Applying Chernoff Weighted Classification Frame Method to MotorImagery Brain Computer Interface
-
摘要:
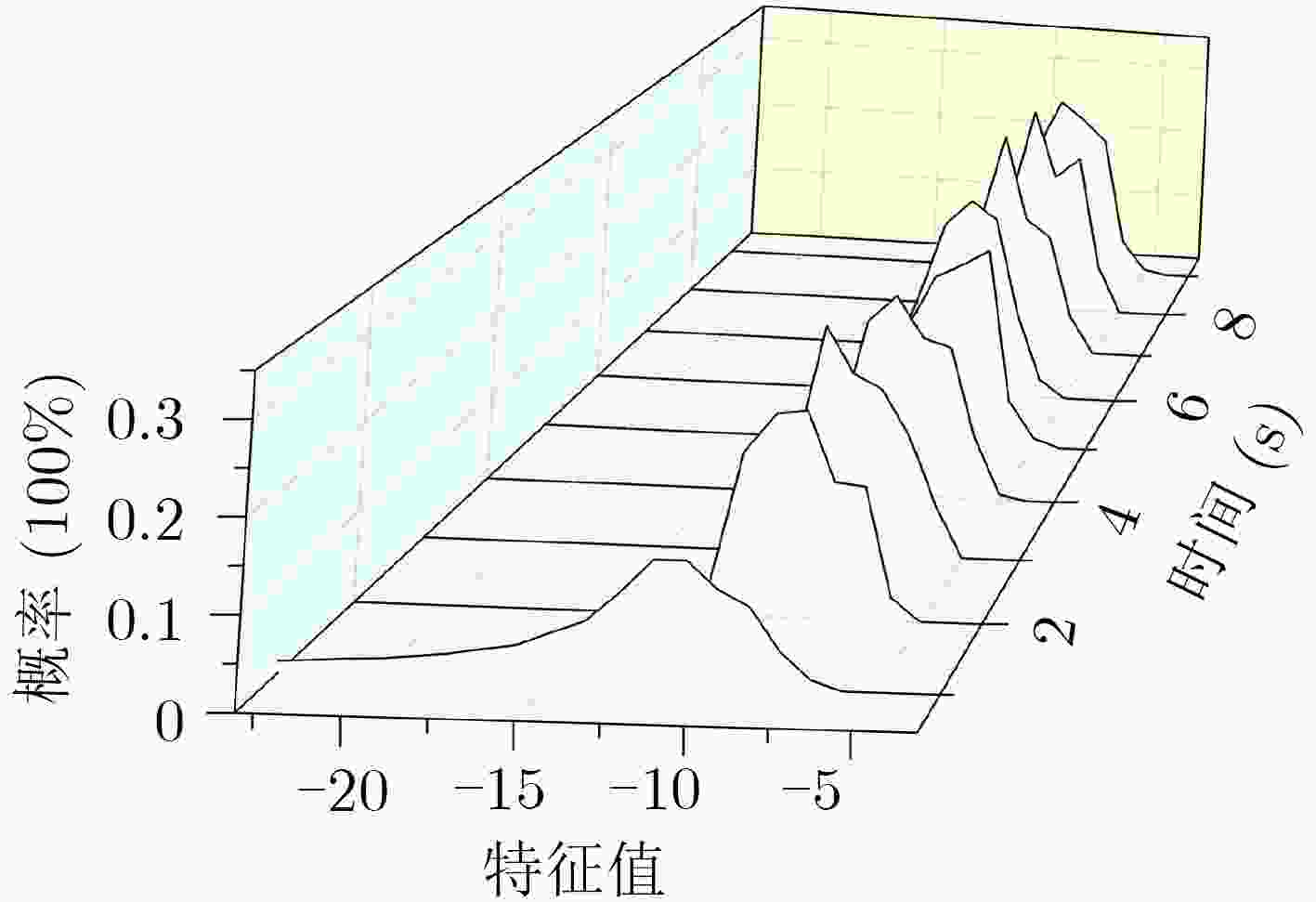
针对现有脑机接口(BCI)分类器与大脑认知过程结合不够紧密的问题,该文提出一种基于Chernoff加权的分类器集成框架方法,并用于同步运动想象脑机接口中。通过对训练数据进行统计分析,获得各时刻脑电信号(EEG)的统计特性,并建立基于大脑认知过程的高斯概率模型。然后利用Chernoff边界特性得到该概率模型的最小误差,并以此确定该时刻分类器的权重,通过对各时刻分类器的加权,实现同步脑机接口的信号分类。以脑机接口竞赛数据作为测试,并与线性判决分析、支持向量机和极限学习方法分别结合构成新的集成方法。由实验结果可知,加权集成框架方法的分类性能比原独立分类方法有显著提高。
-
关键词:
- 脑机接口 /
- 运动想象 /
- 概率模型 /
- Chernoff误差边界 /
- 模式分类
Abstract:For the problem that the classifier is less considered to be combined with the brain's cognitive process in the Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) system, a Chernoff-weighted based classifier integrated frame method is proposed and used in synchronous motor imagery BCI. In the method, the statistic characteristics of ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) are obtained by analyzing in each time point of synchronous BCI, and then the probability model is established to compute the Chernoff error bound, which is adopted as the weight of common classifier to take the discriminant process. The test experiments are based on the datasets from BCI competitions, and the proposed frame method is employed to compose with LDA, SVM, ELM respectively. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed frame method shows competitive performance compared with other methods.
