Target Assignment Method for Phased Array Radar Network Based on Quality of Service
-
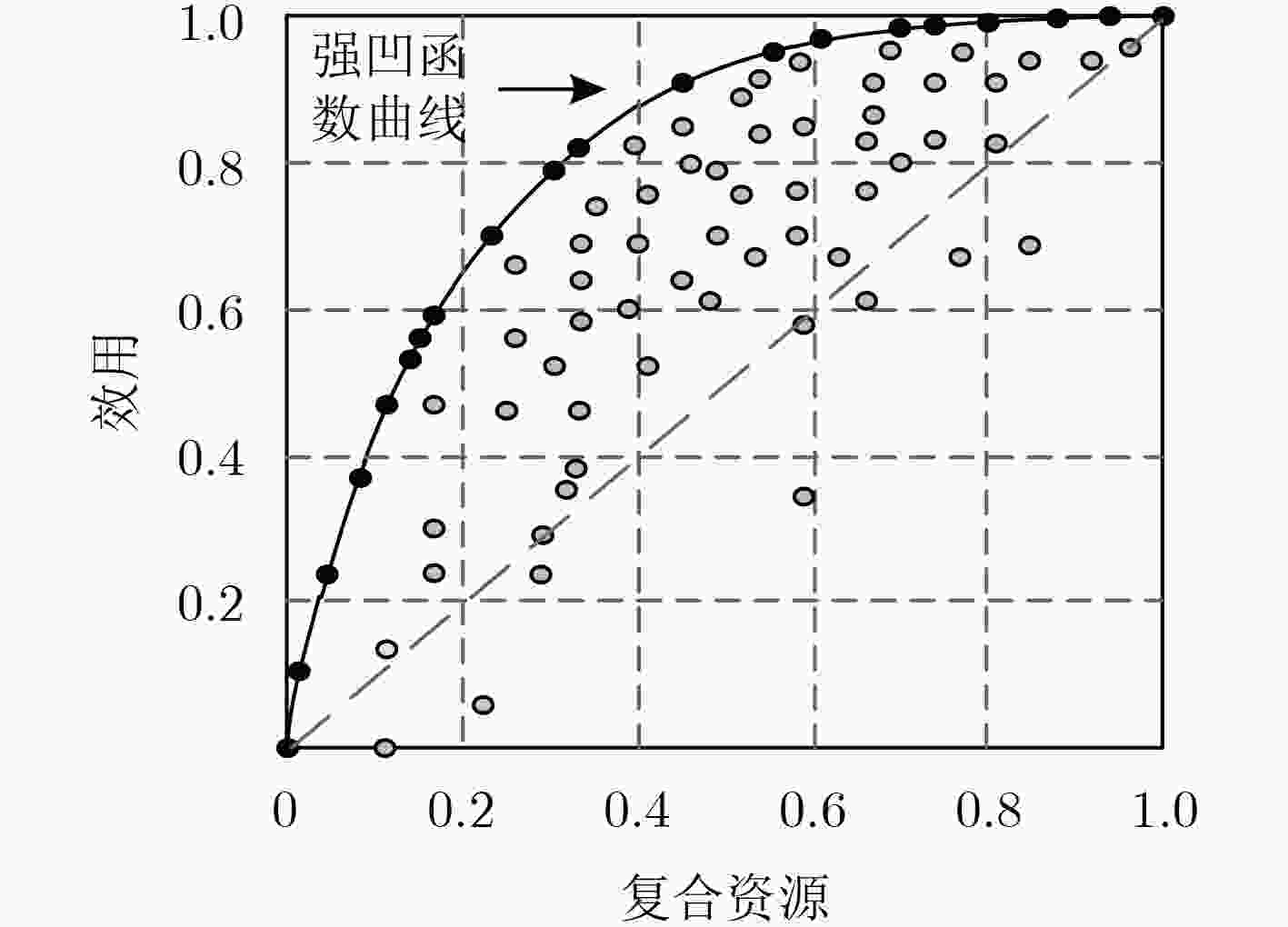
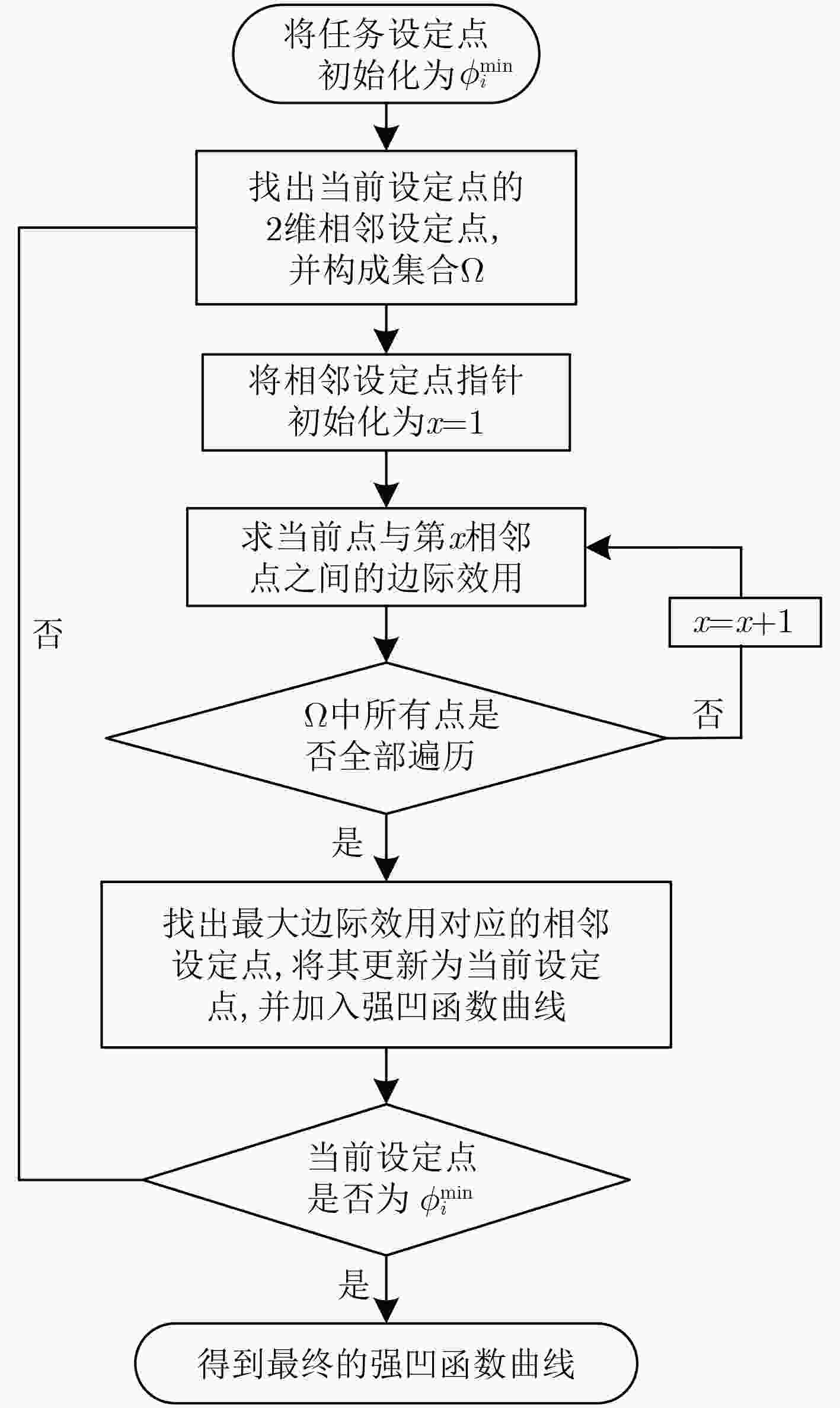
摘要: 针对目前相控阵雷达网目标分配模型中约束条件构建不合理以及求解算法性能不高的问题,该文构建了基于服务质量(QoS)的雷达网目标分配模型,并提出基于强凹曲线逼近的模型求解算法。通过QoS模型中资源空间、环境空间的建立准确描述雷达的资源限制以及雷达与目标的可见性约束;通过库恩-塔克(KKT)条件推导出QoS模型最优解存在的充分条件,利用2维快速遍历方法逼近得到强凹函数曲线,最后对每个目标强凹曲线中的操作设定点进行逐步迭代得出优化分配方案。仿真结果表明:模型能够有效完成雷达网任务分配,且所提模型求解算法相比典型的智能搜索算法有更好的性能。Abstract: The constraint conditions of target assignment model for phased array radar network are unreasonable and the performance of model solving algorithms are not good enough. To solve these problems, a target assignment model for radar network based on Quality of Service (QoS) is constructed in this paper, and a model solving algorithm based on strong concave function approximation is proposed. Through the establishment of resource space and environment space in QoS model, radar resource constraints as well as the visibility constraints between radars and targets are described accurately. Then, sufficient conditions for the optimal solution of QoS model are derived by Karush-Kuhn-Tucker(KKT) condition, and a two-dimensional fast traversal method is used to approximate the strong concave function curve. Finally, the optimal assignment scheme is obtained by the stepwise iteration of operation setting points on the strong concave curve of each target. The simulation results show that the proposed model can effectively accomplish the target assignment of radar network, and model solving algorithm has better performance than the typical intelligent search algorithms.
