An Error Bound of Signal Recovery for Penalized Programs in Linear Inverse Problems
-
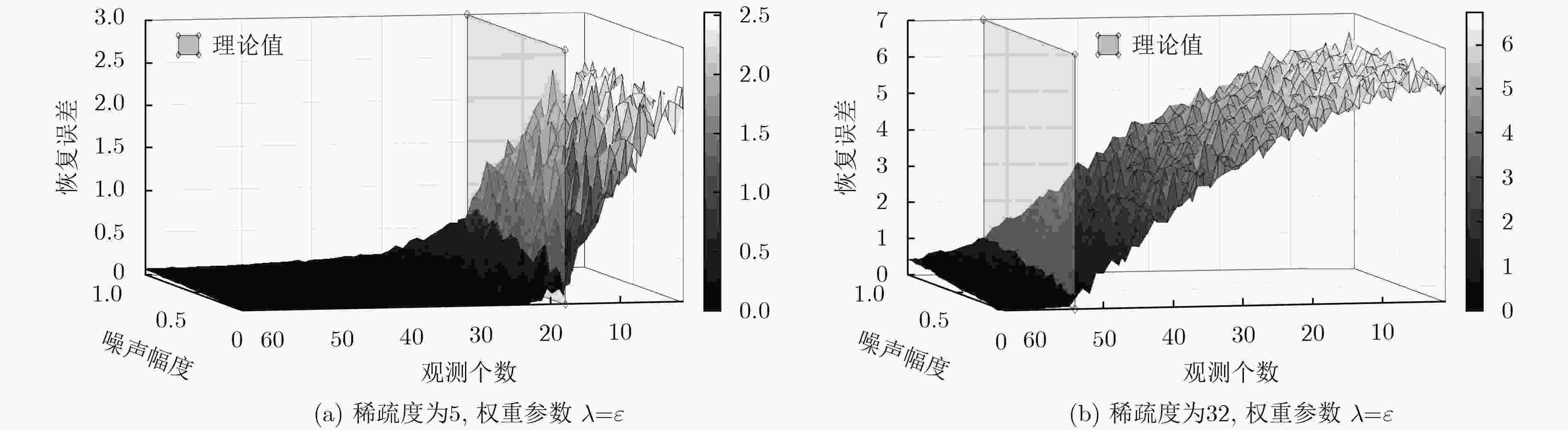
摘要: 惩罚优化问题常常用于在有噪声的条件下用较少的观测个数来求解线性逆问题。目前,对惩罚优化问题恢复误差的研究主要存在以下两点不足:一是对权重参数往往有要求;二是噪声的方向对误差的影响未知。针对这两个问题,该文研究了当存在有界噪声时,惩罚优化问题恢复的误差界。首先,该文从问题的几何出发,给定了一个几何条件。当这一条件满足时,就能够推导出惩罚优化问题恢复的一个明确的误差界。这个误差界保证了恢复的解是稳定的,也就是说,恢复误差不会超过观测误差的常数倍。同时,这一误差界对于任意的正权重参数都成立,并且揭示了恢复误差以及最优的权重选择与观测噪声的方向之间的联系。进一步地,当观测矩阵是一个高斯矩阵时,依据这一几何条件可以得到高概率稳定恢复所需的观测次数。仿真实验证明了理论结果的正确性。Abstract: Penalized programs are widely used to solve linear inverse problems in the presence of noise. For now, the study of the performance of panelized programs has two disadvantages. First, the results have some limitations on the tradeoff parameters. Second, the effect of the direction of the noise is not clear. This paper studies the performance of penalized programs when bounded noise is presented. A geometry condition which is used to study the noise-free problems and constrained problems is provided. Under this condition, an explicit error bound which guarantees stable recovery (i.e., the recovery error is bounded by the observation noise up to some constant factor) is proposed. The results are different from many previous studies in two folds. First, the results provide an explicit bound for all positive tradeoff parameters, while many previous studies require that the tradeoff parameter is sufficiently large. Second, the results clear the role of the direction of the observation noise playing in the recovery error, and reveal the relationship between the optimal tradeoff parameters and the noise direction. Furthermore, if the sensing matrix has independent standard normal entries, the above geometry condition can be studied using Gaussian process theory, and the measurement number needed to guarantee stable recovery with high probability is obtained. Simulations are provided to verify the theoretical results.
-
Key words:
- Linear inverse problem /
- Compressed sensing /
- Stable recovery /
- Penalized program /
- Tradeoff
-
表 1 本文符号说明
符号 说明 ${\text{y}}$ 观测信号 ${\text{A}}$ 观测矩阵 ${{\text{x}}^ * }$ 真实信号 ${\text{z}}$ 观测噪声 $\varepsilon $ 观测噪声${\text{z}}$的幅度 $m$ 观测个数(观测信号${\text{y}}$的维度) $n$ 真实信号${{\text{x}}^ * }$的维度 $f$ 真实信号${{\text{x}}^ * }$的结构函数 $\lambda $ 惩罚优化问题中的权重调节参数 $\partial f({{\text{x}}^ * })$ 函数$f$在点${{\text{x}}^ * }$的次梯度 $D(f,{{\text{x}}^ * })$ 函数$f$在点${{\text{x}}^ * }$的下降锥 $N(f,{{\text{x}}^ * })$ 函数$f$在点${{\text{x}}^ * }$的法锥 $w(D(f,{{\text{x}}^ * }) \cap {{\text{S}}^{n - 1}})$ 下降锥$D(f,{{\text{x}}^ * })$的球面高斯宽度 -
ELDAR Y and KUTYNIOK G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 210-268. 游康勇, 杨立山, 刘玥良, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的网格自适应多源定位[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238YOU Kangyong, YANG Lishan, LIU Yueliang, et al. Adaptive Grid Multiple Sources Localization Based on Sparse Bayesian Learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2150–2157. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171238 王逸林, 马世龙, 王晋晋, 等. 基于稀疏重构的色噪声背景下未知线谱信号估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(11): 2570–2577. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171040WANG Yilin, MA Shilong, WANG Jinjin, et al. Estimation of unknown line spectrum under colored noise via sparse reconstruction[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(11): 2570–2577. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171040 STARCK J L, MURTAGH F, and FADILI J. Sparse Image and Signal Processing: Wavelets and Related Geometric Multiscale Analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2016. BISHOP C M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning[M]. New York: Springer, 2006. CANDES E J, ROMBERG J K, and TAO T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 59(8): 1207–1223. doi: 10.1002/cpa.2012 CANDES E J and PLAN Y. Matrix completion with noise[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(6): 925–936. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2035722 DONOHO D L, MALIKI A, and MONTANATI A. The noise-sensitivity phase transition in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2011, 57(10): 6920–6941. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2011.2165823 BAYATI M, LELARGE M, and MONTANARI A. Universality in polytope phase transitions and message passing algorithms[J]. Annals of Applied Probability, 2015, 25(2): 753–822. doi: 10.1214/14-AAP1010 CHANDRASEKARAN V, RECHT B, PARRILO P A, et al. The convex geometry of linear inverse problems[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2012, 12(6): 805–849. doi: 10.1007/s10208-012-9135-7 AMELUNXEN D, LOTZ M, MCCOY M B, et al. Living on the edge: phase transitions in convex programs with random data[J]. Information and Inference: A Journal of the IMA, 2014, 3(3): 224–294. doi: 10.1093/imaiai/iau005 OYMAK S and TROPP J A. Universality laws for randomized dimension reduction, with applications[J]. Information and Interference, 2017, 7(3): 337–446. doi: 10.1093/imaiai/iax011 NAGAHBAN S N, RAVIKUMAR P, WAINWRIGHT M J, et al. A unified framework for high-dimensional analysis of m-estimators with decomposable regularizers[J]. Statistical Science, 2012, 27(4): 538–557. doi: 10.1214/12-STS400 THRAMPOULIDIS C, ABBASI E, and HASSIBI B. Precise high-dimensional error analysis of regularized m-estimators[C]. The 53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, USA, 2015: 410–417. doi: 10.1109/MASS.1995.528223. ZHANG Han, LIU Yulong, and LEI Hong. On the phase transition of corrupted sensing[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Aachen, Germany, 2017: 521–525. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2017.8006582. CHEN Jinchi and LIU Yulong. Corrupted sensing with sub-Gaussian measurements [C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory, Aachen, Germany, 2017: 516–520. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2017.8006581. FOYGEL R and MACKEY L. Corrupted sensing: Novel guarantees for separating structured signals[J]. IEEE on Transactions on Information Theory, 2014, 60(2): 1223–1247. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2293654 ROCKAFELLAR R T. Convex Analysis[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1970. GRANT M and BOYD S. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.1[OL]. http://cvxr.com/cvx, 2014. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