-
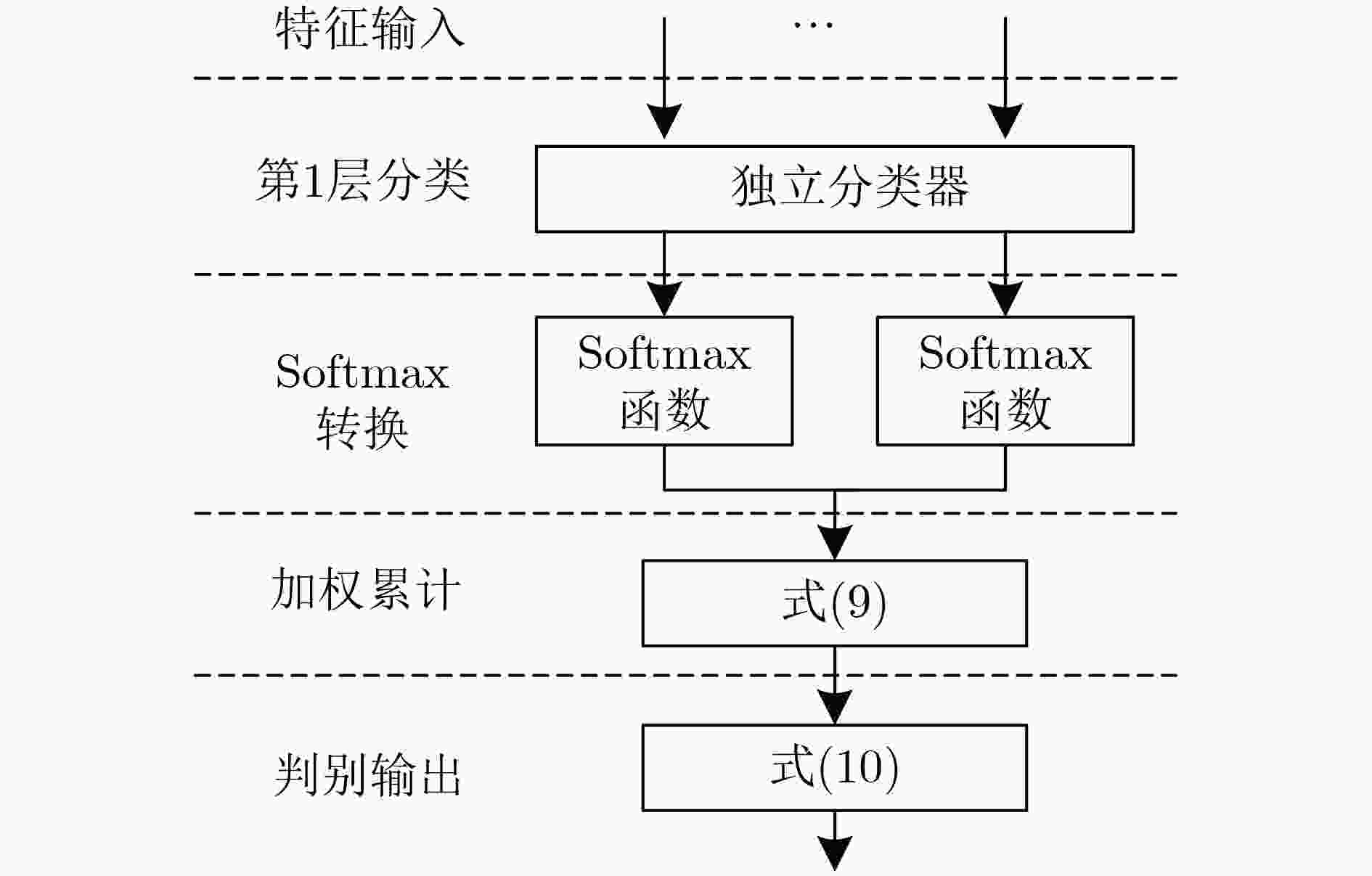
表 1 算法1 Chernoff框架方法的训练过程
输入:EEG训练数据 输出:独立分类器模型参数和概率权重w 步骤 1 对EEG数据进行预处理,提取特征向量; 步骤 2 利用独立分类器训练得到模型参数; 步骤 3 利用式(1)得到特征向量的均值和方差; 步骤 4:利用式(8)得到权重w。 表 2 算法2 Chernoff框架方法的测试过程
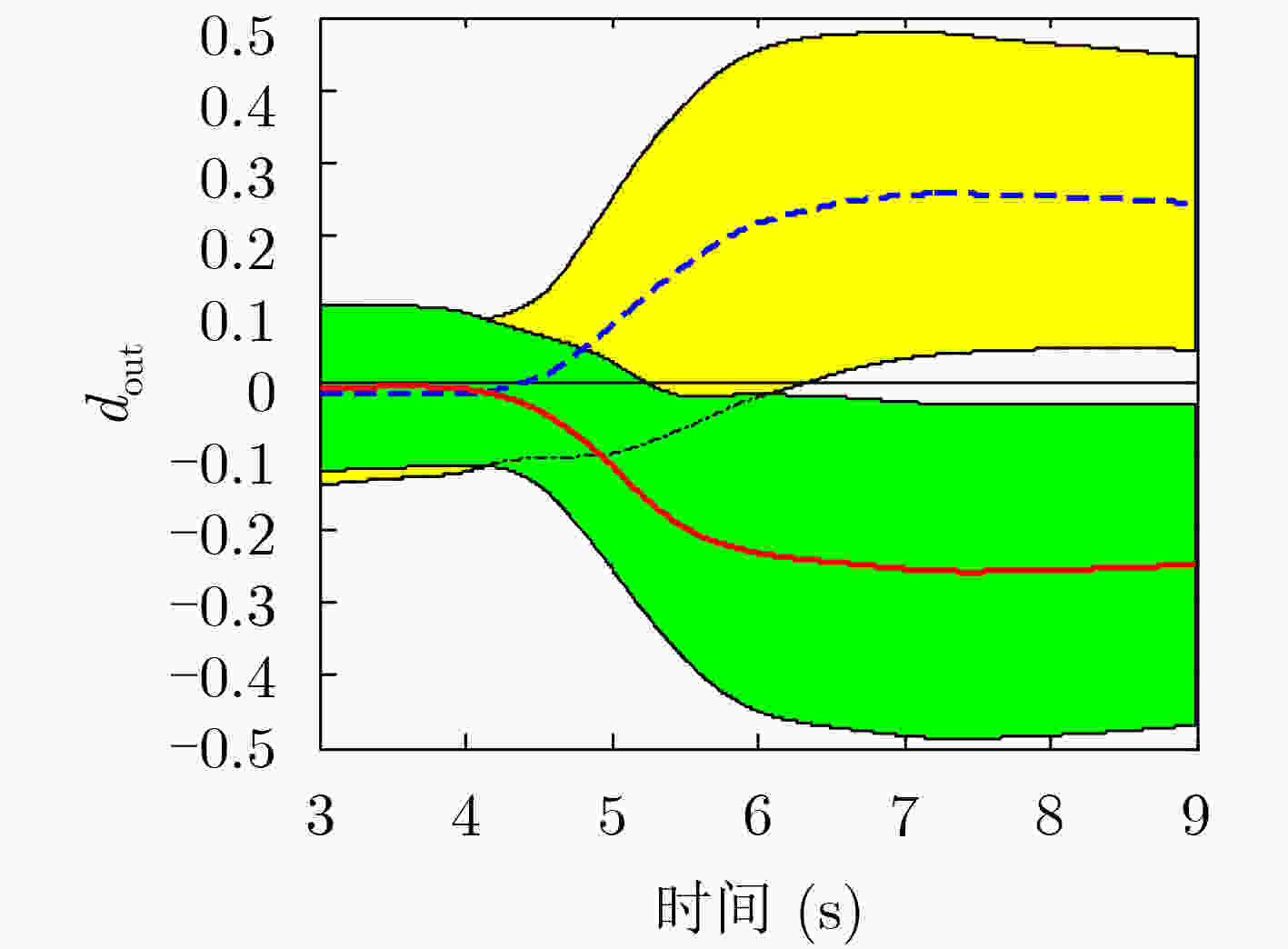
输入:t 时刻的测试 EEG 数据,独立分类器参数和权重w 输出:分类结果和判定值dout(t) 步骤 1 对EEG数据进行预处理,提取特征向量; 步骤 2 通过独立分类器的训练模型得到yc(t); 步骤 3 利用式(11)和式(12)将yc转化到p(t)∈[0, 1]; 步骤 4 利用式(9)计算pout(t); 步骤 5 利用式(10)将pout(t) 变换到dout(t)∈[–1, 1]; 步骤 6 通过dout(t)的符号获得分类结果。 表 3 实验中的数据集
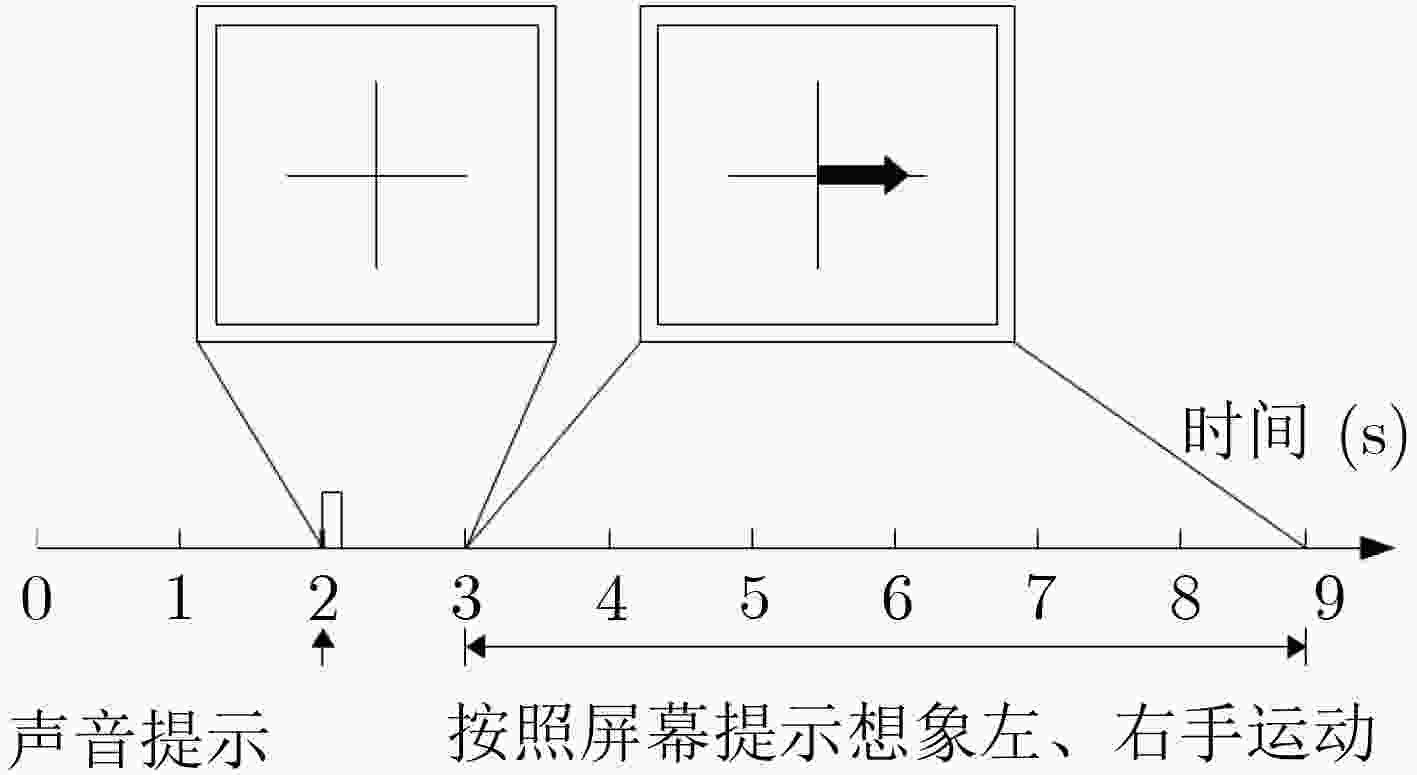
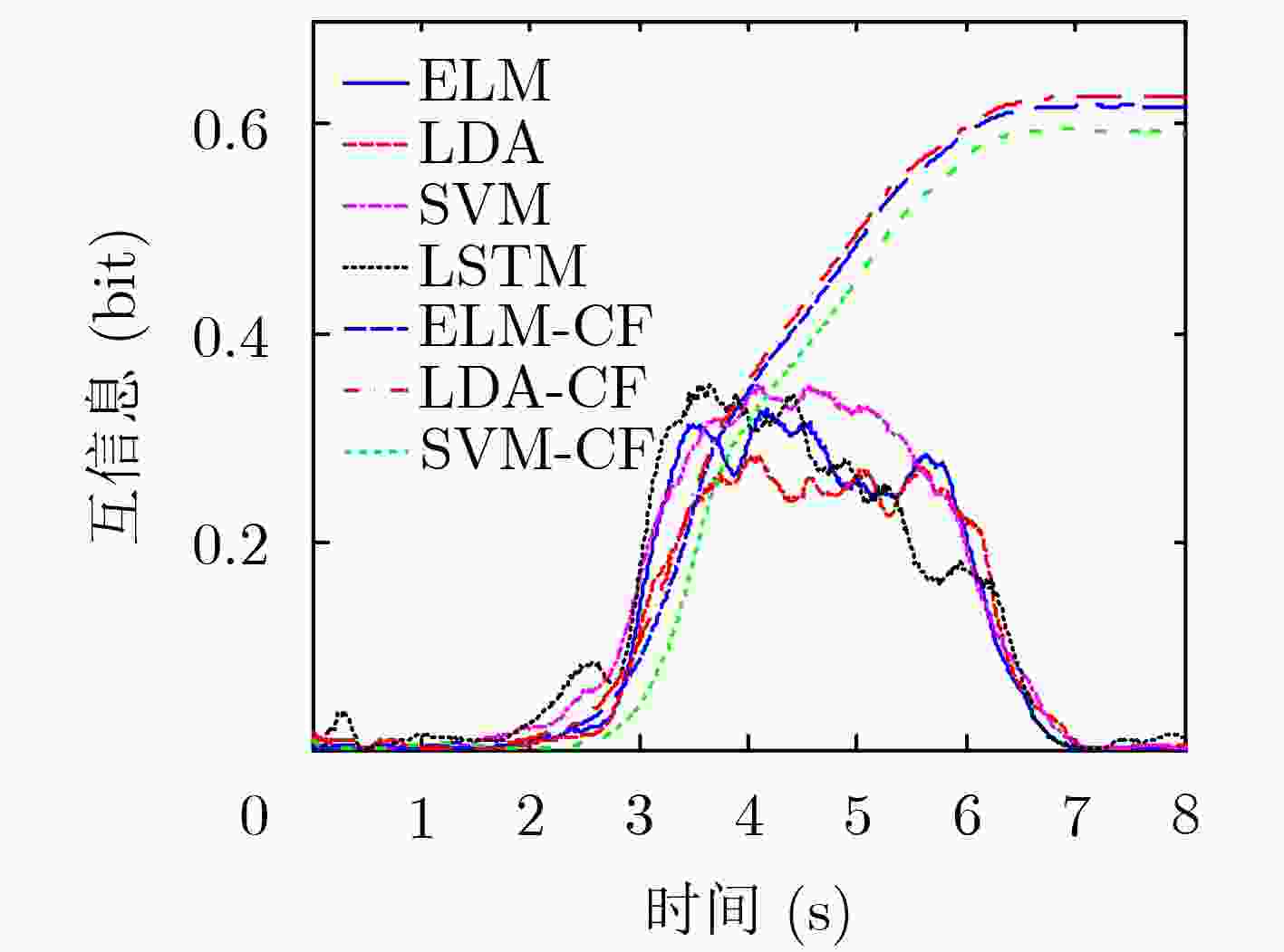
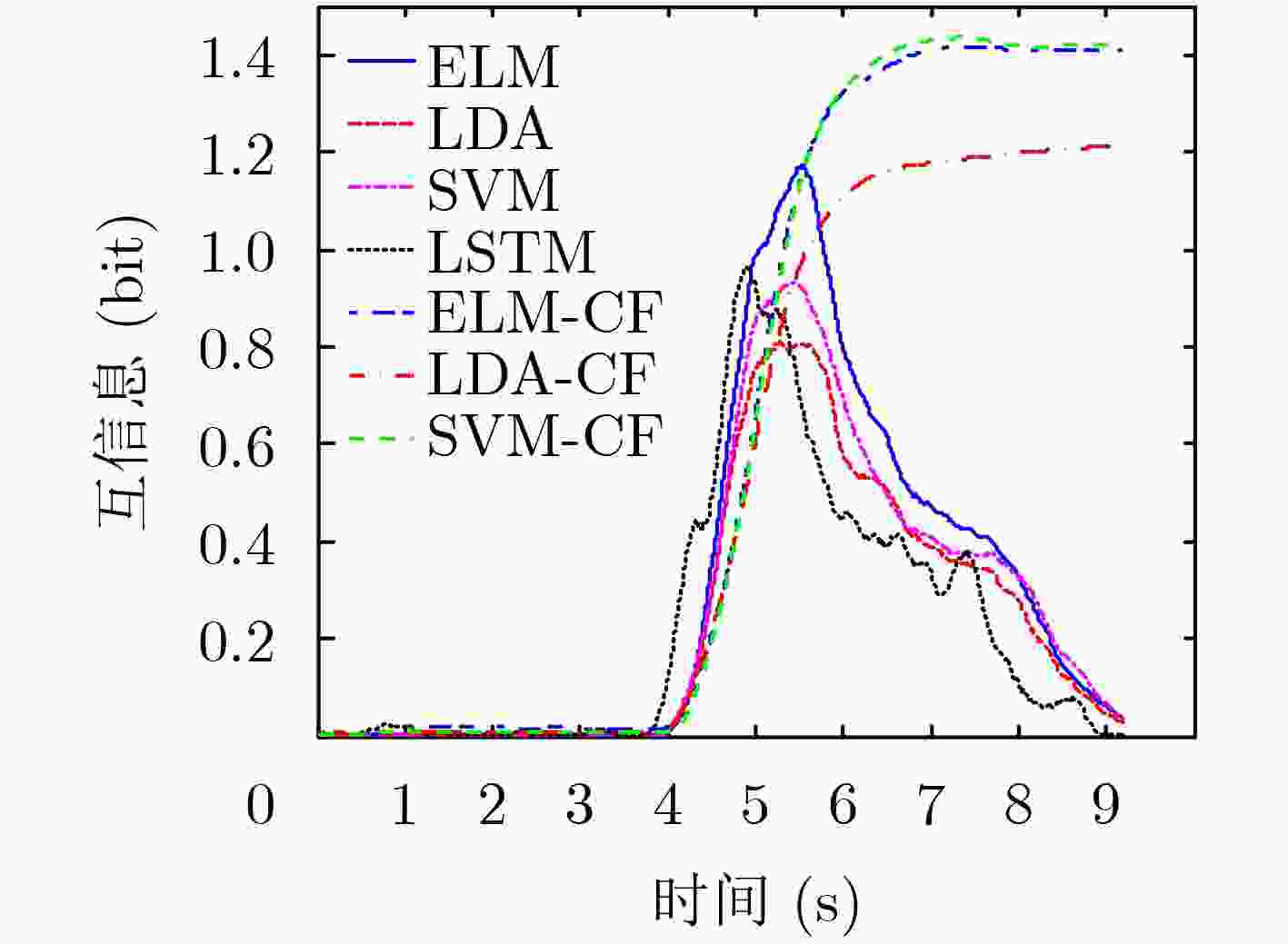
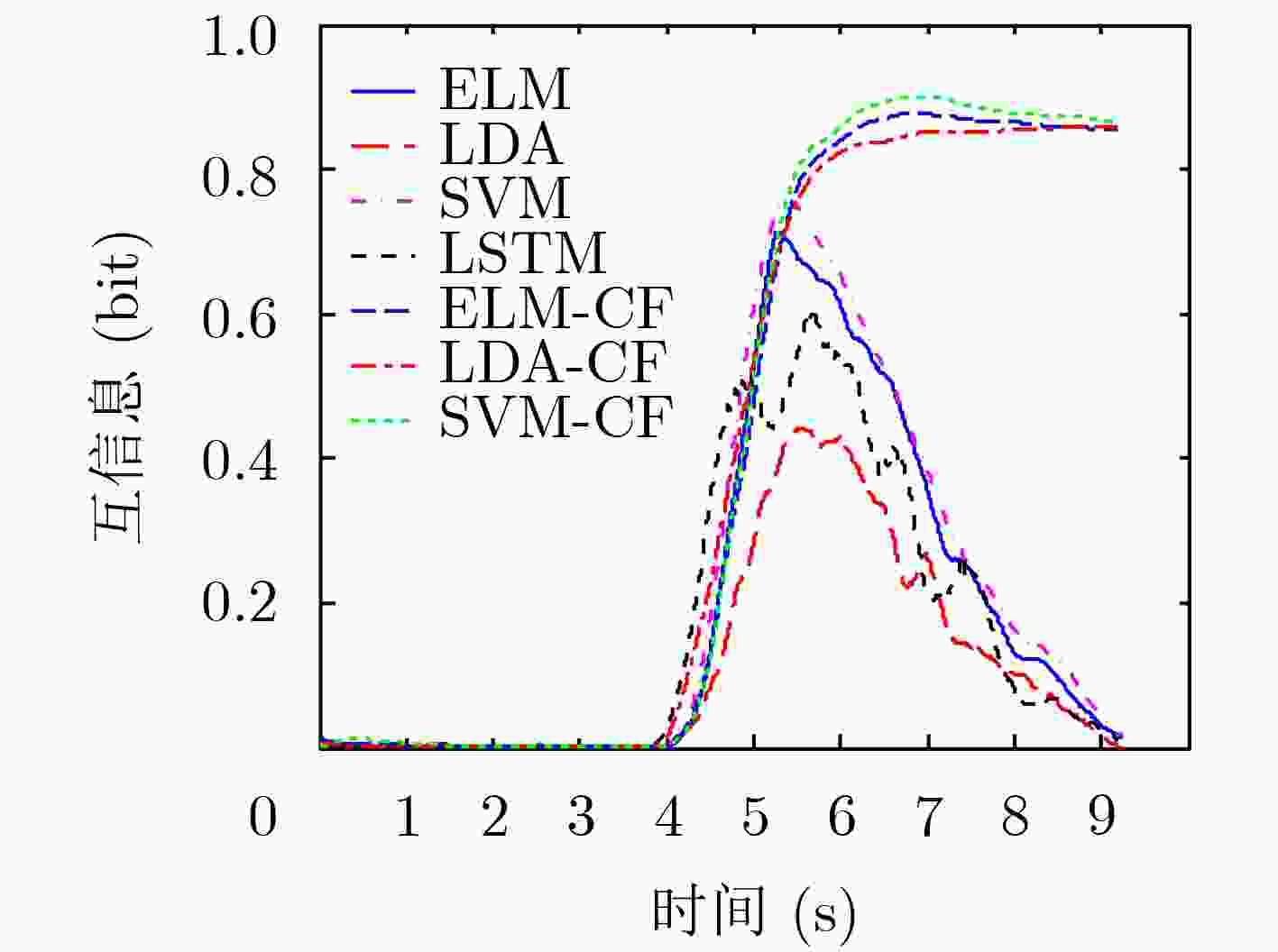
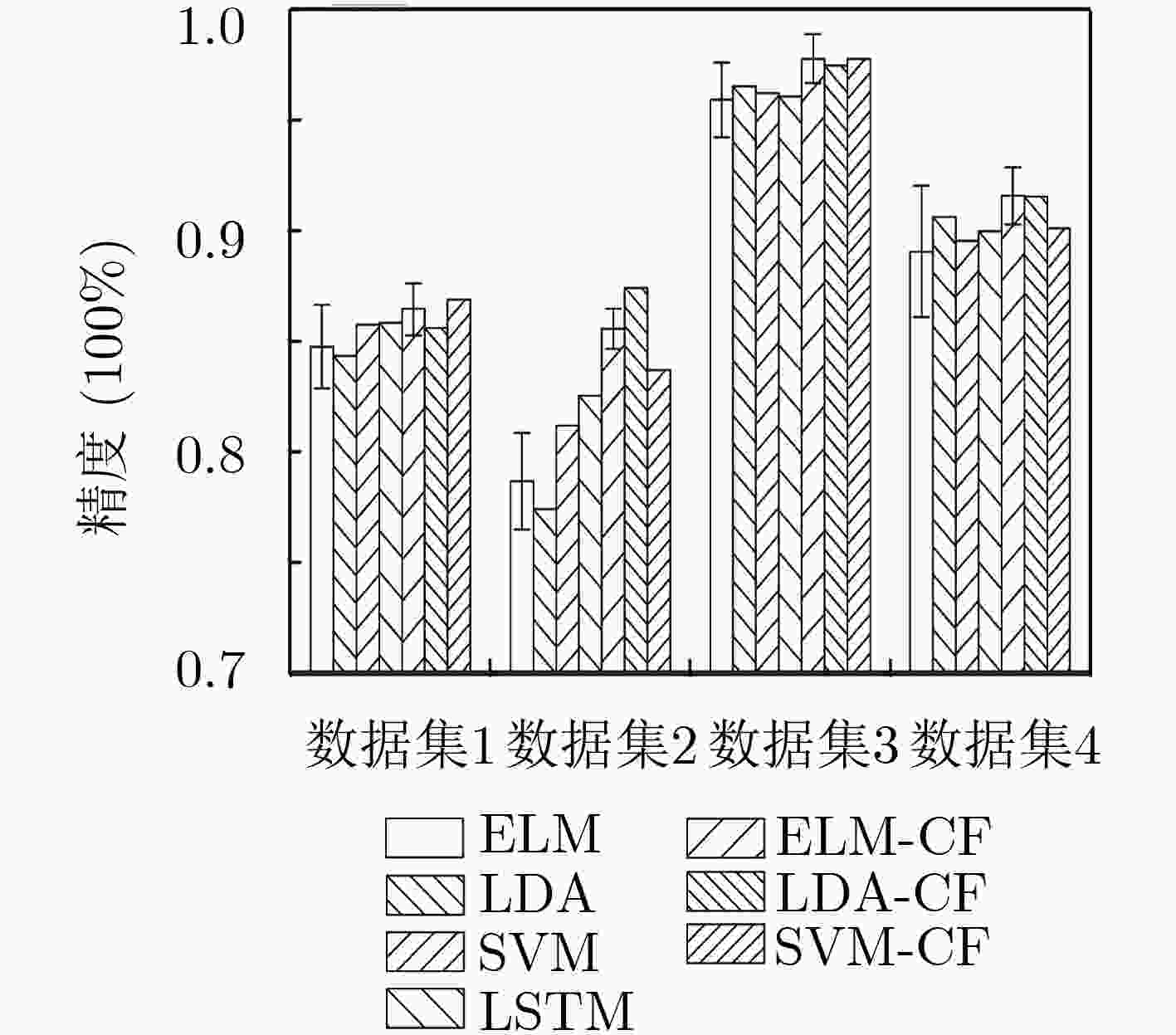
序号 数据集来源 训练集个数(试验次数) 测试集个数(试验次数) 类别 1 BCI II (III) 1 (140) 1 (140) 2 2 BCI III (IIIb) 1 (320) 1 (320) 2 3 BCI IV (IIb) 3 (400) 2 (320) 2 4 BCI IV (IIb) 3 (400) 2 (320) 2 表 4 数据集1的最大互信息(bit)
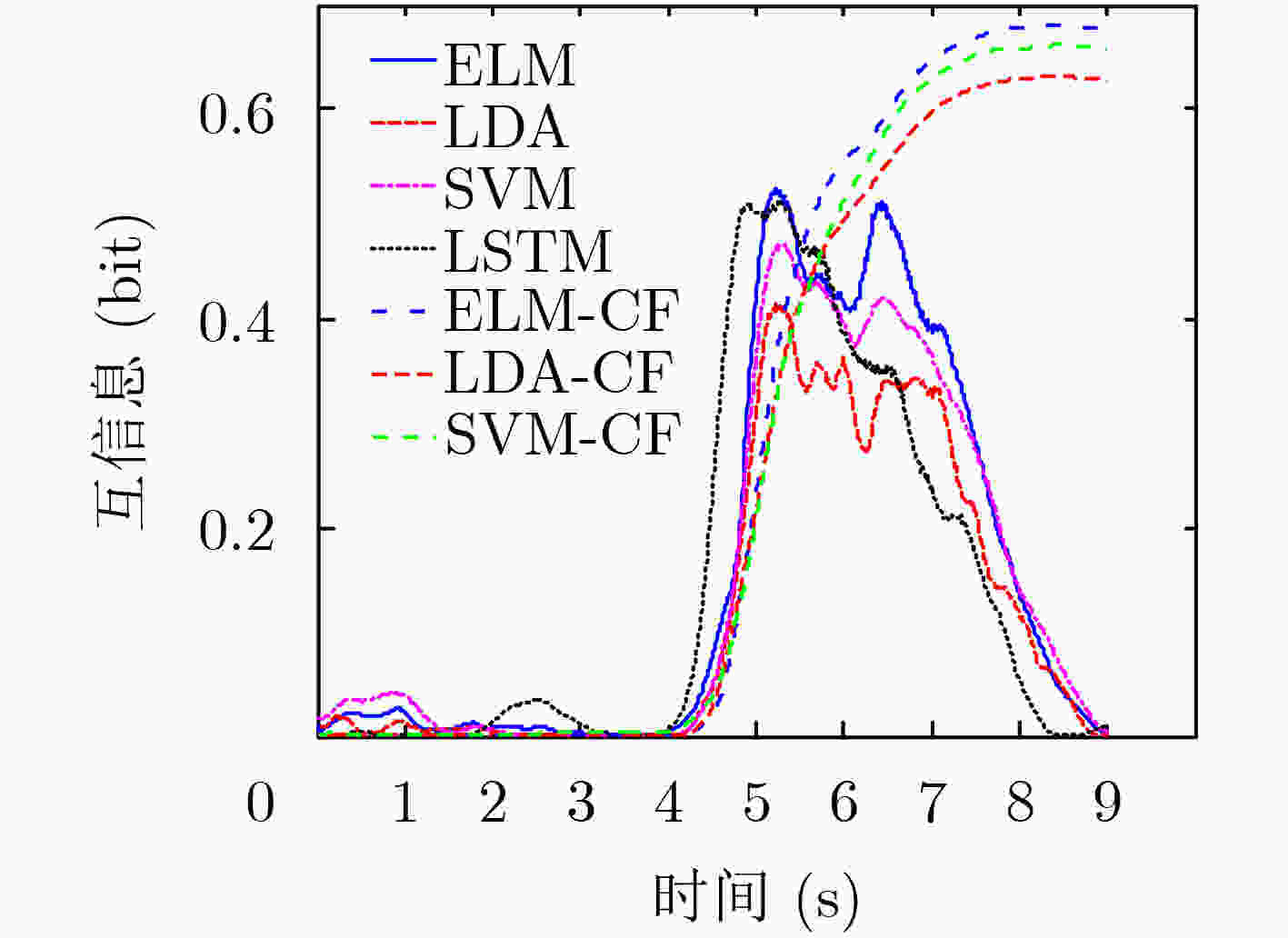
分类方法 最大互信息 ELM 0.524/0.051 LDA 0.414 SVM 0.471 LSTM 0.511 ELM-CF 0.680/0.020 LDA-CF 0.631 SVM-CF 0.662 第II届BCI竞赛的第1名 0.61 -
TIWARI N, EDLA D R, DODIA S, et al. Brain computer interface: A comprehensive survey[J]. Biologically Inspired Cognitive Architectures, 2018, 26: 118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.bica.2018.10.005 杨帮华, 李博. 基于脑机接口的康复训练系统[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2019, 31(2): 174–180. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.18-0791YANG Banghua and LI Bo. Rehabilitation training system based on brain computer interface[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2019, 31(2): 174–180. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.18-0791 ALAZRAI R, ALWANNI H, BASLAN Y, et al. EEG-based brain-computer interface for decoding motor imagery tasks within the same hand using Choi-Williams time-frequency distribution[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(9): 1937. doi: 10.3390/s17091937 LEEB R, LEE F, KEINRATH C, et al. Brain-computer communication: Motivation, aim, and impact of exploring a virtual apartment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2007, 15(4): 473–482. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2007.906956 GUY V, SORIANI M H, BRUNO M, et al. Brain computer interface with the P300 speller: Usability for disabled people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Annals of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, 2018, 61(1): 5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2017.09.004 HASAN M R, IBRAHIMY M I, MOTAKABBER S M A, et al. Classification of multichannel EEG signal by linear discriminant analysis[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Systems Engineering, 2015: 279–282. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-08422-0_42. SELIM S, TANTAWI M M, SHEDEED H A, et al. A CSP\AM-BA-SVM approach for motor imagery BCI system[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 49192–49208. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2868178 BHADURI S, KHASNOBISH A, BOSE R, et al. Classification of lower limb motor imagery using K nearest neighbor and naïve-bayesian classifier[C]. The 3rd IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances in Information Technology (RAIT), Dhanbad, India, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RAIT.2016.7507952. ZHANG Yu, WANG Yu, JIN Jing, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning for obtaining sparsity of EEG frequency bands based feature vectors in motor imagery classification[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2017, 27(2): 1650032. doi: 10.1142/S0129065716500325 HAZRATI M K and ERFANIAN A. An online EEG-based brain-computer interface for controlling hand grasp using an adaptive probabilistic neural network[J]. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2010, 32(7): 730–739. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.04.016 程时伟, 周桃春, 唐智川, 等. 卷积神经网络实现的运动想象脑电分类及人-机器人交互应用[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(10): 1–14. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005782CHENG Shiwei, ZHOU Taochun, TANG Zhichuan, et al. Motor imagery EEG classifcation based on convolutional neural network and its application in human-robot interaction[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(10): 1–14. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005782 LEMM S, SCHAFER C, and CURIO G. BCI competition 2003-data set Ⅲ: Probabilistic modeling of sensorimotorμ-rhythms for classification of imaginary hand movements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(6): 1077–1080. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.827076 TAN Ping, TAN Guanzheng, CAI Zixing, et al. Using ELM-based weighted probabilistic model in the classification of synchronous EEG BCI[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2017, 55(1): 33–43. doi: 10.1007/s11517-016-1493-x MATSUI H. Variable and boundary selection for functional data via multiclass logistic regression modeling[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2014, 78: 176–185. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2014.04.015 SCHLOGL A, KEINRATH C, SCHERER R, et al. Information transfer of an EEG-based brain computer interface[C]. The 1st International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Capri Island, Italy, 2003: 641–644. doi: 10.1109/CNE.2003.1196910. FORSTMANN B U, RATCLIFF R, and WAGENMAKERS E J. Sequential sampling models in cognitive neuroscience: Advantages, applications, and extensions[J]. Annual Review of Psychology, 2016, 67: 641–666. doi: 10.1146/annurev-psych-122414-033645 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