-
表 1 各对象坐标设置
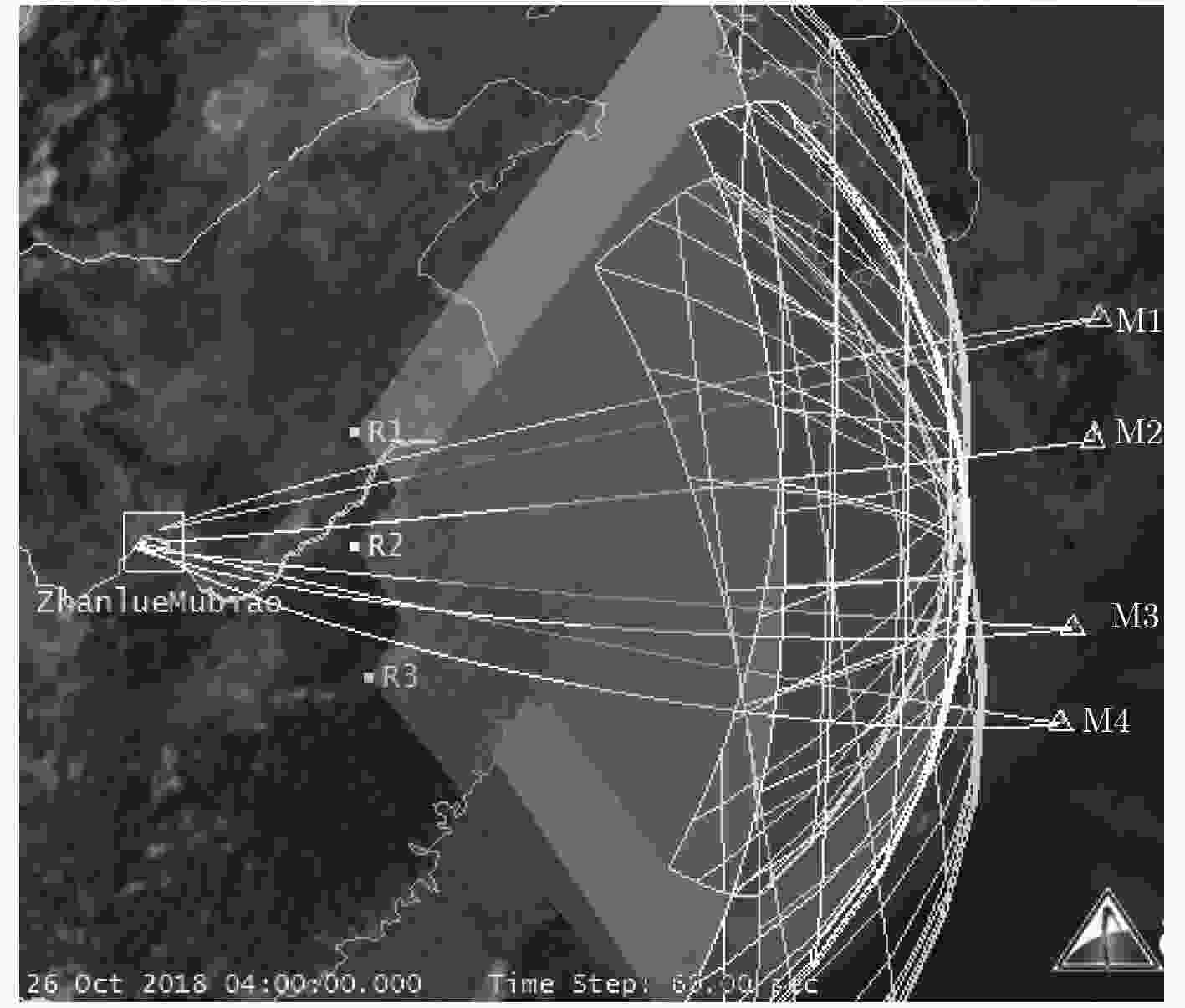
对象 坐标 导弹 M1 (33.720, 131.528) M2 (31.864, 131.156) M3 (28.932, 130.508) M4 (27.630, 130.175) 战略目标 O (30.546, 114.241) 雷达 R1 (32.933, 118.119) R1 (30.646, 118.176) R1 (28.657, 118.467) 表 2 模型相关参数设置
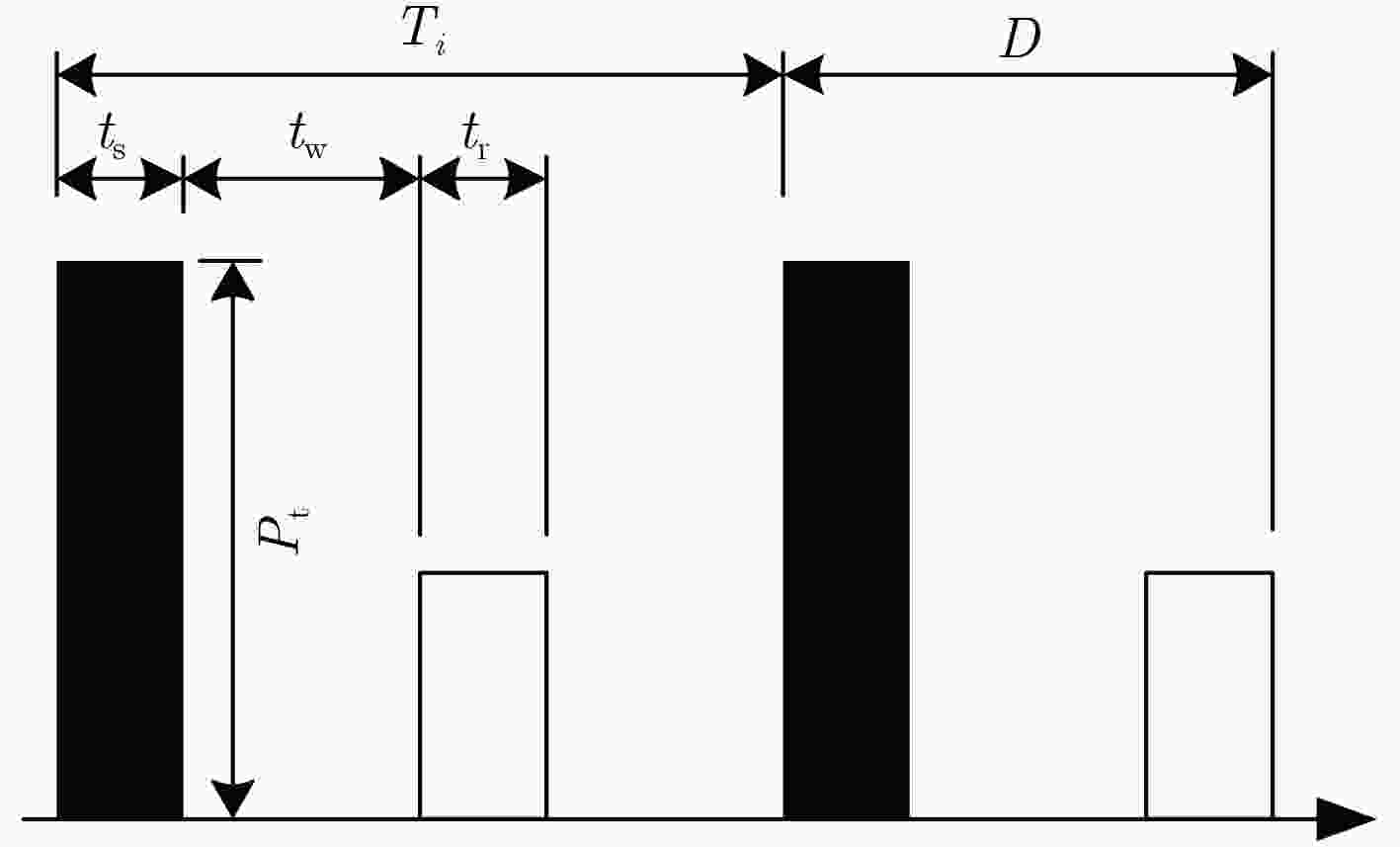
空间 相关参数 取值 资源维 最大时间资源占用率 70% 信号重复周期 20 ms 脉宽 500 μs 雷达最大平均功率 60 kW 雷达峰值功率 250 kW 最大能量资源占用率 70% 波束驻留次数 3 环境维 目标类型 导弹、$\beta {\rm{}} = 300$ 目标速度 7~12 Ma 目标加速度 0.4~3.5 g 目标射程 2000 km 雷达与目标可见性 全程可见 表 3 算法参数设置
算法 参数 取值 粒子群算法 种群规模 20 最大循环代数 200 惯性常量 0.8 学习因子 C1=C2=2 遗传算法 种群规模 20 交叉概率 0.8 变异概率 0.2 -
BIL R and HOLPP W. Modern phased array radar systems in Germany[C]. IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Waltham, USA, 2016: 11–17. MALLICK M, KRISHNAMURTHY V, and VO B N. Integrated Tracking, Classification, and Sensor Management: Theory and Applications[M]. Hoboken, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014: 447–520. MOO P W and DING Zhen. Coordinated radar resource management for networked phased array radars[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2015, 9(8): 1009–1020. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0368 KALANDROS M. Covariance control for sensor management in cluttered tracking environments[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2004, 27(3): 493–496. doi: 10.2514/1.10339 AUGHENBAUGH J M and LA COUR B R. Metric selection for information theoretic sensor management[C]. The 11th International Conference on Information Fusion, Cologne, Germany, 2008: 1–8. 周林. 基于信息论的传感器管理算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 河南大学, 2005: 34–42.ZHOU Lin. The algorithm of sensor management based on information theory[D]. [Master dissertation], Henan University, 2005: 34–42. WANG Xiaoying, HOSEINNEZHAD R, GOSTAR A K, et al. Multi-sensor control for multi-object bayes filters[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 260–270. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.07.031 SEOK J, ZHAO Jinxin, SELVAKUMAR J, et al. Radar resource management: Dynamic programming and dynamic finite state machines[C]. 2013 European Control Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 2013: 4100–4105. DELIGIANNIS A and LAMBOTHARAN S. A Bayesian game theoretic framework for resource allocation in multistatic radar networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 546–551. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944263. 方德亮, 冉晓旻, 李鸥. 一种能量有效的分布式传感器管理算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 44(2): 171–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.02.029FANG Deliang, RAN Xiaomin, and LI Ou. Energy efficient distributed sensor management algorithm[J]. Journal of Xidian University: , 2017, 44(2): 171–177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2017.02.029 RUSU C, THOMPSON J, and ROBERTSON N M. Sensor scheduling with time, energy, and communication constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(2): 528–539. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2773429 JAIN N K, NANGIA U, and JAIN J. A Review of particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India) : Series B, 2018, 99(4): 407–411. doi: 10.1007/s40031-018-0323-y 郭广颂, 文振华, 郝国生. 基于群体决策的多用户协同交互式遗传算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2165–2172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171234GUO Guangsong, WEN Zhenhua, and HAO Guosheng. Interactive genetic algorithm based on collective decision making with multi-user collaboration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2165–2172. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171234 NADJIASNGAR R and CHARLISH A. A performance model for target tracking with a radar network[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Radar Conference, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2015: 117–123. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf.2015.7411887. HANSEN J, RAJKUMAR R, LEHOCZKY J, et al. Resource management for radar tracking[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 358–363. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631788. BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. London, England: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 99–103. FRANCU M, KERMAN R, and SINNAMON G. A new algorithm for approximating the least concave majorant[J]. Czechoslovak Mathematical Journal, 2017, 67(4): 1071–1093. doi: 10.21136/CMJ.2017.0408-16 -





 下载:
下载:
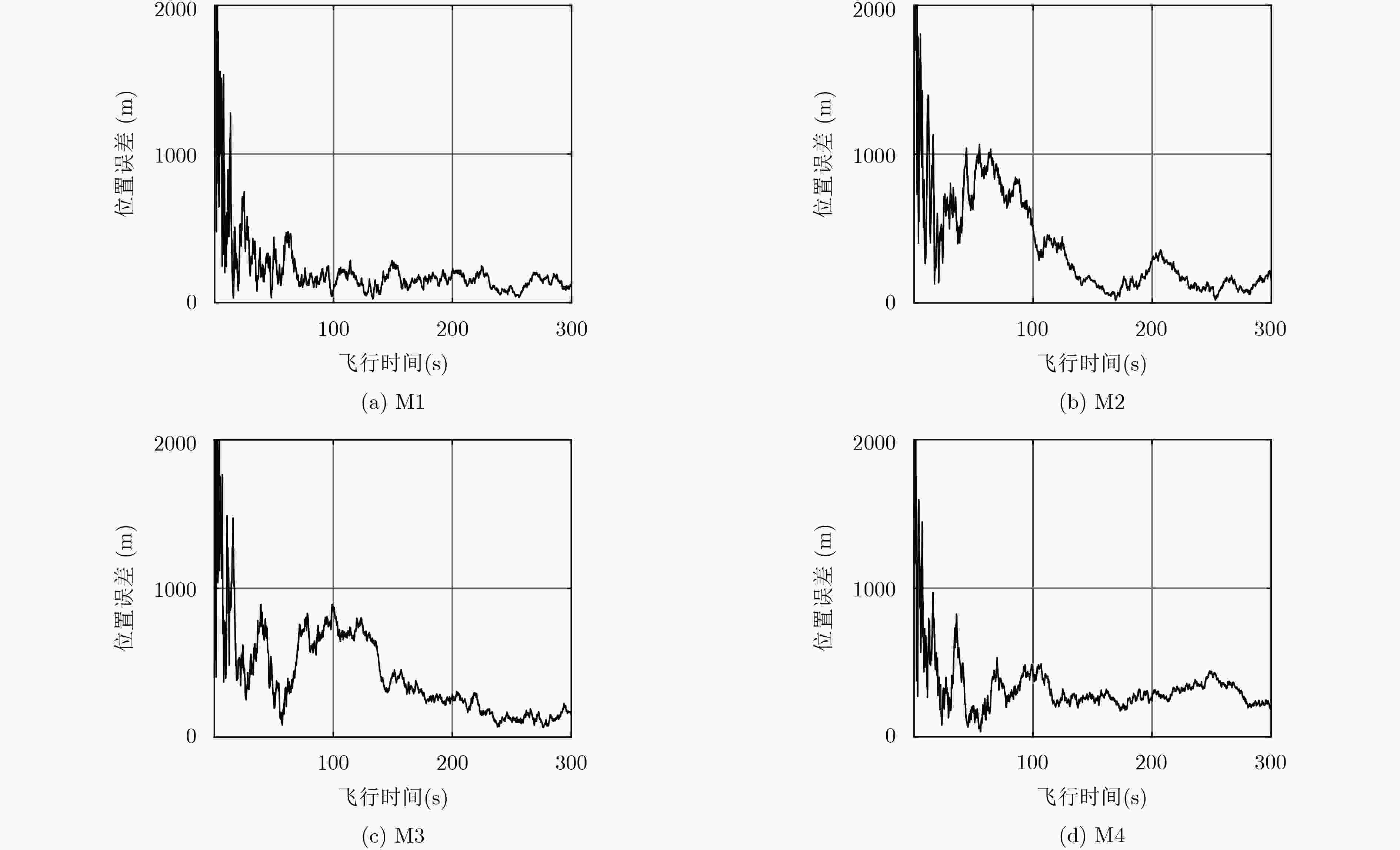
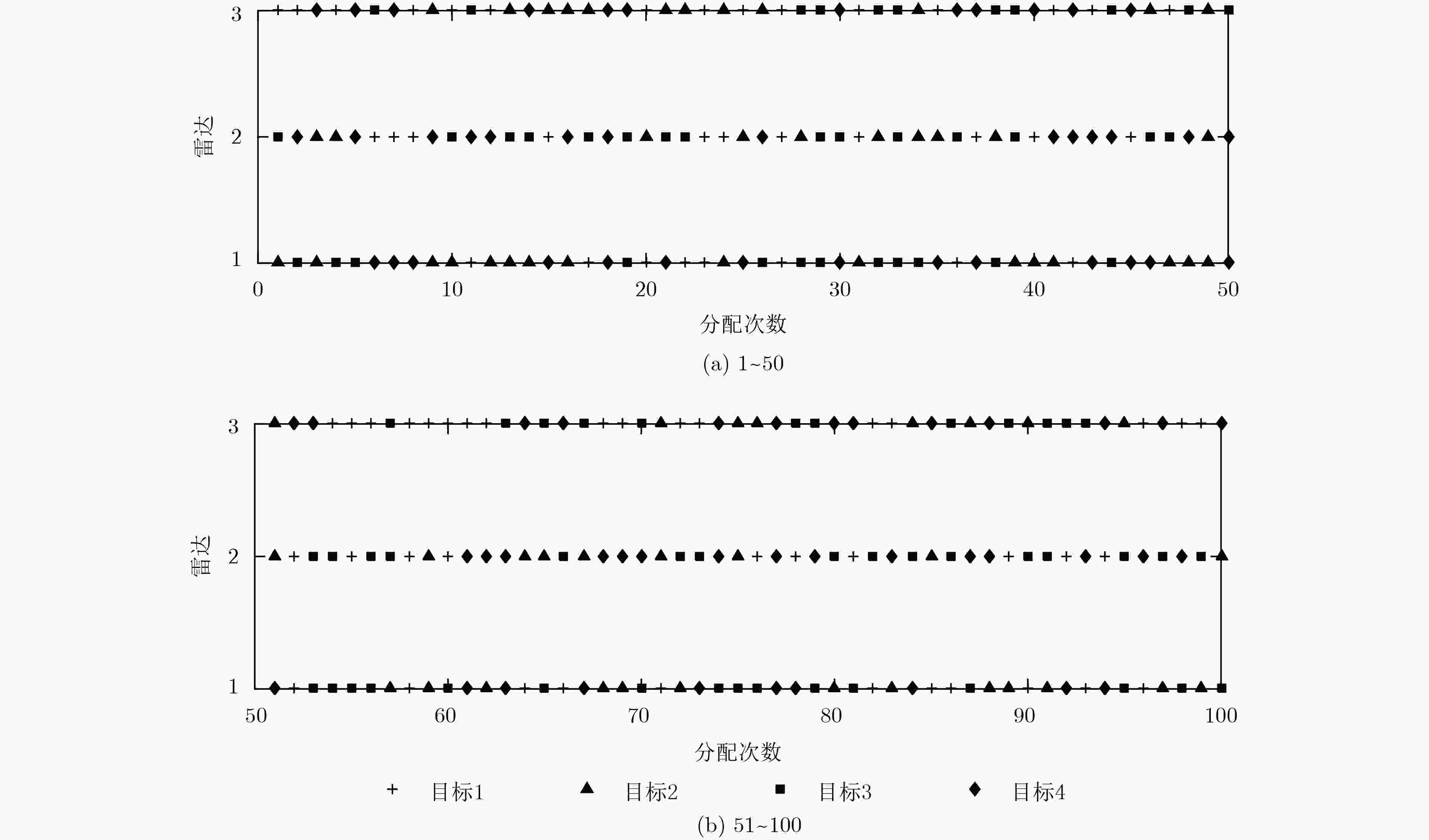
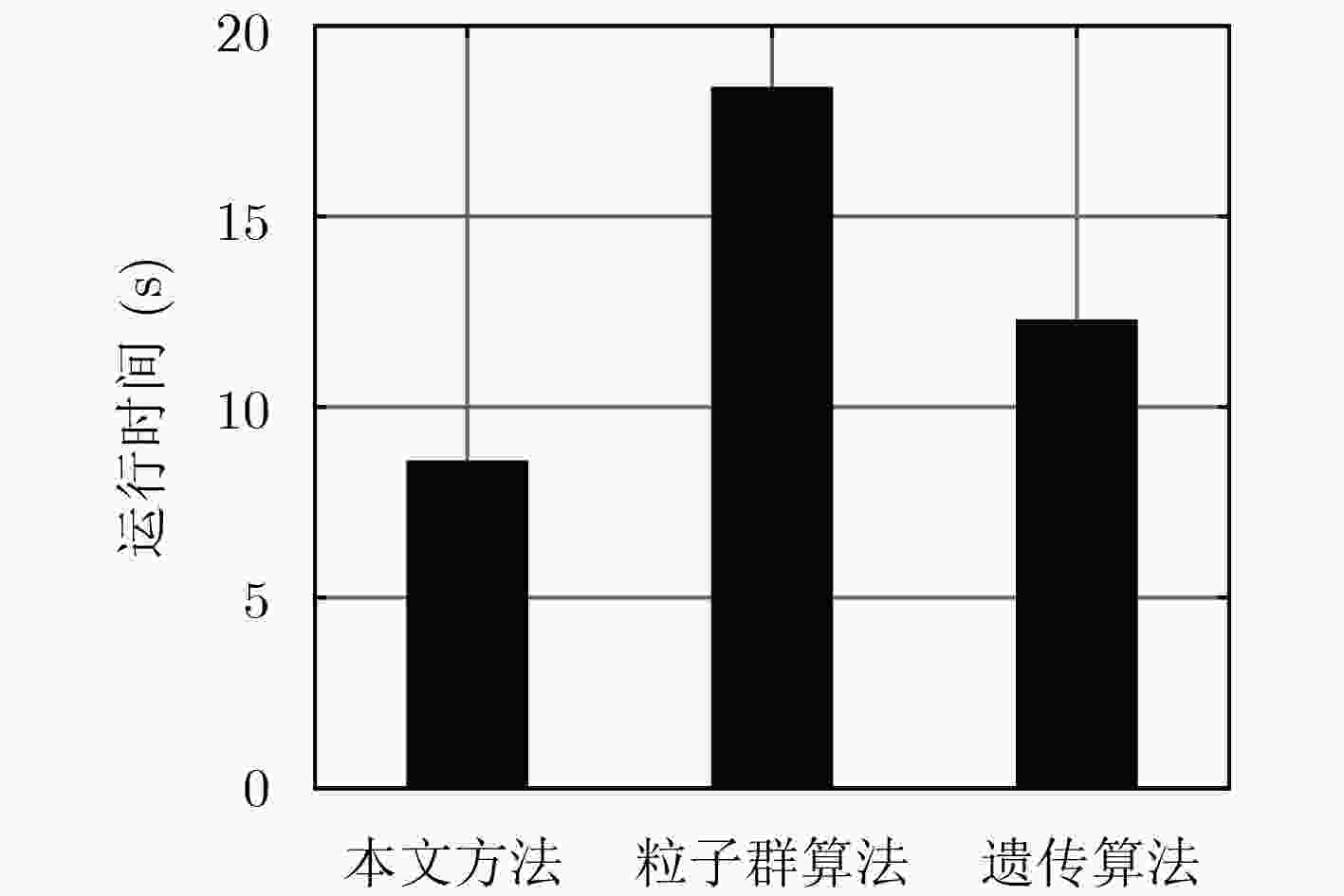
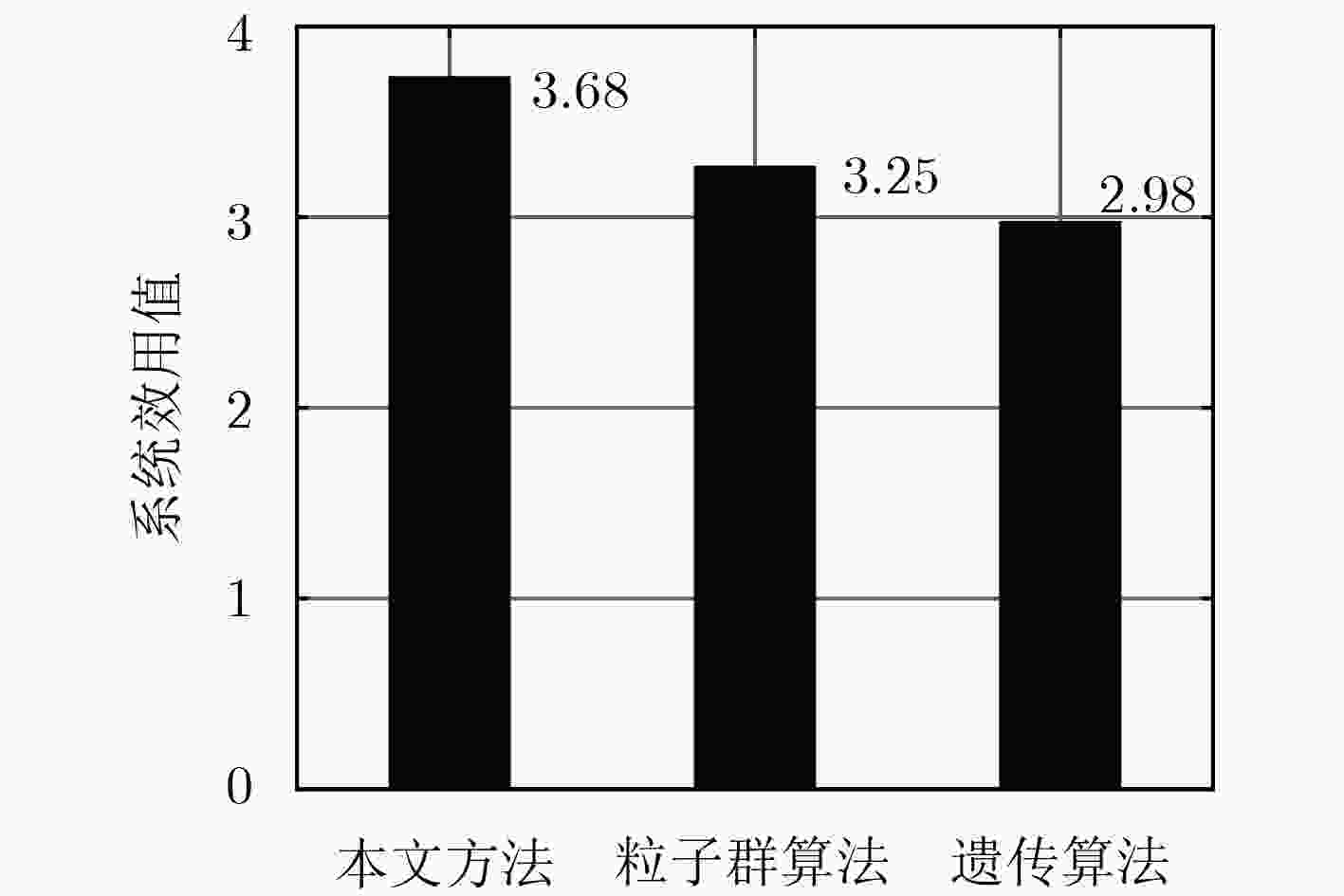


 下载:
下载:
