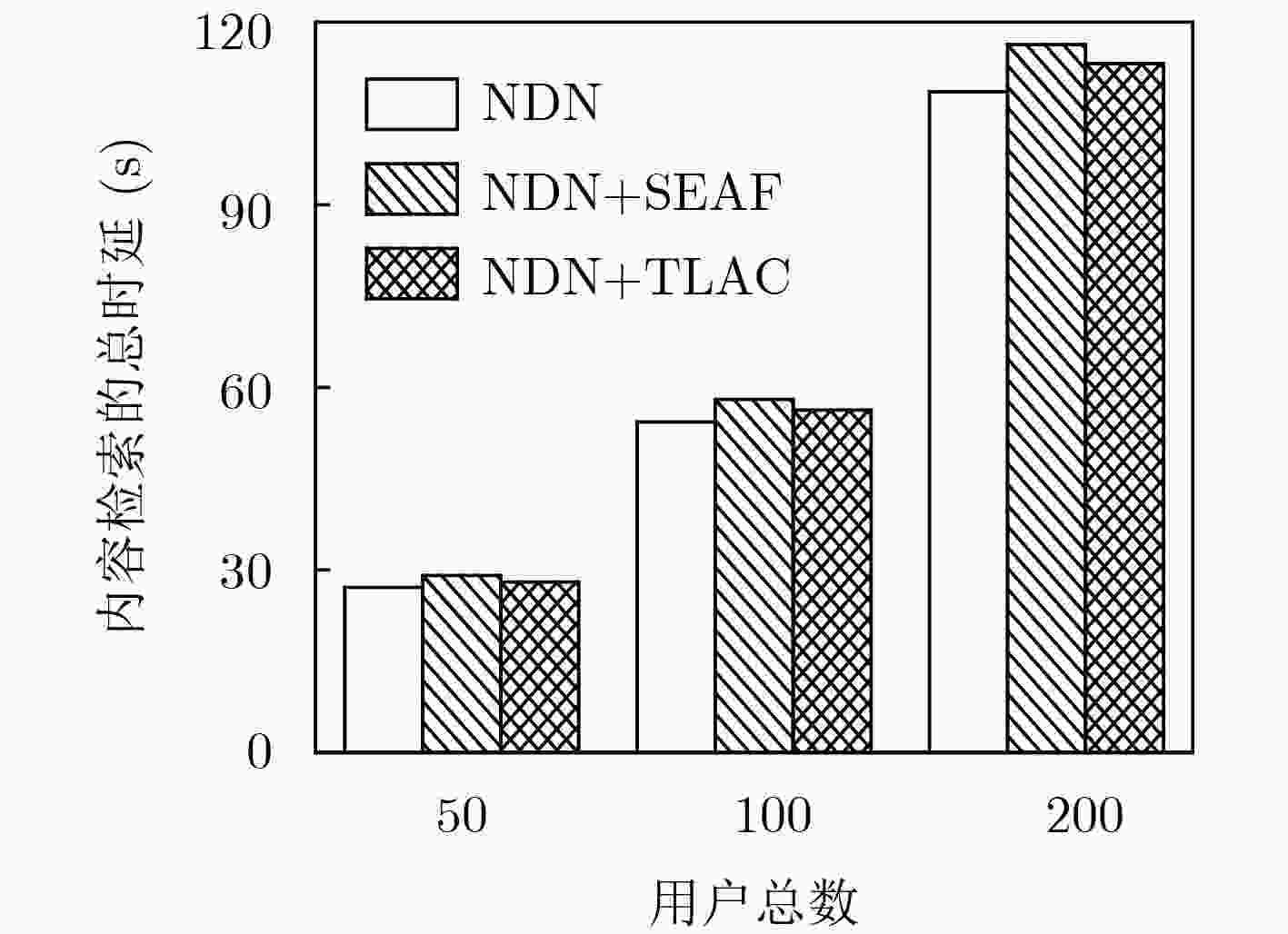
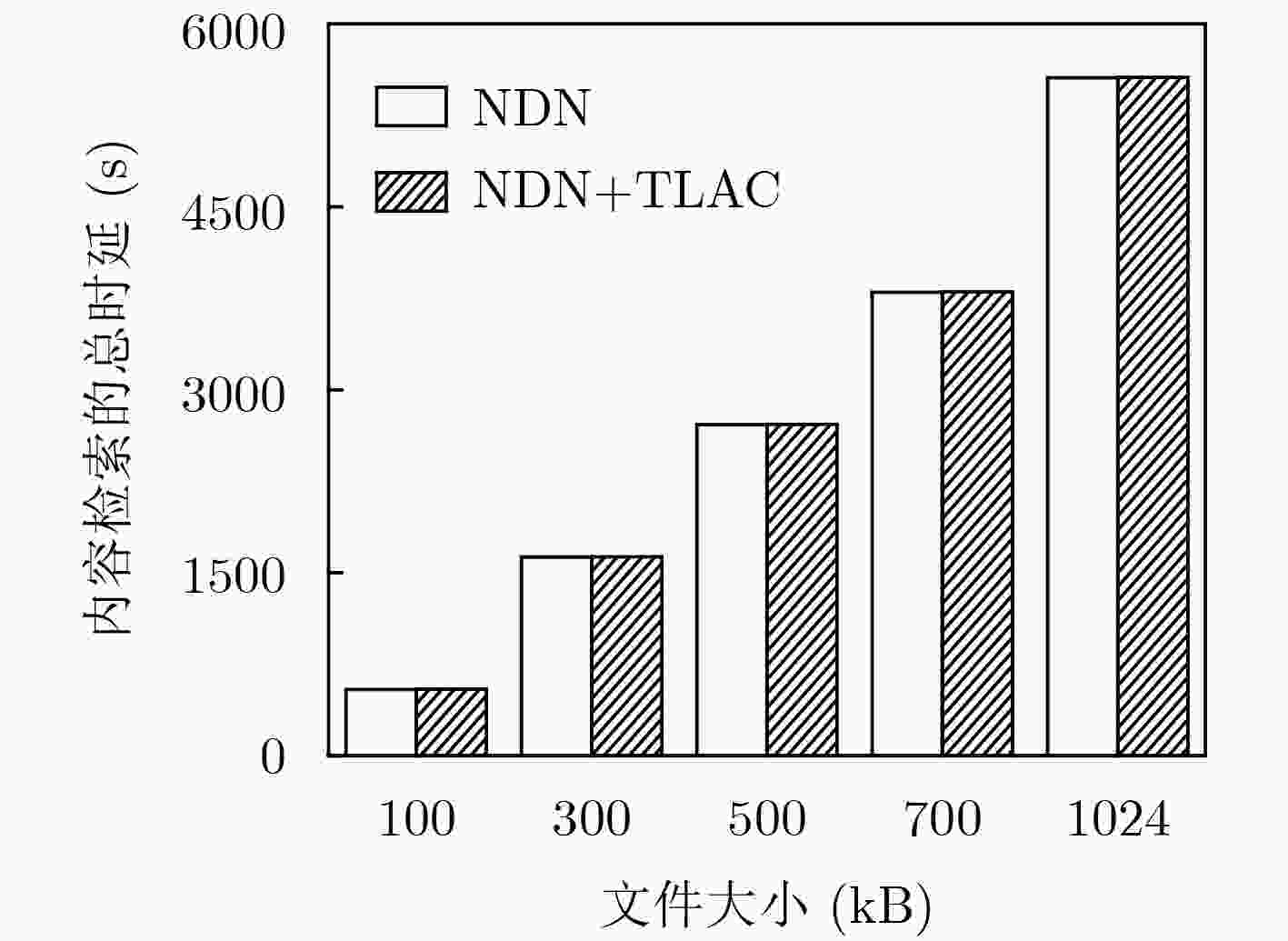
摘要: 由于命名数据网络(NDN)具有网内缓存特点,任意用户可直接从中间路由节点获取数据,同时,内容提供商也无法得知用户的访问信息。针对这些问题,该文结合基于身份的组合公钥和Schnorr签名方法,提出了“三次握手”匿名安全认证协议,同时,采用改进的秘密共享方法来高效分发内容密钥,实现了一种可追溯且轻量级的细粒度访问控制机制(TLAC),最后,通过实验验证了TLAC机制的高效性。Abstract: Due to the feature of in-network caching in Named Data Networking (NDN), any consumer might fetch the cached contents from NDN routers, but the content producers have no idea about details of certain contents being accessed. Considering these problems, a fine-grained Traceable and Lightweight Access Control (TLAC) scheme is presented. In the TLAC scheme, an anonymous and secure " three-way handshake” authentication protocol is presented by collaboratively leveraging the combined public key and the Schnorr signature, and an improved secret sharing method is used to distribute the key efficiently. Finally, the experimental results prove the efficiency of TLAC scheme.
-
Key words:
- Named Data Networking (NDN) /
- Content caching /
- Access control /
- Traceability
-
表 1 认证时的计算开销对比
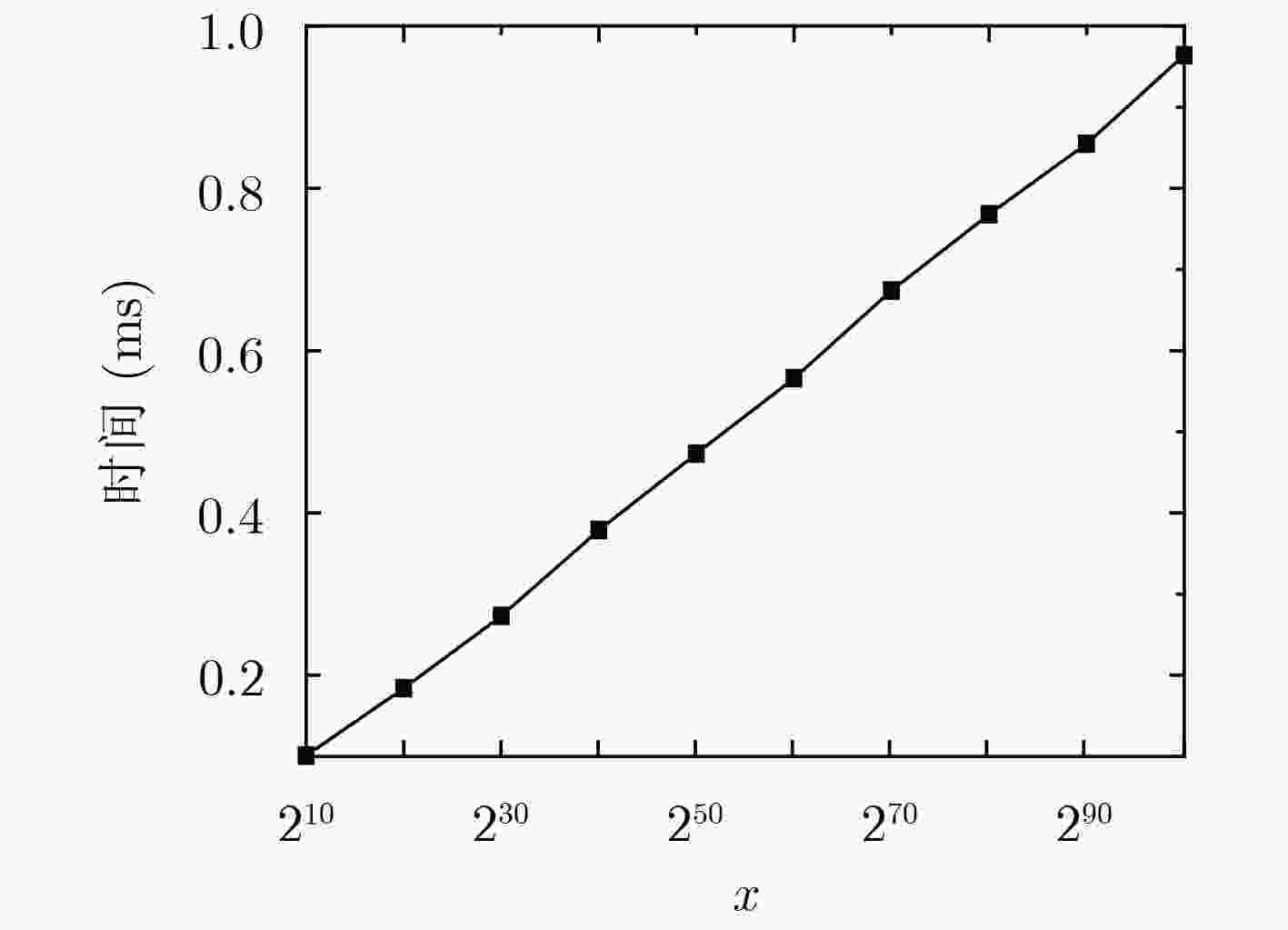
对比项目 TLAC机制 SEAF机制 U(无预计算) $5{m_0}{\rm{ + 5}}h$ $3p{\rm{ + }}3e{\rm{ + 9}}{m_0}{\rm{ + }}h$ U(预计算后) $3{m_0}{\rm{ + 4}}h$ h R(无预计算) $5{m_0}{\rm{ + 4}}h$ $5p{\rm{ + }}4e{\rm{ + 8}}{m_0}{\rm{ + }}h$ R(预计算后) $4{m_0}{\rm{ + 4}}h$ / 表 2 预计算后的时间开销对比(ms)
对比项目 TLAC机制 SEAF机制 U 5.15 0.05 R 6.67 13.75 -
CISCO. Cisco visual networking index: Forecast and methodology, 2016–2021 white paper[EB/OL]. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/global-cloud-index-gci/white-paper-c11-738085.html, 2018. GASTI P and TSUDIK G. Content-centric and named-data networking security: The good, the bad and the rest[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Local and Metropolitan Area Networks, Washington, USA, 2018: 1–6. TOURANI R, MISRA S, MICK T, et al. Security, privacy, and access control in information-centric networking: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(1): 566–600. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2749508 MISRA S, TOURANI R, and MAJD N E. Secure content delivery in information-centric networks: Design, implementation, and analyses[C]. The 3rd ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Information-centric Networking, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 73–78. MISRA S, TOURANI R, NATIVIDAD F, et al. AccConF: An access control framework for leveraging in-network cached data in the ICN-enabled wireless edge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 16(1): 5–17. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2672991 CHEN Tao, LEI Kai, and XU Kuai. An encryption and probability based access control model for named data networking[C]. The 33rd IEEE International Performance Computing and Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014: 1–8. ZHENG Qingji, WANG Guoqiang, RAVINDRAN R, et al. Achieving secure and scalable data access control in information-centric networking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications, London, UK, 2015: 5367–5373. XUE Kaiping, ZHANG Xiang, XIA Qiudong, et al. SEAF: A secure, efficient and accountable access control framework for information centric networking[C]. The IEEE INFOCOM 2018 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, USA, 2018: 2213–2221. CHEN Liqun, CHENG Z, and SMART N P. Identity-based key agreement protocols from pairings[J]. International Journal of Information Security, 2007, 6(4): 213–241. doi: 10.1007/s10207-006-0011-9 南湘浩. 组合公钥(CPK)体制标准(V5.0)[J]. 计算机安全, 2010(10): 1–2, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0428.2010.10.001NAN Xianghao. Combined public key(CPK)cryptosystem standard(V5.0)[J]. Computer Security, 2010(10): 1–2, 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0428.2010.10.001 SCHNORR C P. Efficient signature generation by smart cards[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 1991, 4(3): 161–174. doi: 10.1007/bf00196725 NAOR M and YUNG M. Universal one-way hash functions and their cryptographic applications[C]. The 21st Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Seattle, USA, 1989: 33–43. SHAMIR A. Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes[C]. The Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Berlin, Germany, 1984: 47–53. SHAMIR A. How to share a secret[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1979, 22(11): 612–613. doi: 10.1145/359168.359176 IMINE Y, LOUNIS A, and BOUABDALLAH A. ABR: A new efficient attribute based revocation on access control system[C]. The 13th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference, Valencia, Spain, 2017: 735–740. -





 下载:
下载:

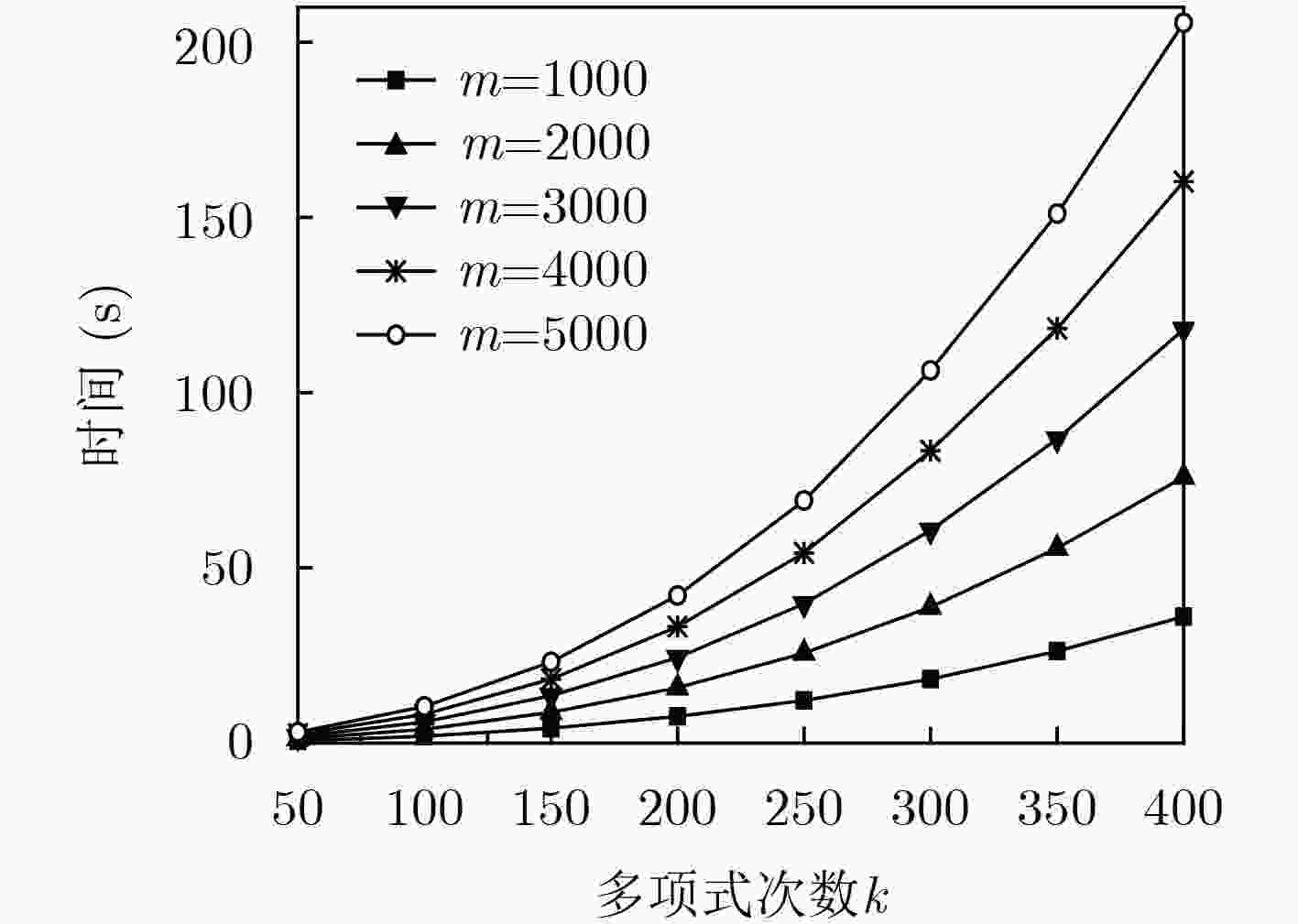


 下载:
下载:
